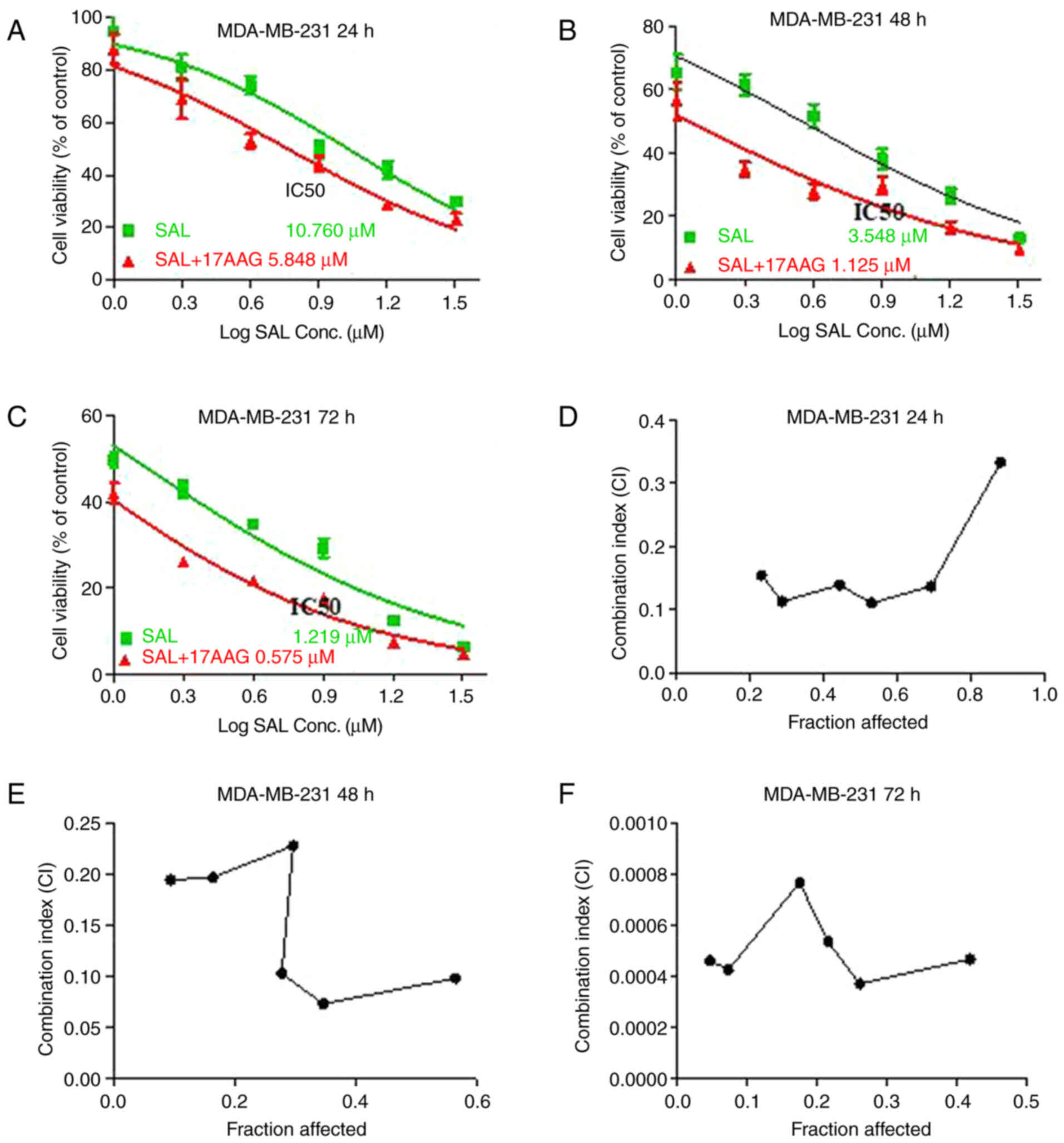
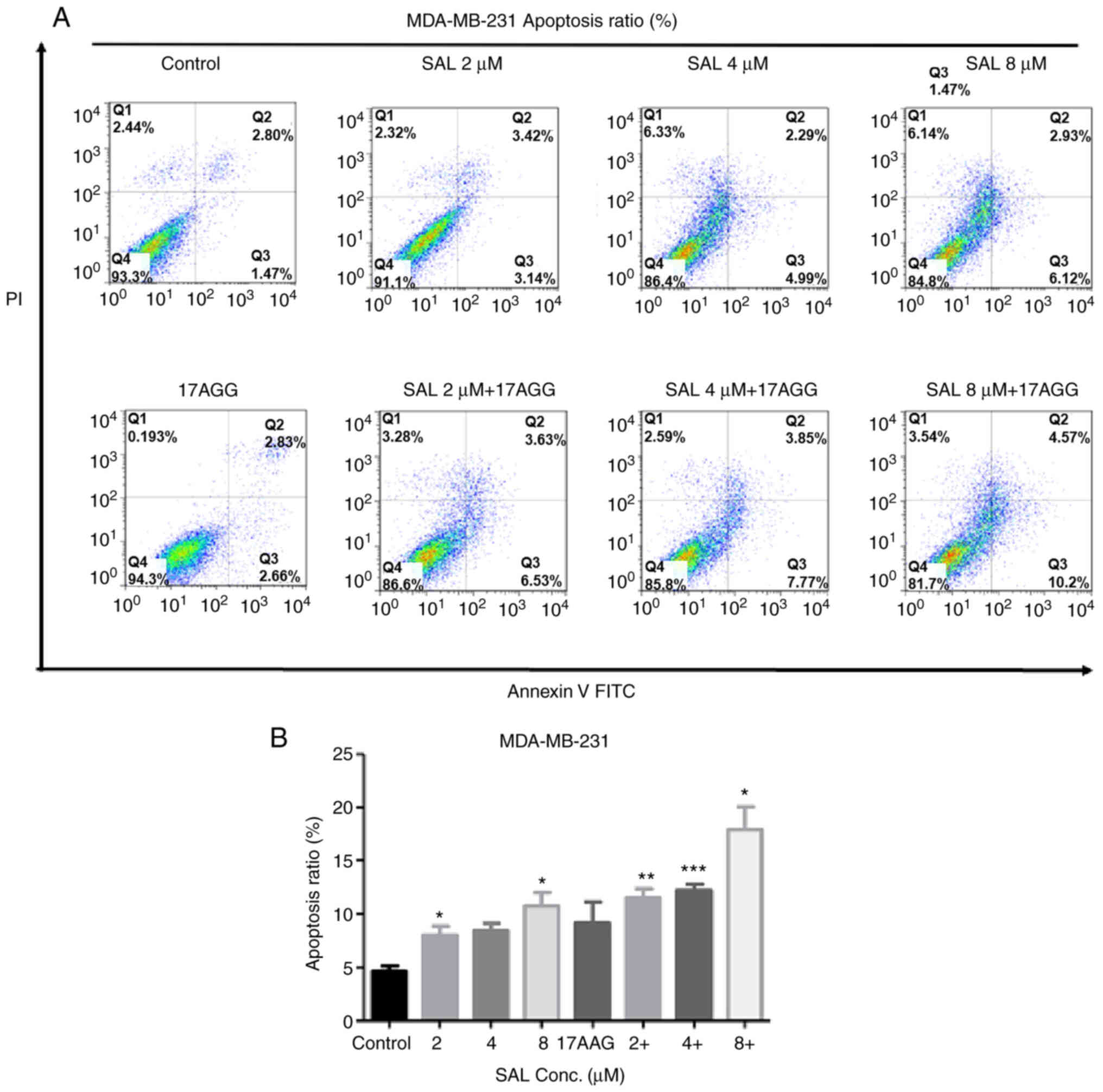
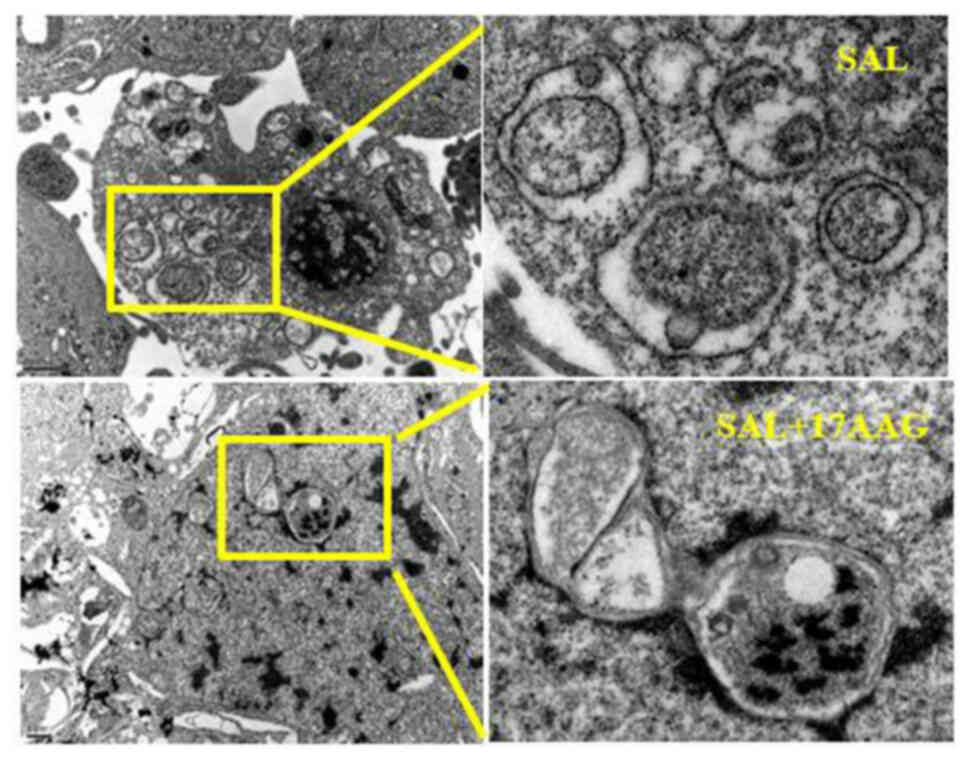
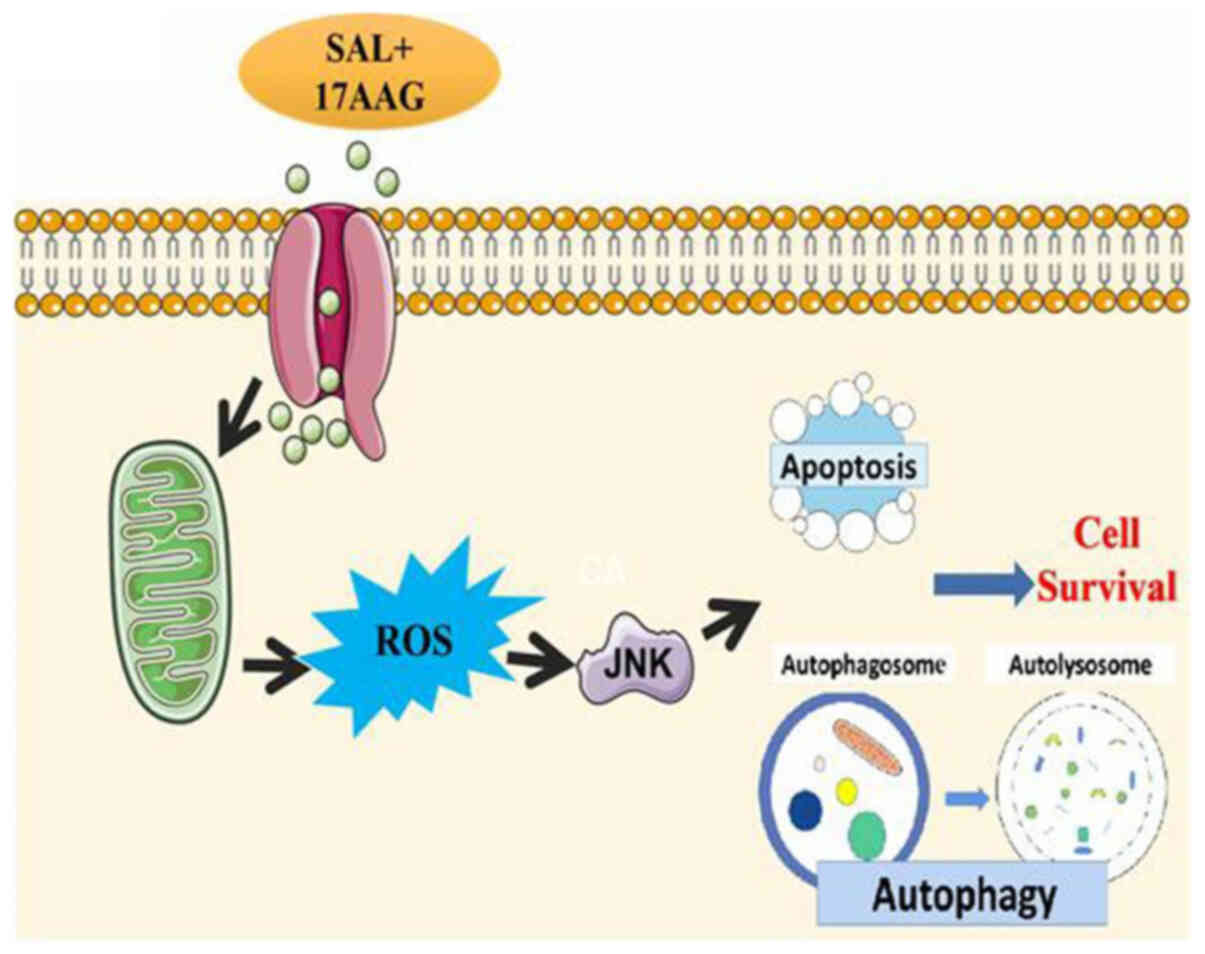
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chaudhary LN, Wilkinson KH and Kong A:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Who should receive neoadjuvant
chemotherapy? Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 27:141–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lee A and Djamgoz MBA: Triple negative
breast cancer: Emerging therapeutic modalities and novel
combination therapies. Cancer Treat Rev. 62:110–122. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Al-Mahmood S, Sapiezynski J, Garbuzenko OB
and Minko T: Metastatic and triple-negative breast cancer:
Challenges and treatment options. Drug Deliv Transl Res.
8:1483–1507. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tang Y, Wang Y, Kiani MF and Wang B:
Classification, treatment strategy, and associated drug resistance
in breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 16:335–343. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Turdo A, Veschi V, Gaggianesi M, Chinnici
A, Bianca P, Todaro M and Stassi G: Meeting the challenge of
targeting cancer stem cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 7:162019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mummery C, Wilmut SI, van de Stolpe A and
Roelen BAJ: Stem cells in cancer and cancer stem cells. Stem Cells.
27. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA: pp. 237–256. 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dewangan J, Srivastava S and Rath SK:
Salinomycin: A new paradigm in cancer therapy. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176950352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gupta PB, Onder TT, Jiang G, Tao K,
Kuperwasser C, Weinberg RA and Lander ES: Identification of
selective inhibitors of cancer stem cells by high-throughput
screening. Cell. 138:645–659. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou J, Liu S, Wang Y, Dai W, Zou H, Wang
S, Zhang J and Pan J: Salinomycin effectively eliminates cancer
stem-like cells and obviates hepatic metastasis in uveal melanoma.
Mol Cancer. 18:1592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao Y, Zhao W, Lim YC and Liu T:
Salinomycin-loaded gold nanoparticles for treating cancer stem
cells by ferroptosis-induced cell death. Mol Pharm. 16:2532–2539.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miyazaki Y, Shibuya M, Sugawara H,
Kawaguchi O and Hirsoe C: Salinomycin, a new polyether antibiotic.
J Antibiot (Tokyo). 27:814–821. 1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qin LS, Jia PF, Zhang ZQ and Zhang SM:
ROS-p53-cyclophilin-D signaling mediates salinomycin-induced glioma
cell necrosis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim KY, Lee SG, Baek SY, Lee EH, Jang EJ,
Lee JH, Ahn SC, Chang JH, Oh TW, Kim SH, et al: Salinomycin
ameliorates oxidative hepatic damage through AMP-activated protein
kinase, facilitating autophagy. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
360:141–149. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang J, Li H, Qaed E, Zhang J, Song Y, Wu
R, Bu X, Wang Q and Tang Z: Salinomycin, as an autophagy
modulator-a new avenue to anticancer: A review. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 37:262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fuchs D, Daniel V, Sadeghi M, Opelz G and
Naujokat C: Salinomycin overcomes ABC transporter-mediated
multidrug and apoptosis resistance in human leukemia stem cell-like
KG-1a cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:1098–1104. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Z, Zhou L, Xiong Y, Yu S, Li H, Fan
J, Li F, Su Z, Song J, Sun Q, et al: Salinomycin exerts
anti-colorectal cancer activity by targeting the β-catenin/T-cell
factor complex. Br J Pharmacol. 176:3390–3406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim KY, Park KI, Kim SH, Yu SN, Park SG,
Kim YW, Seo YK, Ma JY and Ahn SC: Inhibition of autophagy promotes
salinomycin-induced apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/p38 MAPK-dependent signaling in human
prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18:10882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Talaei S, Mellatyar H, Asadi A, Akbarzadeh
A, Sheervalilou R and Zarghami N: Spotlight on 17-AAG as an Hsp90
inhibitor for molecular targeted cancer treatment. Chem Biol Drug
Des. 93:760–786. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hirakawa H, Fujisawa H, Masaoka A, Noguchi
M, Hirayama R, Takahashi M, Fujimori A and Okayasu R: The
combination of Hsp90 inhibitor 17AAG and heavy-ion irradiation
provides effective tumor control in human lung cancer cells. Cancer
Med. 4:426–436. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Moon HJ, Park SY, Lee SH, Kang CD and Kim
SH: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs sensitize
CD44-overexpressing cancer cells to Hsp90 inhibitor through
autophagy activation. Oncol Res. 27:835–847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xie Q, Wondergem R, Shen Y, Cavey G, Ke J,
Thompson R, Bradley R, Daugherty-Holtrop J, Xu Y, Chen E, et al:
Benzoquinone ansamycin 17AAG binds to mitochondrial
voltage-dependent anion channel and inhibits cell invasion. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:4105–4110. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walker T, Mitchell C, Park MA, Yacoub A,
Rahmani M, Häussinger D, Reinehr R, Voelkel-Johnson C, Fisher PB,
Grant S and Dent P: 17-allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and
MEK1/2 inhibitors kill GI tumor cells via Ca2+-dependent
suppression of GRP78/BiP and induction of ceramide and reactive
oxygen species. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:1378–1395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Piredda ML, Gaur G, Catalano G, Divona M,
Banella C, Travaglini S, Puzzangara MC, Voso MT, Lo-Coco F and
Noguera NI: PML/RARA inhibits expression of HSP90 and its target
AKT. Br J Haematol. 184:937–948. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
He D, Wo B and Zhao JM: Effect of
salinomycin on the proliferation and apoptosis of triple negative
breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 by target-regulating ALDH.
Chinese J Oncol Prevention Treatment. 12:72020.
|
|
26
|
Jafari-Gharabaghlou D,
Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y, Dadashpour M, Mota A, Vafajouy-Jamshidi S,
Faramarzi L, Rasouli S and Zarghami N: Combination of metformin and
phenformin synergistically inhibits proliferation and hTERT
expression in human breast cancer cells. Iran J Basic Med Sci.
21:1167–1173. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chatran M, Pilehvar-Soltanahmadi Y,
Dadashpour M, Faramarzi L, Rasouli S, Jafari-Gharabaghlou D,
Asbaghi N and Zarghami N: Synergistic anti-proliferative effects of
metformin and silibinin combination on T47D breast cancer cells via
hTERT and cyclin D1 inhibition. Drug Res (Stuttg). 68:710–716.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y
and Morishima K: KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways,
diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:D353–D361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y and Morishima K:
BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG tools for functional
characterization of genome and metagenome sequences. J Mol Biol.
428:726–731. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Verdoodt B, Vogt M, Schmitz I, Liffers ST,
Tannapfel A and Mirmohammadsadegh A: Salinomycin induces autophagy
in colon and breast cancer cells with concomitant generation of
reactive oxygen species. PLoS One. 7:e441322012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Park E and Chung SW: ROS-mediated
autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by
ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis.
10:8222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zheng Q, Li Q, Zhao G, Zhang J, Yuan H,
Gong D, Guo Y, Liu X, Li K and Lin P: Alkannin induces cytotoxic
autophagy and apoptosis by promoting ROS-mediated mitochondrial
dysfunction and activation of JNK pathway. Biochem Pharmacol.
180:1141672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Su LJ, Zhang JH, Gomez H, Murugan R, Hong
X, Xu D, Jiang F and Peng ZY: Reactive oxygen species-induced lipid
peroxidation in apoptosis, autophagy, and ferroptosis. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019:50808432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang S, Li Z, Liu W, Wei G, Yu N and Ji G:
Neohesperidin induces cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy
via the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Am J
Chin Med. 49:1251–1274. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang J, Wang X, Vikash V, Ye Q, Wu D, Liu
Y and Dong W: ROS and ROS-mediated cellular signaling. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2016:43509652016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang ZD, Yang YJ, Liu XW, Qin Z, Li SH
and Li JY: Aspirin eugenol ester ameliorates paraquat-induced
oxidative damage through ROS/p38-MAPK-mediated mitochondrial
apoptosis pathway. Toxicology. 453:1527212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Diwanji N and Bergmann A: An unexpected
friend-ROS in apoptosis-induced compensatory proliferation:
Implications for regeneration and cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
80:74–82. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu J, Chang F, Li F, Fu H, Wang J, Zhang
S, Zhao J and Yin D: Palmitate promotes autophagy and apoptosis
through ROS-dependent JNK and p38 MAPK. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:262–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peña-Blanco A and García-Sáez AJ: Bax, Bak
and beyond-mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J.
285:416–431. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu J, Zhan AJ, Jiang JL, Chen Y, Xu J, Ye
L and Mao MG: Conserved function of pacific cod caspase-3 in
apoptosis. Gene. 732:1443702020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Tsapras P and Nezis IP: Caspase
involvement in autophagy. Cell Death Differ. 24:1369–1379. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu X, Li Q, Sun L, Chen L, Li Y, Huang B,
Liu Y and Jiang C: miR-30e-5p regulates autophagy and apoptosis by
targeting Beclin1 involved in contrast-induced acute kidney injury.
Curr Med Chem. 28:7974–7984. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Uriarte SM, Joshi-Barve S, Song Z, Sahoo
R, Gobejishvili L, Jala VR, Haribabu B, McClain C and Barve S: Akt
inhibition upregulates FasL, downregulates c-FLIPs and induces
caspase-8-dependent cell death in Jurkat T lymphocytes. Cell Death
Differ. 12:233–242. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Oral O, Oz-Arslan D, Itah Z, Naghavi A,
Deveci R, Karacali S and Gozuacik D: Cleavage of Atg3 protein by
caspase-8 regulates autophagy during receptor-activated cell death.
Apoptosis. 17:810–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mao J, Fan S, Ma W, Fan P, Wang B, Zhang
J, Wang H, Tang B, Zhang Q, Yu X, et al: Roles of Wnt/β-catenin
signaling in the gastric cancer stem cells proliferation and
salinomycin treatment. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|