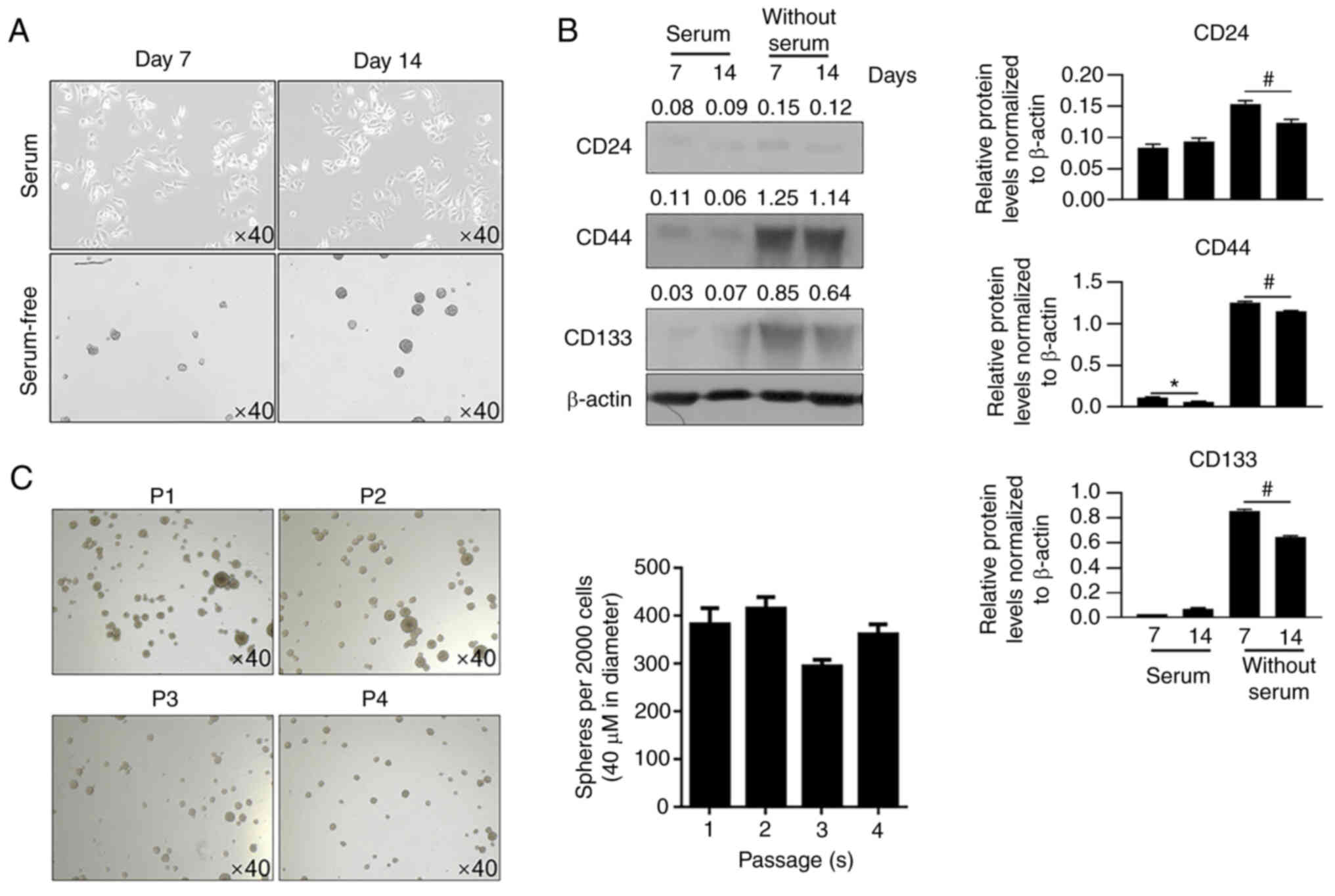
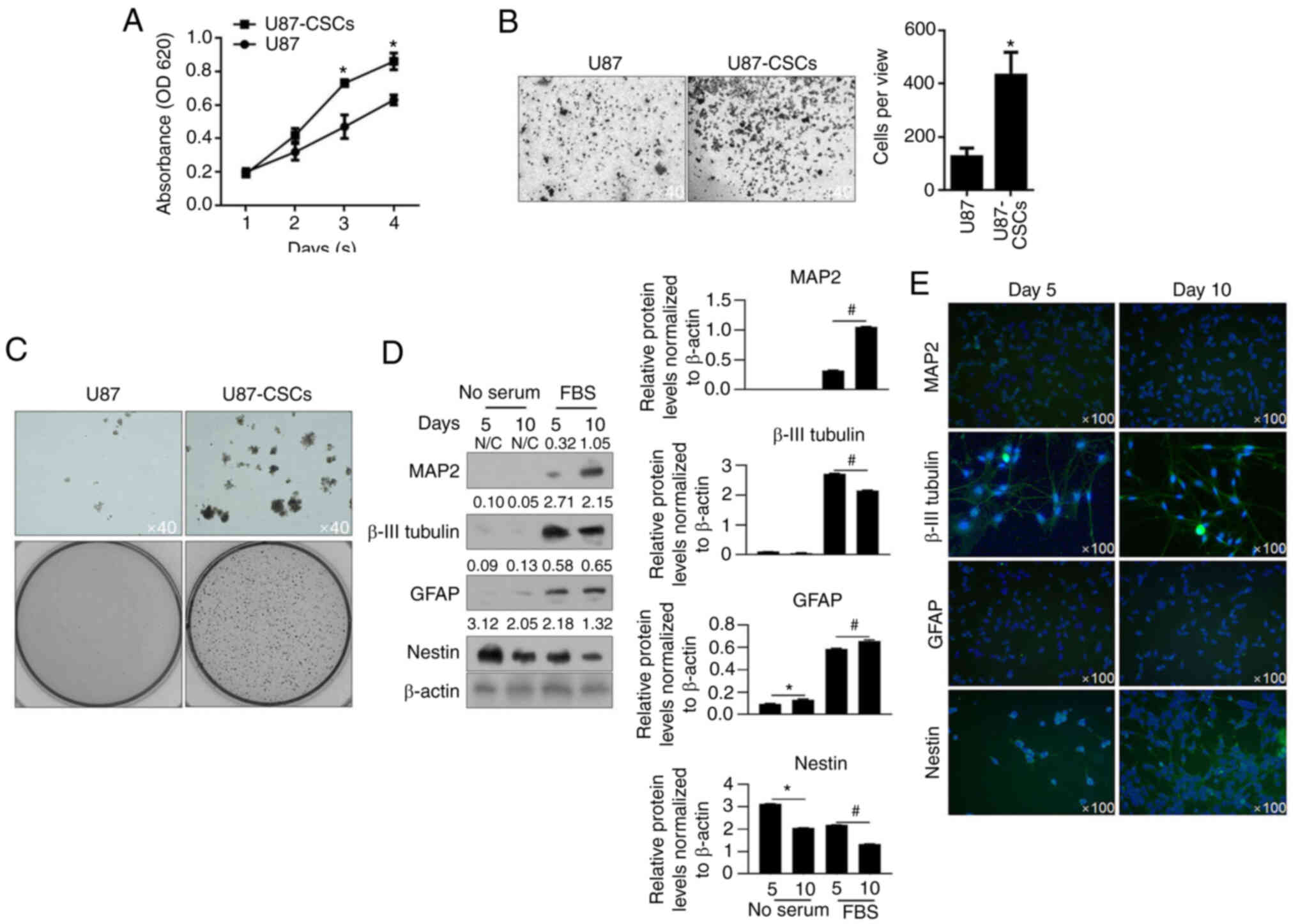
|
1
|
Mitre AO, Florian AI, Buruiana A, Boer A,
Moldovan I, Soritau O, Florian SI and Susman S: Ferroptosis
involvement in glioblastoma treatment. Medicina (Kaunas).
58:3192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y and Jiang T: Understanding high
grade glioma: Molecular mechanism, therapy and comprehensive
management. Cancer Lett. 331:139–146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ramaswamy V and Taylor MD: The amazing and
deadly glioma race. Cancer Cell. 28:275–277. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Alcantara Llaguno S and Parada LF: Cancer
stem cells in gliomas: Evolving concepts and therapeutic
implications. Curr Opin Neurol. 34:868–874. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lathia JD, Mack SC, Mulkearns-Hubert EE,
Valentim CL and Rich JN: Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Genes
Dev. 29:1203–1217. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seifert C, Balz E, Herzog S, Korolev A,
Gaßmann S, Paland H, Fink MA, Grube M, Marx S, Jedlitschky G, et
al: PIM1 inhibition affects glioblastoma stem cell behavior and
kills glioblastoma stem-like cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:111262021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
GrandPré T, Nakamura F, Vartanian T and
Strittmatter SM: Identification of the Nogo inhibitor of axon
regeneration as a reticulon protein. Nature. 403:439–444. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Petrinovic MM, Duncan CS, Bourikas D,
Weinman O, Montani L, Schroeter A, Maerki D, Sommer L, Stoeckli ET
and Schwab ME: Neuronal Nogo-A regulates neurite fasciculation,
branching and extension in the developing nervous system.
Development. 137:2539–2550. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mathis C, Schröter A, Thallmair M and
Schwab ME: Nogo-a regulates neural precursor migration in the
embryonic mouse cortex. Cereb Cortex. 20:2380–2390. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Schwab ME: Functions of Nogo proteins and
their receptors in the nervous system. Nat Rev Neurosci.
11:799–811. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xiong NX, Zhao HY, Zhang FC and He ZQ:
Negative correlation of Nogo-A with the malignancy of
oligodendroglial tumor. Neurosci Bull. 23:41–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Schwab DE, Lepski G, Borchers C, Trautmann
K, Paulsen F and Schittenhelm J: Immunohistochemical comparative
analysis of GFAP, MAP-2, NOGO-A, OLIG-2 and WT-1 expression in WHO
2016 classified neuroepithelial tumors and their prognostic value.
Pathol Res Pract. 214:15–24. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Behling F, Barrantes-Freer A, Behnes CL,
Stockhammer F, Rohde V, Adel-Horowski A, Rodríguez-Villagra OA,
Barboza MA, Brück W, Lehmann U, et al: Expression of Olig2, nestin,
NogoA and AQP4 have no impact on overall survival in IDH-wildtype
glioblastoma. PLoS One. 15:e2292742020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Zhou W, Li X, Ren J, Ji G, Du J,
Tian W, Liu Q and Hao A: Graphene oxide suppresses the growth and
malignancy of glioblastoma stem cell-like spheroids via epigenetic
mechanisms. J Transl Med. 18:2002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shtivelman E and Bishop J: Expression of
CD44 is repressed in neuroblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biol.
11:5446–5453. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nanduri LS, Maimets M, Pringle SA, van der
Zwaag M, van Os RP and Coppes RP: Regeneration of irradiated
salivary glands with stem cell marker expressing cells. Radiother
Oncol. 99:367–372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wälchli T, Pernet V, Weinmann O, Shiu JY,
Guzik-Kornacka A, Decrey G, Yüksel D, Schneider H, Vogel J, Ingber
DE, et al: Nogo-A is a negative regulator of CNS angiogenesis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E1943–E1952. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wirthschaft P, Bode J, Soni H, Dietrich F,
Krüwel T, Fischer B, Knobbe-Thomsen CB, Rossetti G, Hentschel A,
Mack N, et al: RhoA regulates translation of the Nogo-A decoy SPARC
in white matter-invading glioblastomas. Acta Neuropathol.
138:275–293. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S,
Reifenberger G and von Deimling A: Glioblastoma: Pathology,
molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 129:829–848.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zagrebelsky M and Korte M: Maintaining
stable memory engrams: New roles for Nogo-A in the CNS.
Neuroscience. 283:17–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fang Y, Yao L, Li C, Wang J, Wang J, Chen
S, Zhou XF and Liao H: The blockage of the Nogo/NgR signal pathway
in microglia alleviates the formation of Aβ plaques and tau
phosphorylation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. J Neuroinflammation.
13:562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sarkey JP, Chu M, McShane M, Bovo E, Ait
Mou Y, Zima AV, de Tombe PP, Kartje GL and Martin JL: Nogo-A
knockdown inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced activation of
mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 50:1044–1055. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lima FR, Kahn SA, Soletti RC, Biasoli D,
Alves T, da Fonseca AC, Garcia C, Romão L, Brito J, Holanda-Afonso
R, et al: Glioblastoma: Therapeutic challenges, what lies ahead.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826:338–349. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Diaz A and Leon K: Therapeutic approaches
to target cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel). 3:3331–3352. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ortensi B, Setti M, Osti D and Pelicci G:
Cancer stem cell contribution to glioblastoma invasiveness. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 4:182013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Safa AR, Saadatzadeh MR, Cohen-Gadol AA,
Pollok KE and Bijangi-Vishehsaraei K: Glioblastoma stem cells
(GSCs) epigenetic plasticity and interconversion between
differentiated non-GSCs and GSCs. Genes Dis. 2:152–163. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Meng Y, Shang F and Zhu Y: miR-124
participates in the proliferation and differentiation of brain
glioma stem cells through regulating Nogo/NgR expression. Exp Ther
Med. 18:2783–2788. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kern F, Stanika RI, Sarg B, Offterdinger
M, Hess D, Obermair GJ, Lindner H, Bandtlow CE, Hengst L and
Schweigreiter R: Nogo-A couples with Apg-1 through interaction and
co-ordinate expression under hypoxic and oxidative stress. Biochem
J. 455:217–227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|