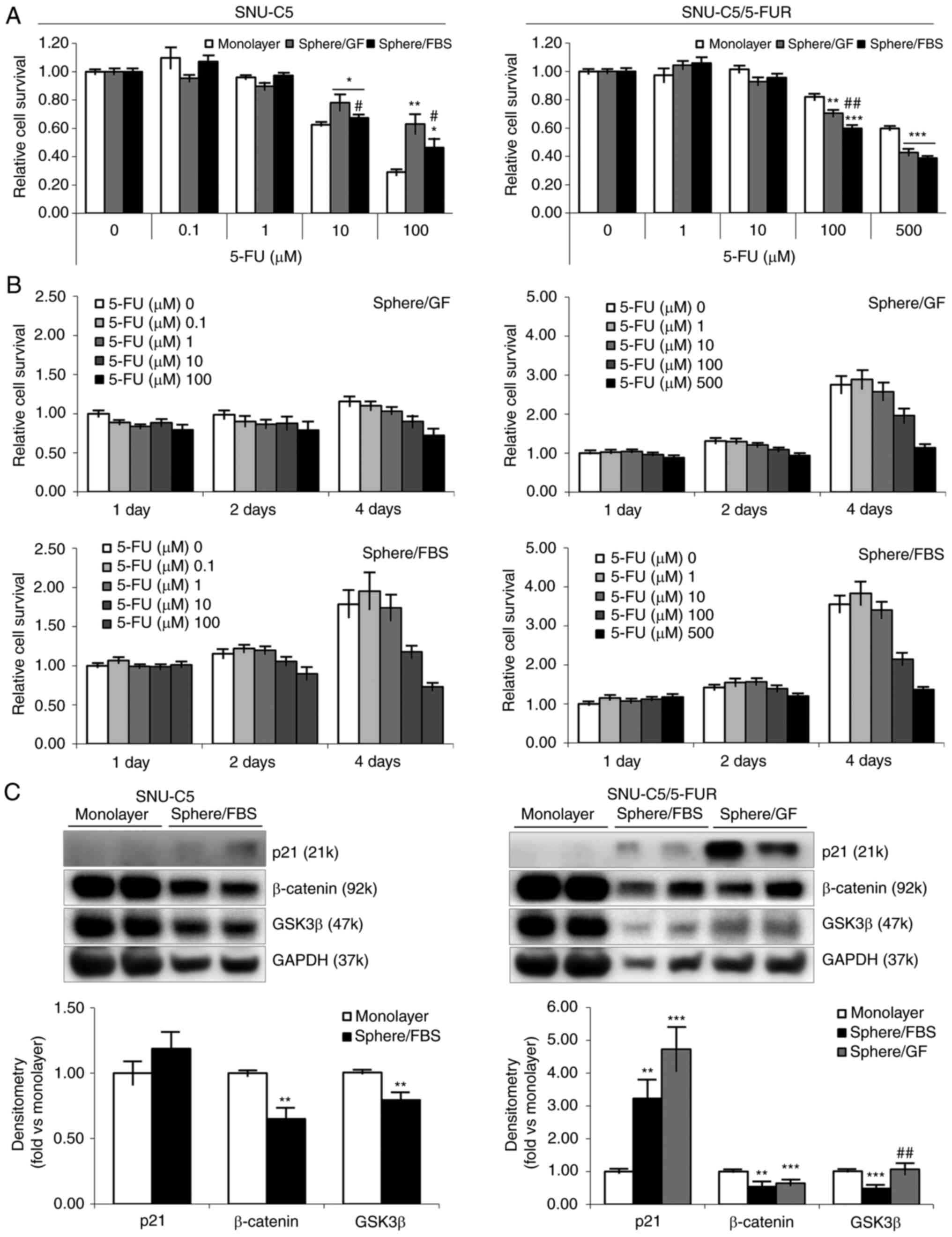
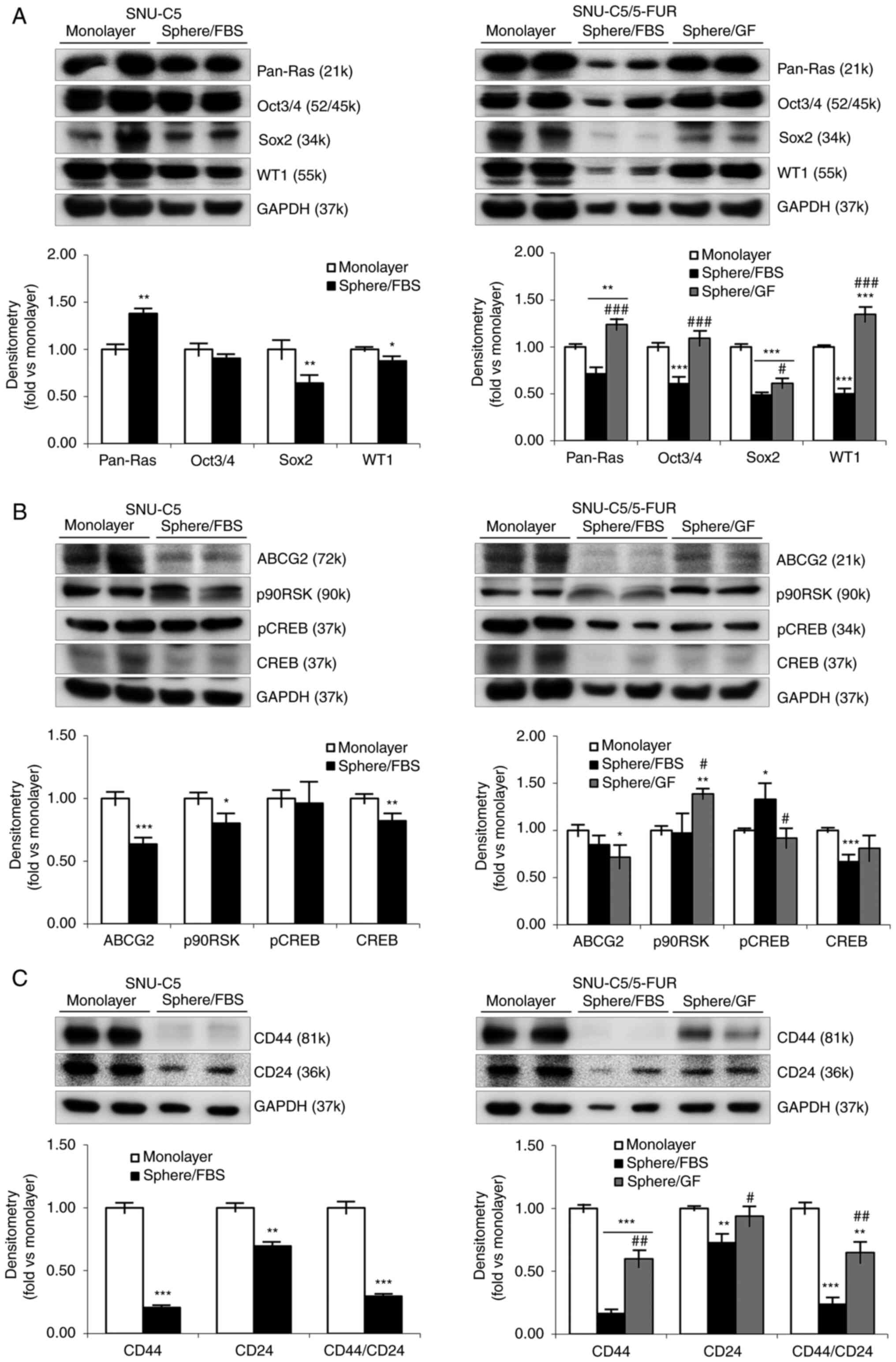
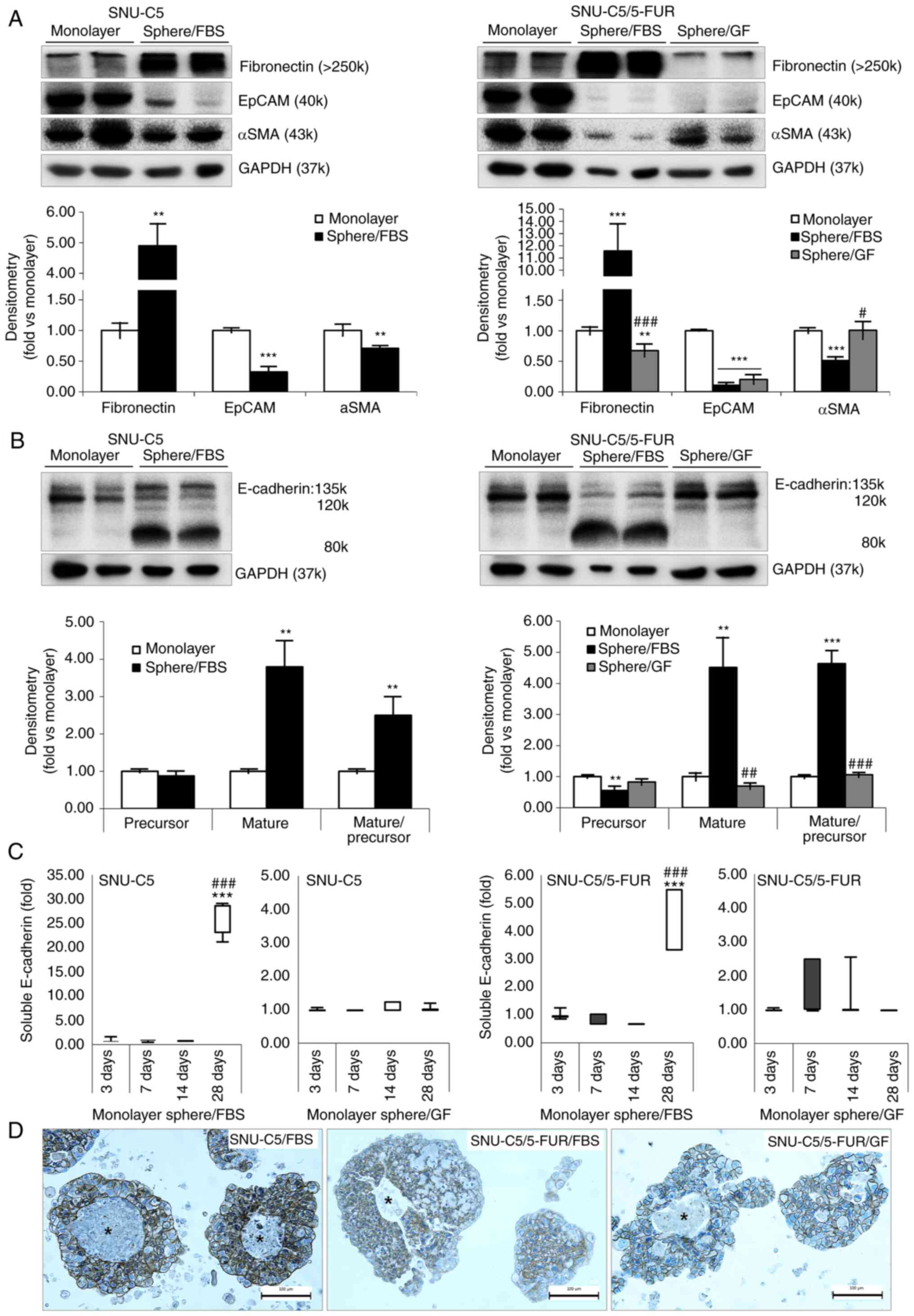
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwakman JJ and Punt CJ: Oral drugs in the
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 17:1351–1361. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stintzing S: Recent advances in
understanding colorectal cancer. F1000Res. 7:F10002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Azwar S, Seow HF, Abdullah M, Jabar MF and
Mohtarrudin N: Recent updates on mechanisms of resistance to
5-fluorouracil and reversal strategies in colon cancer treatment.
Biology (Basel). 10:8542021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi CH, Lee TB, Lee YA, Choi S and Kim
KJ: Up-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostaglandin E(2) in
colon cancer cells resistant to 5-fluorouracil. J Korean Surg Soc.
81:115–121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim EJ, Kang GJ, Kang JI, Boo HJ, Hyun JW,
Koh YS, Chang WY, Kim YR, Kwon JM, Maeng YH, et al: Over-activation
of AKT signaling leading to 5-Fluorouracil resistance in
SNU-C5/5-FU cells. Oncotarget. 9:19911–19928. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moon D, Kang HK, Kim J and Yoon SP: Yeast
extract induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest via activating p38
signal pathway in colorectal cancer cells. Ann Clin Lab Sci.
50:31–44. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JW, Kim SH, Mariappan R, Moon D, Kim J
and Yoon SP: Anti-cancer effects of the aqueous extract of
Orostachys japonica A. Berger on 5-fluorouracil-resistant
colorectal cancer via MAPK signalling pathways in vitro and in
vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 280:1144122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Corrò C and Moch H: Biomarker discovery
for renal cancer stem cells. J Pathol Clin Res. 4:3–18. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nguyen LV, Vanner R, Dirks P and Eaves CJ:
Cancer stem cells: An evolving concept. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:133–143.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Murphy AJ, Pierce J, de Caestecker C,
Ayers GD, Zhao A, Krebs JR, Saito-Diaz VK, Lee E, Perantoni AO, de
Caestecker MP and Lovvorn HN III: CITED1 confers stemness to Wilms
tumor and enhances tumorigenic responses when enriched in the
nucleus. Oncotarget. 5:386–402. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Telang NT: Stem cell models for breast and
colon cancer: Experimental approach for drug discovery. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:92232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu M, Casimiro MC, Wang C, Shirley LA,
Jiao X, Katiyar S, Ju X, Li Z, Yu Z, Zhou J, et al: p21CIP1
attenuates Ras- and c-Myc-dependent breast tumor epithelial
mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like gene expression in
vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:19035–19039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao BD, Zhao YJ, Jia XY, Wu J, Wang YG
and Huang F: Multifaceted p21 in carcinogenesis, stemness of tumor
and tumor therapy. World J Stem Cells. 12:481–487. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Telang N: Drug-resistant stem cells: Novel
approach for colon cancer therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 23:25192022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chang I, Ohn T, Moon D, Maeng YH, Jang BG
and Yoon SP: SNU-333 cells as an appropriate cell line for the
orthotopic renal cell carcinoma model. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
20:153303382110384872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JB, Hwang SE and Yoon SP:
Dexamethasone reduces side population fraction through
downregulation of ABCG2 transporter in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.
Mol Med Rep. 16:453–458. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Singla M, Kumar A, Bal A, Sarkar S and
Bhattacharyya S: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition induces stem
cell like phenotype in renal cell carcinoma cells. Cancer Cell Int.
18:572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Iglesias JM, Beloqui I, Garcia-Garcia F,
Leis O, Vazquez-Martin A, Eguiara A, Cufi S, Pavon A, Menendez JA,
Dopazo J and Martin AG: Mammosphere formation in breast carcinoma
cell lines depends upon expression of E-cadherin. PLoS One.
8:e772812013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Han SJ, Kwon S and Kim KS: Challenges of
applying multicellular tumor spheroids in preclinical phase. Cancer
Cell Int. 21:1522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, Athar
M, Ghazizadeh S, Simon M, O'Banion MK and Ma L: Soluble E-cadherin:
A critical oncogene modulating receptor tyrosine kinases, MAPK and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Oncogene. 33:225–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hu QP, Kuang JY, Yang QK, Bian XW and Yu
SC: Beyond a tumor suppressor: Soluble E-cadherin promotes the
progression of cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:2804–2815. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou G, Lv X, Zhong X, Ying W, Li W, Feng
Y, Xia Q, Li J, Jian S and Leng Z: Suspension culture strategies to
enrich colon cancer stem cells. Oncol Lett. 25:1162023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gheytanchi E, Naseri M, Karimi-Busheri F,
Atyabi F, Mirsharif ES, Bozorgmehr M, Ghods R and Madjd Z:
Morphological and molecular characteristics of spheroid formation
in HT-29 and Caco-2 colorectal cancer cell lines. Cancer Cell Int.
21:2042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Min SO, Lee SW, Bak SY and Kim KS: Ideal
sphere-forming culture conditions to maintain pluripotency in a
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 15:952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Han XY, Wei B, Fang JF, Zhang S, Zhang FC,
Zhang HB, Lan TY, Lu HQ and Wei HB: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition associates with maintenance of stemness in
spheroid-derived stem-like colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e733412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Z, Bu X, Chen H, Wang Q and Sha W:
Bmi-1 promotes the invasion and migration of colon cancer stem
cells through the downregulation of E-cadherin. Int J Mol Med.
38:1199–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Klopp AH, Lacerda L, Gupta A, Debeb BG,
Solley T, Li L, Spaeth E, Xu W, Zhang X, Lewis MT, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells promote mammosphere formation and decrease
E-cadherin in normal and malignant breast cells. PLoS One.
5:e121802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tang T, Yang Z, Zhu Q, Wu Y, Sun K,
Alahdal M, Zhang Y, Xing Y, Shen Y, Xia T, et al: Up-regulation of
miR-210 induced by a hypoxic microenvironment promotes breast
cancer stem cells metastasis, proliferation, and self-renewal by
targeting E-cadherin. FASEB J. 6:fj201801013R2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park NR, Cha JH, Jang JW, Bae SH, Jang B,
Kim JH, Hur W, Choi JY and Yoon SK: Synergistic effects of CD44 and
TGF-β1 through AKT/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling during
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver cancer cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 477:568–574. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Izumiya M, Kabashima A, Higuchi H,
Igarashi T, Sakai G, Iizuka H, Nakamura S, Adachi M, Hamamoto Y,
Funakoshi S, et al: Chemoresistance is associated with cancer stem
cell-like properties and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
pancreatic cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 32:3847–3853.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ohnishi Y, Yasui H, Kakudo K and Nozaki M:
Lapatinib-resistant cancer cells possessing epithelial cancer stem
cell properties develop sensitivity during sphere formation by
activation of the ErbB/AKT/cyclin D2 pathway. Oncol Rep.
36:3058–3064. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Acikgoz E, Guven U, Duzagac F, Uslu R,
Kara M, Soner BC and Oktem G: Enhanced G2/M arrest, caspase related
apoptosis and reduced E-cadherin dependent intercellular adhesion
by trabectedin in prostate cancer stem cells. PLoS One.
10:e01410902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Qian Y, Wu X, Yokoyama Y, Okuzaki D,
Taguchi M, Hirose H, Wang J, Hata T, Inoue A, Hiraki M, et al:
E-cadherin-fc chimera protein matrix enhances cancer stem-like
properties and induces mesenchymal features in colon cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 110:3520–3532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Morata-Tarifa C, Jiménez G, García MA,
Entrena JM, Griñán-Lisón C, Aguilera M, Picon-Ruiz M and Marchal
JA: Low adherent cancer cell subpopulations are enriched in
tumorigenic and metastatic epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition-induced cancer stem-like cells. Sci Rep. 6:187722016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang S, Cai M, Zheng Y, Zhou L, Wang Q
and Chen L: miR-888 in MCF-7 side population sphere cells directly
targets E-cadherin. J Genet Genomics. 41:35–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Patil PU, D'Ambrosio J, Inge LJ, Mason RW
and Rajasekaran AK: Carcinoma cells induce lumen filling and EMT in
epithelial cells through soluble E-cadherin-mediated activation of
EGFR. J Cell Sci. 128:4366–4379. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Deng X, Chen C, Wu F, Qiu L, Ke Q, Sun R,
Duan Q, Luo M and Luo Z: Curcumin inhibits the migration and
invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells through
radiation-induced suppression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and soluble E-cadherin expression. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
19:15330338209474852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liang SC, Yang CY, Tseng JY, Wang HL, Tung
CY, Liu HW, Chen CY, Yeh YC, Chou TY, Yang MH, et al: ABCG2
localizes to the nucleus and modulates CDH1 expression in lung
cancer cells. Neoplasia. 17:265–278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|