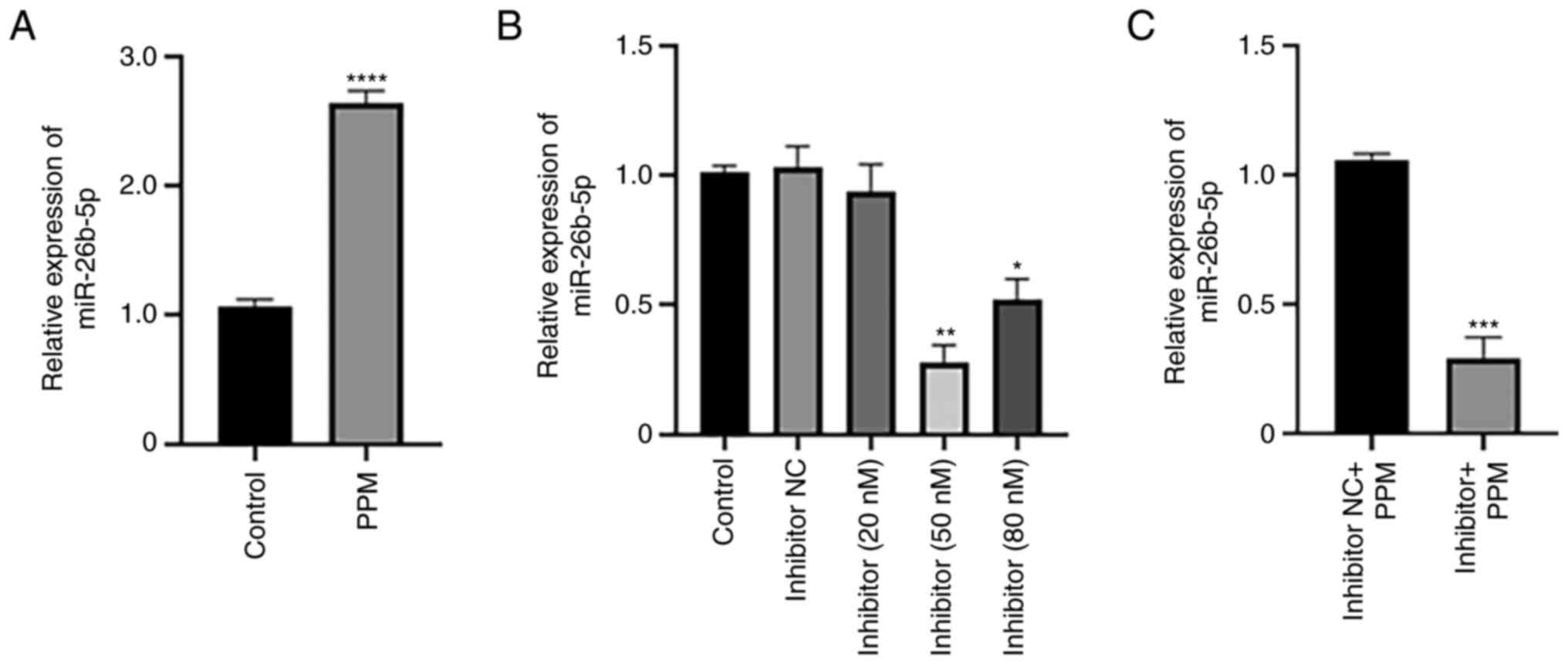
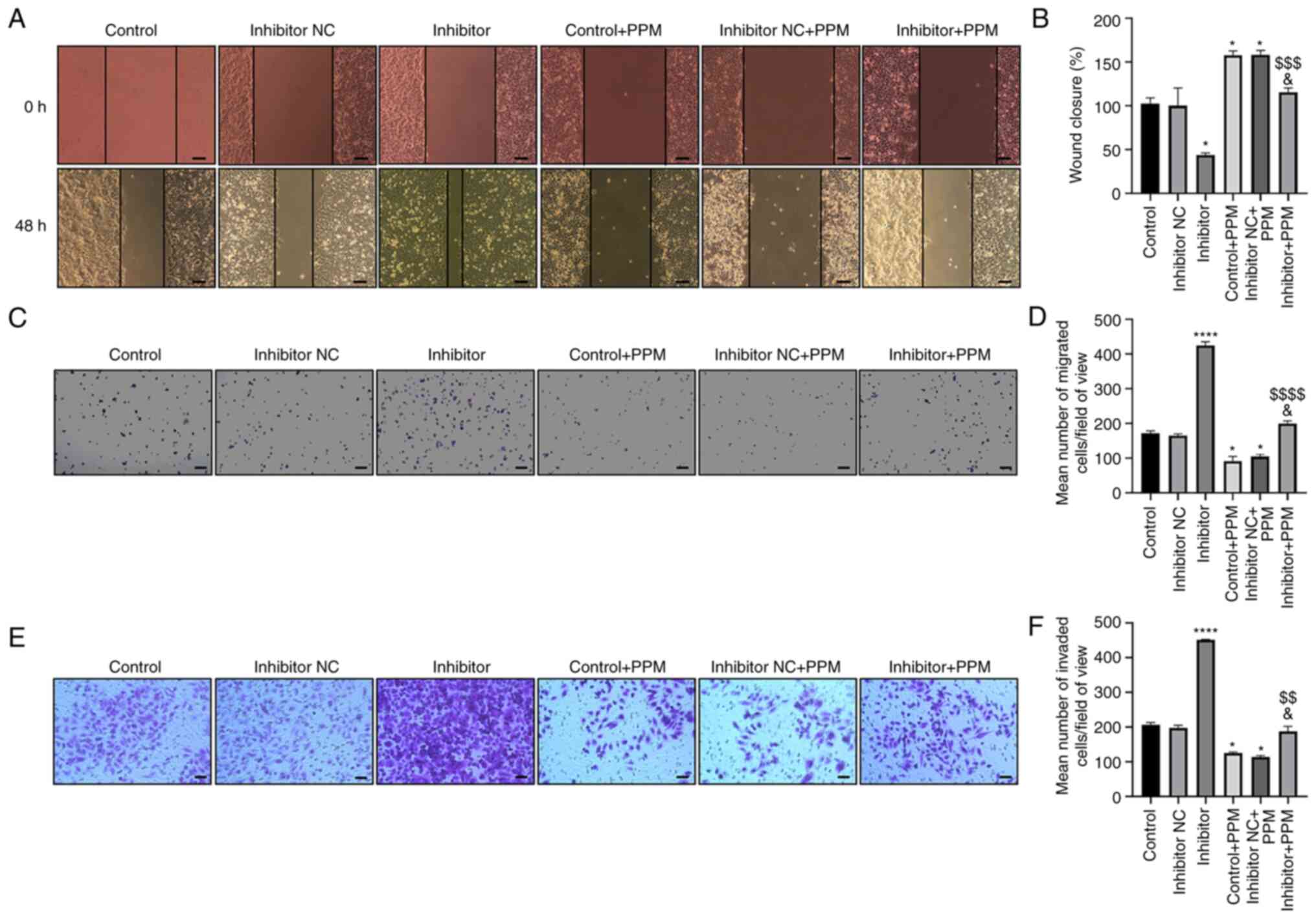
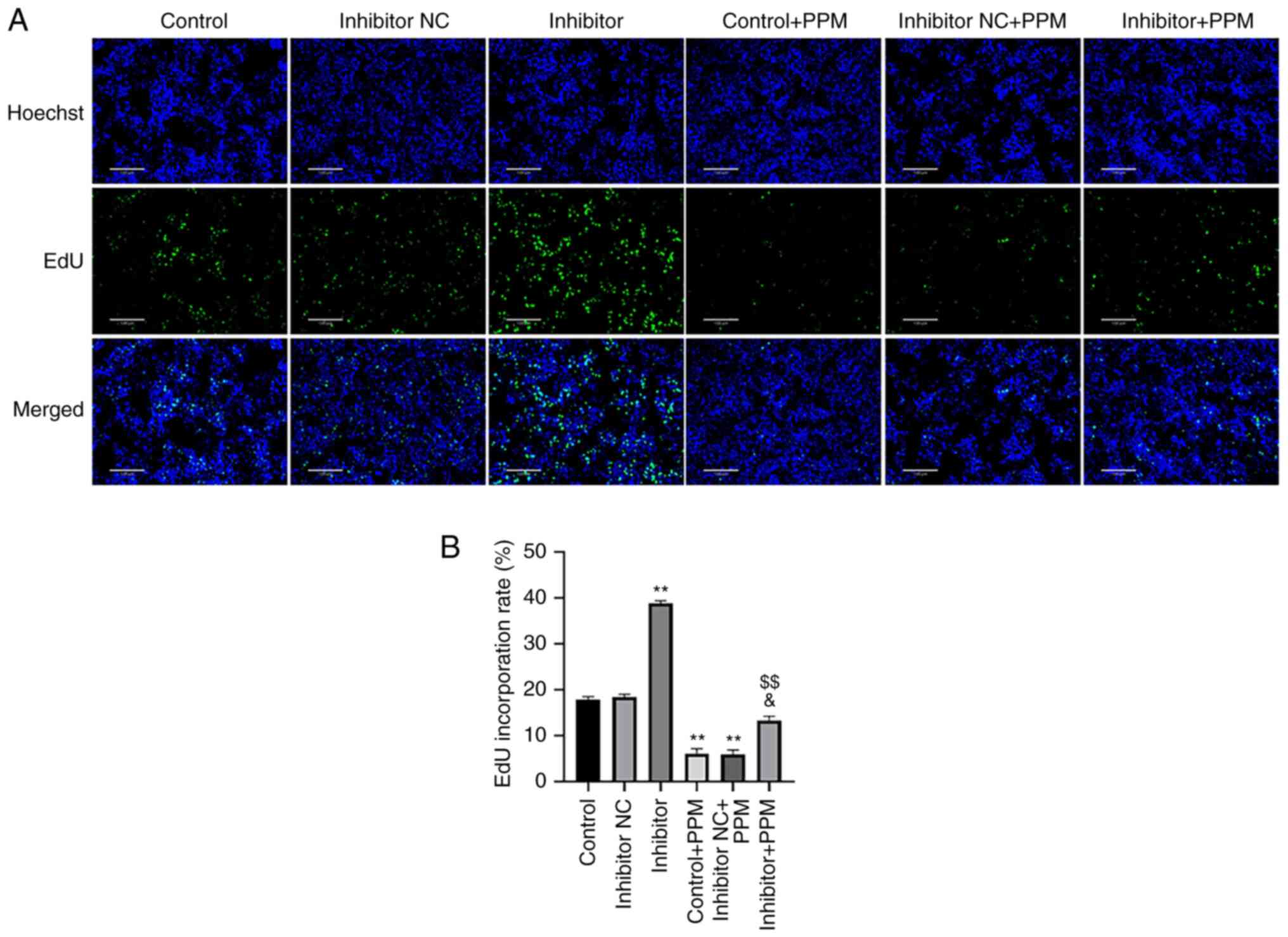
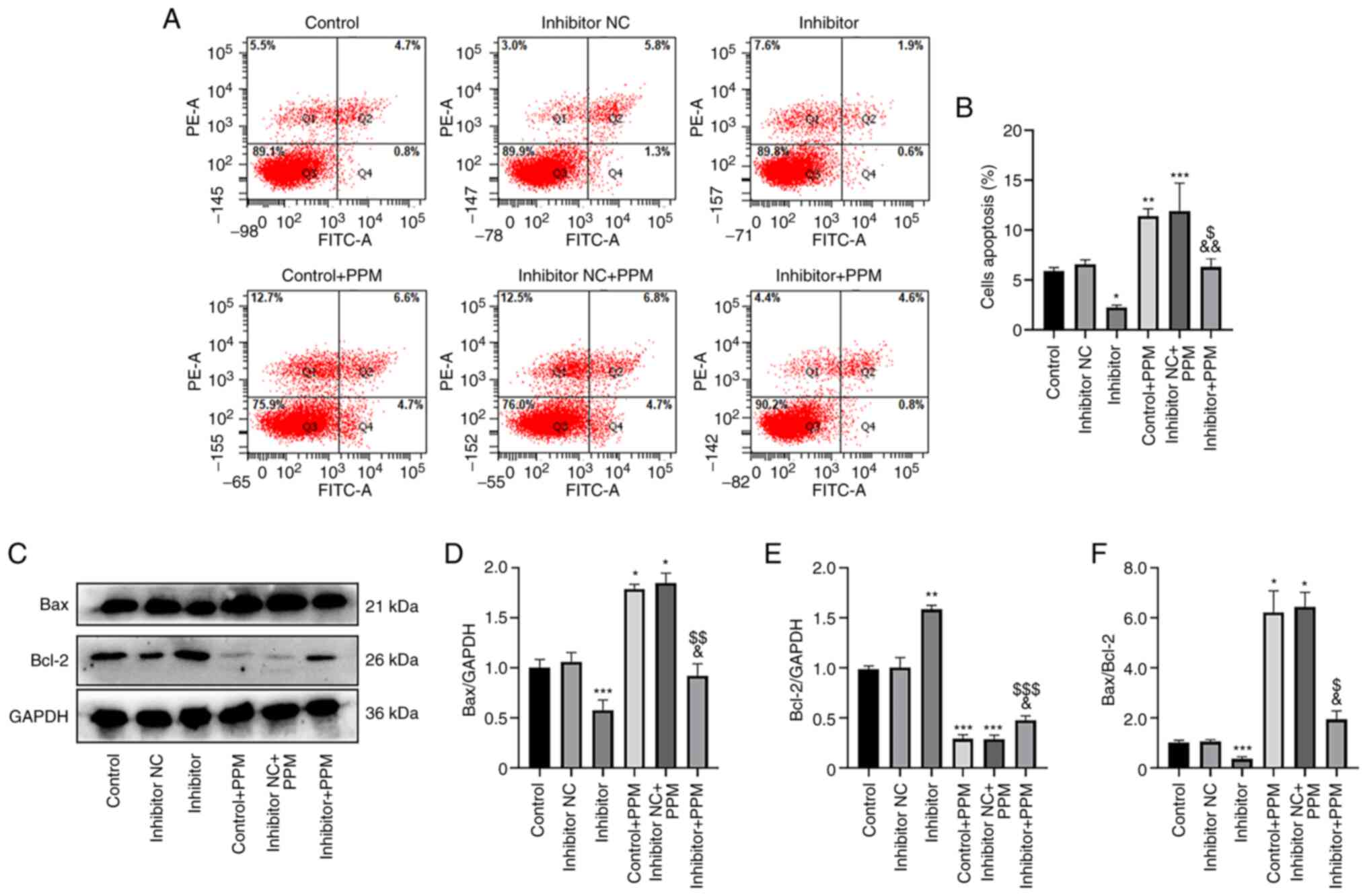
|
1
|
Yang X, Qu S, Wang L, Zhang H, Yang Z,
Wang J, Dai B, Tao K, Shang R, Liu Z, et al: PTBP3 splicing factor
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma by destroying the splicing
balance of NEAT1 and pre-miR-612. Oncogene. 37:6399–6413. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wang Y, Yang L, Chen T, Liu X, Guo Y, Zhu
Q, Tong X, Yang W, Xu Q, Huang D and Tu K: A novel lncRNA
MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis. Mol Cancer. 18:282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nelson KM, Dahlin JL, Bisson J, Graham J,
Pauli GF and Walters MA: The essential medicinal chemistry of
curcumin. J Med Chem. 60:1620–1637. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yin DL, Liang YJ, Zheng TS, Song RP, Wang
JB, Sun BS, Pan SH, Qu LD, Liu JR, Jiang HC and Liu LX: EF24
inhibits tumor growth and metastasis via suppressing NF-kappaB
dependent pathways in human cholangiocarcinoma. Sci Rep.
6:321672016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li N, Xin WY, Yao BR, Cong W, Wang CH and
Hou GG: N-phenylsulfonyl-3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidone
derivatives as activation NF-κB inhibitors in hepatic carcinoma
cell lines. Eur J Med Chem. 155:531–544. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao BR, Sun Y, Chen SL, Suo HD, Zhang YL,
Wei H, Wang CH, Zhao F, Cong W, Xin WY and Hou GG: Dissymmetric
pyridyl-substituted 3,5-bis(arylidene)-4-piperidones as
anti-hepatoma agents by inhibiting NF-κB pathway activation. Eur J
Med Chem. 167:187–199. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun Y, Gao ZF, Yan WB, Yao BR, Xin WY,
Wang CH, Meng QG and Hou GG: Discovery of novel NF-кB inhibitor
based on scaffold hopping:
1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidine. Eur J Med Chem.
198:1123662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou YQ, Sun Y, Luo HL, Gao ZF, Zhang HQ,
Meng QG, Bai XY, Hou GG and Hou Y: Discovery of anti-hepatoma
agents from 1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropyrido[4,3-d]pyrimidine by
inhibiting PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway activation. Eur J Med Chem.
225:1137962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iacona JR and Lutz CS: miR-146a-5p:
Expression, regulation, and functions in cancer. Wiley Interdiscip
Rev RNA. 10:e15332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao X, Han D and Fan W: Down-regulation of
RBP-J mediated by microRNA-133a suppresses dendritic cells and
functions as a potential tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma. Exp Cell
Res. 349:264–272. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nussbacher JK and Yeo GW: Systematic
discovery of RNA binding proteins that regulate MicroRNA levels.
Mol Cell. 69:1005–1016.e7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Du Q, Yuan Z, Huang X, Huang Y, Zhang J
and Li R: miR-26b-5p suppresses chemoresistance in breast cancer by
targeting serglycin. Anticancer Drugs. 33:308–319. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miyamoto K, Seki N, Matsushita R, Yonemori
M, Yoshino H, Nakagawa M and Enokida H: Tumour-suppressive
miRNA-26a-5p and miR-26b-5p inhibit cell aggressiveness by
regulating PLOD2 in bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 115:354–363. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lin Y, Jian Z, Jin H, Wei X, Zou X, Guan R
and Huang J: Long non-coding RNA DLGAP1-AS1 facilitates
tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
hepatocellular carcinoma via the feedback loop of
miR-26a/b-5p/IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 and Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 11:342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Khosla R, Hemati H, Rastogi A, Ramakrishna
G, Sarin SK and Trehanpati N: miR-26b-5p helps in EpCAM+cancer stem
cells maintenance via HSC71/HSPA8 and augments malignant features
in HCC. Liver Int. 39:1692–1703. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu S, Li L, Li M and Zhang J: Effect of
miR-26b-5p on cis-diamine dichloroplatinum-induced ovarian
granulosa cell injury by targeting MAP3K9. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 56:213–221. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu T, Chen W, Liu S, Lu H, Wang H, Kong D,
Huang X, Kong Q, Ning Y and Lu Z: Huaier suppresses proliferation
and induces apoptosis in human pulmonary cancer cells via
upregulation of miR-26b-5p. FEBS Lett. 588:2107–2114. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhu L and Mei M: Interference of long
non-coding RNA HAGLROS inhibits the proliferation and promotes the
apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells by targeting miR-26b-5p. Exp Ther
Med. 22:8792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng Y, Zu LL and Zhang L: MicroRNA-26b
inhibits the tumor growth of human liver cancer through the
PI3K/Akt and NF-κB/MMP-9/VEGF pathways. Oncol Rep. 39:2288–2296.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao N, Wang R, Zhou L, Zhu Y, Gong J and
Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-26b suppresses the NF-κB signaling and enhances
the chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting
TAK1 and TAB3. Mol Cancer. 13:352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen Y, Li S, Zhang Y, Wang M, Li X, Liu
S, Xu D, Bao Y, Jia P, Wu N, et al: The lncRNA Malat1 regulates
microvascular function after myocardial infarction in mice via
miR-26b-5p/Mfn1 axis-mediated mitochondrial dynamics. Redox Biol.
41:1019102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang R, Niu Z, Pei H and Peng Z: Long
noncoding RNA LINC00657 induced by SP1 contributes to the non-small
cell lung cancer progression through targeting miR-26b-5p/COMMD8
axis. J Cell Physiol. 235:3340–3349. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Han F, Huang D, Huang X, Wang W, Yang S
and Chen S: Exosomal microRNA-26b-5p down-regulates ATF2 to enhance
radiosensitivity of lung adenocarcinoma cells. J Cell Mol Med.
24:7730–7742. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wilke CM, Hess J, Klymenko SV, Chumak VV,
Zakhartseva LM, Bakhanova EV, Feuchtinger A, Walch AK,
Selmansberger M, Braselmann H, et al: Expression of miRNA-26b-5p
and its target TRPS1 is associated with radiation exposure in
post-Chernobyl breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 142:573–583. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang X, Zhang X, Wang T, Wang L, Tan Z,
Wei W, Yan B, Zhao J, Wu K, Yang A, et al: MicroRNA-26a is a key
regulon that inhibits progression and metastasis of c-Myc/EZH2
double high advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
426:98–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li J, Li X, Kong X, Luo Q, Zhang J and
Fang L: MiRNA-26b inhibits cellular proliferation by targeting CDK8
in breast cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:558–565. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yi L, Liu Y, Xu A, Li S, Zhang H, Peng M,
Li Z, Ren H, Dai J, Luo C, et al: MicroRNA-26b-5p suppresses the
proliferation of tongue squamous cell carcinoma via targeting
proline rich 11 (PRR11). Bioengineered. 12:5830–5838. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang K, Zhang B, Bai Y and Dai L: E2F1
promotes cancer cell sensitivity to cisplatin by regulating the
cellular DNA damage response through miR-26b in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. J Cancer. 11:301–310. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Liu WB, Liu KJ, Ao L, Cao J, Zhong
JL and Liu JY: Overexpression of miR-26b-5p regulates the cell
cycle by targeting CCND2 in GC-2 cells under exposure to extremely
low frequency electromagnetic fields. Cell Cycle. 15:357–367. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|