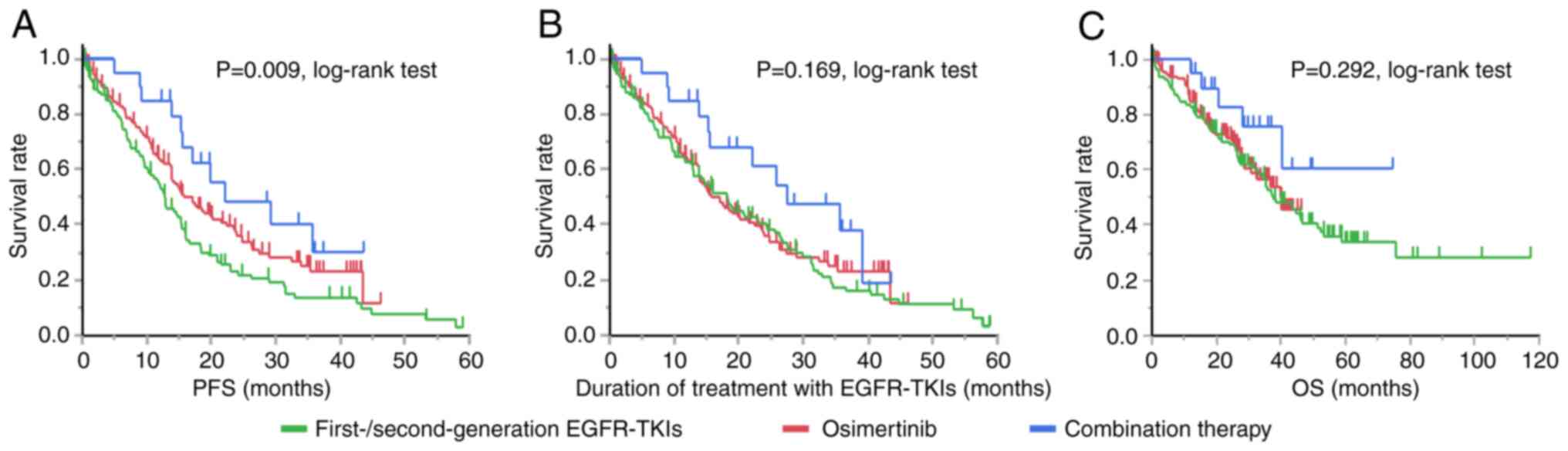
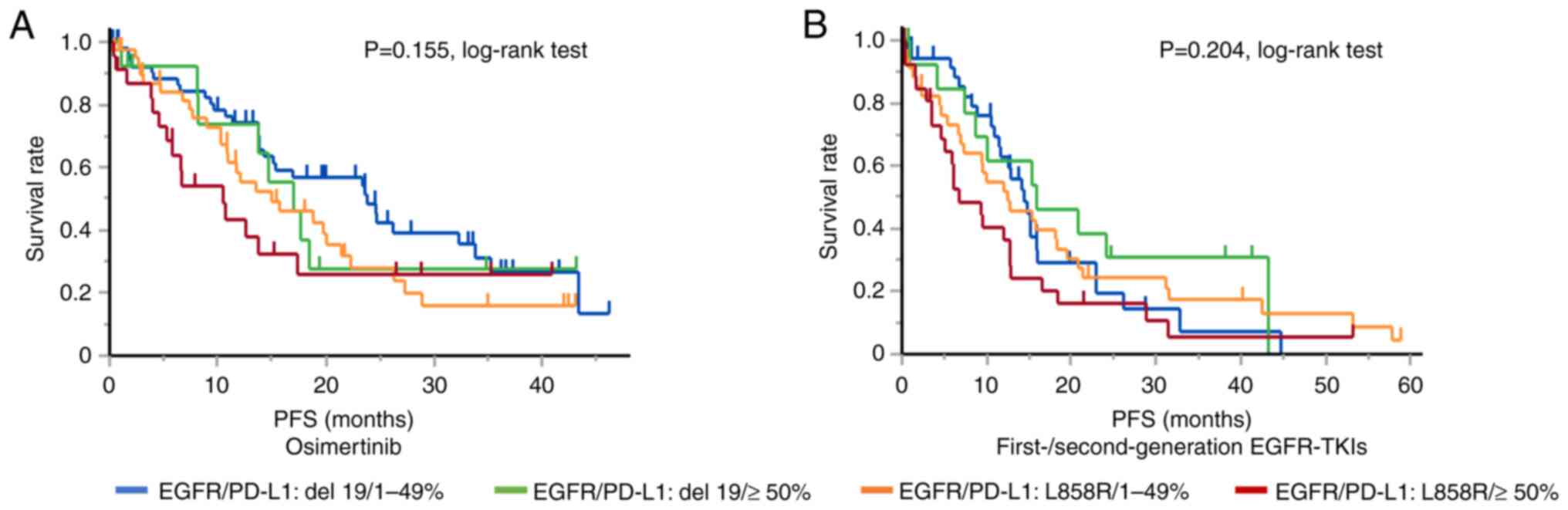
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mitsudomi T, Morita S, Yatabe Y, Negoro S,
Okamoto I, Tsurutani J, Seto T, Satouchi M, Tada H, Hirashima T, et
al: Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal
growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase
3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 11:121–128. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Maemondo M, Inoue A, Kobayashi K, Sugawara
S, Oizumi S, Isobe H, Gemma A, Harada M, Yoshizawa H, Kinoshita I,
et al: Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer
with mutated EGFR. N Engl J Med. 362:2380–2388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang JCH, Wu YL, Schuler M, Sebastian M,
Popat S, Yamamoto N, Zhou C, Hu CP, O'Byrne K, Feng J, et al:
Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR
mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6):
Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3
trials. Lancet Oncol. 16:141–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Takano T, Fukui T, Ohe Y, Tsuta K,
Yamamoto S, Nokihara H, Yamamoto N, Sekine I, Kunitoh H, Furuta K
and Tamura T: EGFR mutations predict survival benefit from
gefitinib in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: A
historical comparison of patients treated before and after
gefitinib approval in Japan. J Clin Oncol. 26:5589–5595. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim
HR, Ramalingam SS, Shepherd FA, He Y, Akamatsu H, Theelen WS, et
al: Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:629–640. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kosaka T, Yatabe Y, Endoh H, Yoshida K,
Hida T, Tsuboi M, Tada H, Kuwano H and Mitsudomi T: Analysis of
epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutation in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer and acquired resistance to gefitinib.
Clin Cancer Res. 12:5764–5769. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J,
Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura
F, Nogami N, Kurata T, et al: Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:113–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard
D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y,
Chewaskulyong B, et al: Overall survival with osimertinib in
untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 382:41–50.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pardoll DM: The blockade of immune
checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:252–264.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Inomata M, Azechi K, Takata N, Hayashi K,
Tokui K, Taka C, Okazawa S, Kambara K, Imanishi S, Miwa T, et al:
Association of tumor PD-L1 expression with the T790M mutation and
progression-free survival in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small
cell lung cancer receiving EGFR-TKI therapy. Diagnostics (Basel).
10:10062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yoon BW, Chang B and Lee SH: High PD-L1
expression is associated with unfavorable clinical outcome in
EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinomas treated with targeted therapy.
Onco Targets Ther. 13:8273–8285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang CY, Liao WY, Ho CC, Chen KY, Tsai TH,
Hsu CL, Su KY, Chang YL, Wu CT, Hsu CC, et al: Association between
programmed death-ligand 1 expression, immune microenvironments, and
clinical outcomes in epidermal growth factor receptor mutant lung
adenocarcinoma patients treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Eur J Cancer. 124:110–122. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lan B, Wang Y, Wu J, Wang K and Wang P:
The predictive and prognostic effects of PD-L1 expression on TKI
treatment and survival of EGFR-mutant NSCLC: A meta-analysis.
Medicine (Baltimore). 100:e270382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Peng Z, Lin H, Zhou K, Deng S and Mei J:
Predictive value of pretreatment PD-L1 expression in EGFR-mutant
non-small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol.
19:1452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshimura A, Yamada T, Okuma Y, Fukuda A,
Watanabe S, Nishioka N, Takeda T, Chihara Y, Takemoto S, Harada T,
et al: Impact of tumor programmed death ligand-1 expression on
osimertinib efficacy in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small
cell lung cancer: A prospective observational study. Transl Lung
Cancer Res. 10:3582–3593. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakata Y, Sakata S, Oya Y, Tamiya M,
Suzuki H, Shibaki R, Okada A, Kobe H, Matsumoto H, Yokoi T, et al:
Osimertinib as first-line treatment for advanced epidermal growth
factor receptor mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer in a
real-world setting (OSI-FACT). Eur J Cancer. 159:144–153. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shiozawa T, Numata T, Tamura T, Endo T,
Kaburagi T, Yamamoto Y, Yamada H, Kikuchi N, Saito K, Inagaki M, et
al: Prognostic implication of PD-L1 expression on osimertinib
treatment for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer
Res. 42:2583–2590. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hsu KH, Tseng JS, Yang TY, Chen KC, Su KY,
Yu SL, Chen JJW, Huang YH and Chang GC: PD-L1 strong expressions
affect the clinical outcomes of osimertinib in treatment naïve
advanced EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer patients. Sci Rep.
12:97532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Inomata M, Matsumoto M, Mizushima I, Seto
Z, Hayashi K, Tokui K, Taka C, Okazawa S, Kambara K, Imanishi S, et
al: Association of tumor PD-L1 expression with time on treatment
using EGFR-TKIs in patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung
cancer. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2:324–329. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saito H, Fukuhara T, Furuya N, Watanabe K,
Sugawara S, Iwasawa S, Tsunezuka Y, Yamaguchi O, Okada M, Yoshimori
K, et al: Erlotinib plus bevacizumab versus erlotinib alone in
patients with EGFR-positive advanced non-squamous non-small-cell
lung cancer (NEJ026): Interim analysis of an open-label,
randomised, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:625–635.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakagawa K, Garon EB, Seto T, Nishio M,
Ponce Aix S, Paz-Ares L, Chiu CH, Park K, Novello S, Nadal E, et
al: Ramucirumab plus erlotinib in patients with untreated,
EGFR-mutated, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (RELAY): A
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 20:1655–1669. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hosomi Y, Morita S, Sugawara S, Kato T,
Fukuhara T, Gemma A, Takahashi K, Fujita Y, Harada T, Minato K, et
al: Gefitinib alone versus gefitinib plus chemotherapy for
non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated epidermal growth factor
receptor: NEJ009 study. J Clin Oncol. 38:115–123. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miyauchi E, Morita S, Nakamura A, Hosomi
Y, Watanabe K, Ikeda S, Seike M, Fujita Y, Minato K, Ko R, et al:
Updated analysis of NEJ009: Gefitinib-Alone versus gefitinib plus
chemotherapy for non-small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. J
Clin Oncol. 40:3587–3592. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ito K, Morise M, Wakuda K, Hataji O,
Shimokawaji T, Takahashi K, Furuya N, Takeyama Y, Goto Y, Abe T, et
al: A multicenter cohort study of osimertinib compared with
afatinib as first-line treatment for EGFR-mutated non-small-cell
lung cancer from practical dataset: CJLSG1903. ESMO Open.
6:1001152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li H, Takayama K, Wang S, Shiraishi Y,
Gotanda K, Harada T, Furuyama K, Iwama E, Ieiri I, Okamoto I and
Nakanishi Y: Addition of bevacizumab enhances antitumor activity of
erlotinib against non-small cell lung cancer xenografts depending
on VEGF expression. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 74:1297–1305. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang M, Wisniewski CA, Xiong C, Chhoy P,
Goel HL, Kumar A, Zhu LJ, Li R, St Louis PA, Ferreira LM, et al:
Therapeutic blocking of VEGF binding to neuropilin-2 diminishes
PD-L1 expression to activate antitumor immunity in prostate cancer.
Sci Transl Med. 15:eade58552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao Y, Liu J, Cai X, Pan Z, Liu J, Yin W,
Chen H, Xie Z, Liang H, Wang W, et al: Efficacy and safety of first
line treatments for patients with advanced epidermal growth factor
receptor mutated, non-small cell lung cancer: Systematic review and
network meta-analysis. BMJ. 367:l54602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maemondo M: Potential of combination
therapy in EGFR mutated lung cancer. Ann Transl Med. 8:5182020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Moore S and Wheatley-Price P: EGFR
combination therapy should become the new standard first-line
treatment in advanced EGFR-mutant NSCLC. J Thorac Oncol.
16:1788–1792. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim EY, Cho EN, Park HS, Hong JY, Lim S,
Youn JP, Hwang SY and Chang YS: Compound EGFR mutation is
frequently detected with co-mutations of actionable genes and
associated with poor clinical outcome in lung adenocarcinoma.
Cancer Biol Ther. 17:237–245. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taniguchi H, Yamada T, Wang R, Tanimura K,
Adachi Y, Nishiyama A, Tanimoto A, Takeuchi S, Araujo LH, Boroni M,
et al: AXL confers intrinsic resistance to osimertinib and advances
the emergence of tolerant cells. Nat Commun. 10:2592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshimura A, Yamada T, Serizawa M, Uehara
H, Tanimura K, Okuma Y, Fukuda A, Watanabe S, Nishioka N, Takeda T,
et al: High levels of AXL expression in untreated EGFR-mutated
non-small cell lung cancer negatively impacts the use of
osimertinib. Cancer Sci. 114:606–618. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsukita Y, Fujino N, Miyauchi E, Saito R,
Fujishima F, Itakura K, Kyogoku Y, Okutomo K, Yamada M, Okazaki T,
et al: Axl kinase drives immune checkpoint and chemokine signalling
pathways in lung adenocarcinomas. Mol Cancer. 18:242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee JE, Park HS, Lee D, Yoo G, Kim T, Jeon
H, Yeo MK, Lee CS, Moon JY, Jung SS, et al: Hippo pathway effector
YAP inhibition restores the sensitivity of EGFR-TKI in lung
adenocarcinoma having primary or acquired EGFR-TKI resistance.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:154–160. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
McGowan M, Kleinberg L, Halvorsen AR,
Helland Å and Brustugun OT: NSCLC depend upon YAP expression and
nuclear localization after acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors.
Genes Cancer. 8:497–504. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kohsaka S, Nagano M, Ueno T, Suehara Y,
Hayashi T, Shimada N, Takahashi K, Suzuki K, Takamochi K, Takahashi
F and Mano H: A method of high-throughput functional evaluation of
EGFR gene variants of unknown significance in cancer. Sci Transl
Med. 9:eaan65662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nanjo S, Wu W, Karachaliou N, Blakely CM,
Suzuki J, Chou YT, Ali SM, Kerr DL, Olivas VR, Shue J, et al:
Deficiency of the splicing factor RBM10 limits EGFR inhibitor
response in EGFR-mutant lung cancer. J Clin Invest.
132:e1450992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|