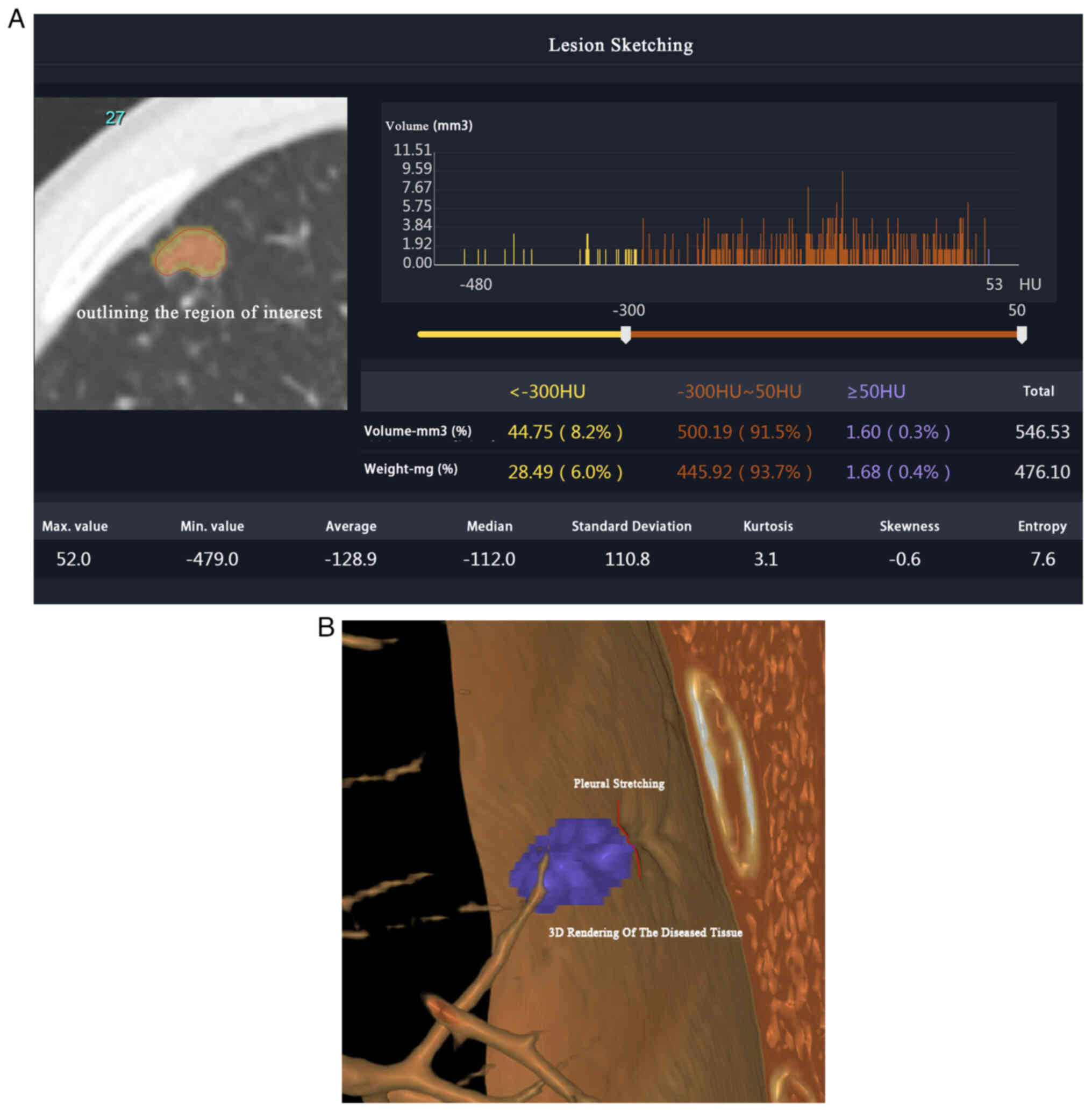
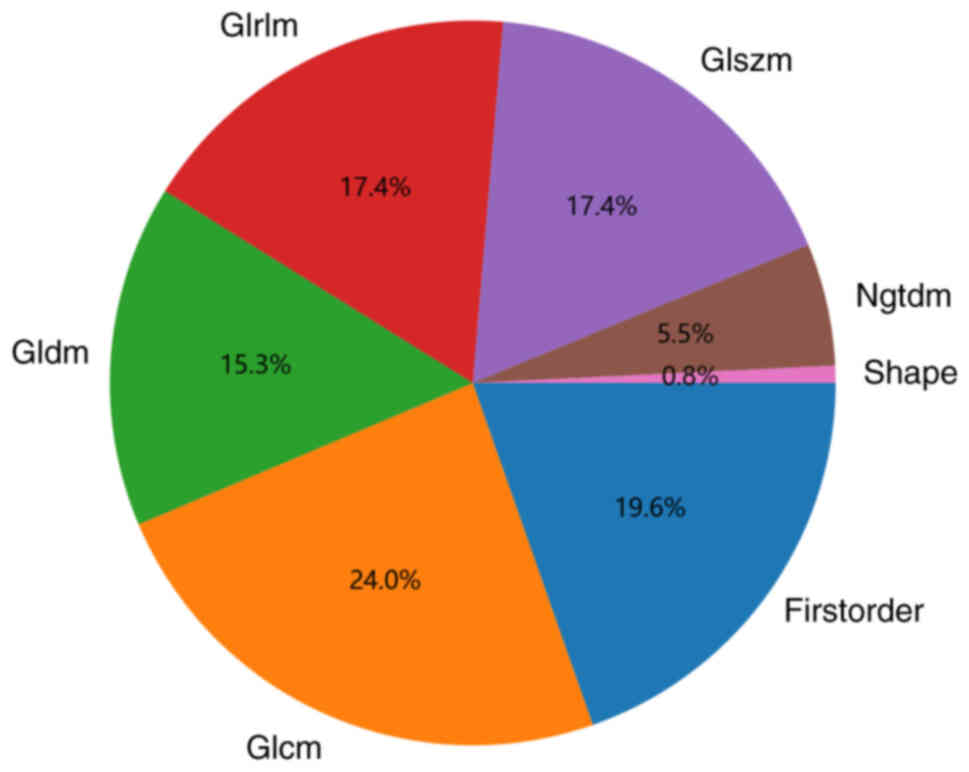
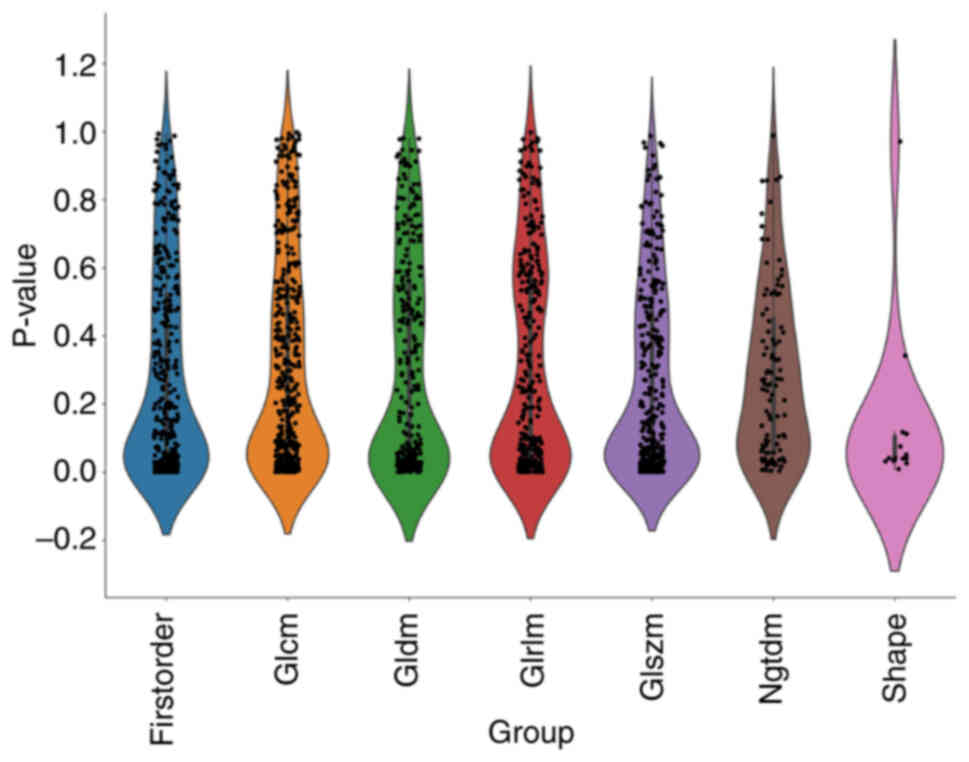
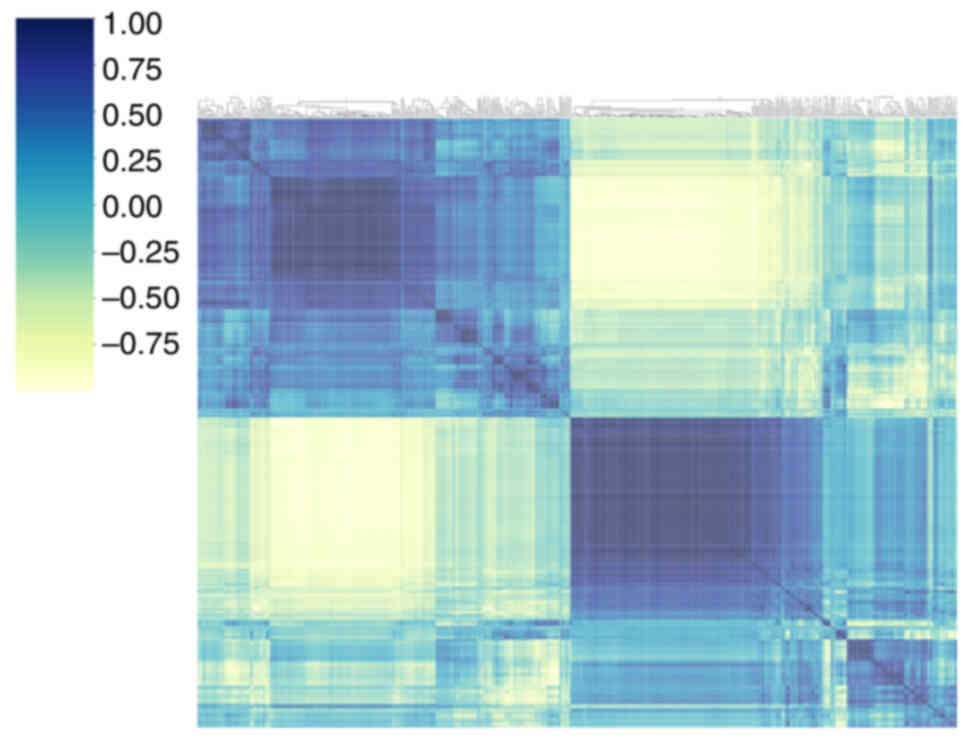
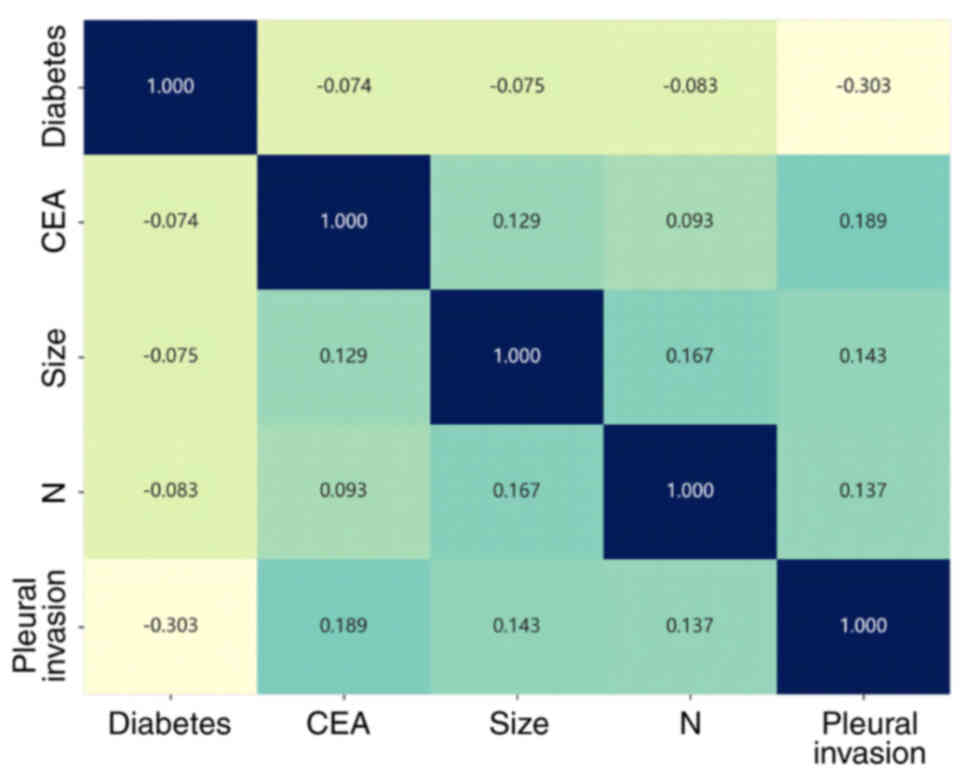
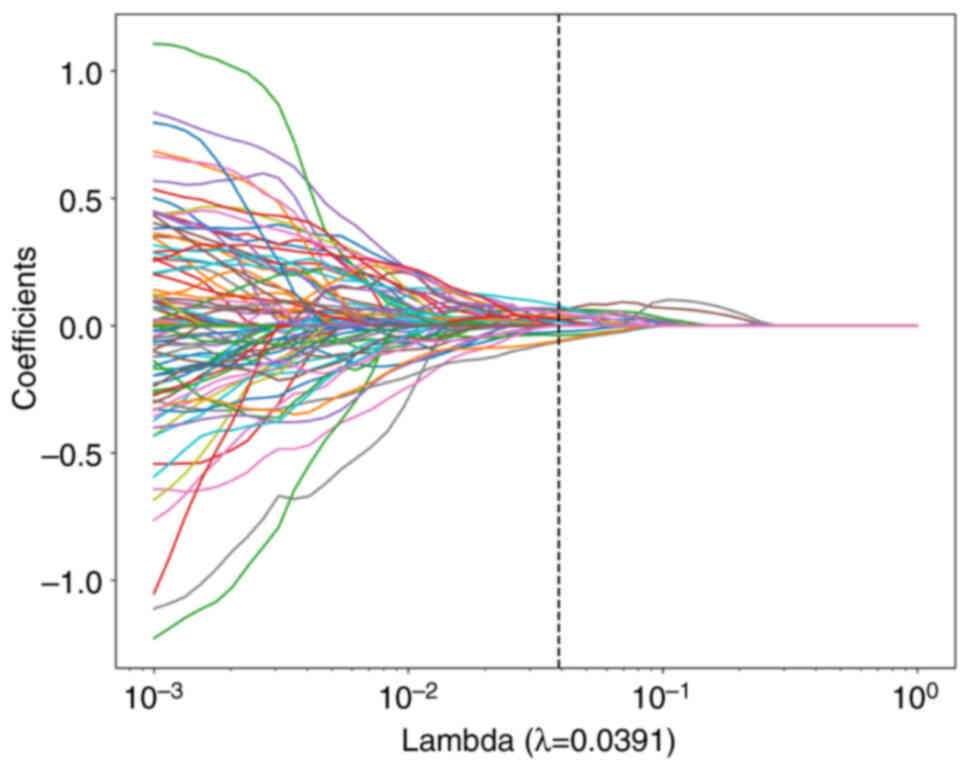
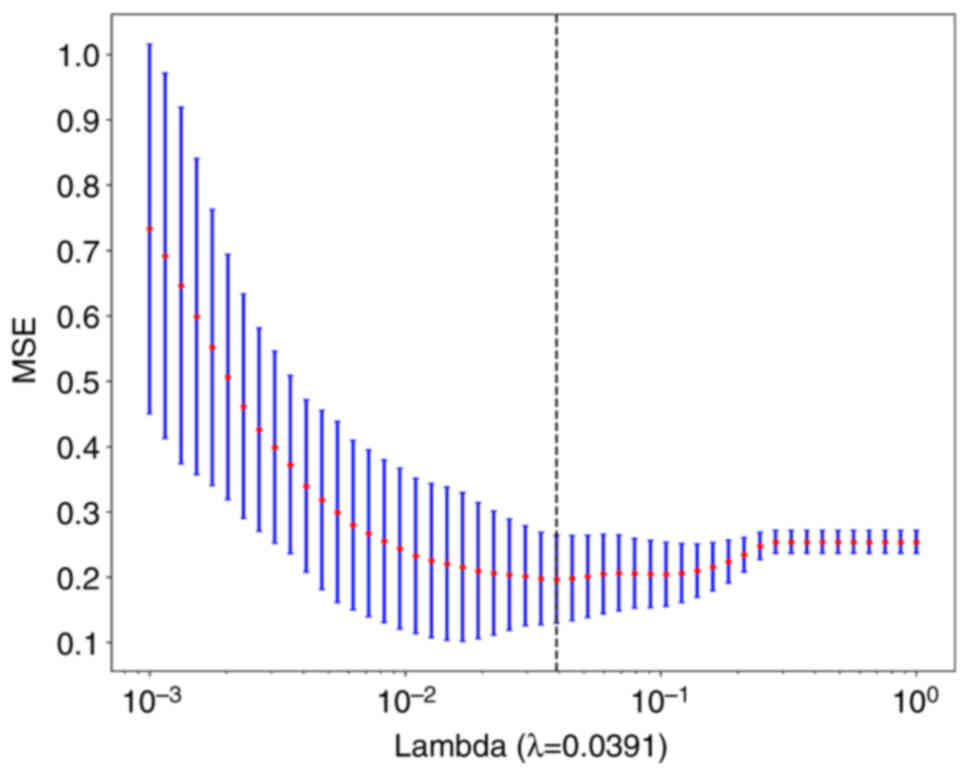
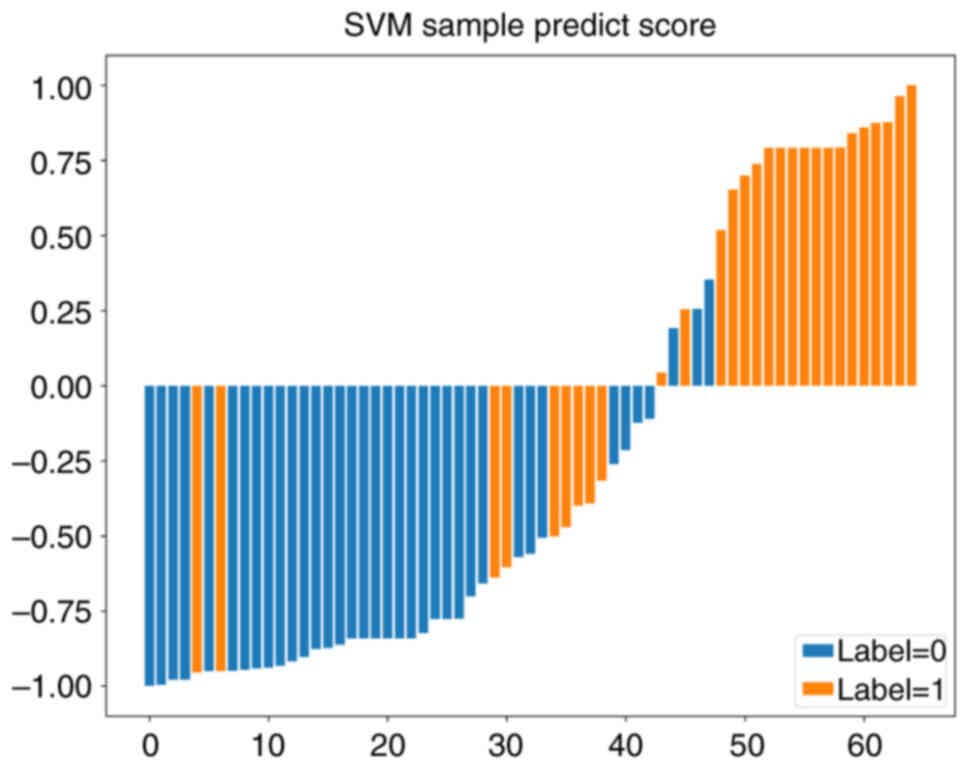
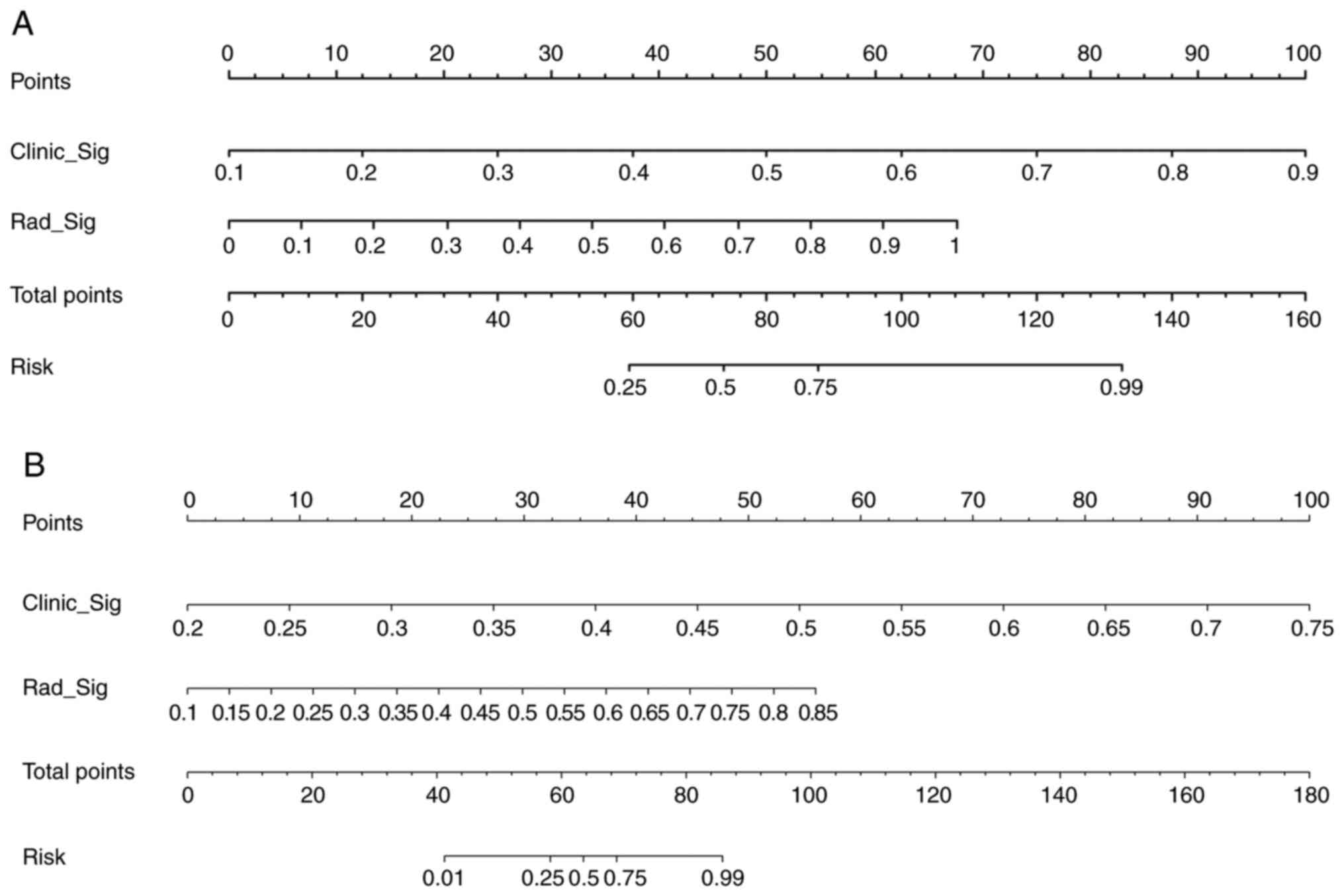
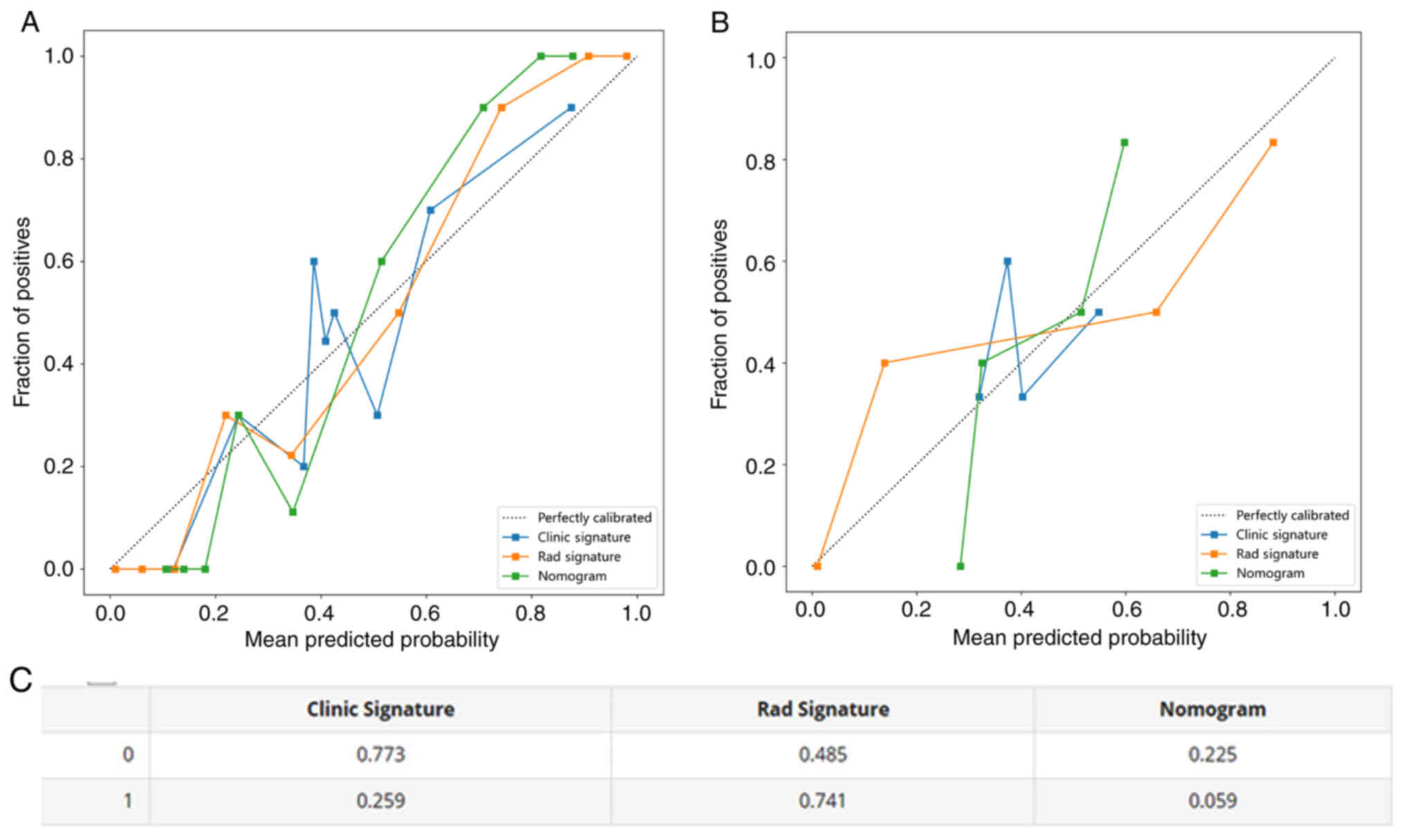
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goldstraw P, Chansky K, Crowley J,
Rami-Porta R, Asamura H, Eberhardt WE, Nicholson AG, Groome P,
Mitchell A, Bolejack V, et al: The IASLC lung cancer staging
project: Proposals for revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the
Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM classification for lung
cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 11:39–51. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mizuno T, Arimura T, Kuroda H, Sakakura N,
Yatabe Y and Sakao Y: P2.16-34 visceral pleural invasion is closely
associated with nodal spread in cStage IA lung adenocarcinoma. J
Thorac Oncol. 13:S8452018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hwang JH, Song KS, Park SI, Lim TH, Kwon
KH and Goo DE: Subtle pleural metastasis without large effusion in
lung cancer patients: Preoperative detection on CT. Korean J
Radiol. 6:94–101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ahn SY, Park CM, Jeon YK, Kim H, Lee JH,
Hwang EJ and Goo JM: Predictive CT features of visceral pleural
invasion by T1-Sized peripheral pulmonary adenocarcinomas
manifesting as subsolid nodules. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 209:561–566.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takizawa H, Kondo K, Kawakita N, Tsuboi M,
Toba H, Kajiura K, Kawakami Y, Sakiyama S, Tangoku A, Morishita A,
et al: Autofluorescence for the diagnosis of visceral pleural
invasion in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
53:987–992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube
SE, Gion M and Clark GM; Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC
Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics, : Reporting recommendations
for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Nat Clin Pract Urol.
2:416–422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, Smith
RG, Ho S, Gee JC and Gerig G: User-guided 3D active contour
segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved
efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage. 31:1116–1128. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung G, Hwang HS, Jang SJ and Ro JY: Are
elastic stain and specialty sign out necessary to evaluate pleural
invasion in lung cancers? Ann Diagn Pathol. 16:250–254. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hsu JS, Han IT, Tsai TH, Lin SF, Jaw TS,
Liu GC, Chou SH, Chong IW and Chen CY: Pleural tags on CT scans to
predict visceral pleural invasion of non-small cell lung cancer
that does not abut the pleura. Radiology. 279:590–596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Imai K, Minamiya Y, Ishiyama K, Hashimoto
M, Saito H, Motoyama S, Sato Y and Ogawa J: Use of CT to evaluate
pleural invasion in non-small cell lung cancer: Measurement of the
ratio of the interface between tumor and neighboring structures to
maximum tumor diameter. Radiology. 267:619–626. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang S, Yang L, Teng L, Zhang S, Cui Y,
Cao Y and Shi H: Visceral pleural invasion by pulmonary
adenocarcinoma ≤3 cm: The pathological correlation with pleural
signs on computed tomography. J Thorac Dis. 10:3992–3999. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Travis WD, Brambilla E, Rami-Porta R,
Vallières E, Tsuboi M, Rusch V and Goldstraw P; International
Staging Committee. Visceral pleural invasion, : Pathologic criteria
and use of elastic stains: Proposal for the 7th edition of the TNM
classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 3:1384–1390. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang T, Zhou C and Zhou Q: Extent of
visceral pleural invasion affects prognosis of resected non-small
cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 7:15272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang RB, Li P, Li BT, Jin JT, Rusch VW,
Jones DR, Wu YL, Liu Q, Yang J, Yang MZ, et al: Modification of
pathologic T classification for non-small cell lung cancer with
visceral pleural invasion: Data from 1,055 cases of cancers ≤3 cm.
Chest. 160:754–764. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao Q, Wang JW, Yang L, Xue LY and Lu WW:
CT diagnosis of pleural and stromal invasion in malignant
subpleural pure ground-glass nodules: An exploratory study. Eur
Radiol. 29:279–286. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zuo Z, Li Y, Peng K, Li X, Tan Q, Mo Y,
Lan Y, Zeng W and Qi W: CT texture analysis-based nomogram for the
preoperative prediction of visceral pleural invasion in cT1N0M0
lung adenocarcinoma: An external validation cohort study. Clin
Radiol. 77:e215–e221. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Iizuka S, Kawase A, Oiwa H, Ema T, Shiiya
N and Funai K: A risk scoring system for predicting visceral
pleural invasion in non-small lung cancer patients. Gen Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 67:876–879. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim H, Goo JM, Kim YT and Park CM:
CT-defined visceral pleural invasion in T1 lung adenocarcinoma:
Lack of relationship to disease-free survival. Radiology.
292:741–749. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi H, Kim H, Hong W, Park J, Hwang EJ,
Park CM, Kim YT and Goo JM: Prediction of visceral pleural invasion
in lung cancer on CT: Deep learning model achieves a
radiologist-level performance with adaptive sensitivity and
specificity to clinical needs. Eur Radiol. 31:2866–2876. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klinkenberg TJ, Dinjens L, Wolf RFE, van
der Wekken AJ, van de Wauwer C, de Bock GH, Timens W, Mariani MA
and Groen HJM: CT-guided percutaneous hookwire localization
increases the efficacy and safety of VATS for pulmonary nodules. J
Surg Oncol. 115:898–904. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|