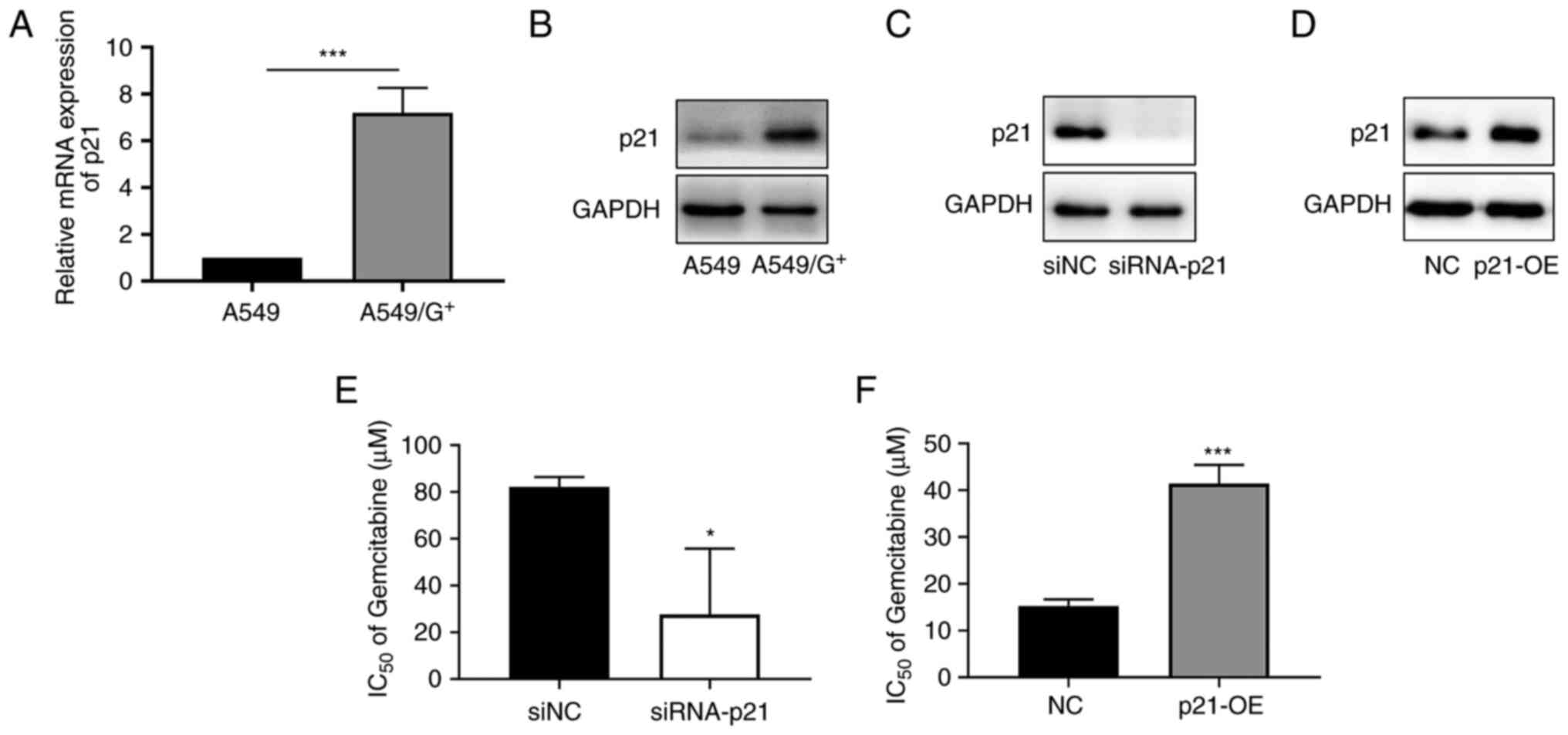
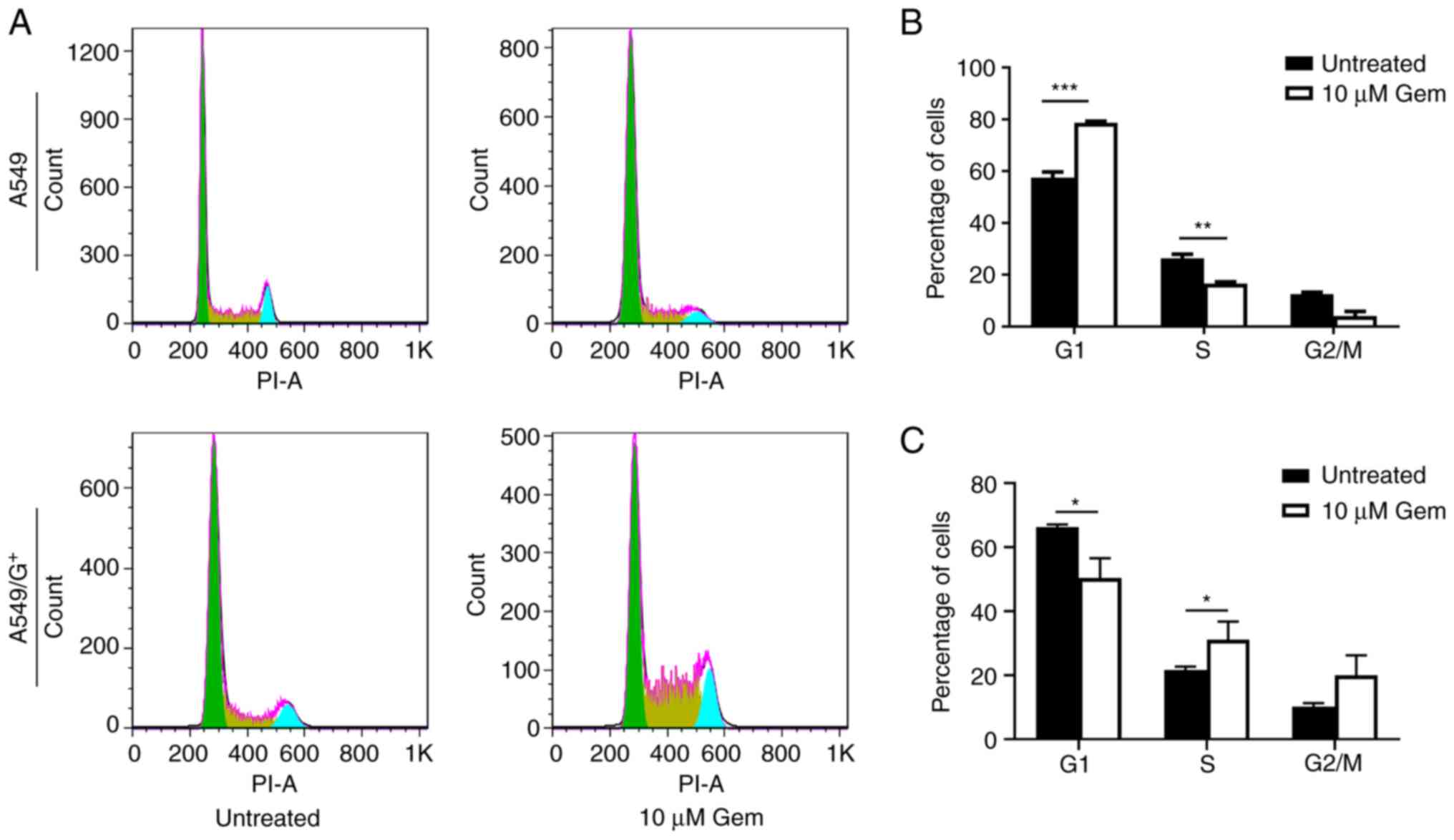
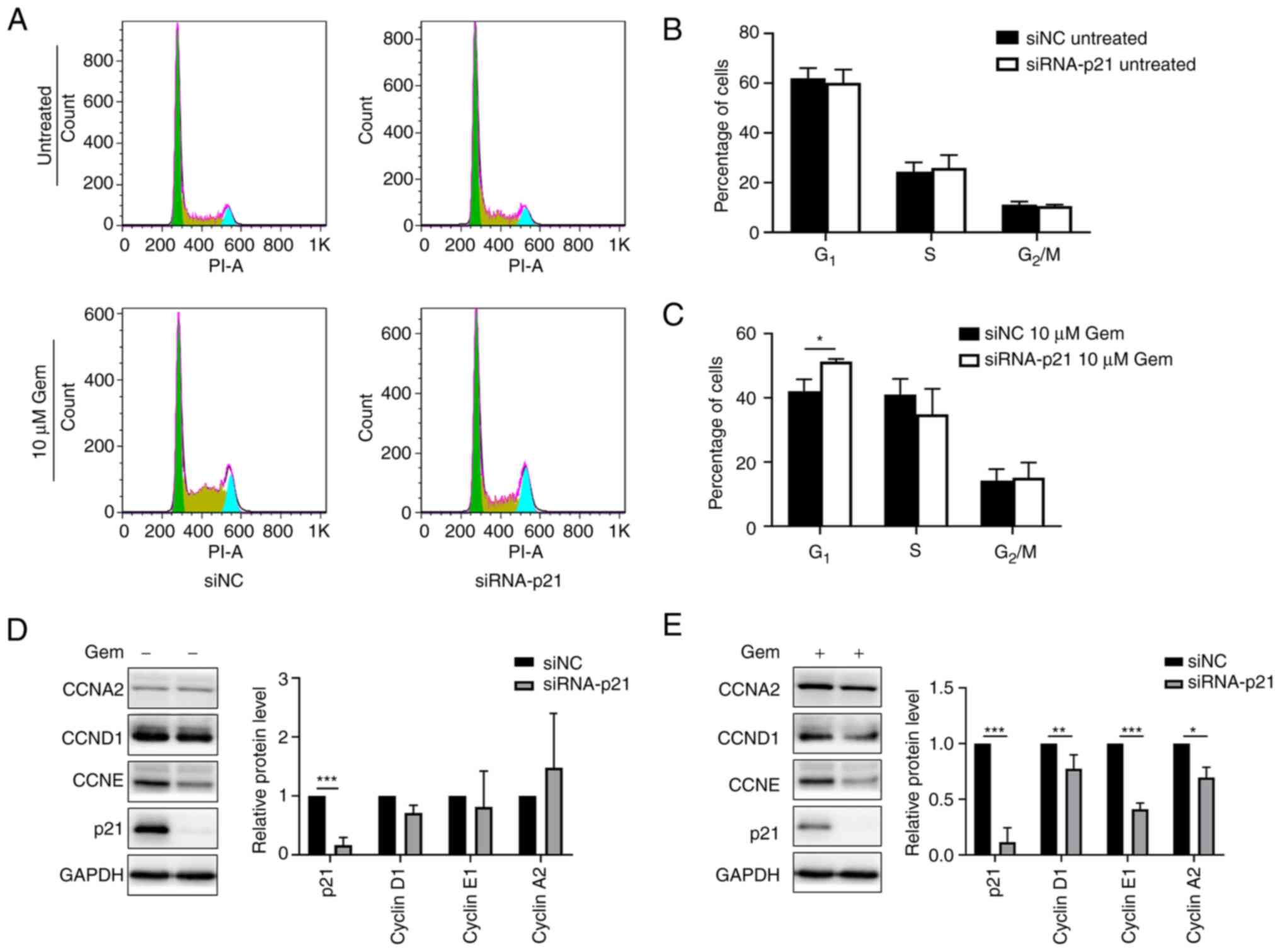
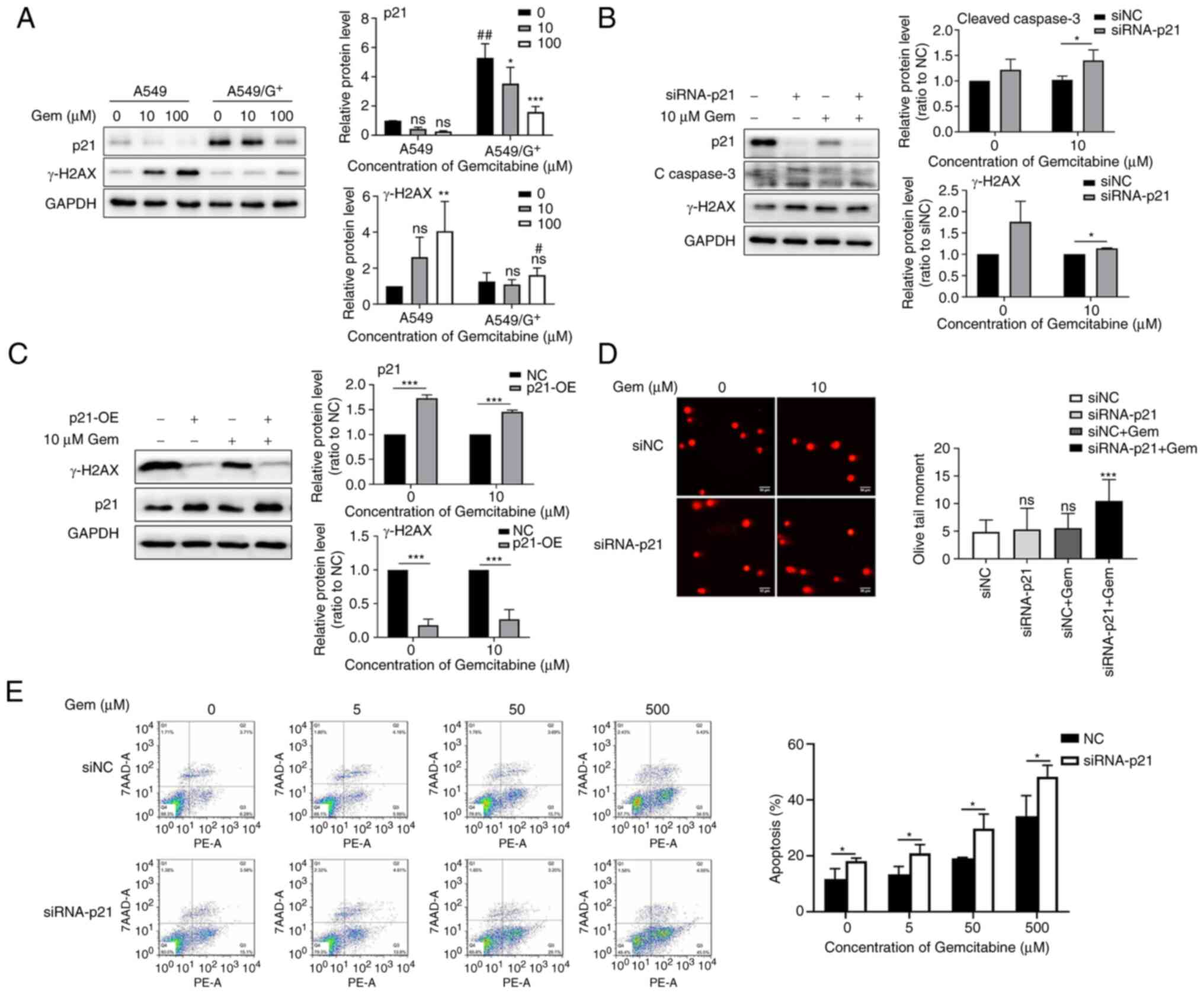
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
He L, Luo L, Zhu H, Yang H, Zhang Y, Wu H,
Sun H, Jiang F, Kathera CS, Liu L, et al: FEN1 promotes tumor
progression and confers cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung
cancer. Mol Oncol. 11:640–654. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang X, Wang D, Li Z, Jiao D, Jin L, Cong
J, Zheng X and Xu L: Low-Dose gemcitabine treatment enhances
immunogenicity and natural killer cell-driven tumor immunity in
lung cancer. Front Immunol. 11:3312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Toschi L, Finocchiaro G, Bartolini S,
Gioia V and Cappuzzo F: Role of gemcitabine in cancer therapy.
Future Oncol. 1:7–17. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mini E, Nobili S, Caciagli B, Landini I
and Mazzei T: Cellular pharmacology of gemcitabine. Ann Oncol. 17
(Suppl 5):v7–v12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li Y, Wang LR, Chen J, Lou Y and Zhang GB:
First-line gemcitabine plus cisplatin in nonsmall cell lung cancer
patients. Dis Markers. 2014:9604582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones RM, Kotsantis P, Stewart GS, Groth P
and Petermann E: BRCA2 and RAD51 promote double-strand break
formation and cell death in response to gemcitabine. Mol Cancer
Ther. 13:2412–2421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Sousa Cavalcante L and Monteiro G:
Gemcitabine: Metabolism and molecular mechanisms of action,
sensitivity and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Eur J
Pharmacol. 741:8–16. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu JS, Yeh CA, Huang IC, Huang GY, Chiu
CH, Mahalakshmi B, Wen SY, Huang CY and Kuo WW: Signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 mediates apoptosis inhibition
through reducing mitochondrial ROS and activating Bcl-2 in
gemcitabine-resistant lung cancer A549 cells. J Cell Physiol.
236:3896–3905. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deng T, Yan G, Song X, Xie L, Zhou Y, Li
J, Hu X, Li Z, Hu J, Zhang Y, et al: Deubiquitylation and
stabilization of p21 by USP11 is critical for cell-cycle
progression and DNA damage responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:4678–4683. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zlotorynski E: Cancer biology: The dark
side of p21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 17:4612016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Warfel NA and El-Deiry WS: p21WAF1 and
tumourigenesis: 20 years after. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:52–58. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Georgakilas AG, Martin OA and Bonner WM:
p21: A two-faced genome guardian. Trends Mol Med. 23:310–319. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang H, Zhu LJ, Yang YC, Wang ZX and Wang
R: MiR-224 promotes the chemoresistance of human lung
adenocarcinoma cells to cisplatin via regulating G1/S
transition and apoptosis by targeting p21WAF1/CIP1. Br J
Cancer. 111:339–354. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, Liu J, Zhang M, Wu W,
De W, Wang Z and Wang R: The long noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes
to cisplatin resistance of human lung adenocarcinoma cells via
downregualtion of p21(WAF1/CIP1) expression. PLoS One.
8:e772932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao J, Fu W, Liao H, Dai L, Jiang Z, Pan
Y, Huang H, Mo Y, Li S, Yang G and Yin J: The regulatory and
predictive functions of miR-17 and miR-92 families on cisplatin
resistance of non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 15:7312015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo Q, Lan F, Yan X, Xiao Z, Wu Y and
Zhang Q: Hypoxia exposure induced cisplatin resistance partially
via activating p53 and hypoxia inducible factor-1α in non-small
cell lung cancer A549 cells. Oncol Lett. 16:801–808.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liang AL, Du SL, Zhang B, Zhang J, Ma X,
Wu CY and Liu YJ: Screening miRNAs associated with resistance
gemcitabine from exosomes in A549 lung cancer cells. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:6311–6321. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma X, Fu T, Ke ZY, Du SL, Wang XC, Zhou N,
Zhong MY, Liu YJ and Liang AL: MiR-17-5p/RRM2 regulated gemcitabine
resistance in lung cancer A549 cells. Cell Cycle. 22:1367–1379.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Galanos P, Vougas K, Walter D, Polyzos A,
Maya-Mendoza A, Haagensen EJ, Kokkalis A, Roumelioti FM, Gagos S,
Tzetis M, et al: Chronic p53-independent p21 expression causes
genomic instability by deregulating replication licensing. Nat Cell
Biol. 18:777–789. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zohny SF, Al-Malki AL, Zamzami MA and
Choudhry H: p21Waf1/Cip1: Its paradoxical effect in the
regulation of breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 26:131–137. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zamagni A, Pasini A, Pirini F, Ravaioli S,
Giordano E, Tesei A, Calistri D, Ulivi P, Fabbri F, Foca F, et al:
CDKN1A upregulation and cisplatin-pemetrexed resistance in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 56:1574–1584.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ewald B, Sampath D and Plunkett W: H2AX
phosphorylation marks gemcitabine-induced stalled replication forks
and their collapse upon S-phase checkpoint abrogation. Mol Cancer
Ther. 6:1239–1248. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Price JG, Idoyaga J, Salmon H, Hogstad B,
Bigarella CL, Ghaffari S, Leboeuf M and Merad M: CDKN1A regulates
Langerhans cell survival and promotes Treg cell generation upon
exposure to ionizing irradiation. Nat Immunol. 16:1060–1068. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Karimian A, Ahmadi Y and Yousefi B:
Multiple functions of p21 in cell cycle, apoptosis and
transcriptional regulation after DNA damage. DNA Repair (Amst).
42:63–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jana S, Patra K, Jana J, Mandal DP and
Bhattacharjee S: Nrf-2 transcriptionally activates
P21Cip/WAF1 and promotes A549cell survival against
oxidative stress induced by H2O2. Chem Biol
Interact. 285:59–68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia X, Ma Q, Li X, Ji T, Chen P, Xu H, Li
K, Fang Y, Weng D, Weng Y, et al: Cytoplasmic p21 is a potential
predictor for cisplatin sensitivity in ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer.
11:3992011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Koster R, di Pietro A, Timmer-Bosscha H,
Gibcus JH, van den Berg A, Suurmeijer AJ, Bischoff R, Gietema JA
and de Jong S: Cytoplasmic p21 expression levels determine
cisplatin resistance in human testicular cancer. J Clin Invest.
120:3594–3605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maiuthed A, Ninsontia C, Erlenbach-Wuensch
K, Ndreshkjana B, Muenzner JK, Caliskan A, Husayn AP, Chaotham C,
Hartmann A, Vial Roehe A, et al: Cytoplasmic p21 mediates
5-fluorouracil resistance by inhibiting pro-apoptotic Chk2. Cancers
(Basel). 10:3732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao WS, Yan WP, Chen DB, Dai L, Yang YB,
Kang XZ, Fu H, Chen P, Deng KJ, Wang XY, et al: Genome-scale CRISPR
activation screening identifies a role of ELAVL2-CDKN1A axis in
paclitaxel resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J
Cancer Res. 9:1183–1200. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ikeda R, Vermeulen LC, Lau E, Jiang Z,
Sachidanandam K, Yamada K and Kolesar JM: Isolation and
characterization of gemcitabine-resistant human non-small cell lung
cancer A549 cells. Int J Oncol. 38:513–519. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gaben AM, Saucier C, Bedin M, Barbu V and
Mester J: Rapamycin inhibits cdk4 activation, p 21(WAF1/CIP1)
expression and G1-phase progression in transformed mouse
fibroblasts. Int J Cancer. 108:200–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dijk SN, Protasoni M, Elpidorou M, Kroon
AM and Taanman JW: Mitochondria as target to inhibit proliferation
and induce apoptosis of cancer cells: The effects of doxycycline
and gemcitabine. Sci Rep. 10:43632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Santarelli R, Pompili C, Gilardini Montani
MS, Romeo MA, Gonnella R, D'Orazi G and Cirone M: Lovastatin
reduces PEL cell survival by phosphorylating ERK1/2 that blocks the
autophagic flux and engages a cross-talk with p53 to activate p21.
IUBMB Life. 73:968–977. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tay VSY, Devaraj S, Koh T, Ke G, Crasta KC
and Ali Y: Increased double strand breaks in diabetic β-cells with
a p21 response that limits apoptosis. Sci Rep. 9:193412019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wettersten HI, Hee Hwang S, Li C, Li C,
Shiu EY, Wecksler AT, Hammock BD and Weiss RH: A novel p21
attenuator which is structurally related to sorafenib. Cancer Biol
Ther. 14:278–285. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yan G, Dawood M, Böckers M, Klauck SM,
Fottner C, Weber MM and Efferth T: Multiple modes of cell death in
neuroendocrine tumors induced by artesunate. Phytomedicine.
79:1533322020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Minagawa Y, Ishino K, Wada R, Kudo M,
Naito Z, Takeshita T and Ohashi R: High Expression of p21 as a
potential therapeutic target in ovarian clear-cell carcinoma.
Anticancer Res. 40:5631–5639. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|