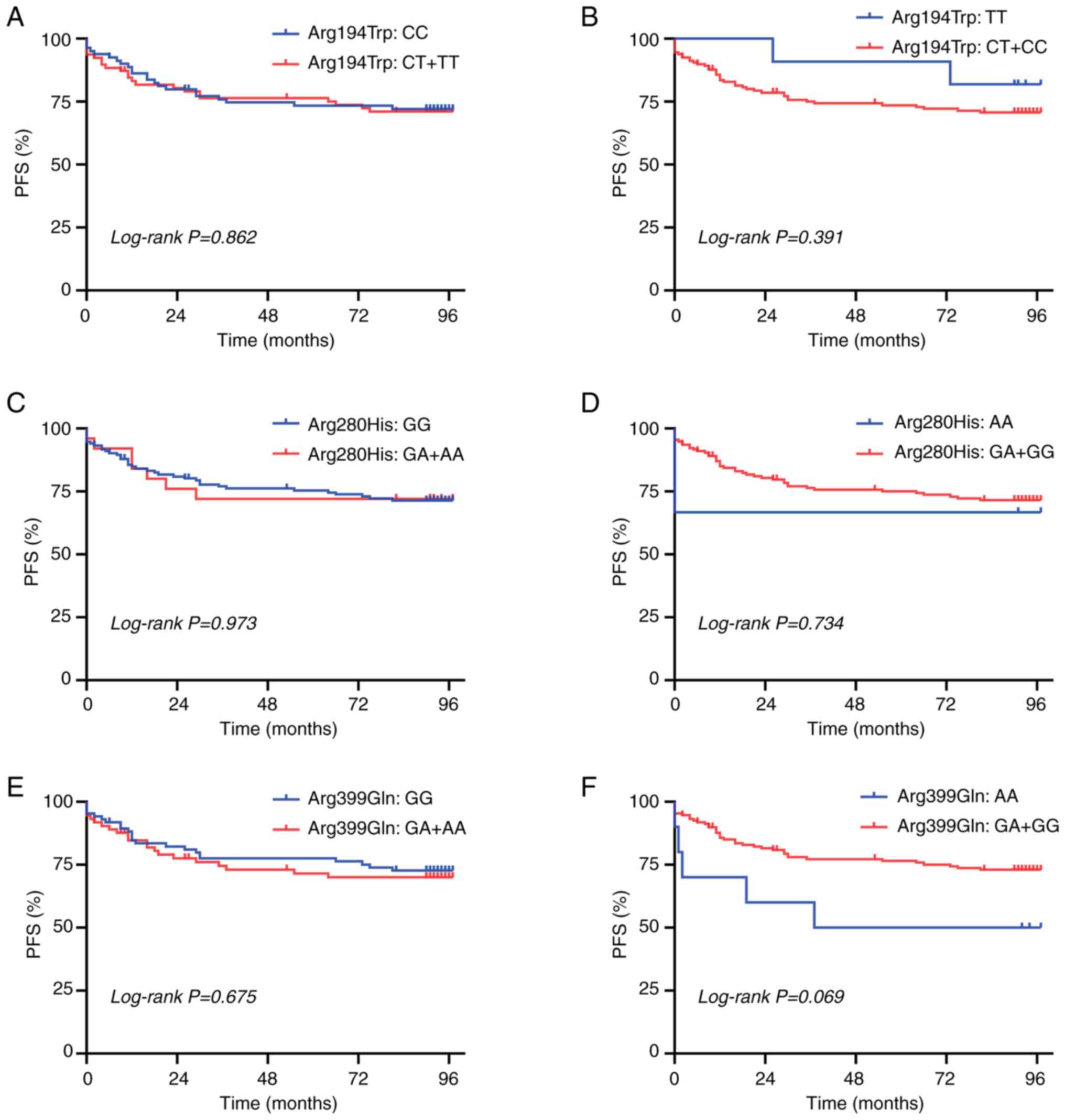
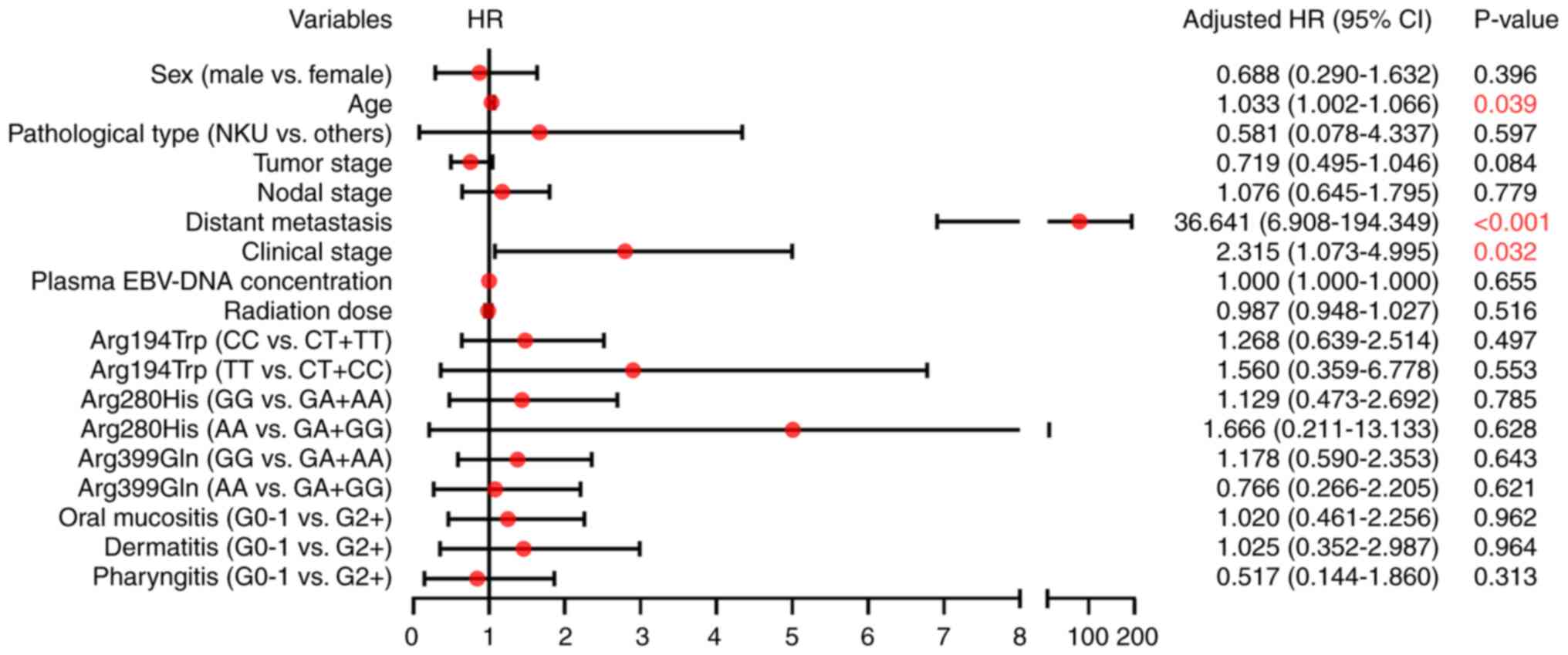
|
1
|
World Health Organization:
4-Nasopharynx-fact-sheet. Global Cancer Observatory. 2020.
|
|
2
|
Lee AW, Ma BB, Ng WT and Chan AT:
Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future
perspective. J Clin Oncol. 33:3356–3364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun
Y and Ma J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 394:64–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma Z, Umezawa R, Yamamoto T, Ishikawa Y,
Takahashi N, Takeda K, Suzuki Y, Tang L, Ito K, Kadoya N and Jingu
K: IMRT improves local control in patients with NPC compared with
conventional radiotherapy: Propensity score-matched analysis. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 51:1444–1451. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yeh SA, Hwang TZ, Wang CC, Yang CC, Lien
CF, Wang CC, Hsu TY, Hsu RF, Shih YC, Huang YC, et al: Outcomes of
patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with
intensity-modulated radiotherapy. J Radiat Res. 62:438–447. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen L, Zhang Y, Lai SZ, Li WF, Hu WH, Sun
R, Liu LZ, Zhang F, Peng H, Du XJ, et al: 10-Year results of
therapeutic ratio by Intensity-Modulated radiotherapy versus
Two-Dimensional radiotherapy in patients with Nasopharyngeal
Carcinoma. Oncologist. 24:e38–e45. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kouloulias V, Thalassinou S, Platoni K,
Zygogianni A, Kouvaris J, Antypas C, Efstathopoulos E and Nikolaos
K: The treatment outcome and radiation-induced toxicity for
patients with head and neck carcinoma in the IMRT era: A systematic
review with dosimetric and clinical parameters. Biomed Res Int.
2013:4012612013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yao Z and Cheng B: Morbidity in patients
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma and Radiation-induced skin lesions:
Cause, risk factors, and dermatitis evolution and severity. Adv
Skin Wound Care. 34:1–8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bossi P, Cossu Rocca M, Corvo R, Depenni
R, Guardamagna V, Marinangeli F, Micciche F and Trippa F: The
vicious circle of treatment-induced toxicities in locally advanced
head and neck cancer and the impact on treatment intensity. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 116:82–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang XL, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang LL, Chen
FP, Lv JW, Kou J, Wen DW, Ma J, Sun Y, et al: Prognostic value of
radiation interruption in different periods for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma patients in the intensity-modulated RT era. Cancer Med.
10:143–155. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yao JJ, Zhang F, Gao TS, Zhang WJ,
Lawrence WR, Zhu BT, Zhou GQ, Ma J, Wang SY and Sun Y: Survival
impact of radiotherapy interruption in nasopharyngeal carcinoma in
the intensity-modulated radiotherapy era: A big-data intelligence
platform-based analysis. Radiother Oncol. 132:178–187. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Applegate KE, Ruhm W, Wojcik A,
Bourguignon M, Brenner A, Hamasaki K, Imai T, Imaizumi M, Imaoka T,
Kakinuma S, et al: Individual response of humans to ionising
radiation: Governing factors and importance for radiological
protection. Radiat Environ Biophys. 59:185–209. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wardill HR, Sonis ST, Blijlevens NMA, Van
Sebille YZA, Ciorba MA, Loeffen EAH, Cheng KKF, Bossi P, Porcello
L, Castillo DA, et al: Prediction of mucositis risk secondary to
cancer therapy: A systematic review of current evidence and call to
action. Support Care Cancer. 28:5059–5073. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang DW, Wang TM, Zhang JB, Li XZ, He YQ,
Xiao R, Xue WQ, Zheng XH, Zhang PF, Zhang SD, et al: Genome-wide
association study identifies genetic susceptibility loci and
pathways of radiation-induced acute oral mucositis. J Transl Med.
18:2242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Brothwell MRS, West CM, Dunning AM, Burnet
NG and Barnett GC: Radiogenomics in the era of advanced
radiotherapy. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 31:319–325. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J, Bi K, Yang R, Li H, Nikitaki Z and
Chang L: Role of DNA damage and repair in radiation cancer therapy:
A current update and a look to the future. Int J Radiat Biol.
96:1329–1338. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
London RE: XRCC1-Strategies for
coordinating and assembling a versatile DNA damage response. DNA
Repair (Amst). 93:1029172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Guo Z, Shu Y, Zhou H, Zhang W and Wang H:
Radiogenomics helps to achieve personalized therapy by evaluating
patient responses to radiation treatment. Carcinogenesis.
36:307–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xi T, Jones IM and Mohrenweiser HW: Many
amino acid substitution variants identified in DNA repair genes
during human population screenings are predicted to impact protein
function. Genomics. 83:970–979. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rosen EM, Fan S, Goldberg ID and Rockwell
S: Biological basis of radiation sensitivity. Part 2: Cellular and
molecular determinants of radiosensitivity. Oncology. 14:741–757.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao J, Zhi Z, Zhang M, Li Q, Li J, Wang X
and Ma C: Predictive value of single nucleotide polymorphisms in
XRCC1 for radiation-induced normal tissue toxicity. Onco Targets
Ther. 11:3901–3918. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin J, Ye Q, Wang Y, Wang Y and Zeng Y:
Association between XRCC1 single-nucleotide polymorphisms and
susceptibility to nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An update
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e118522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Li L, Yin X, Wu F, Shen J, Peng Y,
Liu Y, Sun Y, Lu H and Zhang Y: The association between gene
polymorphisms and risk of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Med Oncol.
32:3982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang SQ, Pan SM, Liang SX, Han YS, Chen
HB and Li JC: Research status and prospects of biomarkers for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of highthroughput omics
(Review). Int J Oncol. 58:92021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Siak PY, Khoo AS, Leong CO, Hoh BP and
Cheah SC: Current status and future perspectives about molecular
biomarkers of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
13:34902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mor V, Laliberte L, Morris JN and Wiemann
M: The karnofsky performance status scale. An examination of its
reliability and validity in a research setting. Cancer.
53:2002–2007. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lin S, Pan J, Han L, Guo Q, Hu C, Zong J,
Zhang X and Lu JJ: Update report of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
treated with reduced-volume intensity-modulated RT and hypothesis
of the optimal margin. Radiother Oncol. 110:385–389. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cox JD, Stetz J and Pajak TF: Toxicity
criteria of the radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) and the
european organization for research and treatment of cancer (EORTC).
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 31:1341–1346. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Seventh
Edition. New York; Springer: 2010
|
|
30
|
Jiqian Fang: Health Statistics. People's
Medical Publishing House; Beijing: pp. 150–171. 2012
|
|
31
|
Prescott RJ: Two-tailed significance tests
for 2×2 contingency tables: What is the alternative? Stat Med.
38:4264–4269. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang J, Guo C, Gong X, Ao F, Huang Y,
Huang L, Tang Y, Jiang C, Xie X, Dong Q, et al: The impacts of
genetic polymorphisms in genes of base excision repair pathway on
the efficacy and acute toxicities of (chemo)radiotherapy in
patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:78633–78641.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhai XM, Hu QC, Gu K, Wang JP, Zhang JN
and Wu YW: Significance of XRCC1 Codon399 polymorphisms in Chinese
patients with locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated
with radiation therapy. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 12:e125–e132. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen H, Wu M, Li G, Hua L, Chen S and
Huang H: Association between XRCC1 single-nucleotide polymorphism
and acute radiation reaction in patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e82022017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li H, You Y, Lin C, Zheng M, Hong C, Chen
J, Li D, Au WW and Chen Z: XRCC1 codon 399Gln polymorphism is
associated with radiotherapy-induced acute dermatitis and mucositis
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients. Radiat Oncol. 8:312013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin H, Xie X, Wang H, Hu J, Liu F, Liu Z,
Zhou J, Zhang Y, Xi X, Hu B, et al: ERCC1 Cys8092Ala and XRCC1
Arg399Gln polymorphisms predict progression-free survival after
curative radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One.
9:e1012562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chiang CL, Guo Q, Ng WT, Lin S, Ma TSW, Xu
Z, Xiao Y, Li J, Lu T, Choi HCW, et al: Prognostic factors for
overall survival in nasopharyngeal cancer and implication for TNM
staging by UICC: A systematic review of the literature. Front
Oncol. 11:7039952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Alami IE, Gihbid A, Charoute H, Khaali W,
Brahim SM, Tawfiq N, Cadi R, Belghmi K, El Mzibri M and Khyatti M:
Prognostic value of Epstein-Barr virus DNA load in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Pan Afr Med J. 41:62022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qu H, Huang Y, Zhao S, Zhou Y and Lv W:
Prognostic value of Epstein-Barr virus DNA level for nasopharyngeal
carcinoma: A meta-analysis of 8128 cases. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 277:9–18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zong J, Zheng Y, Lin C, Chen Y, Chen C,
Pan J and Lin S: The value of plasma EBV DNA in monitoring the
therapeutic effect of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin J Radiat
Oncol. 28:881–885. 2019.
|
|
41
|
Zong JF, Zheng YH, Weng YI, Chen LS, Yun
XU, Chen Y, Pan JJ and Lin SJ: Prognostic Value of Pre-treatment
plasma EBV DNA in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with
intensity-modulated radiation therapy. J Chin Oncol. 22:810–815.
2016.
|
|
42
|
Nanda SS, Gandhi AK, Rastogi M, Khurana R,
Hadi R, Sahni K, Mishra SP, Srivastava AK, Bhatt MLB and Parmar D:
Evaluation of XRCC1 gene polymorphism as a biomarker in head and
neck cancer patients undergoing chemoradiation therapy. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 101:593–601. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Leopold SS and Porcher R: Editorial:
Sparse-data Bias-What the savvy reader needs to know. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 476:657–659. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Greenland S, Mansournia MA and Altman DG:
Sparse-data bias: A problem hiding in plain sight. BMJ.
352:i19812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vera-Llonch M, Oster G, Hagiwara M and
Sonis S: Oral mucositis in patients undergoing radiation treatment
for head and neck carcinoma. Cancer. 106:329–336. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang C, Wang F, Min X, Zhang Q, Shen LJ,
Jiang Y and Yan J: Toxicities of chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: An updated meta-analysis. J Int Med
Res. 47:2832–2847. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xu YC, Chen KH, Liang ZG and Zhu XD: A
systematic review and Meta-Analysis of studies comparing concurrent
chemoradiotherapy with radiotherapy alone in the treatment of stage
II Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Front Oncol. 12:8436752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ma WL, Liu R, Huang LH, Zou C, Huang J,
Wang J, Chen SJ, Meng XG, Yang JK, Li H, et al: Impact of
polymorphisms in angiogenesis-related genes on clinical outcomes of
radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 44:539–548. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yang Z and Liu Z: Potentially functional
variants of autophagy-related genes are associated with the
efficacy and toxicity of radiotherapy in patients with
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 7:e10302019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu J, Huang Y, Liu L, Wang J, Yin J, Huang
L, Chen S, Li J, Yuan H, Yang G, et al: Genetic polymorphisms of
Wnt/β-catenin pathway genes are associated with the efficacy and
toxicities of radiotherapy in patients with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:82528–82537. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guo C, Huang Y, Yu J, Liu L, Gong X, Huang
M, Jiang C, Liao Y, Huang L, Yang G and Li J: The impacts of single
nucleotide polymorphisms in genes of cell cycle and NF-kB pathways
on the efficacy and acute toxicities of radiotherapy in patients
with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncotarget. 8:25334–25344. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Andreassen CN, Schack LM, Laursen LV and
Alsner J: Radiogenomics-current status, challenges and future
directions. Cancer Lett. 382:127–136. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|