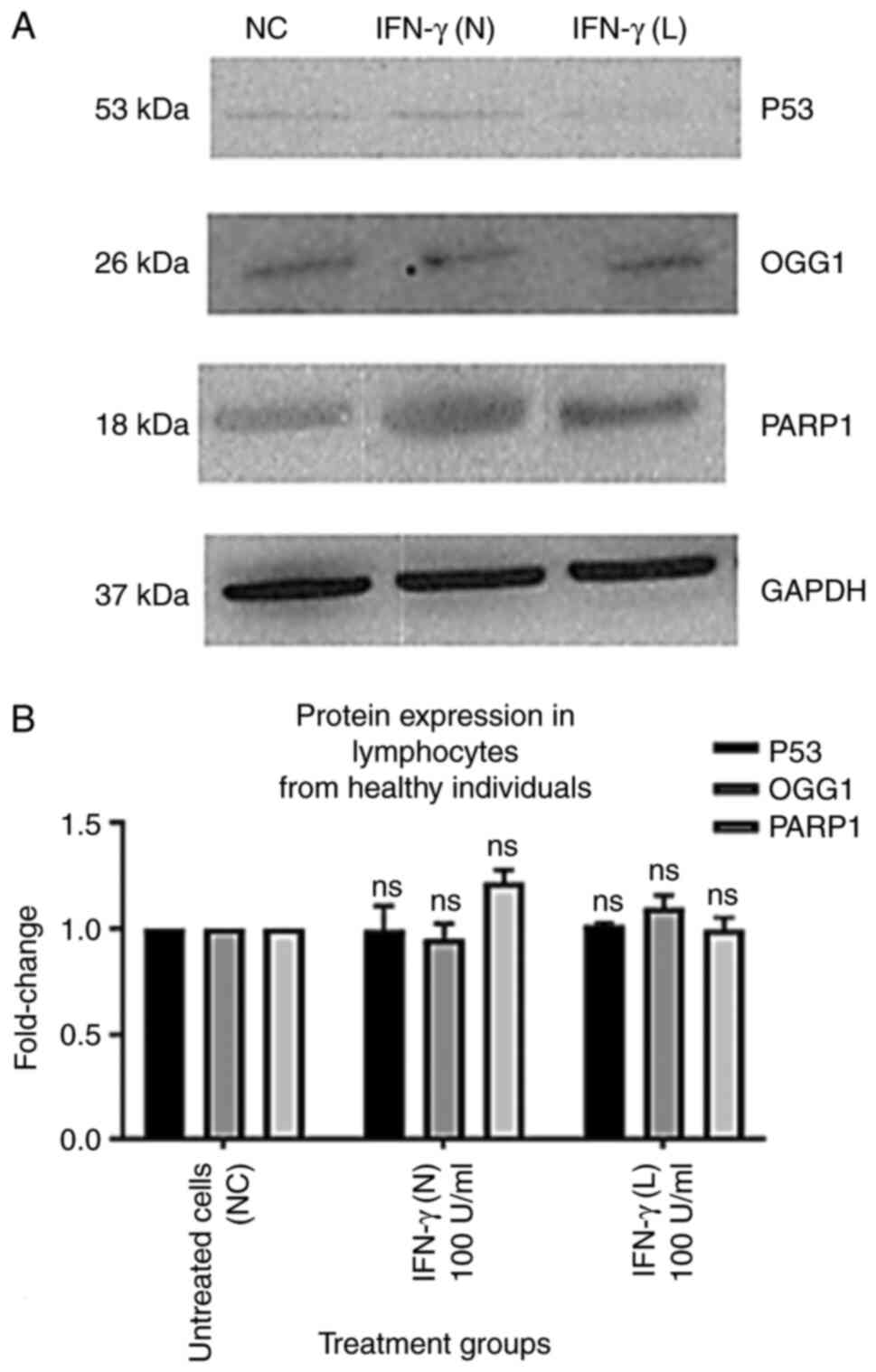
|
1
|
Oo AM, Mohd Adnan LH, Nor NM, Simbak N,
Ahmad NZ and Lwin OM: Immunomodulatory effects of flavonoids: An
experimental study on natural-killer-cell-mediated cytotoxicity
against lung cancer and cytotoxic granule secretion profile.
Proceedings Singapore Healthcare. 30:279–285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Daud NNNNM, Septama AW, Simbak N, Bakar
NHA and Rahmi EP: Synergistic effect of flavonoids from artocarpus
heterophyllus heartwoods on anticancer activity of cisplatin
against H460 and MCF-7 cell lines. Nat Product Sci. 25:311–316.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Miller CH, Maher SG and Young HA: Clinical
use of interferon-γ. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1182:69–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferreira VL, Borba HHL, Bonetti AdF,
Leonart LP and Pontarolo R: Cytokines and interferons: Types and
functions. Autoantibodies Cytokines. 13:2018.
|
|
5
|
Castro F, Cardoso AP, Gonçalves RM, Serre
K and Oliveira MJ: Interferon-gamma at the crossroads of tumor
immune surveillance or evasion. Front Immunol. 9:8472018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hishinuma S, Ogata Y, Tomikawa M, Ozawa I,
Hirabayashi K and Igarashi S: Patterns of recurrence after curative
resection of pancreatic cancer, based on autopsy findings. J
Gastrointest Surg. 10:511–518. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Bao Q, Yang S, Yang M and Mao C:
Bionanoparticles in cancer imaging, diagnosis, and treatment. View.
3:202000272022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
de Ruiter MV, Klem R, Luque D, Cornelissen
JJ and Castón JR: Structural nanotechnology: Three-dimensional
cryo-EM and its use in the development of nanoplatforms for in
vitro catalysis. Nanoscale. 11:4130–4146. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Z and Chen H: The recent progress of
inorganic-based intelligent responsive nanoplatform for tumor
theranostics. View. 3:202200092022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Koizumi S-i, Wakita D, Sato T, Mitamura R,
Izumo T, Shibata H, Kiso Y, Chamoto K, Togashi Y, Kitamura H and
Nishimura T: Essential role of Toll-like receptors for dendritic
cell and NK1. 1+ cell-dependent activation of type 1 immunity by
Lactobacillus pentosus strain S-PT84. Immunol Lett. 120:14–19.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ramos TI, Villacis-Aguirre CA, Santiago
Vispo N, Santiago Padilla L, Pedroso Santana S, Parra NC and Alonso
JRT: Forms and methods for interferon's encapsulation.
Pharmaceutics. 13:15332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jailani MTM, Totten J, Nevin J and Halbert
G: ID 180. Fabrication, characterisation and in vitro study of
dual-loaded irinotecan/cisplatin liposomes. J Pharmacy Bioallied
Sci. 12:2020.
|
|
13
|
Hirai M, Kimura R, Takeuchi K, Hagiwara Y,
Kawai-Hirai R, Ohta N, Igarashi N and Shimuzu N: Structure of
liposome encapsulating proteins characterized by X-ray scattering
and shell-modeling. J Synchrotron Radiat. 20:869–874. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao H, Wu L, Yan G, Chen Y, Zhou M, Wu Y
and Li Y: Inflammation and tumor progression: Signaling pathways
and targeted intervention. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:2632021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalm M, Andreasson U, Björk-Eriksson T,
Zetterberg H, Pekny M, Blennow K, Pekna M and Blomgren K: C3
deficiency ameliorates the negative effects of irradiation of the
young brain on hippocampal development and learning. Oncotarget.
7:193822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wirth M, Plattner V and Gabor F:
Strategies to improve drug delivery in bladder cancer therapy.
Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 6:727–744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pisal DS, Kosloski MP and Balu-Iyer SV:
Delivery of therapeutic proteins. J Pharm Sci. 99:2557–2575. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu H, Gao HY, Guo H, Wang GZ, Yang YQ, Hu
Q, Liang LJ, Zhao Q, Xie DW, Rao Y and Zhou GB: Upregulation of
wild-type p53 by small molecule-induced elevation of NQO1 in
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sinica.
43:692–702. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Almajali B, Johan MF, Al-Wajeeh AS, Wan
Taib WR, Ismail I, Alhawamdeh M, Al-Tawarah NM, Ibrahim WN,
Al-Rawashde FA and Al-Jamal HAN: Gene expression profiling and
protein analysis reveal suppression of the C-Myc oncogene and
inhibition JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling by thymoquinone in
acute myeloid leukemia cells. Pharmaceuticals. 15:3072022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams AB and Schumacher B: p53 in the
DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med.
6:a0260702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xu X, Jin S, Ma Y, Fan Z, Yan Z, Li W,
Song Q, You W, Lyu Z, Song Y, et al: miR-30a-5p enhances paclitaxel
sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer through targeting BCL-2
expression. J Mol Med (Berl). 95:861–871. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Slupphaug G, Kavli B and Krokan HE: The
interacting pathways for prevention and repair of oxidative DNA
damage. Mutat Res. 531:231–251. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Noren Hooten N, Kompaniez K, Barnes J,
Lohani A and Evans MK: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) binds
to 8-oxoguanine-DNA glycosylase (OGG1). J Biol Chem.
286:44679–44690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Alhawamdeh M, Isreb M, Aziz A, Jacob BK,
Anderson D and Najafzadeh M: Interferon-γ liposome: A new system to
improve drug delivery in the treatment of lung cancer. ERJ Open
Res. 7:00555–2020. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Van Slooten M, Boerman O, Romøren K, Kedar
E, Crommelin D and Storm G: Liposomes as sustained release system
for human interferon-γ: Biopharmaceutical aspects. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1530:134–145. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Haggag YA, Matchett KB, Falconer RA, Isreb
M, Jones J, Faheem A, McCarron P and El-Tanani M: Novel ran-RCC1
inhibitory peptide-loaded nanoparticles have anti-cancer efficacy
in vitro and in vivo. Cancers. 11:2222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fouad YA and Aanei C: Revisiting the
hallmarks of cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 7:10162017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Collins AR: The comet assay for DNA damage
and repair: principles, applications, and limitations. Mol
Biotechnol. 26:249–261. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Alhawamdeh MF: Applying a new technique,
the interferon gamma liposomal delivery system to improve drug
delivery in the treatment of lung cancer. University of Bradford;
2021, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rivlin N, Brosh R, Oren M and Rotter V:
Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: important milestones at
the various steps of tumorigenesis. Genes Cancer. 2:466–474. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yin T, Wang P, Li J, Wang Y, Zheng B,
Zheng R, Cheng D and Shuai X: Tumor-penetrating codelivery of siRNA
and paclitaxel with ultrasound-responsive nanobubbles
hetero-assembled from polymeric micelles and liposomes.
Biomaterials. 35:5932–5943. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lieschke E, Wang Z, Kelly GL and Strasser
A: Discussion of some ‘knowns’ and some ‘unknowns’ about the tumour
suppressor p53. J Mol Cell Biol. 11:212–223. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chatterjee N and Walker GC: Mechanisms of
DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen.
58:235–263. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fukui T, Matsui K, Kato H, Takao H,
Sugiyama Y, Kunieda K and Saji S: Significance of apoptosis induced
by tumor necrosis factor-α and/or interferon-γ against human
gastric cancer cell lines and the role of the p53 gene. Surg Today.
33:847–853. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Thiem A, Hesbacher S, Kneitz H, di Primio
T, Heppt MV, Hermanns HM, Goebeler M, Meierjohann S, Houben R and
Schrama D: IFN-gamma-induced PD-L1 expression in melanoma depends
on p53 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Midgley CA and Lane DP: p53 protein
stability in tumour cells is not determined by mutation but is
dependent on Mdm2 binding. Oncogene. 15:1179–1189. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang M, Zhang Y, Xu E, Mohibi S, de Anda
DM, Jiang Y, Zhang J and Chen X: Rbm24, a target of p53, is
necessary for proper expression of p53 and heart development. Cell
Death Differ. 25:1118–1130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|