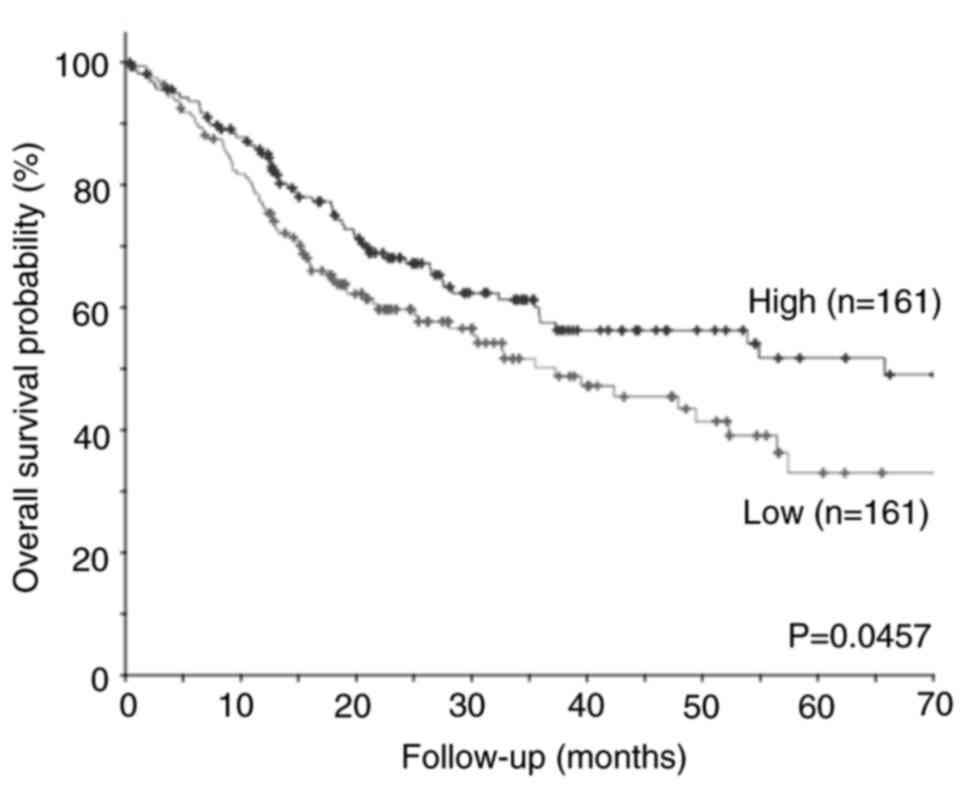
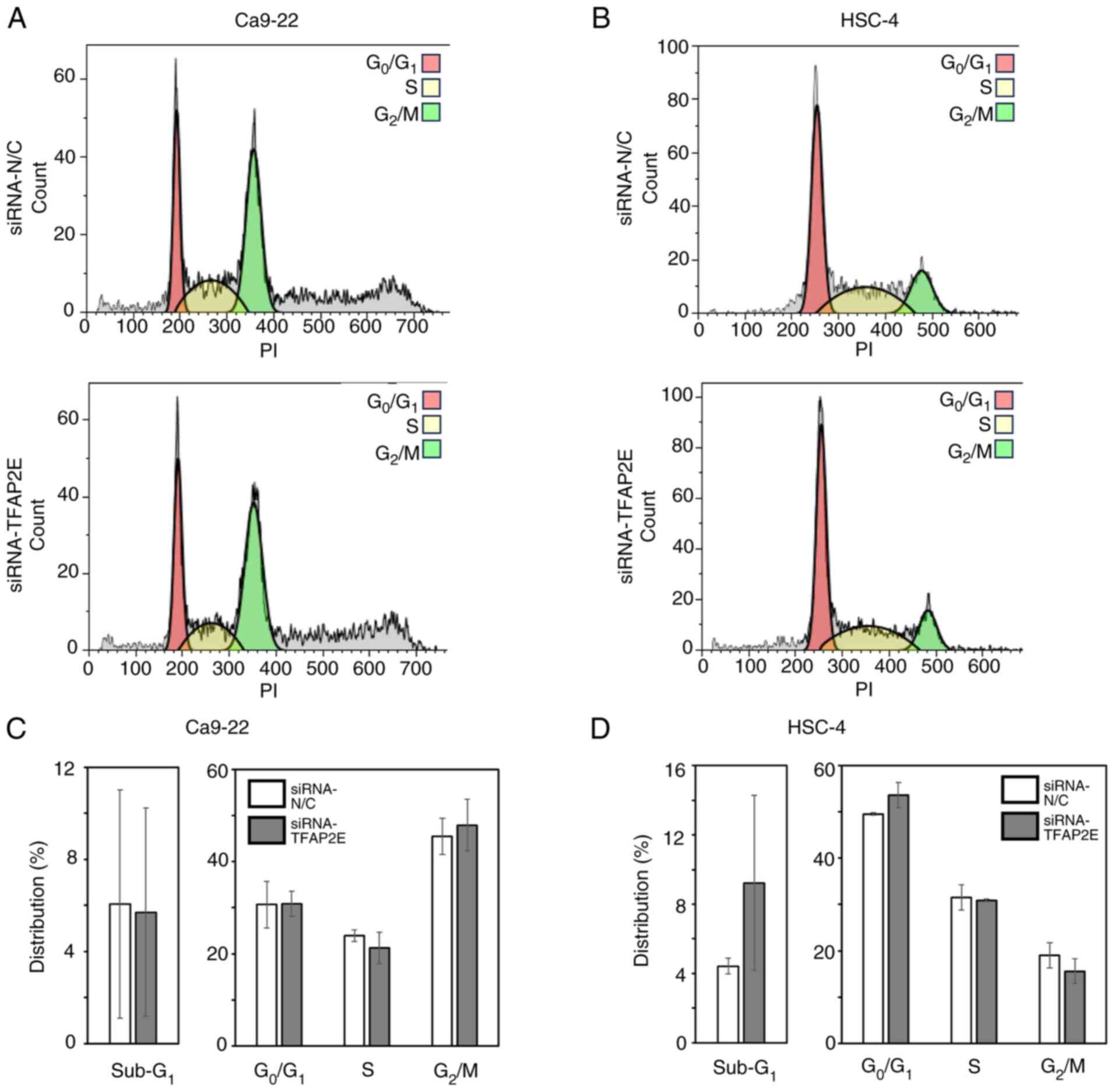
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
National Cancer Institute, . SEER Cancer
Statistics Review (CSR) 1975–2018. NCI; Bethesda, MD: 2021,
https://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2018/
|
|
4
|
Kumar M, Nanavati R, Modi TG and Dobariya
C: Oral cancer: Etiology and risk factors: A review. J Cancer Res
Ther. 12:458–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous
cell carcinomas. Nature. 517:576–582. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujiwara K, Ghosh S, Liang P, Morien E,
Soma M and Nagase H: Genome-wide screening of aberrant DNA
methylation which associated with gene expression in mouse skin
cancers. Mol Carcinog. 54:178–188. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kolat D, Kaluzí Nska Z, Bednarek AK and
Zbieta Pluciennik E: The biological characteristics of
transcription factors AP-2α and AP-2γ and their importance in
various types of cancers. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201819282019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eckert D, Buhl S, Weber S, Jäger R and
Schorle H: The AP-2 family of transcription factors. Genome Biol.
6:2462005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang HV, Vaupel K, Buettner R, Bosserhoff
AK and Moser M: Identification and embryonic expression of a new
AP-2 transcription factor, AP-2 epsilon. Dev Dyn. 231:128–135.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feng W, Simoes-de-Souza F, Finger TE,
Restrepo D and Williams T: Disorganized olfactory bulb lamination
in mice deficient for transcription factor AP-2epsilon. Mol Cell
Neurosci. 42:161–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jain S, Glubrecht DD, Germain DR, Moser M
and Godbout R: AP-2ε Expression in developing retina: Contributing
to the nolecular diversity of amacrine cells. Sci Rep. 8:33862018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wenke AK, Grä Ssel S, Moser M and
Bosserhoff AK: The cartilage-specific transcription factor Sox9
regulates AP-2e expression in chondrocytes. FEBS J. 276:2494–2504.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wenke AK, Rothhammer T, Moser M and
Bosserhoff AK: Regulation of integrin alpha10 expression in
chondrocytes by the transcription factors AP-2epsilon and Ets-1.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 345:495–501. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giaretti W, Molinu S, Ceccarelli J and
Prevosto C: Chromosomal instability, aneuploidy, and gene mutations
in human sporadic colorectal adenomas. Cell Oncol. 26:301–305.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ebert MP, Tänzer M, Balluff B,
Burgermeister E, Kretzschmar AK, Hughes DJ, Tetzner R, Lofton-Day
C, Rosenberg R, Reinacher-Schick AC, et al: TFAP2E-DKK4 and
chemoresistance in colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:44–53.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sun J, Du N, Li J, Zhou J, Tao G, Sun S
and He J: Transcription Factor AP2ε: A potential predictor of
chemoresistance in patients with gastric cancer. Technol Cancer Res
Treat. 15:285–295. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Payne SR, Serth J, Schostak M, Kamradt J,
Strauss A, Thelen P, Model F, Day JK, Liebenberg V, Morotti A, et
al: DNA methylation biomarkers of prostate cancer: Confirmation of
candidates and evidence urine is the most sensitive body fluid for
non-invasive detection. Prostate. 69:1257–1269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hoshi R, Watanabe Y, Ishizuka Y, Hirano T,
Nagasaki-Maeoka E, Yoshizawa S, Uekusa S, Kawashima H, Ohashi K,
Sugito K, et al: Depletion of TFAP2E attenuates adriamycin-mediated
apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cells. Oncol Rep. 37:2459–2464.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao M, Sano D, Pickering CR, Jasser SA,
Henderson YC, Clayman GL, Sturgis EM, Ow TJ, Lotan R, Carey TE, et
al: Assembly and initial characterization of a panel of 85
genomically validated cell lines from diverse head and neck tumor
sites. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7248–7264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jordan MA, Thrower D and Wilson L: Effects
of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles.
Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis. J
Cell Sci. 102((Pt 3)): 401–416. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fox MH: A model for the computer analysis
of synchronous DNA distributions obtained by flow cytometry.
Cytometry. 1:71–77. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Larionov A, Krause A and Miller W: A
standard curve based method for relative real time PCR data
processing. BMC Bioinformatics. 6:622005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thellin O, Zorzi W, Lakaye B, De Borman B,
Coumans B, Hennen G, Grisar T, Igout A and Heinen E: Housekeeping
genes as internal standards: Use and limits. J Biotechnol.
75:291–295. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:971–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sherman J and Wang R: Rapid profiling of
G2 phase to mitosis progression by flow cytometry in asynchronous
cells. Cell Cycle. 19:2897–2905. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pérez-Cadahía B, Drobic B and Davie JR: H3
phosphorylation: Dual role in mitosis and interphase. Biochem Cell
Biol. 87:695–709. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
De Wever V, Lloyd VC, Nasa I, Nimick I,
Trinkle-Mulcahy M, Gourlay R, Morrice N and Moorhead GB: Isolation
of human mitotic protein phosphatase complexes: Identification of a
complex between protein phosphatase 1 and the RNA helicase Ddx21.
PLoS One. 7:e395102012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matthews HK, Bertoli C and de Bruin RAM:
Cell cycle control in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:74–88.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Medema RH and Macurek L: Checkpoint
control and cancer. Oncogene. 31:2601–2613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stark GR and Taylor WR: Control of the
G2/M transition. Mol Biotechnol. 32:227–248. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yan W and Chen X: Characterization of
functional domains necessary for mutant p53 gain of function. J
Biol Chem. 285:14229–14238. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ng JW, Lama D, Lukman S, Lane DP, Verma CS
and Sim AY: R248Q mutation-Beyond p53-DNA binding. Proteins.
83:2240–2250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang J, Liu W, Zhang L and Zhang J:
Targeting mutant p53 stabilization for cancer therapy. Front
Pharmacol. 14:12159952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|