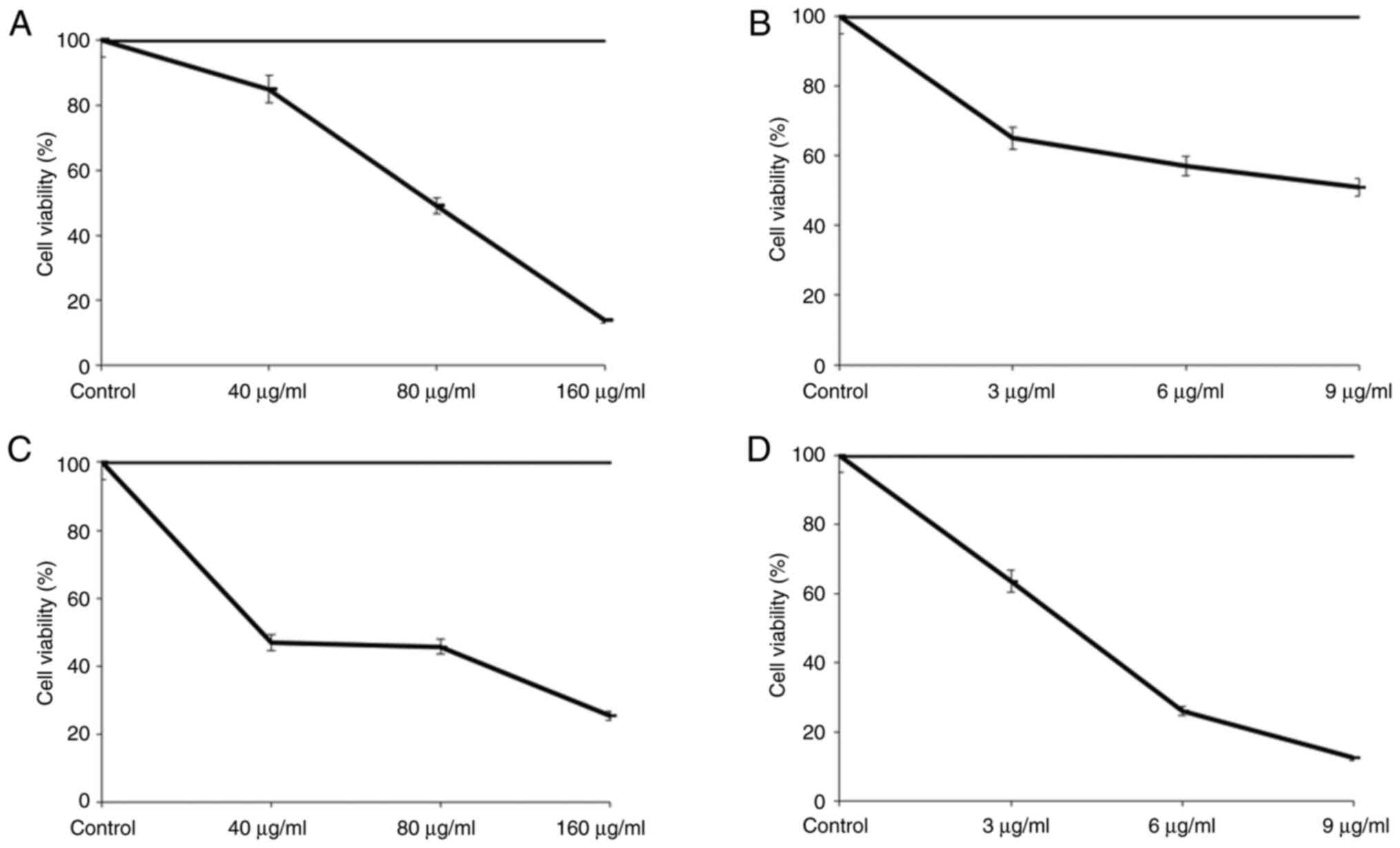
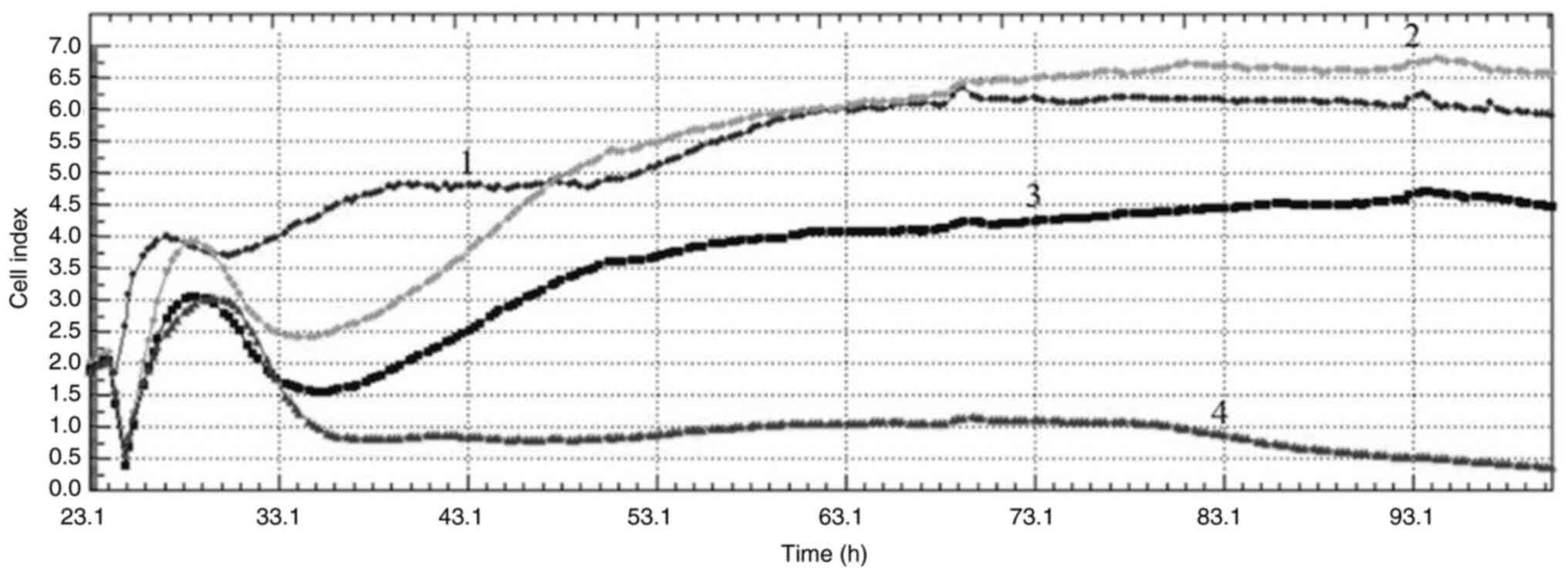
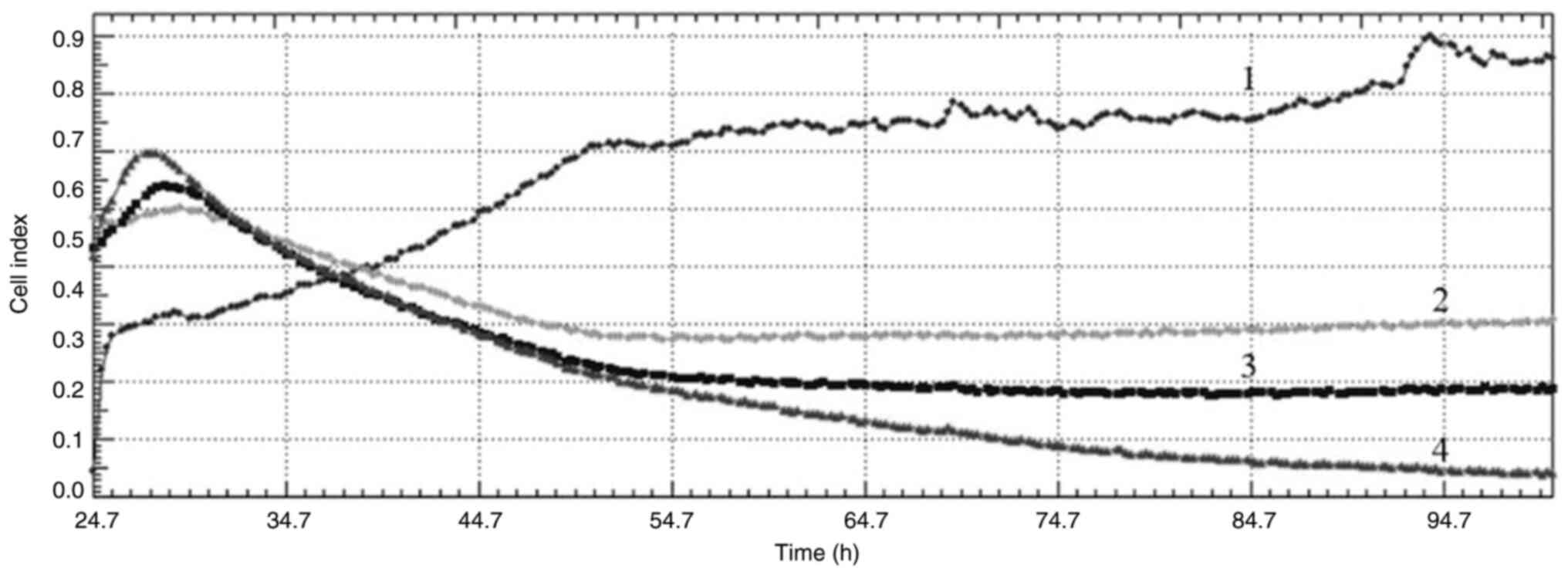
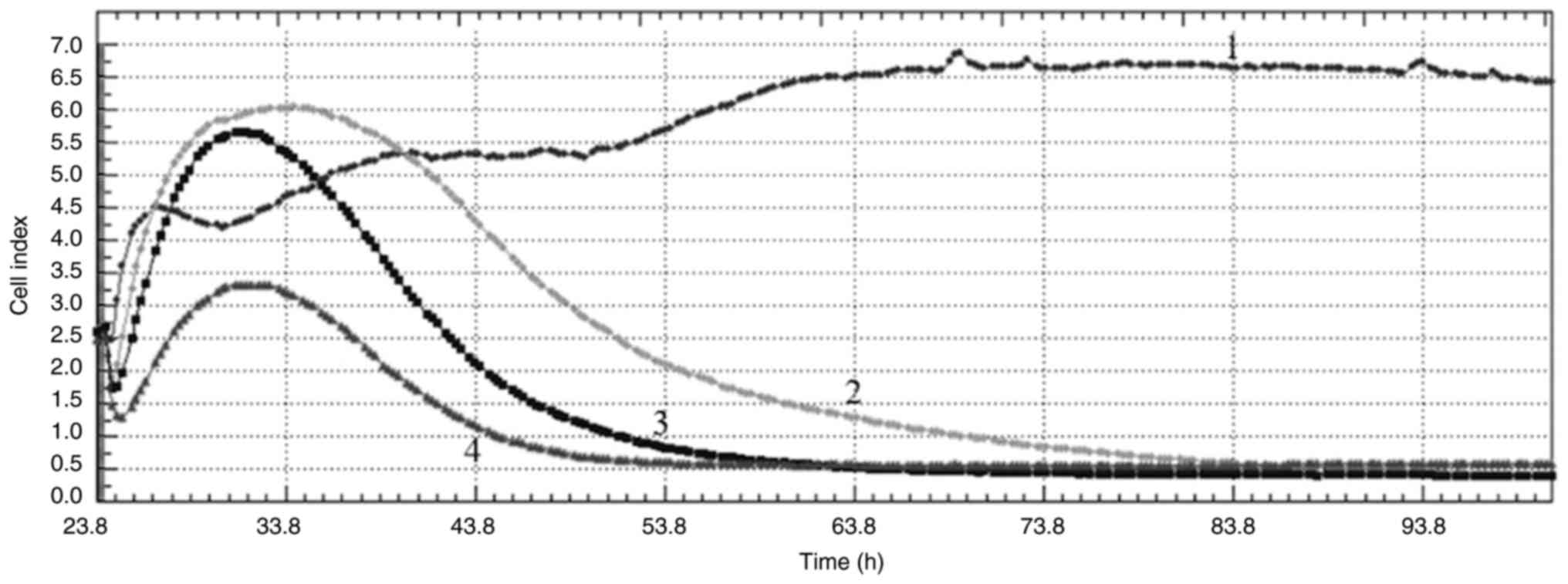
|
1
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Veronesi U, Boyle P, Goldhirsch A,
Orecchia R and Viale G: Breast cancer. Lancet. 365:1727–1741. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cliffton EE and Young LE: Carcinoma of the
breast; five to twenty-year follow-up following radical mastectomy.
Am J Surg. 82:185–190. 1951. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Figueiredo MI, Cullen J, Hwang YT, Rowland
JH and Mandelblatt JS: Breast cancer treatment in older women: Does
getting what you want improve your long-term body image and mental
health? J Clin Oncol. 22:4002–4009. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mathews FS: The ten-year survivors of
radical mastectomy. Ann Surg. 98:635–643. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nagarajan D and McArdle SEB: Immune
landscape of breast cancers. Biomedicines. 6:202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Makhoul I, Atiq M, Alwbari A and
Kieber-Emmons T: Breast cancer immunotherapy: An update. Breast
Cancer (Auckl). 12:11782234187748022018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Investig. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Xu D, Li X, Zhang J, Xu W, Hou J,
Zhang W and Tang J: Latest overview of the cyclindependent kinases
4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: The past, the present, and the
future. J Cancer. 10:6608–6617. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hulka BS: Epidemiology of susceptibility
to breast cancer. Prog Clin Biol Res. 395:159–174. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reinert T and Barrios CH: Optimal
management of hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer in
2016. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 7:304–320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wuerstlein R and Harbeck N: Neoadjuvant
therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer. Rev Recent Clin Trials.
12:81–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Riggi N, Aguet M and Stamenkovic I: Cancer
metastasis: A reappraisal of its underlying mechanisms and their
relevance to treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 13:117–140. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Weigelt B, Peterse JL and van't Veer LJ:
Breast cancer metastasis: Markers and models. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:591–602. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G and Yu Y: Breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:311–320.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Poratti M and Marzaro G: Third-generation
CDK inhibitors: A review on the synthesis and binding modes of
palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib. Eur J Med Chem.
172:143–153. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo X and Kraus WL: A one and a two …
expanding roles for poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases in metabolism.
Cell Metab. 13:353–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou D, Chu W, Xu J, Jones LA, Peng X, Li
S, Chen DL and Mach RH: Synthesis, [18F] radiolabeling,
and evaluation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1)
inhibitors for in vivo imaging of PARP-1 using positron emission
tomography. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 22:1700–1707. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Giannini G, Battistuzzi G, Vesci L,
Milazzo FM, Paolis FD, Barbarino M, Guglielmi MB, Carollo V, Gallo
G, Artali R and Dallavalle S: Novel PARP-1 inhibitors based on a
2-propanoyl-3H-quinazolin-4-one scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
24:462–466. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berger NA: Poly(ADP-ribose) in the
cellular response to DNA damage. Radiat Res. 101:4–15. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Topçul M, Çeti N İL, Özbaş Turan S and
Kolusayin Ozar MÖ: In vitro cytotoxic effect of PARP
inhibitor alone and in combination with nab-paclitaxel on
triple-negative and luminal A breast cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
40:527–535. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Silberholz J, Bertsimas D and Vahdat L:
Clinical benefit, toxicity and cost of metastatic breast cancer
therapies: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 176:535–543. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Malumbres M and Barbacid M: Cell cycle,
CDKs, and cancer: A changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:153–166.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sherr CJ, Beach D and Shapiro GI:
Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov.
6:353–367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiong Y, Menninger J, Beach D and Ward DC:
Molecular cloning and chromosomal mapping of CCND genes encoding
human D-type cyclins. Genomics. 13:575–584. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Braal CL, Jongbloed EM, Wilting SM,
Mathijssen RHJ, Koolen SLW and Jager A: Inhibiting CDK4/6 in breast
cancer with palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib: Similarities
and differences. Drugs. 81:317–331. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap
YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Petrakova K, Blackwell
KL, Winer EP, et al: Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III
trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus
letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced
breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 29:1541–1547. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Slamon DJ, Neven P, Chia S, Fasching PA,
De Laurentiis M, Im SA, Petrakova K, Bianchi GV, Esteva FJ, Martín
M, et al: Phase III randomized study of ribociclib and fulvestrant
in hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2-negative advanced breast cancer: MONALEESA-3. J Clin
Oncol. 36:2465–2472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tripathy D, Im SA, Colleoni M, Franke F,
Bardia A, Harbeck N, Hurvitz SA, Chow L, Sohn J, Lee KS, et al:
Ribociclib plus endocrine therapy for premenopausal women with
hormone-receptor-positive, advanced breast cancer (MONALEESA-7): A
randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 19:904–915. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Fang H, Huang D, Yang F and Guan X:
Potential biomarkers of CDK4/6 inhibitors in hormone
receptor-positive advanced breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
168:287–297. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cortesi L, Rugo HS and Jackisch C: An
overview of PARP ınhibitors for the treatment of breast cancer.
Target Oncol. 16:255–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Eek D, Krohe M, Mazar I, Horsfeld A,
Pompilus F, Friebe R and Shields AL: Patient-reported preferences
for oral versus intravenous administration for the treatment of
cancer: A review of the literature. Patient Prefer Adherence.
10:1609–1621. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tomimatsu N, Mukherjee B, Catherine
Hardebeck M, Ilcheva M, Vanessa Camacho C, Louise Harris J, Porteus
M, Llorente B, Khanna KK and Burma S: Phosphorylation of EXO1 by
CDKs 1 and 2 regulates DNA end resection and repair pathway choice.
Nat Commun. 5:35612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bajrami I, Frankum JR, Konde A, Miller RE,
Rehman FL, Brough R, Campbell J, Sims D, Rafiq R, Hooper S, et al:
Genome-wide profiling of genetic synthetic lethality identifies
CDK12 as a novel determinant of PARP1/2 inhibitor sensitivity.
Cancer Res. 74:287–297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Joshi PM, Sutor SL, Huntoon CJ and Karnitz
LM: Ovarian cancer-associated mutations disable catalytic activity
of CDK12, a kinase that promotes homologous recombination repair
and resistance to cisplatin and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 289:9247–9253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Johnson SF, Cruz C, Greifenberg AK, Dust
S, Stover DG, Chi D, Primack B, Cao S, Bernhardy AJ, Coulson R, et
al: CDK12 ınhibition reverses de novo and acquired PARP inhibitor
resistance in BRCA wild-type and mutated models of triple-negative
breast cancer. Cell Rep. 17:2367–2381. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ning JF, Stanciu M, Humphrey MR, Gorham J,
Wakimoto H, Nishihara R, Lees J, Zou L, Martuza RL, Wakimoto H and
Rabkin SD: Myc targeted CDK18 promotes ATR and homologous
recombination to mediate PARP inhibitor resistance in glioblastoma.
Nat Commun. 10:29102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Militello AM, Zielli T, Boggiani D,
Michiara M, Naldi N, Bortesi B, Zanelli P, Uliana V, Giuliotti S
and Musolino A: Mechanism of action and clinical efficacy of CDK4/6
inhibitors in BRCA-mutated, estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancers: Case report and literature review. Front Oncol. 9:7592019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carey JPW, Karakas C, Bui T, Chen X,
Vijayaraghavan S, Zhao Y, Wang J, Mikule K, Litton JK, Hunt KK and
Keyomarsi K: Synthetic lethality of PARP inhibitors in combination
with MYC blockade is independent of BRCA status in triple-negative
breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 78:742–757. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li S, Zhang Y, Wang N, Guo R, Liu Q, Lv C,
Wang J, Wang L and Yang Q: Pan-cancer analysis reveals synergistic
effects of CDK4/6i and PARPi combination treatment in RB-proficient
and RB-deficient breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 11:2192020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Eskiler GG, Ozman Z, Haciefendi A and
Cansaran-Duman D: Novel combination treatment of CDK 4/6 inhibitors
with PARP inhibitors in triple negative breast cancer cells. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 396:1031–1041. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li H, Liu ZY, Wu N, Chen YC, Cheng Q and
Wang J: PARP inhibitor resistance: The underlying mechanisms and
clinical implications. Mol Cancer. 19:1072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Klein FG, Granier C, Zhao Y, Pan Q, Tong
Z, Gschwend JE, Holm PS and Nawroth R: Combination of talazoparib
and palbociclib as a potent treatment strategy in bladder cancer. J
Pers Med. 11:3402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhu X, Chen L, Huang B, Li X, Yang L, Hu
X, Jiang Y, Shao Z and Wang Z: Efficacy and mechanism of the
combination of PARP and CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of
triple-negative breast cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 40:1222021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|