|
1
|
Nolan E, Lindeman GJ and Visvader JE:
Deciphering breast cancer: From Biology to the Clinic. Cell.
186:1708–1728. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yeo SK and Guan JL: Breast cancer:
Multiple subtypes within a tumor? Trends Cancer. 3:753–760. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Z, Wei H, Li S, Wu P and Mao X: The
role of progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 16:305–314. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang L, Chen W, Liu S and Chen C:
Targeting breast cancer stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 19:552–570.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slepicka PF, Cyrill SL and Dos Santos CO:
Pregnancy and breast cancer: Pathways to understand risk and
prevention. Trends Mol Med. 25:866–881. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Houghton SC and Hankinson SE: Cancer
progress and priorities: Breast cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 30:822–844. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
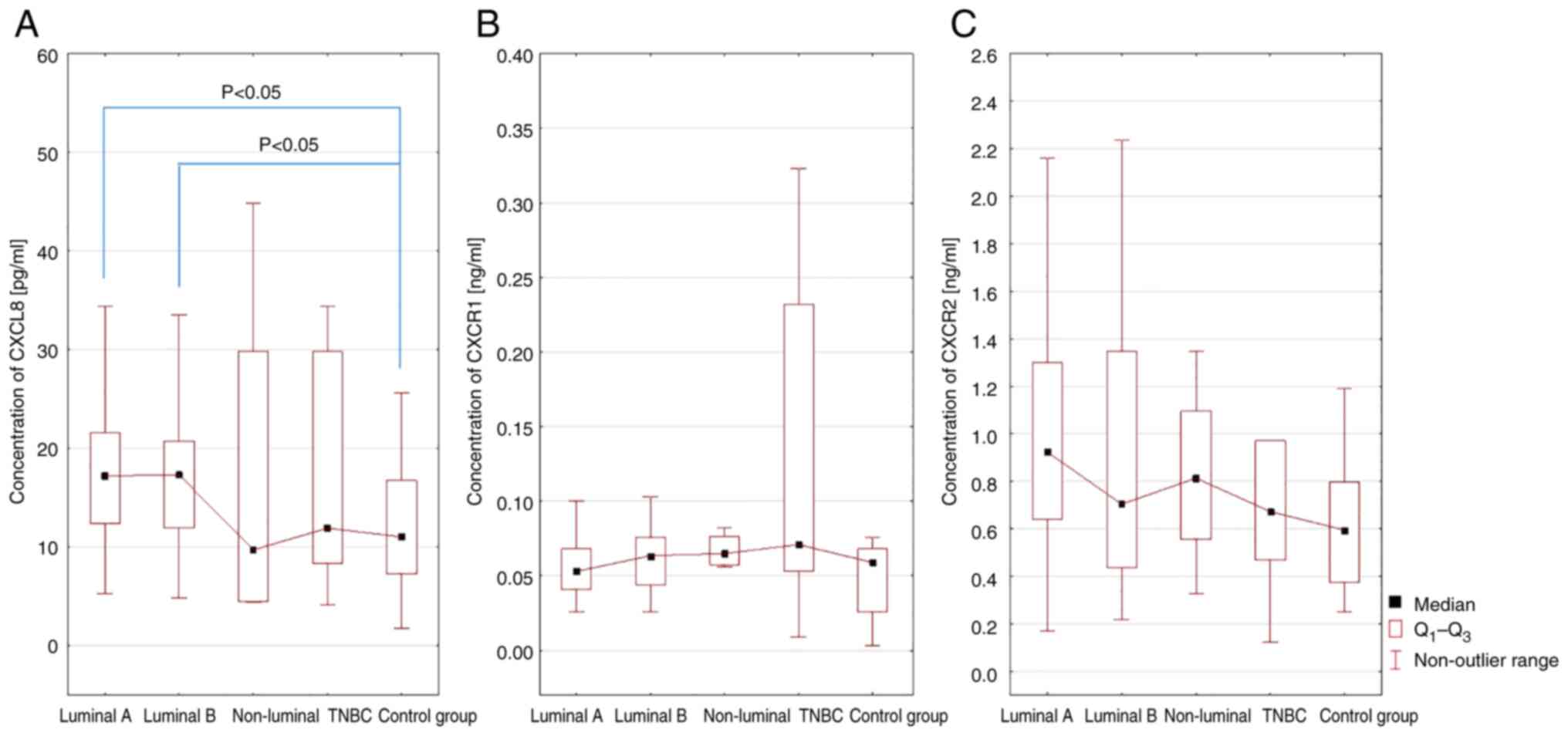
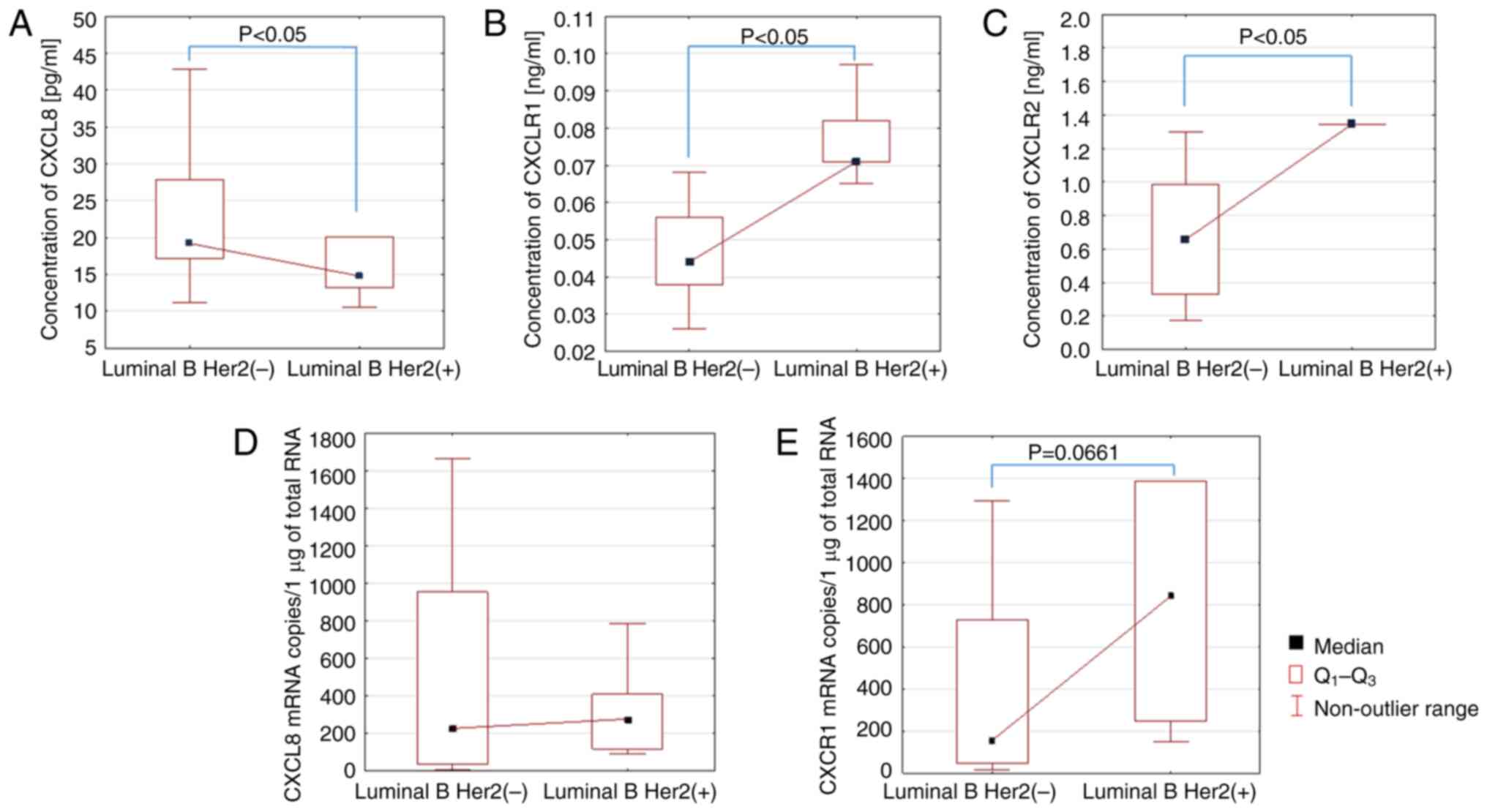
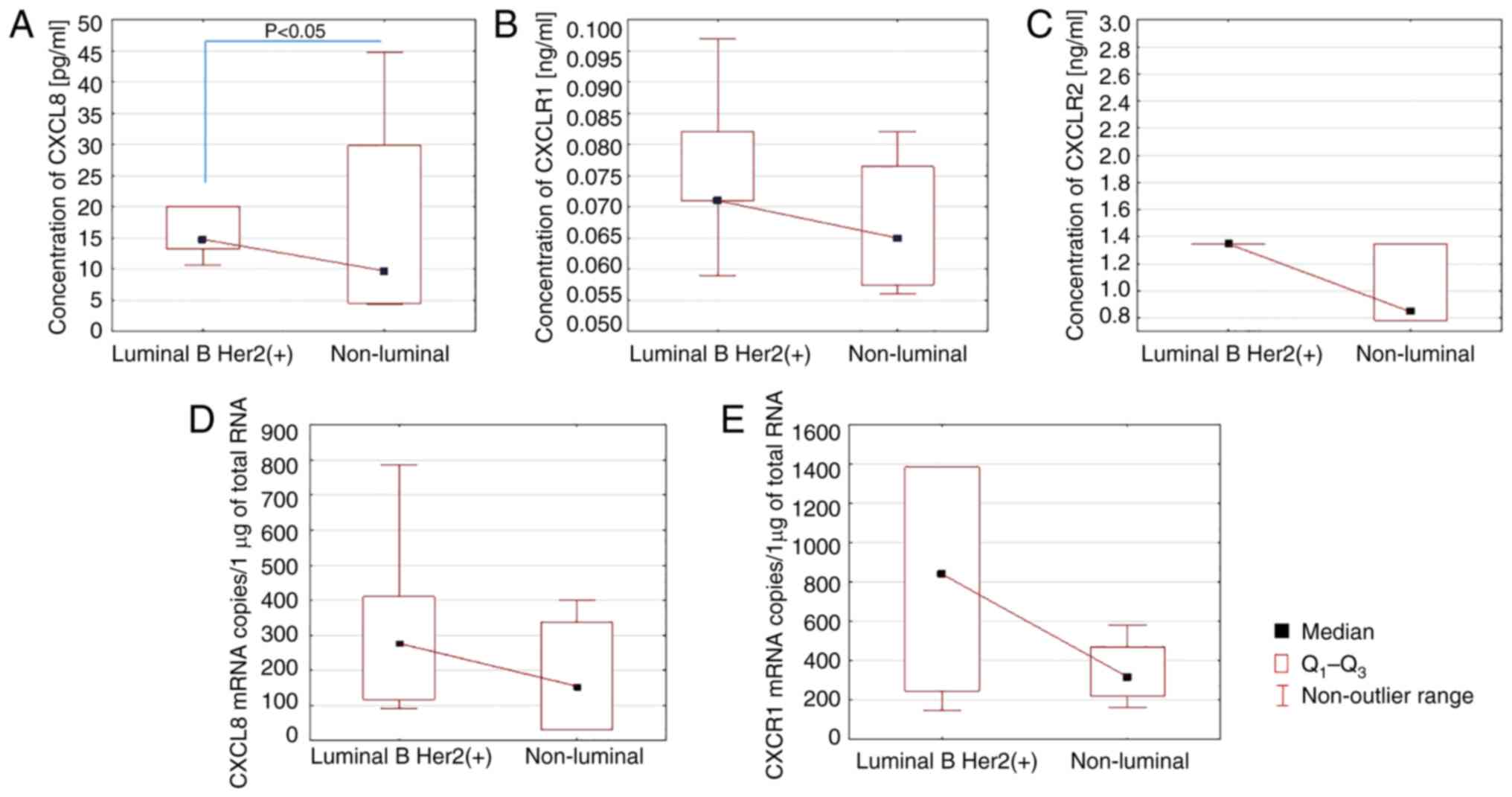
|
7
|
Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU and Polyak K:
Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast
cancer: Improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov.
9:176–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cocco S, Piezzo M, Calabrese A, Cianniello
D, Caputo R, Lauro VD, Fusco G, Gioia GD, Licenziato M and De
Laurentiis M: Biomarkers in triple-negative breast cancer:
State-of-the-art and future perspectives. Int J Mol Sci.
21:45792020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Faria SS, Costantini S, De Lima VCC, De
Andrade VP, Rialland M, Cedric R, Budillon A and Magalhães KG:
NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated cytokine production and pyroptosis cell
death in breast cancer. J Biomed Sci. 28:262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jenkins S, Kachur ME, Rechache K, Wells JM
and Lipkowitz S: Rare breast cancer subtypes. Curr Oncol Rep.
23:542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu H, Yang Z, Lu W, Chen Z, Chen L, Han
S, Wu X, Cai T and Cai Y: Chemokines and chemokine receptors: A new
strategy for breast cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 9:3786–3799. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ha H, Debnath B and Neamati N: Role of the
CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in cancer and inflammatory diseases.
Theranostics. 7:1543–1588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ma Y, Ren Y, Dai ZJ, Wu CJ, Ji YH and Xu
J: IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α Levels Correlate with Disease Stage in
Breast Cancer Patients. Adv Clin Exp Med. 26:421–426. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
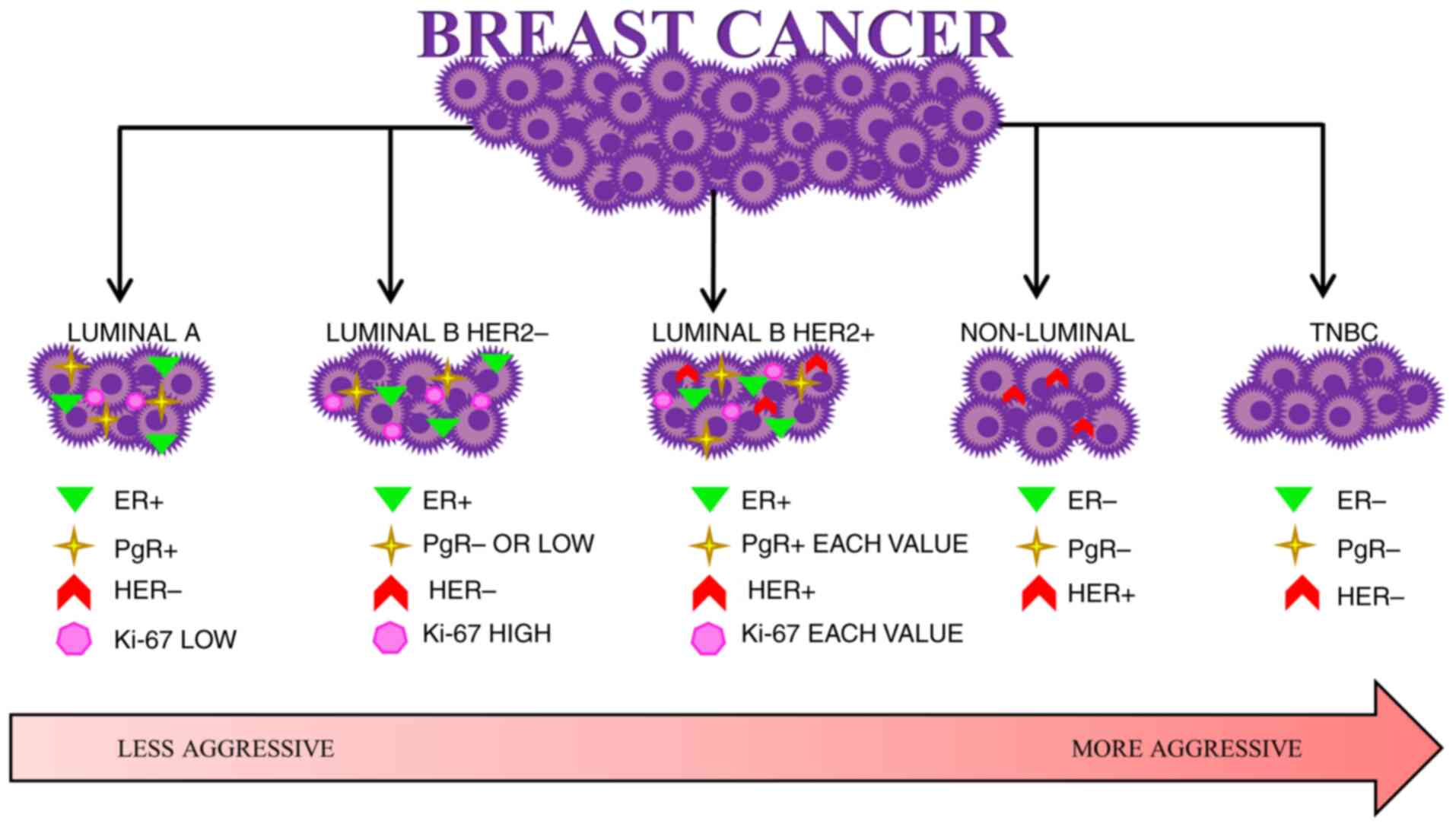
Gao JJ and Swain SM: Luminal A breast
cancer and molecular assays: A review. Oncologist. 23:556–565.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kudela E, Samec M, Koklesova L, Liskova A,
Kubatka P, Kozubik E, Rokos T, Pribulova T, Gabonova E, Smolar M
and Biringer K: MiRNA expression profiles in luminal A breast
cancer-implications in biology, prognosis, and prediction of
response to hormonal treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 21:76912020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wełnicka-Jaśkiewicz M: Zalecenia Dotyczące
Uzupełniającego Leczenia Chorych Na Wczesnego Raka Piersi
Sprawozdanie z 13. Międzynarodowej Konferencji w St. Gallen.
Nowotwory. J Oncol. 63:432–435. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Melitto AS, Arias VEA, Shida JY, Gebrim LH
and Silveira L Jr: Diagnosing molecular subtypes of breast cancer
by means of raman spectroscopy. Lasers Surg Med. 54:1143–1156.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mueller C, Haymond A, Davis JB, Williams A
and Espina V: Protein biomarkers for subtyping breast cancer and
implications for future research. Expert Rev Proteomics.
15:131–152. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yin L, Duan JJ, Bian XW and Yu S:
Triple-Negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment
progress. Breast Cancer Res. 22:612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Q, Li A, Tian Y, Wu JD, Liu Y, Li T,
Chen Y, Han X and Wu K: The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 31:61–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xiong X, Liao X, Qiu S, Xu H, Zhang S,
Wang S, Ai J and Yang L: CXCL8 in tumor biology and its
implications for clinical translation. Front Mol Biosci.
9:7238462022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bie Y, Ge W, Yang Z, Cheng X, Zhao Z, Li
S, Wang W, Wang Y, Zhao X, Yin Z and Li Y: The crucial role of
CXCL8 and its receptors in colorectal liver metastasis. Dis
Markers. 2019:80234602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Joseph PRB, Sawant KV and Rajarathnam K:
Heparin-Bound chemokine CXCL8 monomer and dimer are impaired for
CXCR1 and CXCR2 Activation: Implications for gradients and
neutrophil trafficking. Open Biol. 7:1701682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Waugh DJJ and Wilson C: The Interleukin-8
pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6735–6741. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han ZJ, Li YB, Yang LX, Cheng HJ, Liu X
and Chen H: Roles of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis in the tumor
microenvironment and immunotherapy. Molecules. 27:1372021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zha C, Meng X, Li L, Mi S, Qian D, Li Z,
Wu P, Hu S, Zhao S, Cai J and Liu Y: Neutrophil extracellular traps
mediate the crosstalk between glioma progression and the tumor
microenvironment via the HMGB1/RAGE/IL-8 Axis. Cancer Biol Med.
17:154–168. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liubomirski Y, Lerrer S, Meshel T,
Rubinstein-Achiasaf L, Morein D, Wiemann S, Körner C and Ben-Baruch
A: Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation networks promote pro-metastatic
chemokines and aggressiveness characteristics in triple-negative
breast cancer. Front Immunol. 10:7572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng X, Ji Z and Yang G: ASS1 Regulates
Immune Microenvironment via CXCL8 Signaling in Ovarian Cancer.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 631:86–92. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gonzalez-Aparicio M and Alfaro C:
Influence of interleukin-8 and neutrophil extracellular trap (NET)
formation in the tumor microenvironment: Is there a pathogenic
role? J Immunol Res. 2019:62521382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ospina-Muñoz N and Vernot JP: Partial
acquisition of stemness properties in tumorspheres obtained from
interleukin-8-treated MCF-7 cells. Tumour Biol.
42:10104283209794382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mishra A, Suman KH, Nair N, Majeed J and
Tripathi V: An updated review on the role of the CXCL8-CXCR1/2 axis
in the progression and metastasis of breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
48:6551–6561. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nie G, Cao X, Mao Y, Lv Z, Lv M, Wang Y,
Wang H and Liu C: Tumor-Associated Macrophages-Mediated CXCL8
infiltration enhances breast cancer metastasis: Suppression by
danirixin. Int Immunopharmacol. 95:1071532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cai Z, Zhang M, Boafo Kwantwi L, Bi X,
Zhang C, Cheng Z, Ding X, Su T, Wang H and Wu Q: Breast cancer
cells promote self-migration by secreting interleukin 8 to induce
NET Formation. Gene. 754:1449022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Todorović-Raković N and Milovanović J:
Interleukin-8 in breast cancer progression. J Interferon Cytokine
Res. 33:563–570. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benoy IH, Salgado R, Van Dam P, Geboers K,
Van Marck E, Scharpé S, Vermeulen PB and Dirix LY: Increased serum
interleukin-8 in patients with early and metastatic breast cancer
correlates with early dissemination and survival. Clin Cancer Res.
10:7157–7162. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Antonosante A, Brandolini L, d'Angelo M,
Benedetti E, Castelli V, Maestro MD, Luzzi S, Giordano A, Cimini A
and Allegretti M: Autocrine CXCL8-Dependent invasiveness triggers
modulation of actin cytoskeletal network and cell dynamics. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:1928–1951. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gales D, Clark C, Manne U and Samuel T:
The chemokine CXCL8 in carcinogenesis and drug response. ISRN
Oncol. 2013:8591542013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC),
. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer; 2017
|
|
39
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zare Moaiedi M, Ahmadpoor F, Rashidi M,
Ahmadzadeh A, Salmasi AA and Mohammadzadeh G: The Association
between MRNA Expression of Resistin, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8, and ER-α in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells and breast cancer. Turk J Med
Sci. 51:1345–1353. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Snoussi K, Mahfoudh W, Bouaouina N, Fekih
M, Khairi H, Helal AN and Chouchane L: Combined Effects of IL-8 and
CXCR2gene polymorphisms on breast cancer susceptibility and
aggressiveness. BMC Cancer. 10:2832010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Motyka J, Gacuta E, Kicman A, Kulesza M,
Ławicki P and Ławicki S: Plasma levels of CXC motif chemokine 1
(CXCL1) and chemokine 8 (CXCL8) as diagnostic biomarkers in Luminal
A and B breast cancer. J Clin Med. 11:66942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang J, He Q, Shao YG and Ji M: Chemokines
fluctuate in the progression of primary breast cancer. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 17:596–608. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Amante RJ, Auf Der Maur P, Richina V,
Sethi A, Iesmantavicius V, Bonenfant D, Aceto N and Bentires-Alj M:
Protein tyrosine phosphatase shp2 controls interleukin-8 expression
in breast cancer cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 27:145–153.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Messeha SS, Zarmouh NO, Mendonca P, Cotton
C and Soliman KFA: Molecular mechanism of gossypol mediating CCL2
and IL-8 attenuation in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Mol
Med Rep. 22:1213–1226. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Erlichman N, Baram T, Meshel T, Morein D,
Da'adoosh B and Ben-Baruch A: Tumor cell-autonomous pro-metastatic
activities of PD-L1 in human breast cancer are mediated by
PD-L1-S283 and chemokine axes. Cancers (Basel). 14:10422022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Molczyk C and Singh RK: CXCR1: A cancer
stem cell marker and therapeutic target in solid tumors.
Biomedicines. 11:5762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xue MQ, Liu J, Sang JF, Su L and Yao YZ:
Expression characteristic of CXCR1 in different breast tissues and
the relevance between its expression and efficacy of neo-adjuvant
chemotherapy in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:48930–48937. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Guo F, Long L, Wang J, Wang Y, Liu Y, Wang
L and Luo F: Insights on CXC chemokine receptor 2 in breast cancer:
An emerging target for oncotherapy. Oncol Lett. 18:5699–5708.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Romero-Moreno R, Curtis KJ, Coughlin TR,
Miranda-Vergara MC, Dutta S, Natarajan A, Facchine BA, Jackson KM,
Nystrom L, Li J, et al: The CXCL5/CXCR2 Axis is sufficient to
promote breast cancer colonization during bone metastasis. Nat
Commun. 10:44042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Boissière-Michot F, Jacot W, Fraisse J,
Gourgou S, Timaxian C and Lazennec G: Prognostic value of CXCR2 in
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 12:20762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Vazquez ED, Fang X, Levesque LA, Huynh M,
Venegas C, Lu N and Salazar N: Chemokine receptors differentially
expressed by race category and molecular subtype in the breast
cancer TCGA Cohort. Sci Rep. 12:108252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Olsen KS, Holden M, Thalabard JC,
Rasmussen Busund LT, Lund E and Holden L: Global blood gene
expression profiles following a breast cancer diagnosis-clinical
follow-up in the NOWAC post-genome cohort. PLoS One.
16:e02466502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Delgado AB, Tylden ES, Lukic M, Moi L,
Busund LR, Lund E and Olsen KS: Cohort profile: The clinical and
multi-omic (CAMO) cohort, part of the norwegian women and cancer
(NOWAC) study. PLoS One. 18:e02812182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|