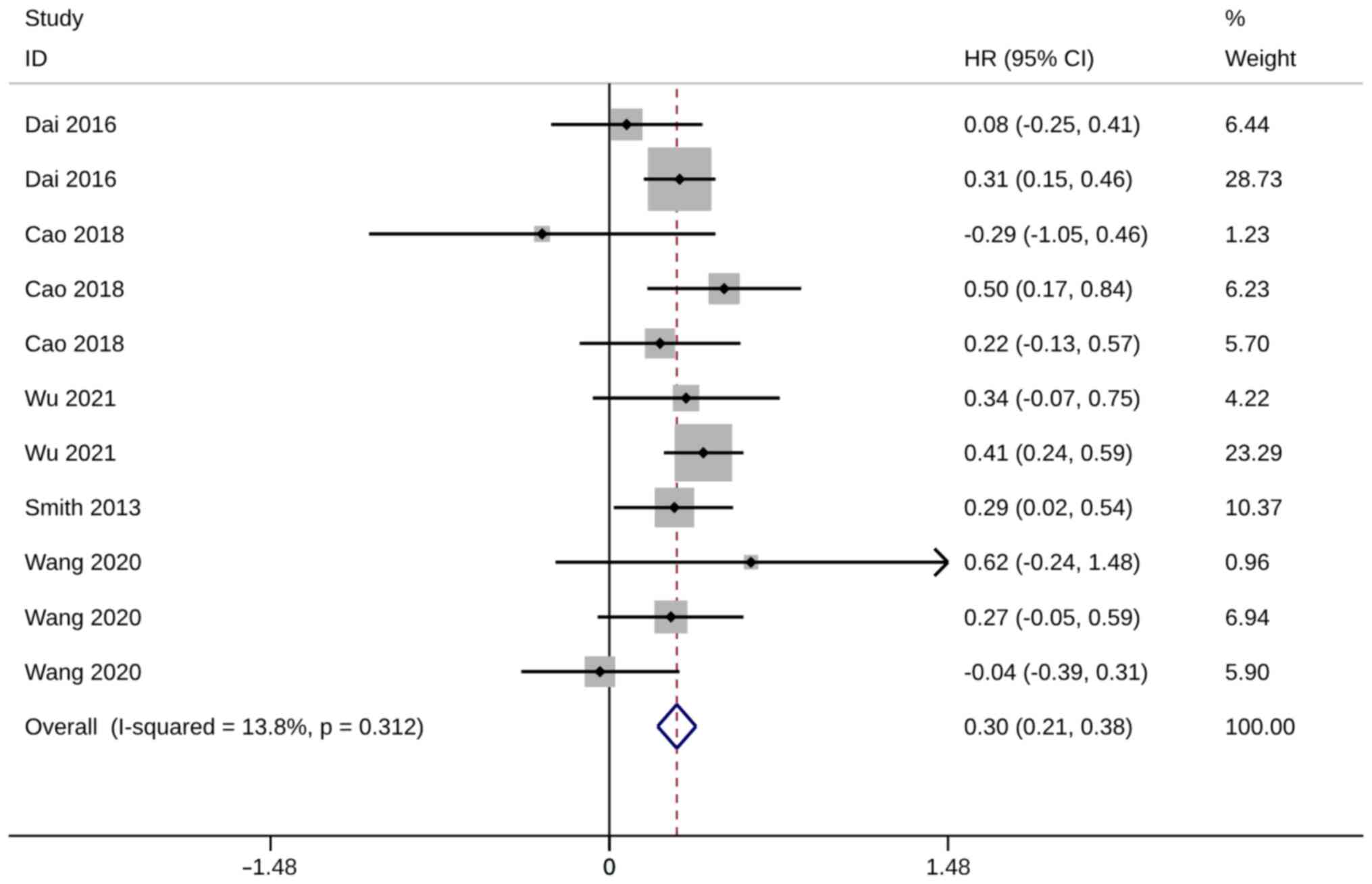
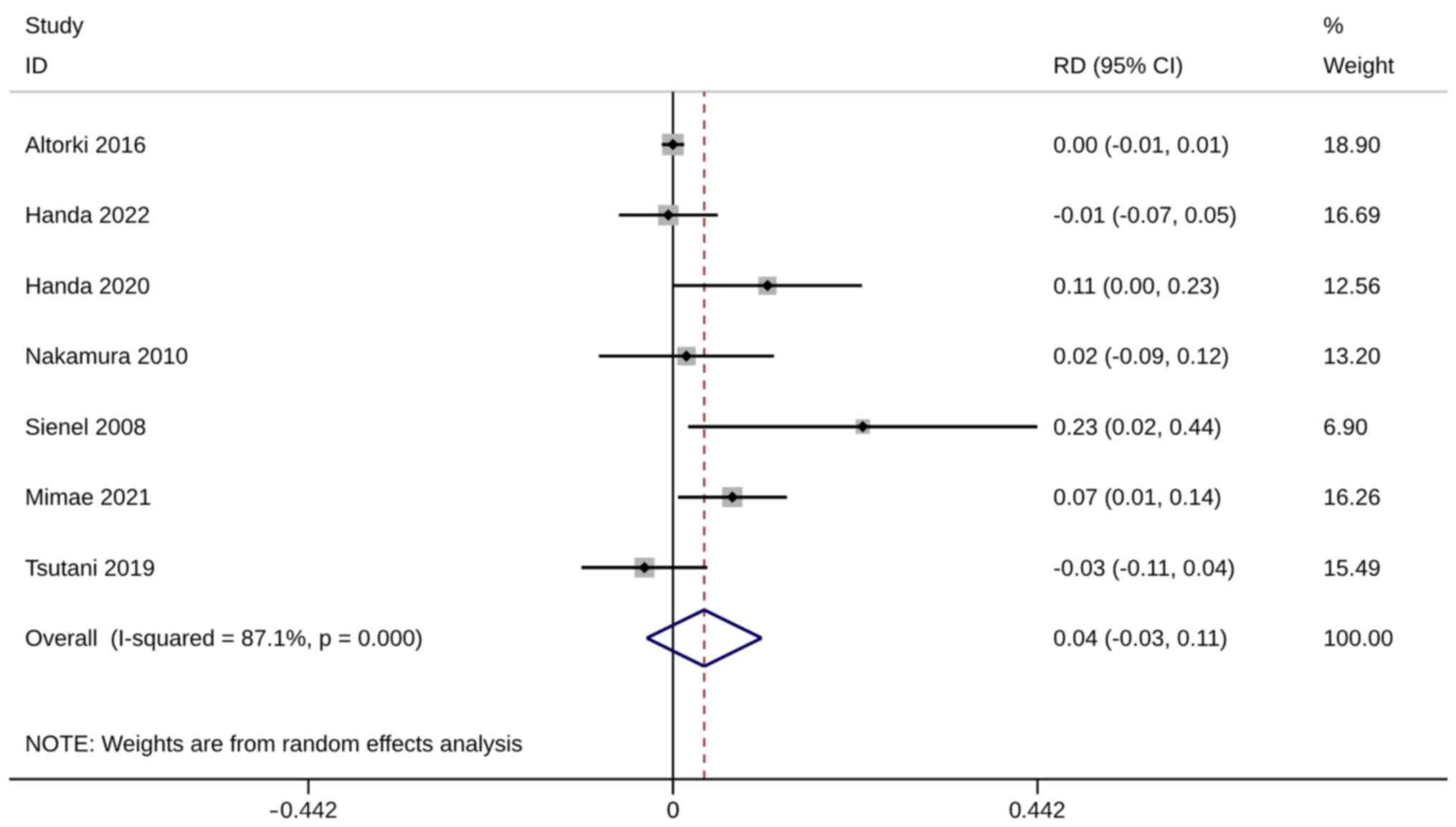
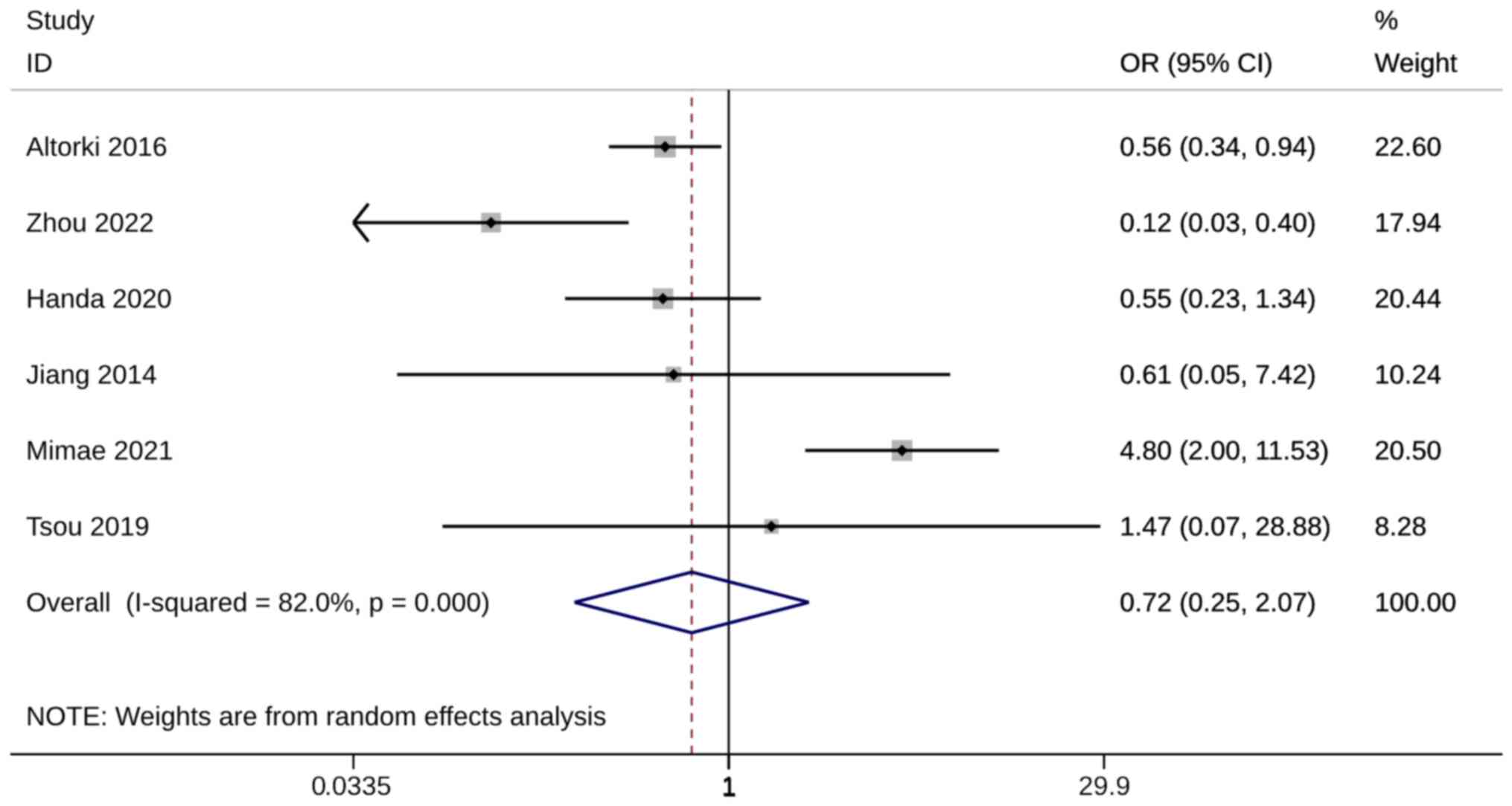
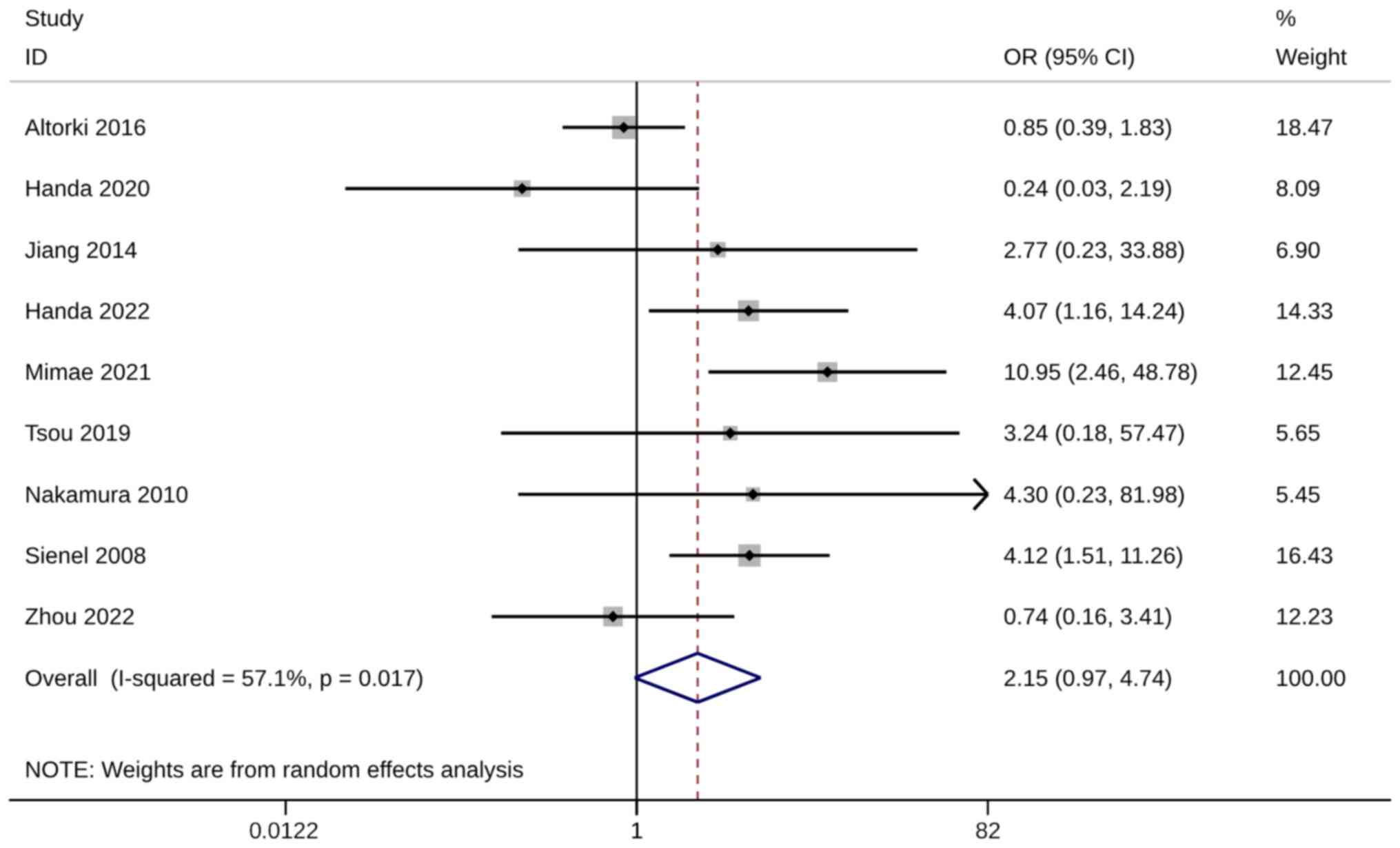
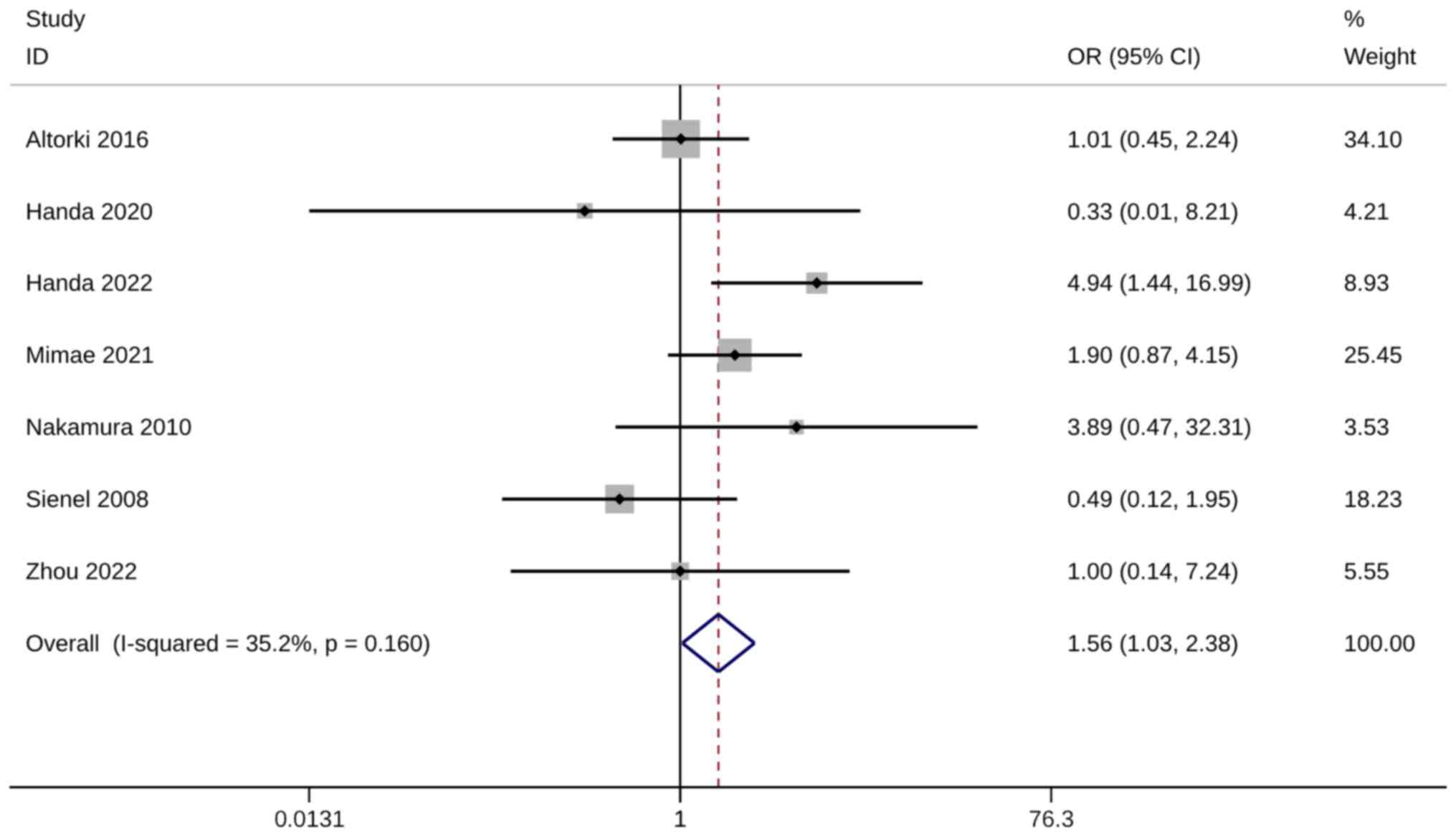
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forquer JA, Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Cheung
MK, Watson C, Harkenrider M, Henderson MA and Lo SS: Treatment
options for stage I non-small-cell lung carcinoma patients not
suitable for lobectomy. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 9:1443–1153.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scott WJ, Howington J, Feigenberg S,
Movsas B and Pisters K; American College of Chest Physicians, :
Treatment of non-small cell lung cancer stage I and stage II: ACCP
evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (2nd edition). Chest.
132 (Suppl):S234–S242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nakamura H, Kazuyuki S, Kawasaki N,
Taguchi M and Kato H: History of limited resection for non-small
cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 11:356–362.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martini N, Bains MS, Burt ME, Zakowski MF,
McCormack P, Rusch VW and Ginsberg RJ: Incidence of local
recurrence and second primary tumors in resected stage I lung
cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 109:120–129. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jatoi A, Schild SE, Foster N, Henning GT,
Dornfeld KJ, Flynn PJ, Fitch TR, Dakhil SR, Rowland KM, Stella PJ,
et al: A phase II study of cetuximab and radiation in elderly
and/or poor performance status patients with locally advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (N0422). Ann Oncol. 21:2040–2044. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heiden BT, Eaton DB Jr, Engelhardt KE,
Chang SH, Yan Y, Patel MR, Kreisel D, Nava RG, Meyers BF, Kozower
BD and Puri V: Analysis of delayed surgical treatment and oncologic
outcomes in clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Netw
Open. 4:e21116132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Celli JP, Spring BQ, Rizvi I, Evans CL,
Samkoe KS, Verma S, Pogue BW and Hasan T: Imaging and photodynamic
therapy: Mechanisms, monitoring, and optimization. Chem Rev.
110:2795–2838. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cao C, Gupta S, Chandrakumar D, Tian DH,
Black D and Yan TD: Meta-analysis of intentional sublobar
resections versus lobectomy for early stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 3:134–141. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hou B, Deng XF, Zhou D, Liu QX and Dai JG:
Segmentectomy versus wedge resection for the treatment of high-risk
operable patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer: A
meta-analysis. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 10:435–443. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding H, Song N, Zhang P, Jiang G and Wang
H: Wedge resection plus adequate lymph nodes resection is
comparable to lobectomy for small-sized non-small cell lung cancer.
Front Oncol. 12:10229042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Detterbeck FC, Mase VJ Jr, Li AX, Kumbasar
U, Bade BC, Park HS, Decker RH, Madoff DC, Woodard GA, Brandt WS
and Blasberg JD: A guide for managing patients with stage I NSCLC:
Deciding between lobectomy, segmentectomy, wedge, SBRT and
ablation-part 2: Systematic review of evidence regarding resection
extent in generally healthy patients. J Thorac Dis. 14:2357–2386.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ding H, Wang H, Xu L, Song N and Jiang G:
Survival and resected lymph node number during sublobar resection
for n0 non-small cell lung cancer 2 cm or less. Ann Thorac Surg.
107:1647–1655. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tsutani Y, Miyata Y, Nakayama H, Okumura
S, Adachi S, Yoshimura M and Okada M: Appropriate sublobar
resection choice for ground glass opacity-dominant clinical stage
IA lung adenocarcinoma: Wedge resection or segmentectomy. Chest.
145:66–71. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fiorelli A, Caronia FP, Daddi N, Loizzi D,
Ampollini L, Ardò N, Ventura L, Carbognani P, Potenza R and
Ardissone F: Sublobar resection versus lobectomy for stage I
non-small cell lung cancer: An appropriate choice in elderly
patients? Surg Today. 46:1370–1382. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hamatake D, Yoshida Y, Miyahara S,
Yamashita S, Shiraishi T and Iwasaki A: Surgical outcomes of lung
cancer measuring less than 1 cm in diameter. Interact Cardiovasc
Thorac Surg. 15:854–858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kent MS, Mandrekar SJ, Landreneau R,
Nichols F, Foster NR, DiPetrillo TA, Meyers B, Heron DE, Jones DR,
Tan AD, et al: A nomogram to predict recurrence and survival of
high-risk patients undergoing sublobar resection for lung cancer:
An analysis of a multicenter prospective study (ACOSOG Z4032). Ann
Thorac Surg. 102:239–246. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
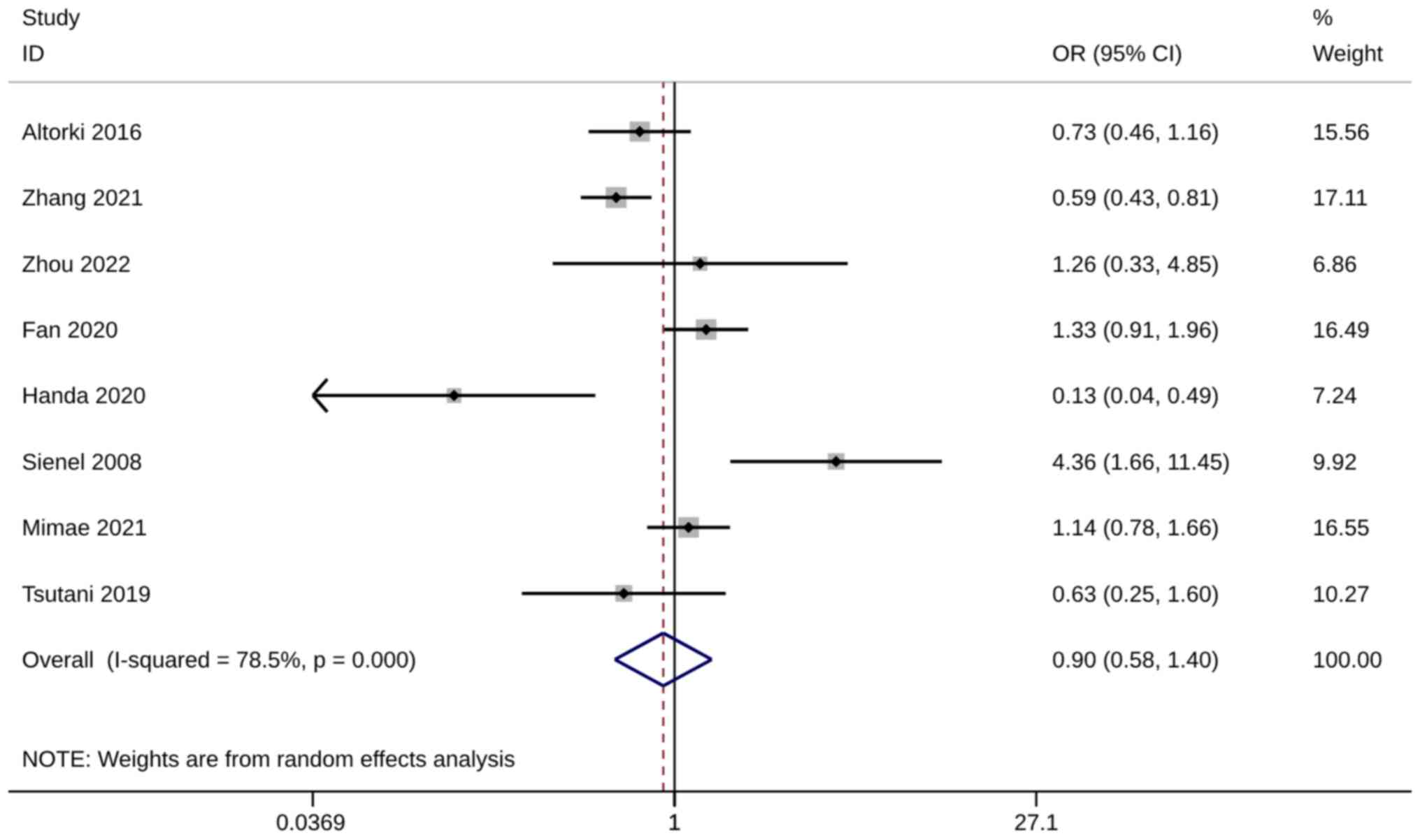
Zhang H, Liu C, Tan Z and Zhang T:
Segmentectomy versus wedge resection for stage I non-small cell
lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J Surg Res. 243:371–379. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Lin G and Li J: Comparative
effectiveness of lobectomy, segmentectomy, and wedge resection for
pathological stage I non-small cell lung cancer in elderly
patients: A population-based study. Front Surg. 8:6527702021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
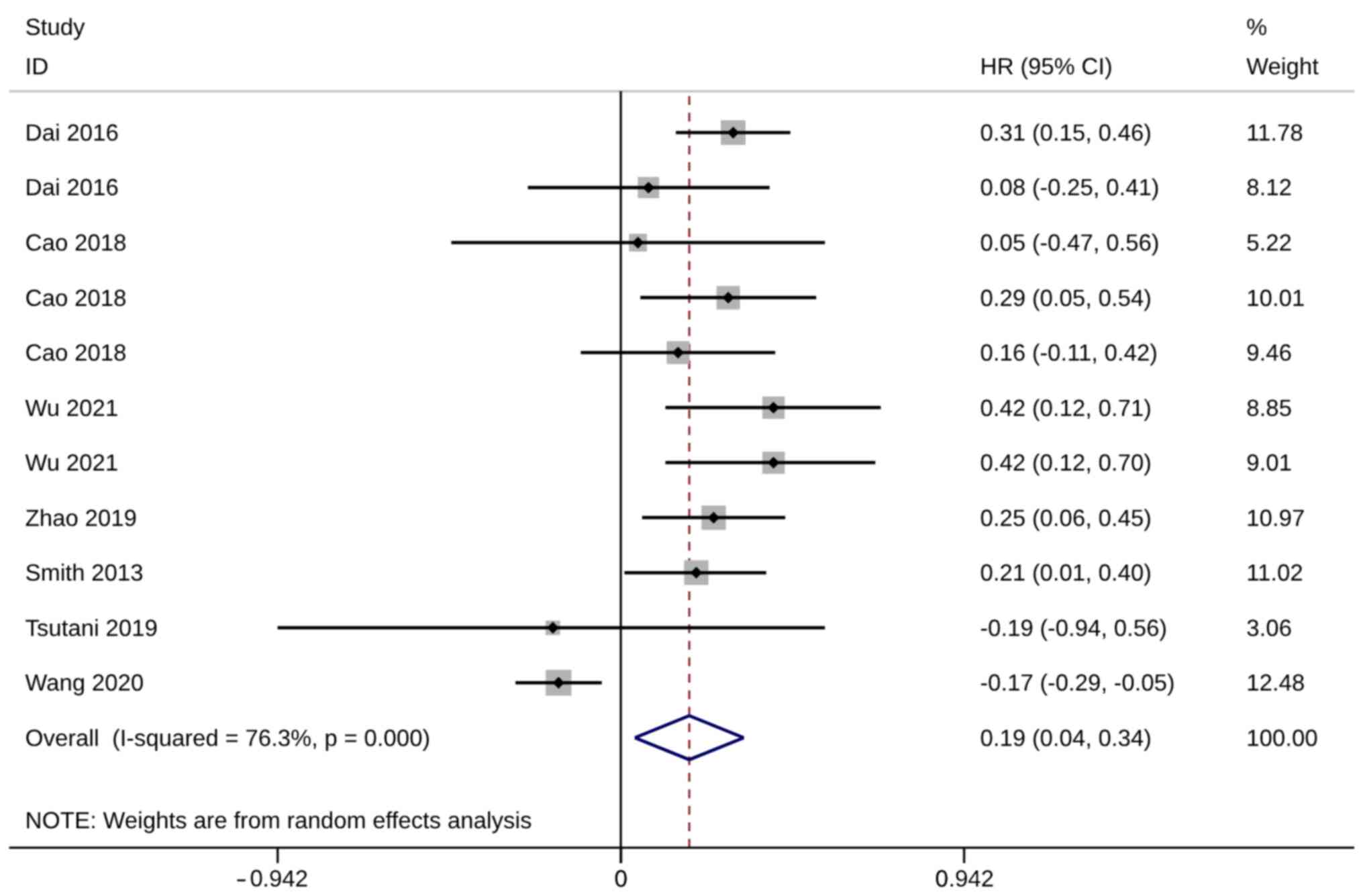
Wang W, Sun Y, Li H, Bao M, Liu X, Jiang
G, Ye C and Hu Y: Surgical modality for stage IA non-small cell
lung cancer among the elderly: Analysis of the surveillance,
epidemiology, and end results database. J Thorac Dis. 12:6731–6742.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
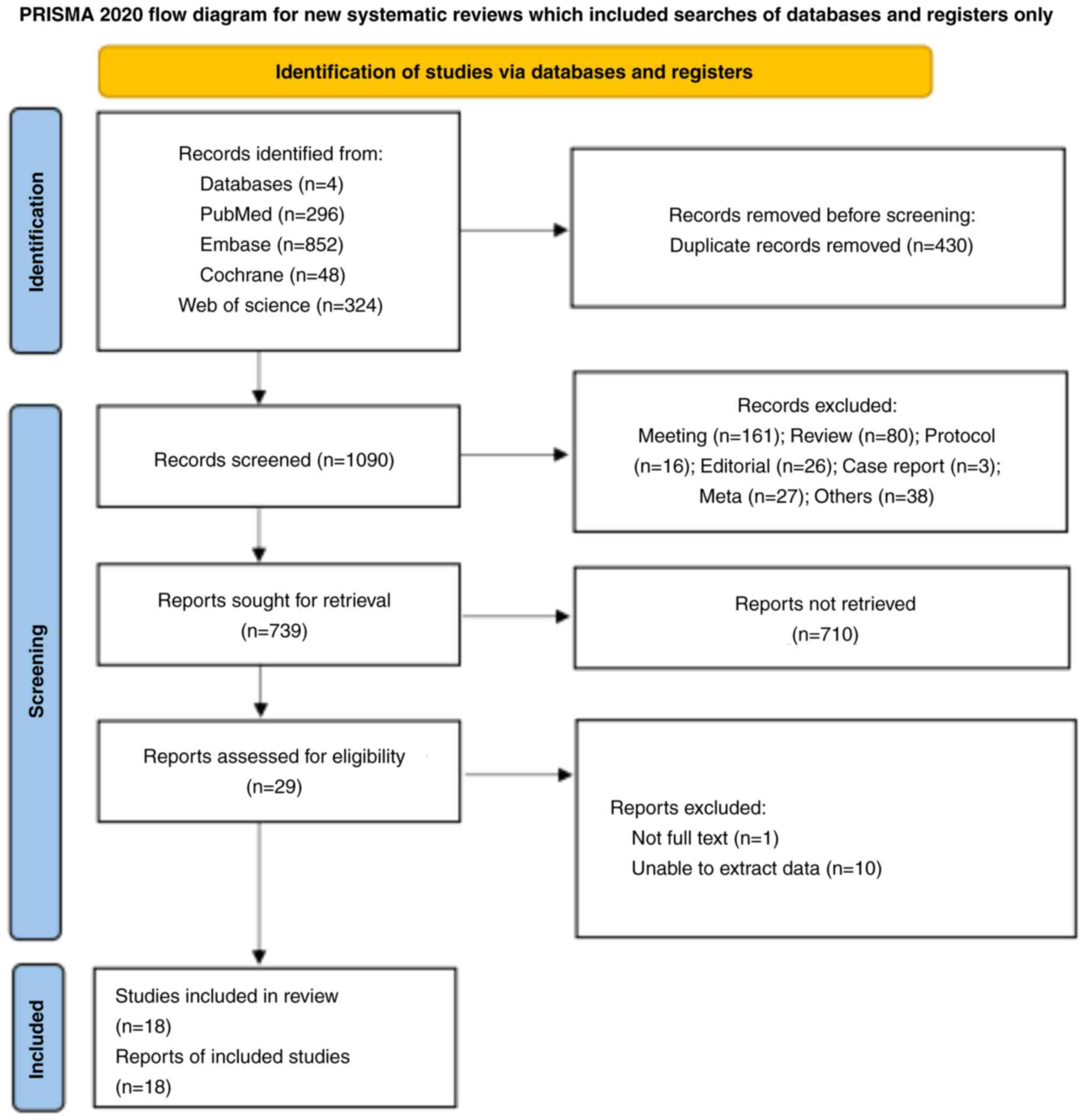
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Aslam S and Emmanuel P: Formulating a
researchable question: A critical step for facilitating good
clinical research. Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS. 31:47–50. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sterne JA, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović
J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT,
Boutron I, et al: ROBINS-I: A tool for assessing risk of bias in
non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ. 355:i49192016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
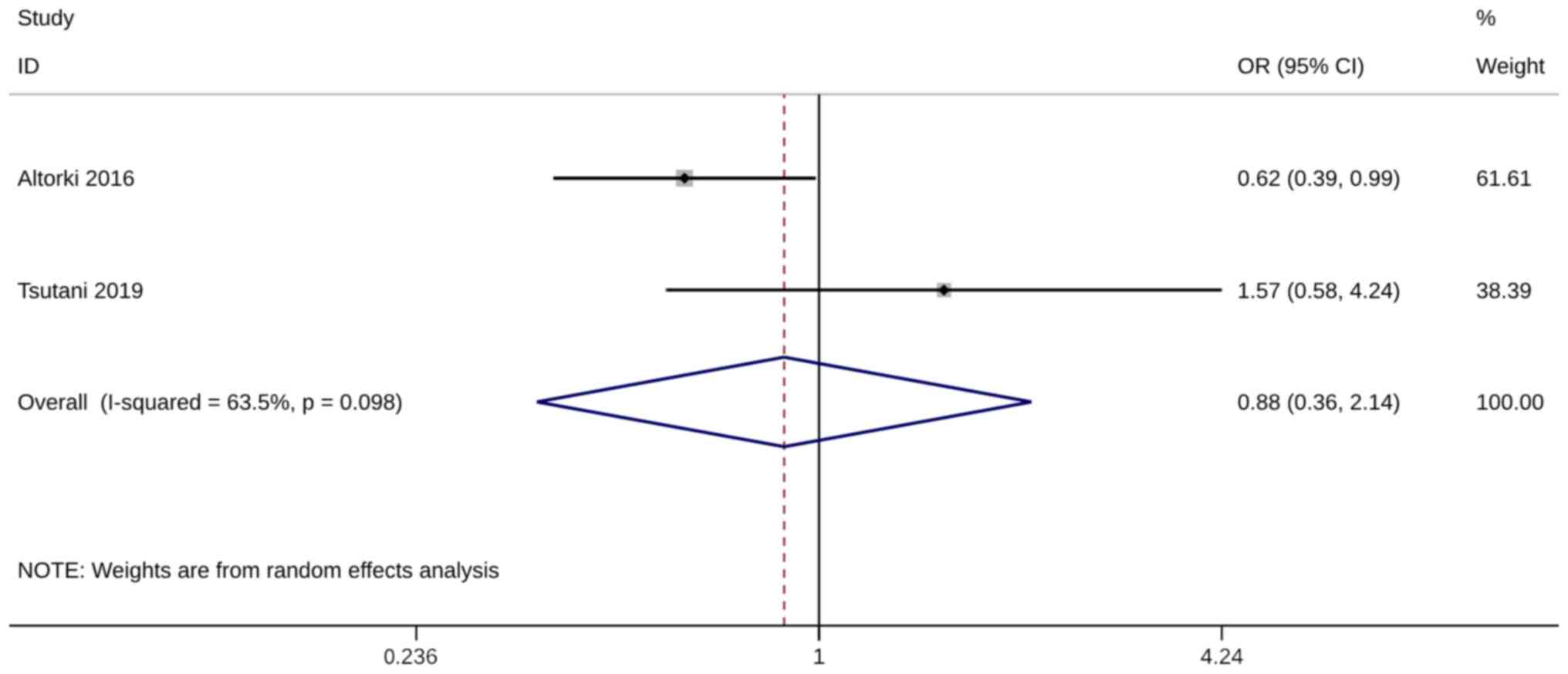
Altorki NK, Kamel MK, Narula N, Ghaly G,
Nasar A, Rahouma M, Lee PC, Port JL and Stiles BM: Anatomical
segmentectomy and wedge resections are associated with comparable
outcomes for patients with small cT1N0 non-small cell lung cancer.
J Thorac Oncol. 11:1984–1992. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cao J, Yuan P, Wang Y, Xu J, Yuan X, Wang
Z, Lv W and Hu J: Survival rates after lobectomy, segmentectomy,
and wedge resection for non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac
Surg. 105:1483–1491. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai C, Shen J, Ren Y, Zhong S, Zheng H, He
J, Xie D, Fei K, Liang W, Jiang G, et al: Choice of surgical
procedure for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer ≤1 cm or
>1 to 2 cm among lobectomy, segmentectomy, and wedge resection:
A population-based study. J Clin Oncol. 34:3175–3182. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fan X, Liang Y, Bai Y, Yang C and Xu S:
Conditional survival rate estimates of lobectomy, segmentectomy and
wedge resection for stage IA1 non-small cell lung cancer: A
population-based study. Oncol Lett. 20:1607–1618. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Handa Y, Tsutani Y, Mimae T, Miyata Y,
Shimada Y, Ito H, Nakayama H, Ikeda N and Okada M: A multicenter
study of complex segmentectomy versus wedge resection in clinical
stage 0-IA non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer.
23:393–401. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Handa Y, Tsutani Y, Mimae T, Miyata Y and
Okada M: Surgical procedure selection for stage I lung cancer:
Complex segmentectomy versus wedge resection. Clin Lung Cancer.
22:e224–e233. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang W, Pang X, Xi J, Chen X, Wang Q,
Qian C and Fan H: Clinical outcome of subcentimeter non-small cell
lung cancer after surgical resection: Single institution experience
of 105 patients. J Surg Oncol. 110:233–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nakamura H, Taniguchi Y, Miwa K, Adachi Y,
Fujioka S, Haruki T, Takagi Y and Yurugi Y: Comparison of the
surgical outcomes of thoracoscopic lobectomy, segmentectomy, and
wedge resection for clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer.
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 59:137–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sienel W, Dango S, Kirschbaum A, Cucuruz
B, Hörth W, Stremmel C and Passlick B: Sublobar resections in stage
IA non-small cell lung cancer: Segmentectomies result in
significantly better cancer-related survival than wedge resections.
Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 33:728–734. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smith CB, Swanson SJ, Mhango G and
Wisnivesky JP: Survival after segmentectomy and wedge resection in
stage I non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 8:73–78. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tsou KC, Hsu HH, Tsai TM, Chen KC and Chen
JS: Clinical outcome of subcentimeter non-small cell lung cancer
after VATS resection: Single institute experience with 424
patients. J Formos Med Assoc. 119:399–405. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsutani Y, Kagimoto A, Handa Y, Mimae T,
Miyata Y and Okada M: Wedge resection versus segmentectomy in
patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer unfit for
lobectomy. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 49:1134–1142. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wu L, Zhao W, Chen T and Yang Y: Surgical
choice for patients with stage I non-small-cell lung cancer ≤2 cm:
An analysis from surveillance, epidemiology, and end results
database. J Cardiothorac Surg. 16:1912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Y, Yu T, Zhang Y, Qian L and Xia Q:
Comparison of surgical outcomes and prognosis between wedge
resection and simple Segmentectomy for GGO diameter between 2 cm
and 3 cm in non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter and
propensity score matching analysis. BMC Cancer. 22:712022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mimae T, Saji H, Nakamura H, Okumura N,
Tsuchida M, Sonobe M, Miyazaki T, Aokage K, Nakao M, Haruki T, et
al: Survival of octogenarians with early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer is comparable between wedge resection and
lobectomy/segmentectomy: JACS1303. Ann Surg Oncol. 28:7219–7227.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhao M, Lu T, Huang Y, Yin J, Jiang T, Li
M, Yang X, Zhan C, Feng M and Wang Q: Survival and long-term
cause-specific mortality associated with stage IA lung
adenocarcinoma after wedge resection vs. segmentectomy: A
population-based propensity score matching and competing risk
analysis. Front Oncol. 9:5932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley
W, Bauman J, Chirieac LR, D'Amico TA, DeCamp MM, Dilling TJ,
Dobelbower M, et al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 5.2017,
NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 15:504–535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi Y, Wu S, Ma S, Lyu Y, Xu H, Deng L and
Chen X: Comparison between wedge resection and
lobectomy/segmentectomy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer:
A bayesian meta-analysis and systematic review. Ann Surg Oncol.
29:1868–1879. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hoebeke PB, Rottey S, Van Heddeghem N,
Villeirs G, Pauwels P, Schrauwen W, Ceulemans P and Monstrey S:
One-stage penectomy and phalloplasty for epithelioid sarcoma of the
penis in an adolescent: Part 2. Eur Urol. 51:1744–1747. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stish BJ, Hallemeier CL, Olivier KR,
Harmsen WS, Allen MS and Garces YI: Long-term outcomes and patterns
of failure after surgical resection of small-cell lung cancer. Clin
Lung Cancer. 16:e67–e73. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S and
Yendamuri S: Evaluation of microRNA expression profiles that may
predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer
after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 70:36–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wu Y, Han C, Wang Z, Gong L, Liu J, Chong
Y, Liu X, Liang N and Li S: An externally-validated dynamic
nomogram based on clinicopathological characteristics for
evaluating the risk of lymph node metastasis in small-size
non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol. 10:13222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Altorki NK, Yip R, Hanaoka T, Bauer T, Aye
R, Kohman L, Sheppard B, Thurer R, Andaz S, Smith M, et al:
Sublobar resection is equivalent to lobectomy for clinical stage 1A
lung cancer in solid nodules. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
147:754–762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sato M, Kobayashi M, Kojima F, Tanaka F,
Yanagiya M, Kosaka S, Fukai R and Nakajima J: Effect of
virtual-assisted lung mapping in acquisition of surgical margins in
sublobar lung resection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
156:1691–1701.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kadota K, Nitadori JI, Sima CS, Ujiie H,
Rizk NP, Jones DR, Adusumilli PS and Travis WD: Tumor spread
through air spaces is an important pattern of invasion and impacts
the frequency and location of recurrences after limited resection
for small stage I lung adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 10:806–814.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tsutani Y, Handa Y, Shimada Y, Ito H,
Ikeda N, Nakayama H, Yoshimura K and Okada M: Comparison of cancer
control between segmentectomy and wedge resection in patients with
clinical stage IA non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 162:1244–1252.e1. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Suzuki K, Watanabe SI, Wakabayashi M, Saji
H, Aokage K, Moriya Y, Yoshino I, Tsuboi M, Nakamura S, Nakamura K,
et al: A single-arm study of sublobar resection for ground-glass
opacity dominant peripheral lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
163:289–301.e2. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
He Z, Li Z, Xu S, Wu W, Zhu Q, Wang J, Wen
W and Chen L: Prognostic significance of lymph node count removed
at sublobar resection in pathologic stage IA non-small-cell lung
cancer: A population-based analysis. Clin Lung Cancer. 22:e563–e73.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Baig MZ, Razi SS, Stroever S, Weber JF,
Connery CP and Bhora FY: Anatomic resection has superior long-term
survival compared with wedge resection for second primary lung
cancer after prior lobectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
59:1014–1020. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|