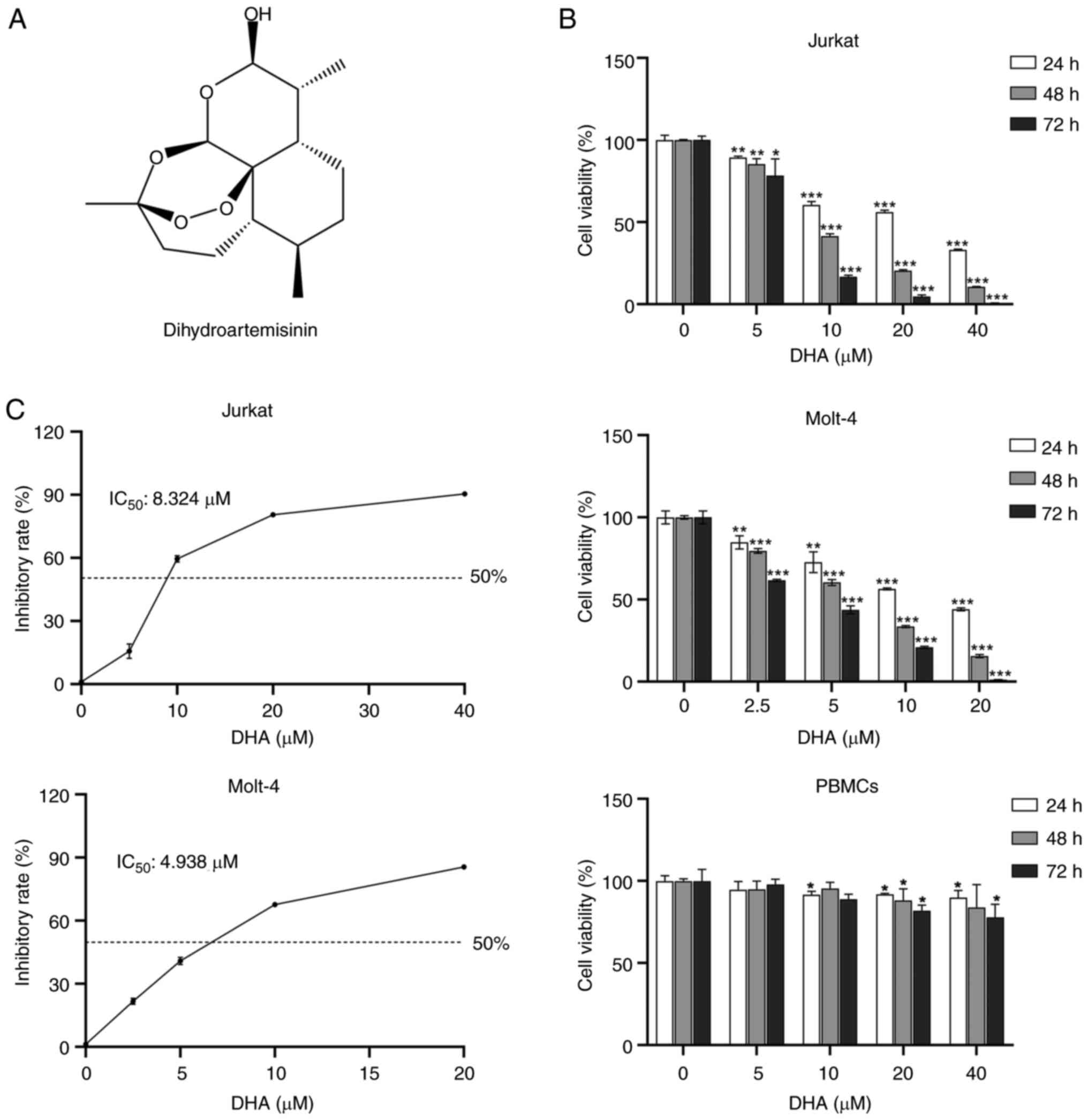
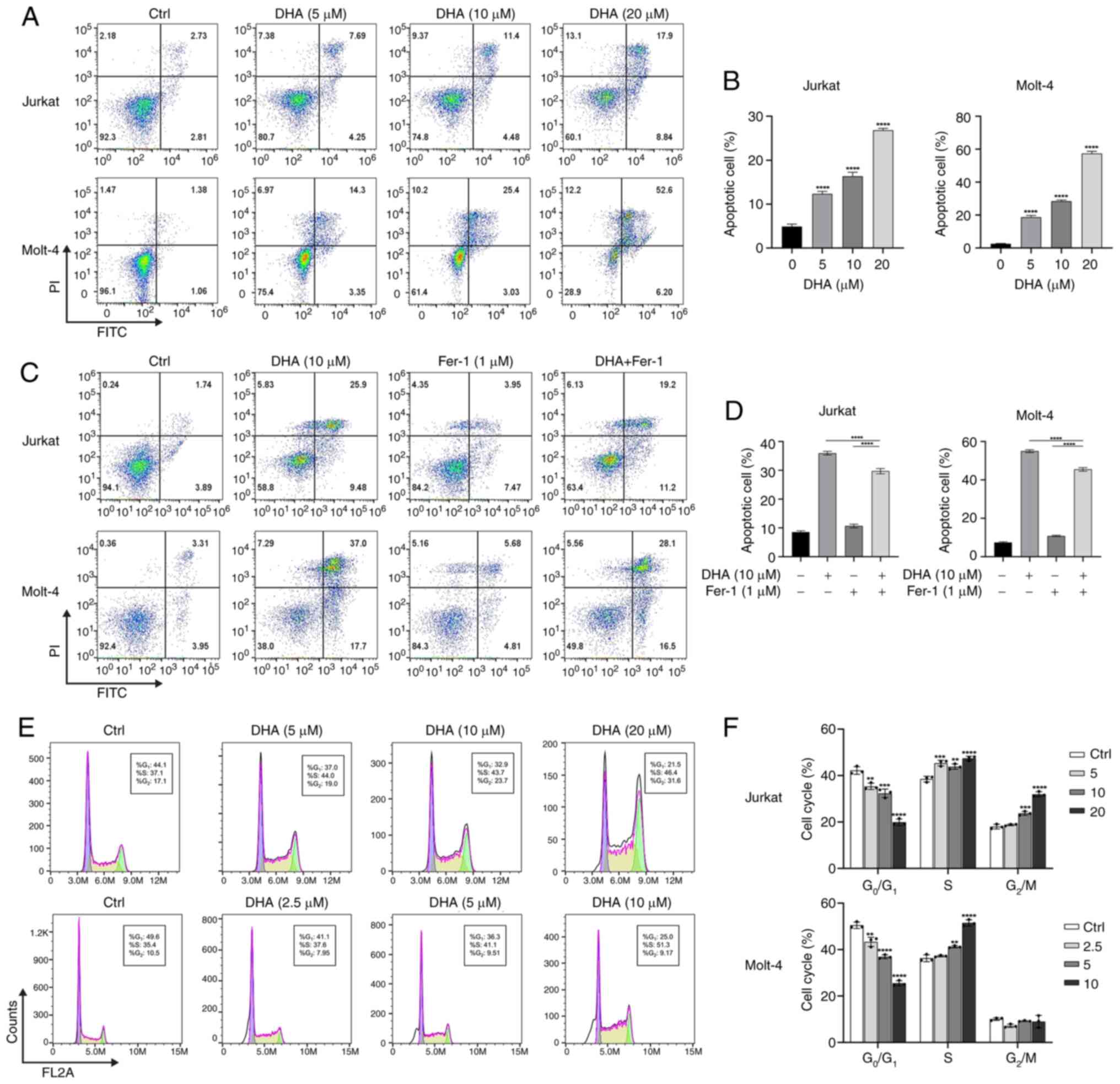
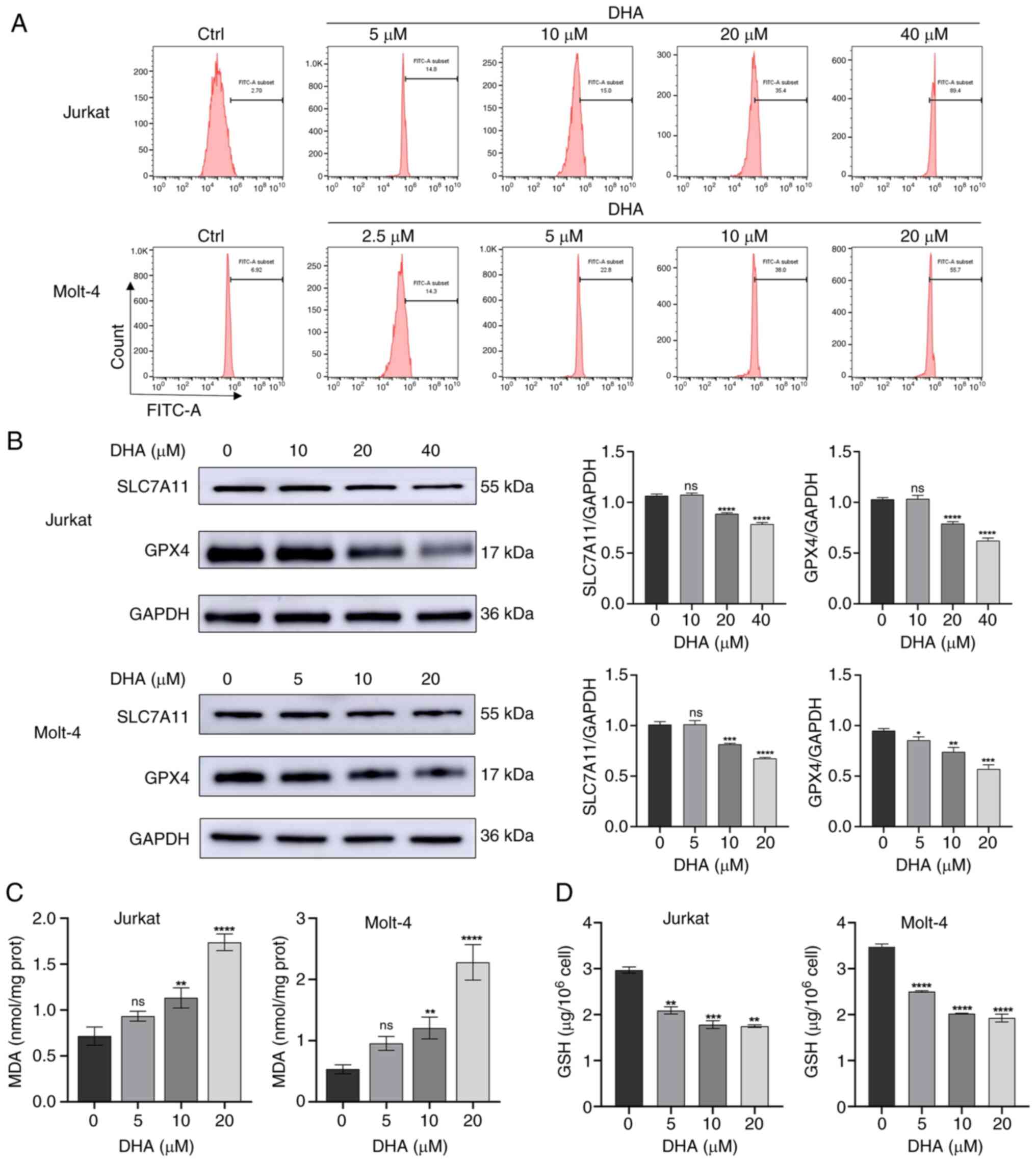
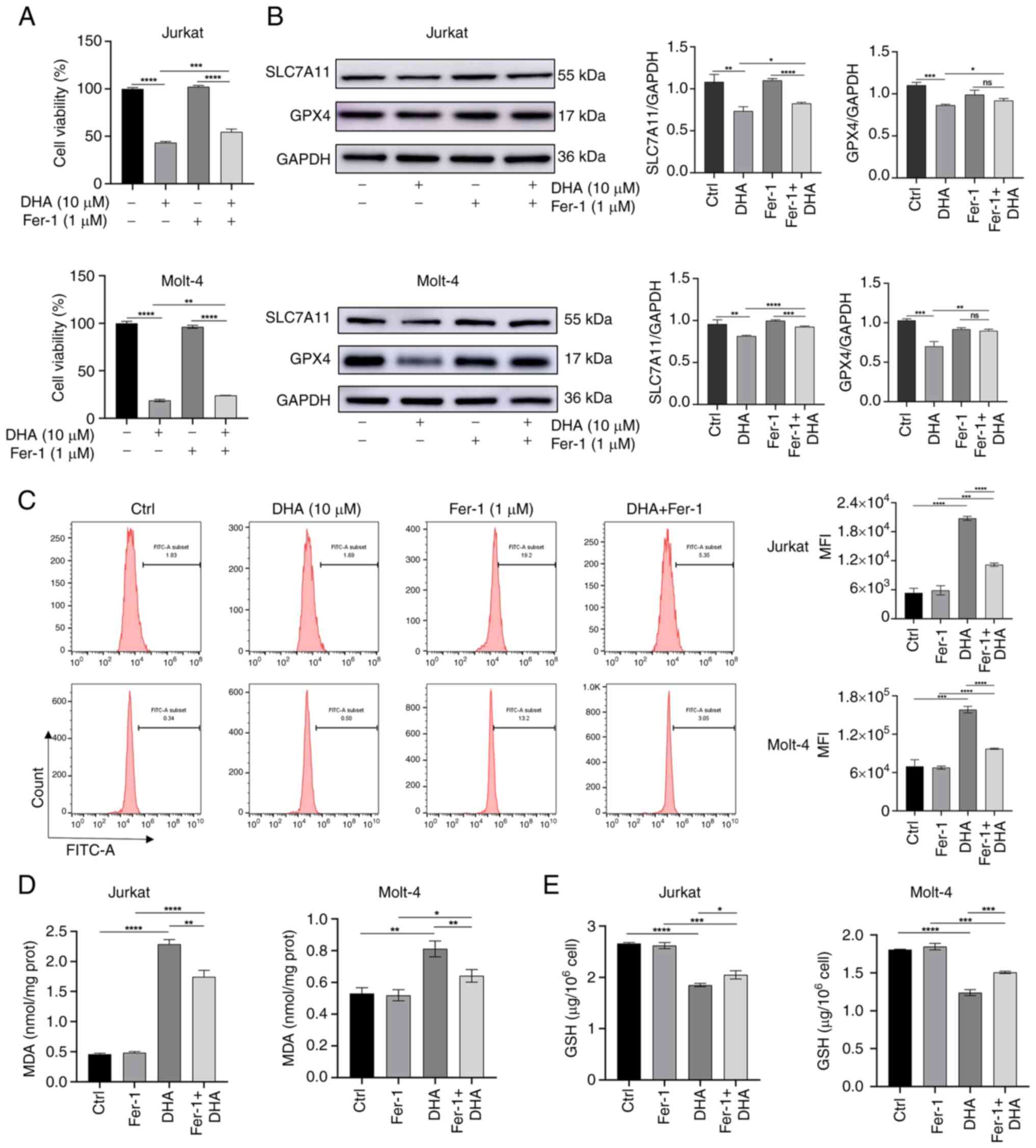
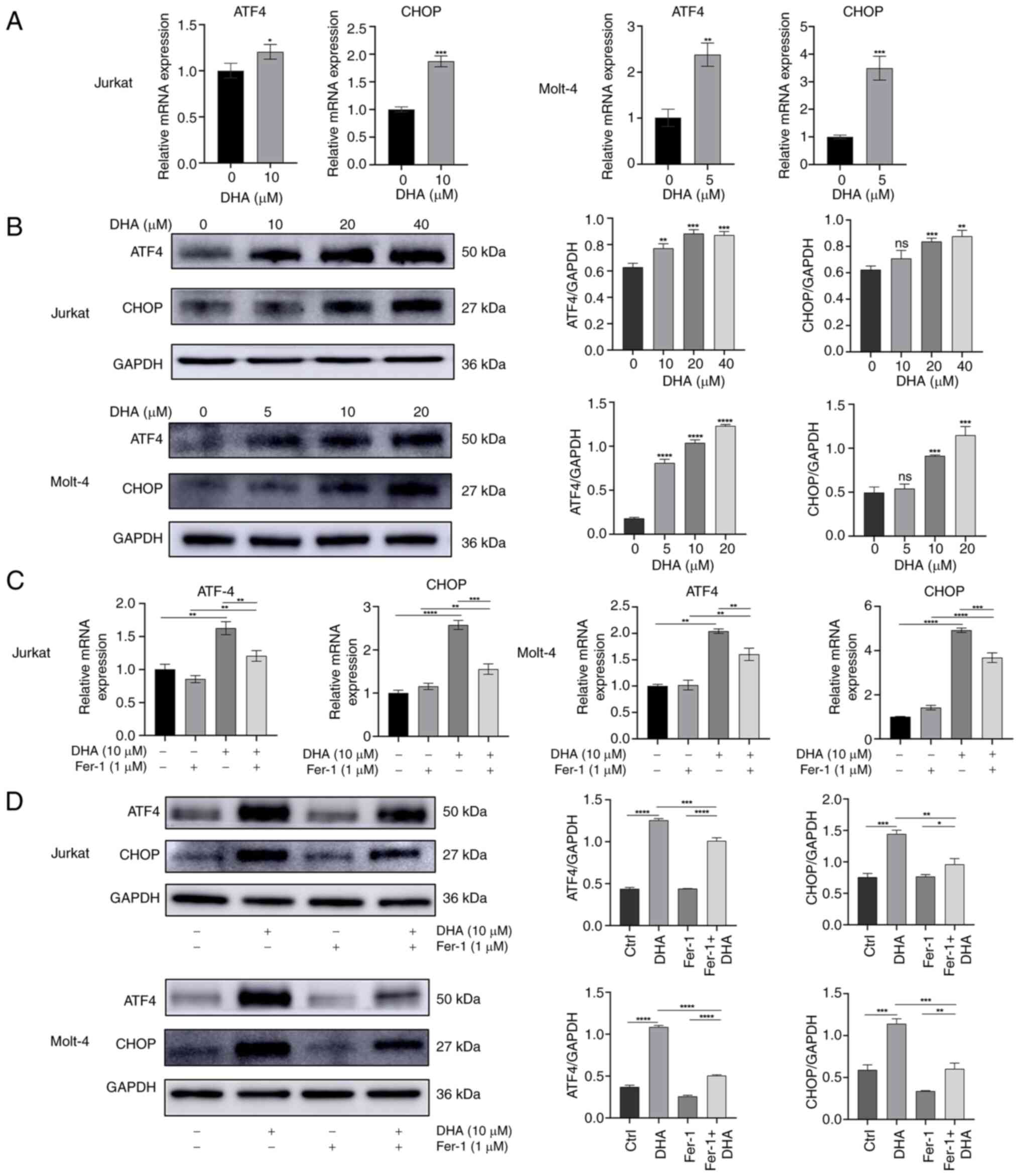
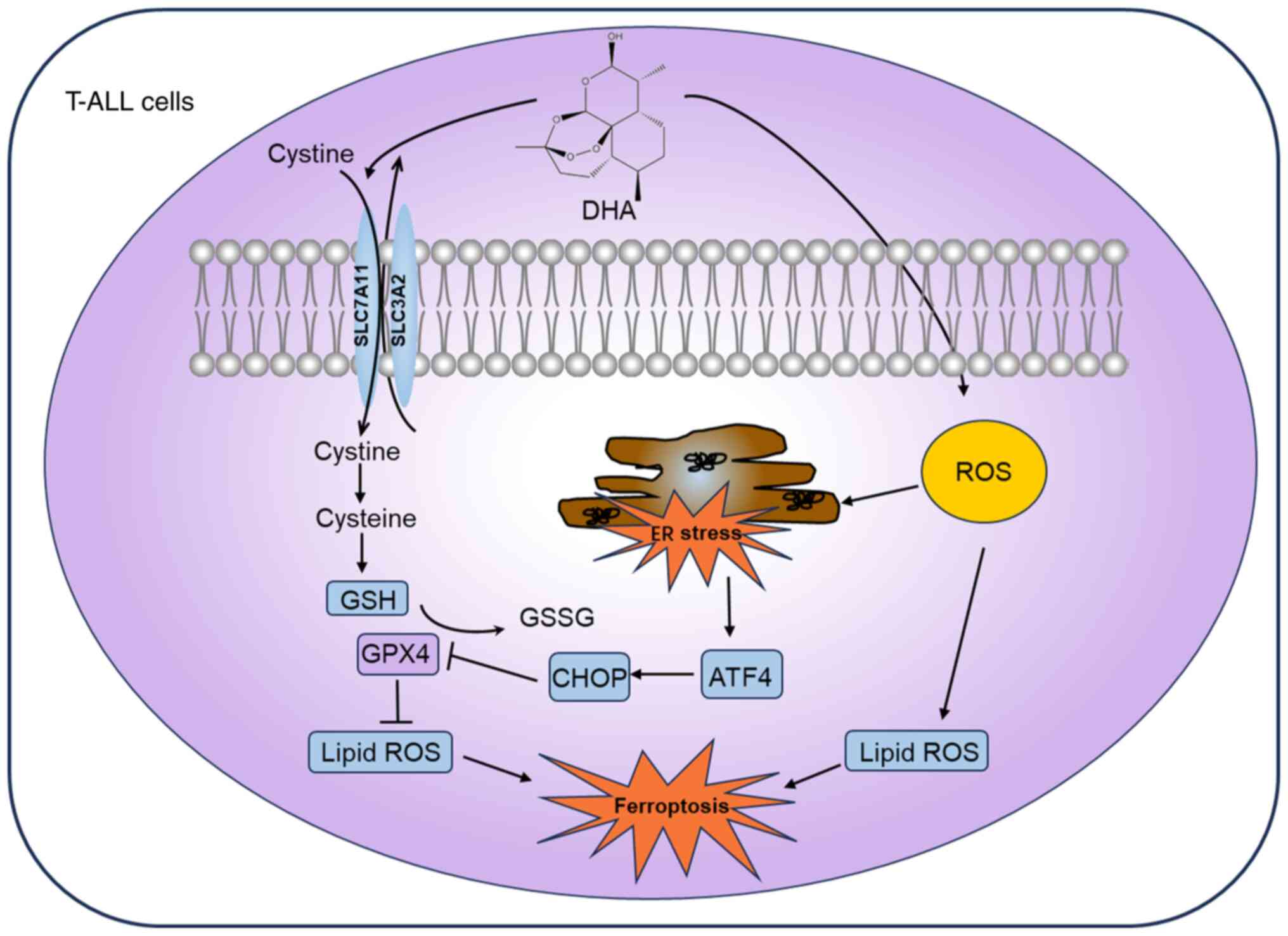
|
1
|
Belver L and Ferrando A: The genetics and
mechanisms of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nat Rev Cancer.
16:494–507. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vadillo E, Dorantes-Acosta E, Pelayo R and
Schnoor M: T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL): New
insights into the cellular origins and infiltration mechanisms
common and unique among hematologic malignancies. Blood Rev.
32:36–51. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raetz EA and Teachey DT: T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
2016:580–588. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Newman DJ, Cragg GM and Snader KM: Natural
products as sources of new drugs over the period 1981–2002. J Nat
Prod. 66:1022–1037. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Neill US: From branch to bedside: Youyou
Tu is awarded the 2011 Lasker~DeBakey Clinical Medical Research
Award for discovering artemisinin as a treatment for malaria. J
Clin Invest. 121:3768–3773. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheong DHJ, Tan DWS, Wong FWS and Tran T:
Anti-malarial drug, artemisinin and its derivatives for the
treatment of respiratory diseases. Pharmacol Res. 158:1049012020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lemke D, Pledl HW, Zorn M, Jugold M, Green
E, Blaes J, Löw S, Hertenstein A, Ott M, Sahm F, et al: Slowing
down glioblastoma progression in mice by running or the
anti-malarial drug dihydroartemisinin? Induction of oxidative
stress in murine glioblastoma therapy. Oncotarget. 7:56713–56725.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang CZ, Zhang H, Yun J, Chen GG and Lai
PBS: Dihydroartemisinin exhibits antitumor activity toward
hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
83:1278–1289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Zhou X, Liu J, Gao N, Yang R, Wang
Q, Ji J, Ma L and He Q: Dihydroartemisinin inhibits the
tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer via downregulating
CIZ1 expression associated with TGF-β1 signaling. Life Sci.
248:1174542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai X, Zhang X, Chen W, Chen Y, Zhang Q,
Mo S and Lu J: Dihydroartemisinin: A potential natural Anti-Cancer
drug. Int J Biol Sci. 17:603–622. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li S, Huang P, Gan J, Ling X, Du X, Liao
Y, Li L, Meng Y, Li Y and Bai Y: Dihydroartemisinin represses
esophageal cancer glycolysis by down-regulating pyruvate kinase M2.
Eur J Pharmacol. 854:232–239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang T, Luo R, Li W, Yan H, Xie S, Xiao W,
Wang Y, Chen B, Bai P and Xing J: Dihydroartemisinin suppresses
bladder cancer cell invasion and migration by regulating KDM3A and
p21. J Cancer. 11:1115–1124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun WD, Yu XX, An YH, Wang X, Wang Y and
Tong XM: Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis of human acute T
lymphocytic leukemia cells by activating oxidative stress. Zhongguo
Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 28:753–757. 2020.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wong KH, Yang D, Chen S, He C and Chen M:
Development of nanoscale drug delivery systems of
dihydroartemisinin for cancer therapy: A review. Asian J Pharm Sci.
17:475–490. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi H, Xiong L, Yan G, Du S, Liu J and Shi
Y: Susceptibility of cervical cancer to dihydroartemisinin-induced
ferritinophagy-dependent ferroptosis. Front Mol Biosci.
10:11560622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Du J, Wang X, Li Y, Ren X, Zhou Y, Hu W,
Zhou C, Jing Q, Yang C, Wang L, et al: DHA exhibits synergistic
therapeutic efficacy with cisplatin to induce ferroptosis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via modulation of iron metabolism.
Cell Death Dis. 12:7052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao JY and Dixon SJ: Mechanisms of
ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2195–2209. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tu H, Tang LJ, Luo XJ, Ai KL and Peng J:
Insights into the novel function of system Xc-in regulated cell
death. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:1650–1662. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of non-apoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patanè GT, Putaggio S, Tellone E, Barreca
D, Ficarra S, Maffei C, Calderaro A and Laganà G: Ferroptosis:
Emerging role in diseases and potential implication of bioactive
compounds. Int J Mol Sci. 24:172792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qin Y, Qiao Y, Wang D, Tang C and Yan G:
Ferritinophagy and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease:
Mechanisms and potential applications. Biomed Pharmacother.
141:1118722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dixon SJ, Patel DN, Welsch M, Skouta R,
Lee ED, Hayano M, Thomas AG, Gleason CE, Tatonetti NP, Slusher BS,
et al: Pharmacological inhibition of Cystine-glutamate exchange
induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. Elife.
3:e025232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ursini F, Maiorino M, Valente M, Ferri L
and Gregolin C: Purification from pig liver of a protein which
protects liposomes and biomembranes from peroxidative degradation
and exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity on phosphatidylcholine
hydroperoxides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 710:197–211. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, Orian
L, Venerando R, Roveri A, Vučković AM, Bosello Travain V, Zaccarin
M, Zennaro L, et al: Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis
inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 28:1013282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boelens J, Lust S, Offner F, Bracke ME and
Vanhoecke BW: Review. The endoplasmic reticulum: A target for new
anti-cancer drugs. In Vivo. 21:215–226. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu S, Zhang Q, Sun X, Zeh HJ III, Lotze
MT, Kang R and Tang D: HSPA5 regulates ferroptotic cell death in
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 77:2064–2077. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dai X, Zhang X, Chen W, Chen Y, Zhang Q,
Mo S and Lu J: Dihydroartemisinin: A potential natural anticancer
drug. Int J Biol Sci. 17:6032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kiani BH, Kayani WK, Khayam AU, Dilshad E,
Ismail H and Mirza B: Artemisinin and its derivatives: A promising
cancer therapy. Mol Biol Rep. 47:6321–6336. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin H, Jiang AY, Wang H, Cao Y, Wu Y and
Jiang XF: Dihydroartemisinin and gefitinib synergistically inhibit
NSCLC cell growth and promote apoptosis via the Akt/mTOR/STAT3
pathway. Mol Med Rep. 16:3475–3481. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ketelut-Carneiro N and Fitzgerald KA:
Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and Necroptosis-Oh my! the many ways a cell
can die. J Mol Biol. 434:1673782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hänggi K and Ruffell B: Cell death,
therapeutics, and the immune response in cancer. Trends Cancer.
9:381–396. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R and Kroemer G:
Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell
Res. 31:107–125. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lin R, Zhang Z, Chen L, Zhou Y, Zou P,
Feng C, Wang L and Liang G: Dihydroartemisinin (DHA) induces
ferroptosis and causes cell cycle arrest in head and neck carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 381:165–175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Du J, Wang T, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu X,
Ren X, An Y, Wu Y, Sun W, et al: DHA inhibits proliferation and
induces ferroptosis of leukemia cells through autophagy dependent
degradation of ferritin. Free Radic Biol Med. 131:356–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lai K, Song C, Gao M, Deng Y, Lu Z, Li N
and Geng Q: Uridine alleviates Sepsis-Induced acute lung injury by
inhibiting ferroptosis of macrophage. Int J Mol Sci. 24:50932023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu GZ, Xu XW, Tao SH, Gao MJ and Hou ZH:
HBx facilitates ferroptosis in acute liver failure via EZH2
mediated SLC7A11 suppression. J Biomed Sci. 28:672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, Orian
L, Venerando R, Roveri A, Vučković AM, Bosello Travain V, Zaccarin
M, Zennaro L, et al: Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis
inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 28:1013282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li L, Qiu C, Hou M, Wang X, Huang C, Zou
J, Liu T and Qu J: Ferroptosis in ovarian cancer: A Novel
therapeutic strategy. Front Oncol. 11:6659452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheung EC and Vousden KH: The role of ROS
in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 22:280–297.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Seibt TM, Proneth B and Conrad M: Role of
GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic
Biol Med. 133:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lee N, Carlisle AE, Peppers A, Park SJ,
Doshi MB, Spears ME and Kim D: xCT-Driven expression of GPX4
determines sensitivity of breast cancer cells to ferroptosis
inducers. Antioxidants (Basel). 10:3172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang Z, Zhang L, Zhou L, Lei Y, Zhang Y
and Huang C: Redox signaling and unfolded protein response
coordinate cell fate decisions under ER stress. Redox Biol.
25:1010472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bhardwaj M, Leli NM, Koumenis C and
Amaravadi RK: Regulation of autophagy by canonical and
non-canonical ER stress responses. Semin Cancer Biol. 66:116–128.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ma R, Qin W, Xie Y, Han Z, Li S, Jiang Y
and Lv H: Dihydroartemisinin induces ER stress-dependent apoptosis
of Echinococcus protoscoleces in vitro. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 52:1140–1147. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Chen D, Fan Z, Rauh M, Buchfelder M,
Eyupoglu IY and Savaskan N: ATF4 promotes angiogenesis and neuronal
cell death and confers ferroptosis in a xCT-dependent manner.
Oncogene. 36:5593–5608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen D, Rauh M, Buchfelder M, Eyupoglu IY
and Savaskan N: The oxide-metabolic driver ATF4 enhances
temozolomide chemo-resistance in human gliomas. Oncotarget.
8:51164–51176. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chang LC, Chiang SK, Chen SE, Yu YL, Chou
RH and Chang WC: Heme oxygenase-1 mediates BAY 11-7085 induced
ferroptosis. Cancer Lett. 416:124–137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang N, Zeng GZ, Yin JL and Bian ZX:
Artesunate activates the ATF4-CHOP-CHAC1 pathway and affects
ferroptosis in Burkitt's Lymphoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
519:533–539. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|