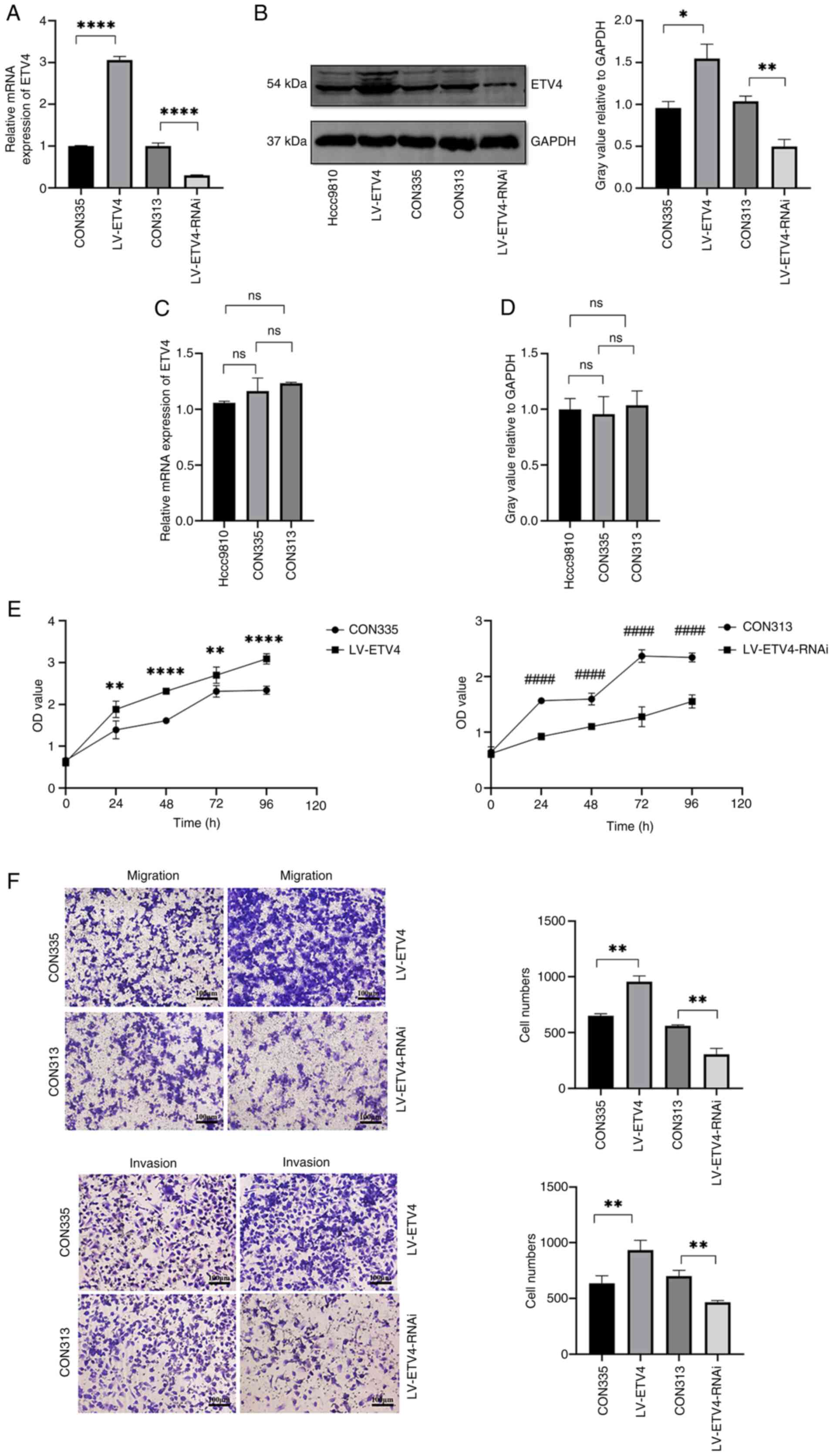
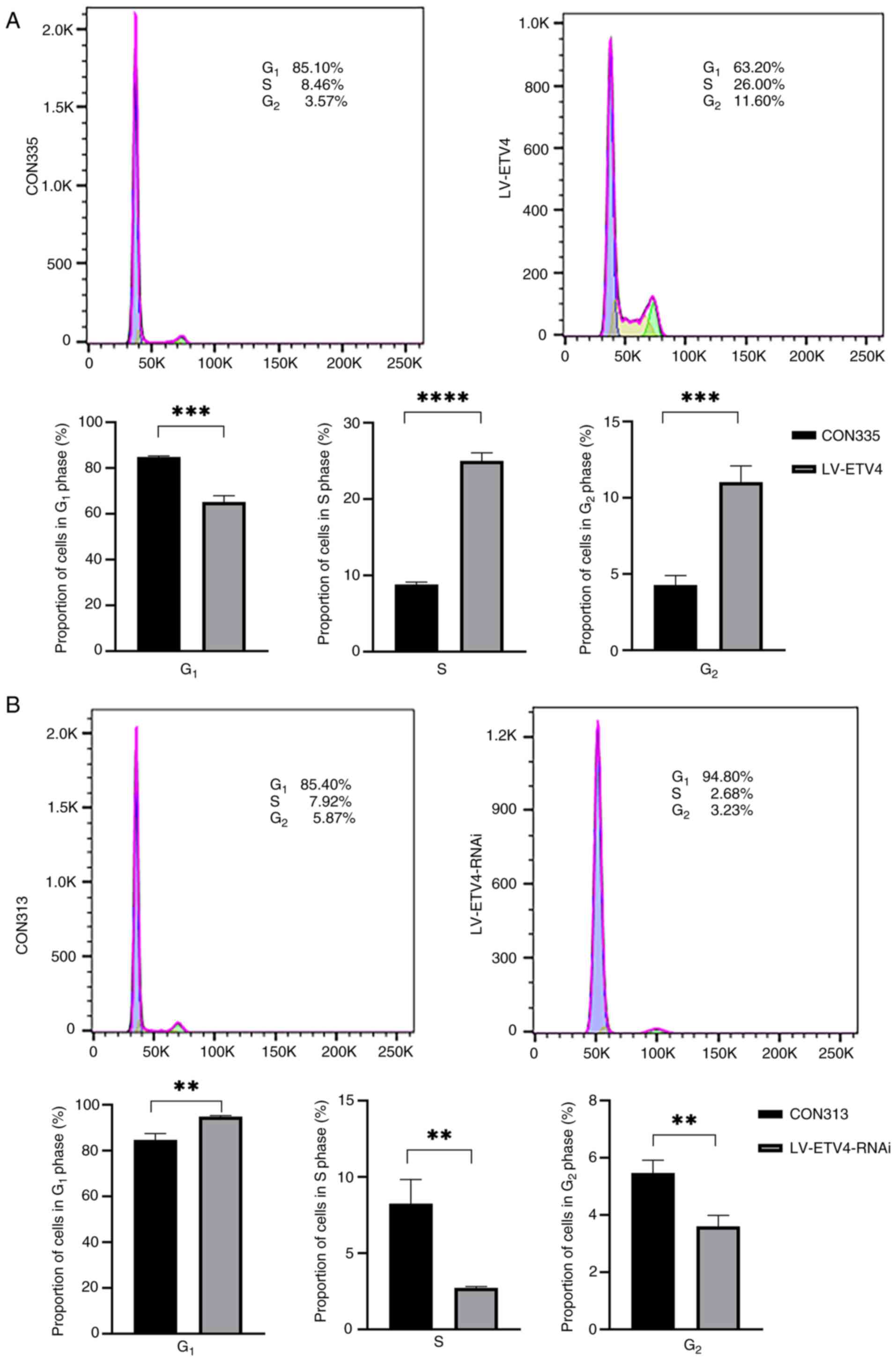
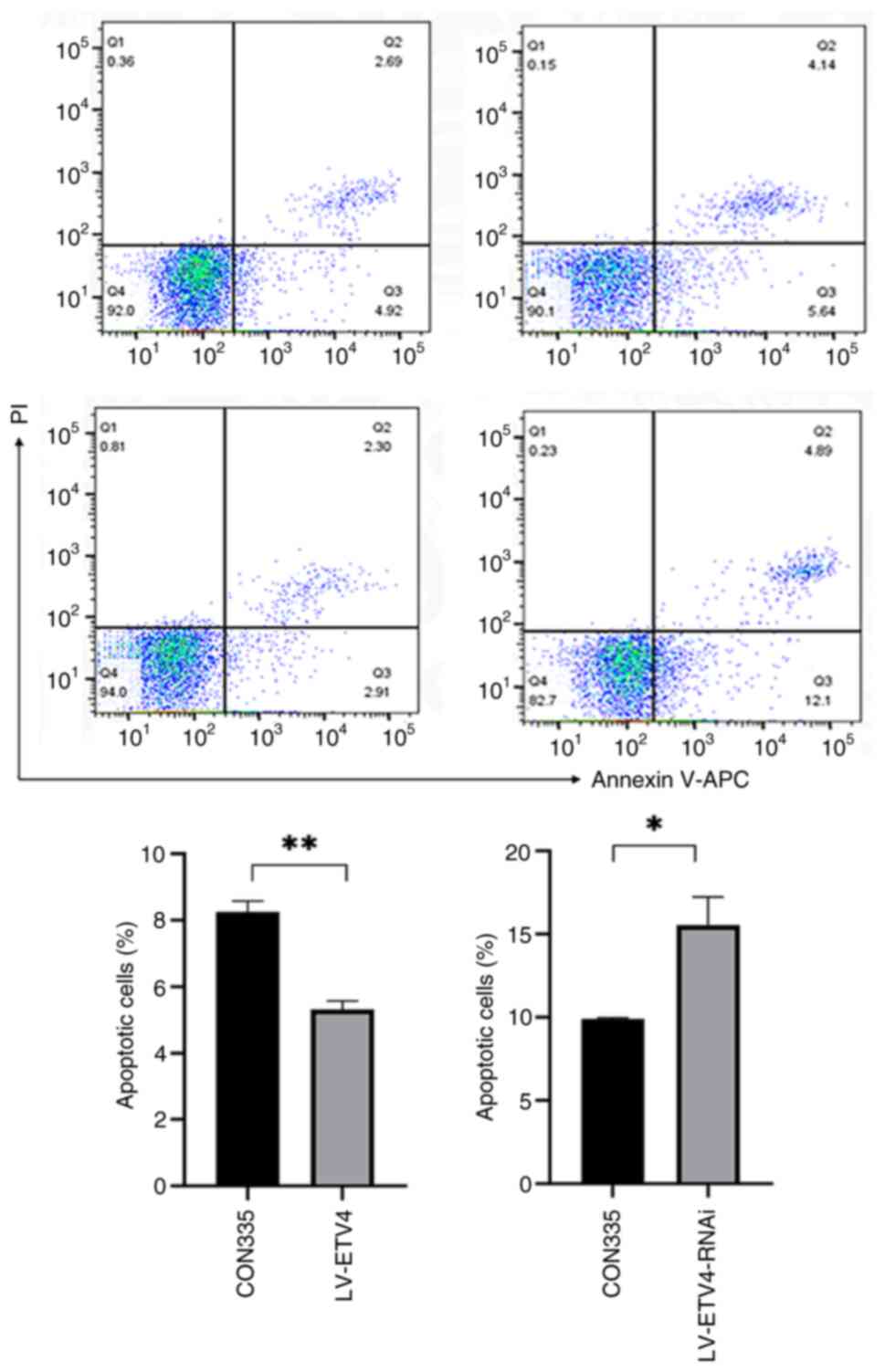
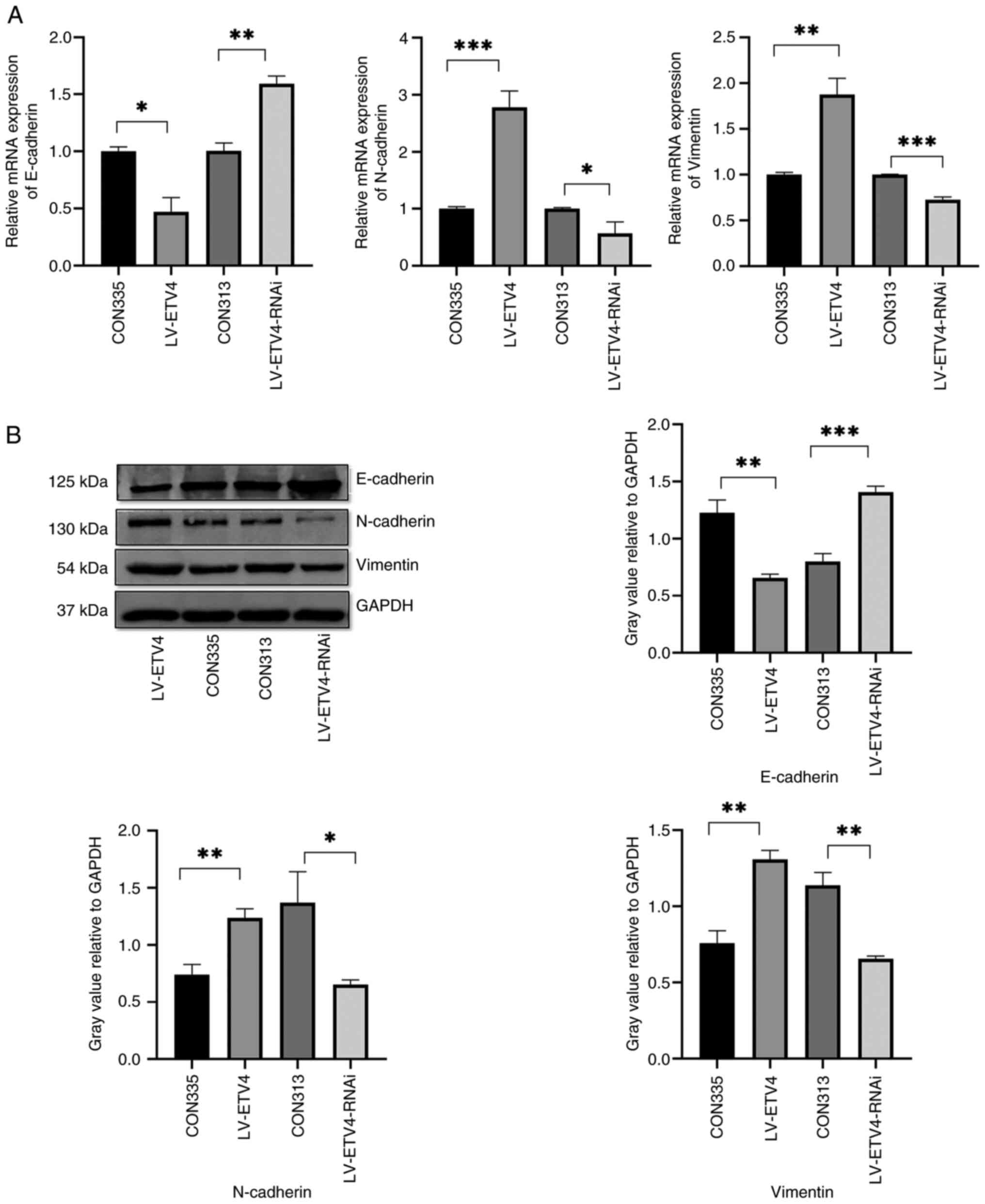
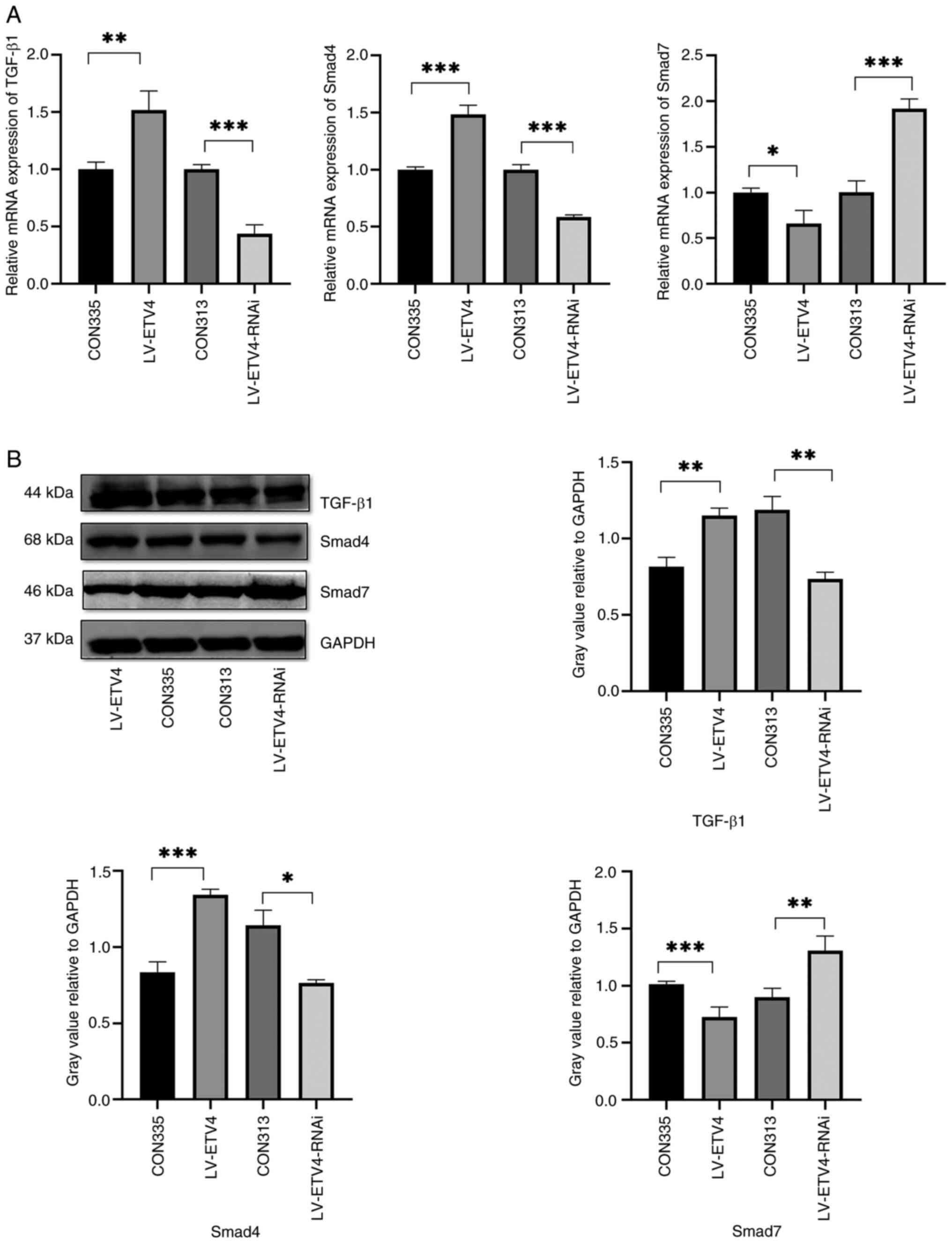
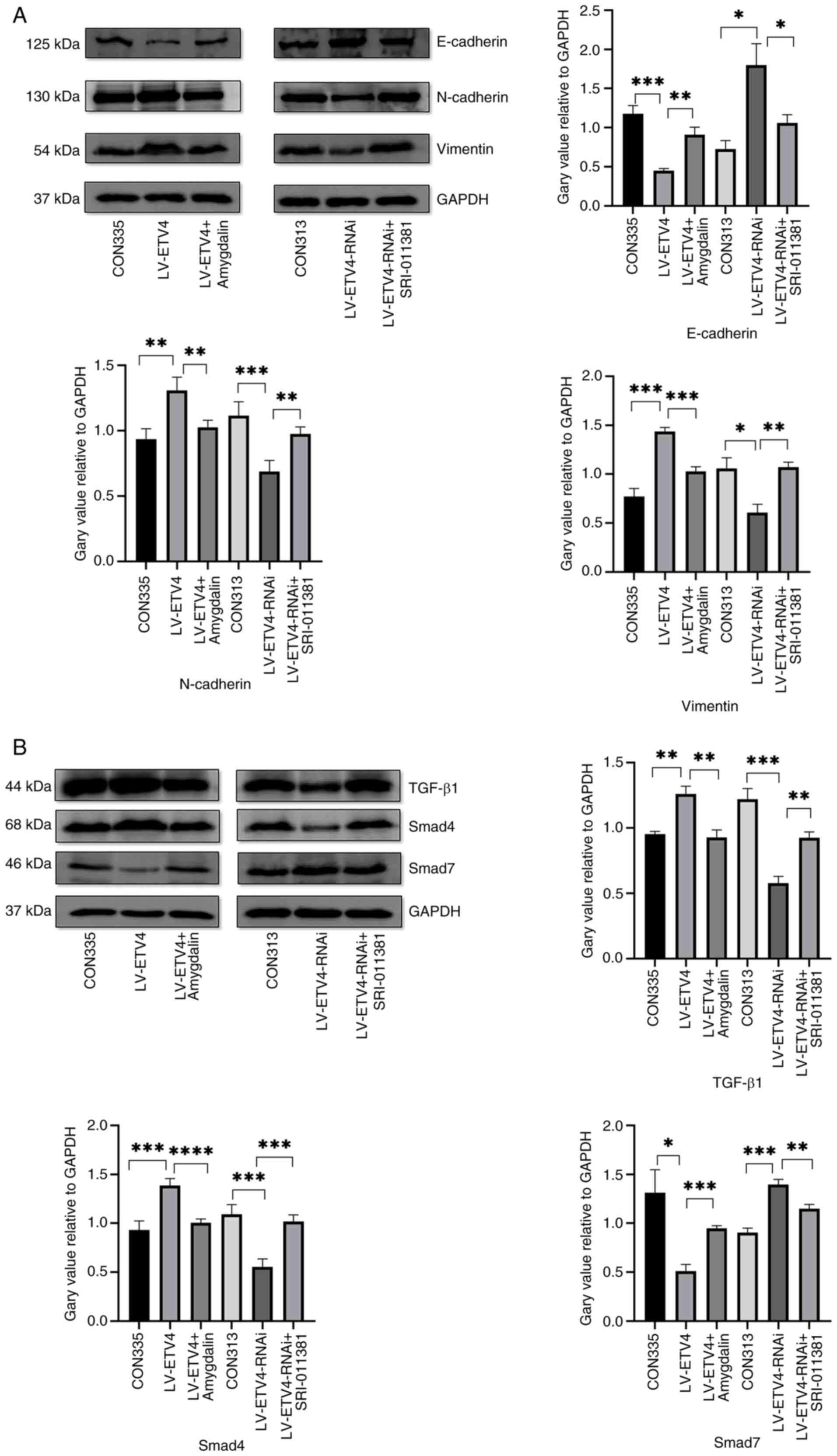
|
1
|
El-Diwany R, Pawlik TM and Ejaz A:
Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 28:587–599.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee AJ and Chun YS: Intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: The AJCC/UICC 8th edition updates. Chin Clin
Oncol. 7:522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moris D, Palta M, Kim C, Allen PJ, Morse
MA and Lidsky ME: Advances in the treatment of intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma: An overview of t-he current and future
therapeutic landscape for clinicians. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:198–222.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Qi T, Qu Q, Li G, Wang J, Zhu H, Yang Z,
Sun Y, Lu Q and Qu J: Function and regulation of the PEA3 subfamily
of ETS transcription factors in cancer. Am J Cancer Res.
10:3083–3105. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gao X, Jiang M, Chu Y, Han Y, Jin Y, Zhang
W, Wang W, Yang S, Li W, Fan A, et al: ETV4 promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis through activation of the
CXCL13/CXCR5 signaling axis. Cancer Lett. 524:42–56. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cosi I, Pellecchia A, De Lorenzo E, Torre
E, Sica M, Nesi G, Notaro R and De Angioletti M: ETV4 promotes late
development of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia and cell
proliferation through direct and p53-mediated downregulation of
p21. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singsuksawat E, Thuwajit C, Charngkaew K
and Thuwajit P: Increased ETV4 expression correlates with
estrogen-enhanced proliferation and invasiveness of
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 18:252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ang HL, Mohan CD, Shanmugam MK, Leong HC,
Makvandi P, Rangappa KS, Bishayee A, Kumar AP and Sethi G:
Mechanism of epithelial mesenchymal transition in cancer and its
regulation by natural compounds. Med Res Rev. 43:1141–1200. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Derynck R and Weinberg RA: EMT and cancer:
More than meets the eye. Dev Cell. 49:313–316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Navas T, Kinders RJ, Lawrence SM,
FerryGalow KV, Borgel S, Hollingshead MG, Srivastava AK, Alcoser
SY, Makhlouf HR, Chuaqui R, et al: Clinical evolution of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human carcinomas. Cancer Res.
80:304–318. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Williams ED, Gao D, Redfern A and Thompson
EW: Controversies around epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in
cancer metastasis. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:716–732. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lim W, Jeon BN, Kim YJ, Kim KH and Ko H:
FBI-1 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, migration, and
invasion in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells by downregulating
transforming growth factor-β1 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
123:644–656. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sawanyawisuth K, Sashida G and Sheng G:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver fluke-induced
cholangiocarcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 13:7912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vaquero J, Guedj N, Clapéron A,
Ho-Bouldoires TH, Paradis V and Fouassier L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to
regulatory networks. J Hepatol. 66:424–441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Clapéron A, Mergey M, Ho-Bouldoires TH,
Vignjevic D, Wendum D, Chrétien Y, Merabtene F, Frazao A, Paradis
V, Housset C, et al: EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the progression
of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Hepatol. 61:325–332. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Huang Y, Liu J, Lin W, Chen C,
Chen Y, Ding Y, Yang Y, Chen Y, Wang H and Teng L: EXOSC5 promotes
proliferation of gastric cancer through regulating AKT/STAT3
signaling pathways. J Cancer. 13:1456–1467. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xiang C, Sun WH, Ke Y, Yu X and Wang Y:
CDCA8 contributes to the development and progression of thyroid
cancer through regulating CDK1. J Cancer. 13:2322–2335. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xia XL, Xue D, Xiang TH, Xu HY, Song DK,
Cheng PG and Wang JQ: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA CRNDE
facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and correlates with
poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Lett.
15:4105–4112. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vermani L, Kumar R and Kumar NS: GAPDH and
PUM1: Optimal housekeeping genes for quantitative polymerase chain
reaction-based analysis of cancer stem cells and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene expression in rectal tumors.
Cureus. 12:e120202020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang AN, Li N, Chen ZC, Guo YL, Tian CJ,
Cheng DJ, Tang XY and Zhang XY: Amygdalin alleviated TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bronchial epithelial cells.
Chem Biol Interact. 369:1102352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Huang Y, Wen Q, Li Y, Guo L and
Ge N: INHBA gene silencing inhibits proliferation, migration, and
invasion of osteosarcoma cells by repressing TGF-β signaling
pathway activation. J Orthop Surg Res. 18:8482023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang W, Xu Y, Chen X, Pan S and Zhu X:
E26 transformation-specific variant 4 as a tumor promotor in human
cancers through specific molecular mechanisms. Mol Ther Oncolytics.
22:518–527. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng C, Liu M, Ge Y, Qian Y and Fan H:
HBx increases chromatin accessibility and ETV4 expression to
regulate dishevelled-2 and promote HCC progression. Cell Death Dis.
13:1162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Sun C, Li J, Jiang H, Qiu Y and
Gong M: Knockdown of ETV4 promotes autophagy-dependent apoptosis in
GBM cells by reducing the transcriptional activation of EMP1. Oncol
Lett. 23:412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tyagi N, Deshmukh SK, Srivastava SK, Azim
S, Ahmad A, AlGhadhban A, Singh AP, Carter JE, Wang B and Singh S:
ETV4 facilitates cell-cycle progression in pancreatic cells through
transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cancer Res.
16:187–196. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pastushenko I and Blanpain C: EMT
transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends
Cell Biol. 29:212–226. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lu W and Kang Y: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell.
49:361–374. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bure IV, Nemtsova MV and Zaletaev DV:
Roles of E-cadherin and Noncoding RNAs in the
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and progression in gastric
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20:28702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rosso M, Majem B, Devis L, Lapyckyj L,
Besso MJ, Llauradó M, Abascal MF, Matos ML, Lanau L, Castellví J,
et al: E-cadherin: A determinant molecule associated with ovarian
cancer progression, dissemination and aggressiveness. PLoS One.
12:e01844392017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathwa-ys. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ali AN, Ghoneim SM, Ahmed ER, Salam LO and
Saleh SM: Cadherin switching in oral squamous cell carcinoma: A
clinicopathological study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 13:486–494.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cao ZQ, Wang Z and Leng P: Aberrant
N-cadherin expression in cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1093202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M and Alahari
SK: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer.
15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ridge KM, Eriksson JE, Pekny M and Goldman
RD: Roles of vimentin in health and disease. Genes Dev. 36:391–407.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou Z, Wu B, Chen J, Shen Y, Wang J, Chen
X, Fei F and Li L: ETV4 facilitates proliferation, migration, and
invasion of liver cancer by mediating TGF-β signal transduction
through activation of B3GNT 3. Genes Genomics. 45:1433–1443. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yao D, Bao Z, Qian X, Yang Y and Mao Z:
ETV4 transcriptionally activates HES1 and promotes Stat3
phosphorylation to promote malignant behaviors of colon
adenocarcinoma. Cell Biol Int. 45:2129–2139. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hao Y, Baker D and Dijke PT:
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:27672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Katsuno Y, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-β signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:76–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, van Dinther M, Thorikay M,
Gourabi BM, Kruithof BPT and Ten Dijke P: Opposing USP19 splice
variants in TGF-β signaling and TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 80:432023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hu HH, Chen DQ, Wang YN, Feng YL, Cao G,
Vaziri ND and Zhao YY: New insights into TGF-β/Smad signaling in
tissue fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact. 292:76–83. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao M, Mishra L and Deng CX: The role of
TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling in cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 14:111–123. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Moon H, Ju HL, Chung SI, Cho KJ, Eun JW,
Nam SW, Han KH, Calvisi DF and Ro SW: Transforming growth factor-β
promotes liver tumorigenesis in mice via up-regulation of snail.
Gastroenterology. 153:1378–1391. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Deckers M, van Dinther M, Buijs J, Que I,
Löwik C, van der Pluijm G and ten Dijke P: The tumor suppressor
Smad4 is required for transforming growth factor beta-induced
epithelial to mesenchymal transition and bone metastasis of breast
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:2202–2209. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Thuault S, Valcourt U, Petersen M,
Manfioletti G, Heldin CH and Moustakas A: Transforming growth
factor-beta employs HMGA2 to elicit epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. J Cell Biol. 174:175–183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen HY, Chiang YF, Huang CY, Shieh TM,
Kao C, Chang FK, Huang TC, Ali M, Chang HY, Hong YH and Hsia SM:
Spirulina phycocyanin extract and its active components suppress
epithelial-mesenchymal transition process in endometrial cancer via
targeting TGF-beta1/SMAD4 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
152:1132192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
David CJ, Huang YH, Chen M, Su J, Zou Y,
Bardeesy N, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA and Massagué J: TGF-β tumor
suppression through a lethal EMT. Cell. 164:1015–1030. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yan X, Liao H, Cheng M, Shi X, Lin X, Feng
XH and Chen YG: Smad7 protein interacts with receptor-regulated
smads (R-Smads) to inhibit transforming growth factor-β
(TGF-β)/Smad Signaling. J Biol Chem. 291:382–392. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang JY, Gao YB, Zhang N, Zou DW, Wang P,
Zhu ZY, Li JY, Zhou SN, Wang SC, Wang YY and Yang JK: miR-21
overexpression enhances TGF-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by target smad7 and aggravates renal damage in diabetic
nephropathy. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 392:163–172. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|