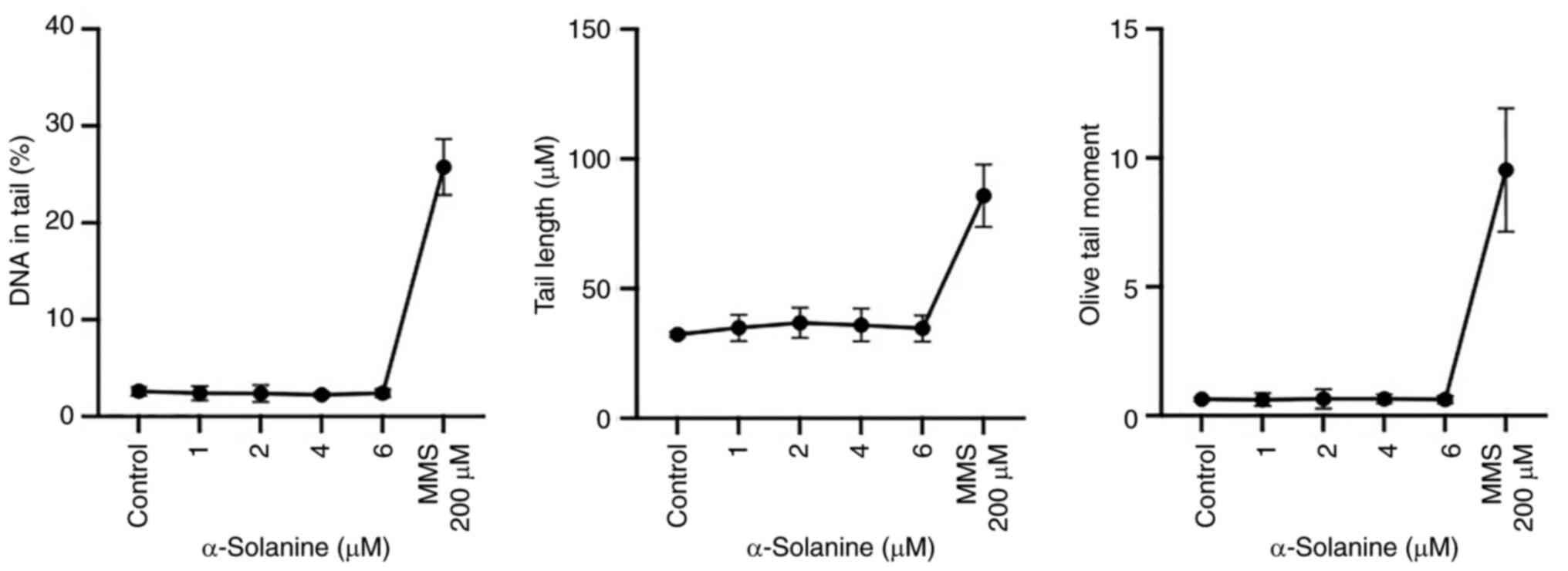
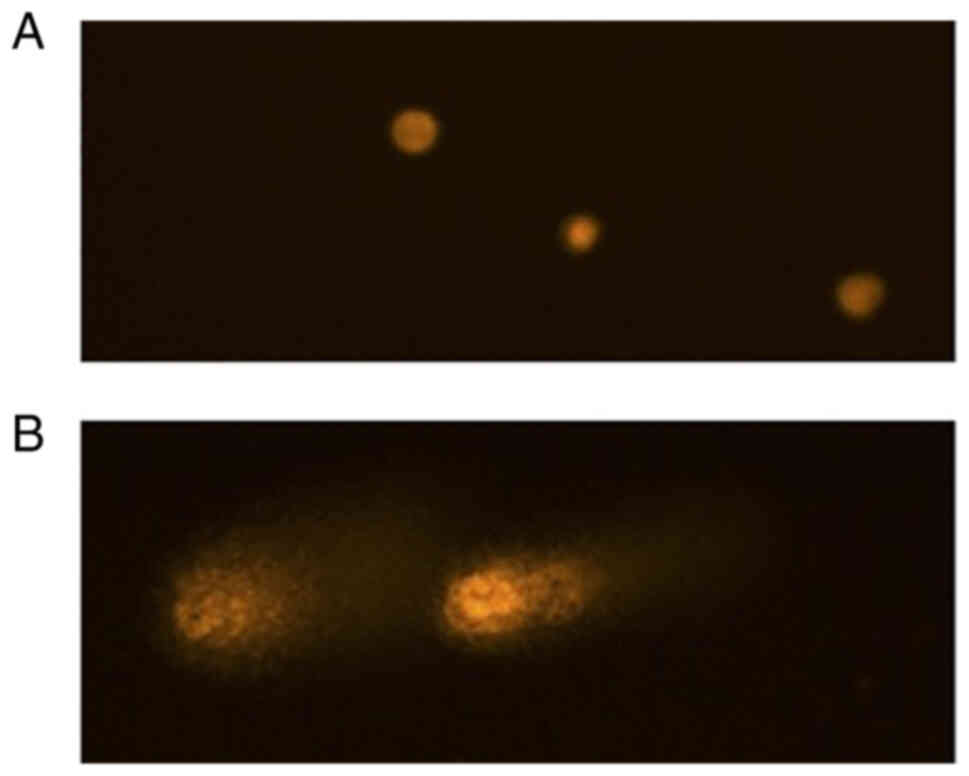
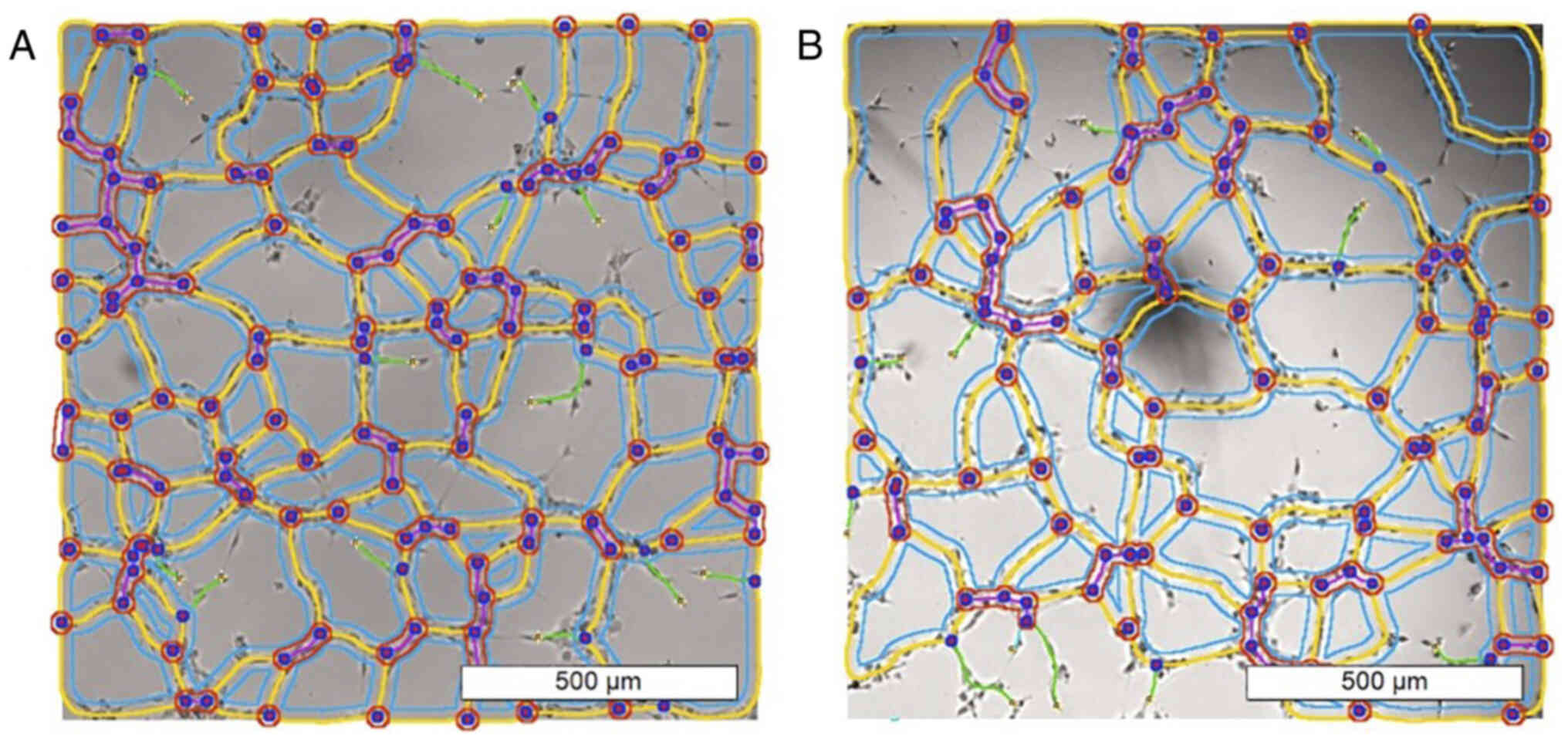
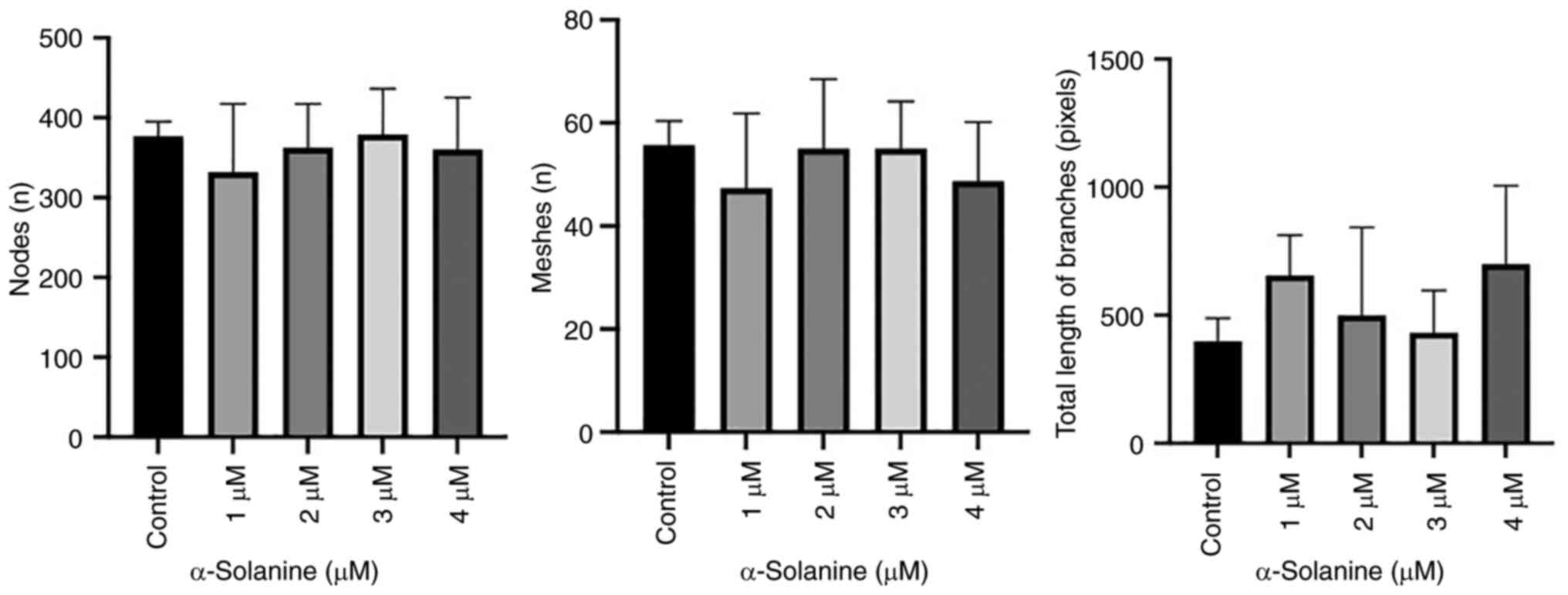
|
1
|
Friedman M: Potato glycoalkaloids and
metabolites: Roles in the plant and in the diet. J Agric Food Chem.
54:8655–8681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman M: Chemistry and anticarcinogenic
mechanisms of glycoalkaloids produced by eggplants, potatoes, and
tomatoes. J Agric Food Chem. 63:3323–3337. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ordóñez Vásquez A, Aguirre-Arzola V,
Garza-Ramos M, Urrutia-Baca V and Suárez-Obando F: Toxicity,
teratogenicity and anti-cancer activity of α-solanine: A
perspective on anti-cancer potential. Int J Pharmacol. 15:301–310.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Allen JR, Marlar RJ, Chesney CF, Helgeson
JP, Kelman A, Weckel G, Traisman E and White JW Jr: Teratogenicity
studies on late blighted potatoes in nonhuman primates (Macaca
mulatta and Saguinus labiatus). Teratology. 15:17–23. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hassan SH, Gul S, Zahra HS, Maryam A,
Shakir HA, Khan M and Irfan M: Alpha solanine: A novel natural
bioactive molecule with anticancer effects in multiple human
malignancies. Nutr Cancer. 73:1541–1552. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Luo S, Tian GJ, Yu FX and Wen ZD: A
narrative review of the antitumor studies of solanine. Transl
Cancer Res. 10:1578–1582. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng XQ, Zhang W, Zhang F, Yin SY, Xie HY,
Zhou L and Zheng SS: Solanine-induced reactive oxygen species
inhibit the growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells.
Oncol Lett. 11:2145–2151. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yan X, Li M, Chen L, Peng X, Que ZJ, An
HM, Shen KP and Hu B: α-Solanine inhibits growth and metastatic
potential of human colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
43:1387–1396. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun H, Lv C, Yang L, Wang Y, Zhang Q, Yu
S, Kong H, Wang M, Xie J, Zhang C and Zhou M: Solanine induces
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:8059262014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Daly SM, Gouhar SA, Gamal-Eldeen AM,
Abdel Hamid FF, Ashour MN and Hassan NS: Synergistic effect of
α-solanine and cisplatin induces apoptosis and enhances cell cycle
arrest in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Agents
Med Chem. 19:2197–2210. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui
VWY, Bauman JE and Grandis JR: Head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rangan SR: A new human cell line (FaDu)
from a hypopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer. 29:117–121. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Scherzed A, Hackenberg S, Froelich K, Rak
K, Schendzielorz P, Gehrke T, Hagen R and Kleinsasser N: The
differentiation of hMSCs counteracts their migration capability and
pro-angiogenic effects in vitro. Oncol Rep. 35:219–226.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scherzad A, Hackenberg S, Schramm C,
Froelich K, Ginzkey C, Hagen R and Kleinsasser N: Geno- and
cytotoxicity of salinomycin in human nasal mucosa and peripheral
blood lymphocytes. Toxicol In Vitro. 29:813–818. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
DeCicco-Skinner KL, Henry GH, Cataisson C,
Tabib T, Gwilliam JC, Watson NJ, Bullwinkle EM, Falkenburg L,
O'Neill RC, Morin A and Wiest JS: Endothelial cell tube formation
assay for the in vitro study of angiogenesis. J Vis Exp.
e513122014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R,
Soulières D, Tahara M, de Castro G Jr, Psyrri A, Basté N, Neupane
P, Bratland Å, et al: Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy
versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic
squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (KEYNOTE-048): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 394:1915–1928. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szturz P and Vermorken JB: Translating
KEYNOTE-048 into practice recommendations for head and neck cancer.
Ann Transl Med. 8:9752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shen KH, Liao AC, Hung JH, Lee WJ, Hu KC,
Lin PT, Liao RF and Chen PS: α-Solanine inhibits invasion of human
prostate cancer cell by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and mMPs expression. Molecules. 19:11896–11914. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karaboga Arslan AK and Yerer MB:
α-Chaconine and α-Solanine inhibit RL95-2 endometrium cancer cell
proliferation by reducing expression of Akt (Ser473) and ERα
(Ser167). Nutrients. 10:6722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu MK, Shih YW, Chang Chien TT, Fang LH,
Huang HC and Chen PS: α-Solanine inhibits human melanoma cell
migration and invasion by reducing matrix metalloproteinase-2/9
activities. Biol Pharm Bull. 33:1685–1691. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ji YB, Gao SY, Ji CF and Zou X: Induction
of apoptosis in HepG2 cells by solanine and Bcl-2 protein. J
Ethnopharmacol. 115:194–202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang SA, Paek SH, Kozukue N, Lee KR and
Kim JA: Alpha-chaconine, a potato glycoalkaloid, induces apoptosis
of HT-29 human colon cancer cells through caspase-3 activation and
inhibition of ERK 1/2 phosphorylation. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:839–846. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pan B, Zhong W, Deng Z, Lai C, Chu J, Jiao
G, Liu J and Zhou Q: Inhibition of prostate cancer growth by
solanine requires the suppression of cell cycle proteins and the
activation of ROS/P38 signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 5:3214–3222.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hasanain M, Bhattacharjee A, Pandey P,
Ashraf R, Singh N, Sharma S, Vishwakarma AL, Datta D, Mitra K and
Sarkar J: α-Solanine induces ROS-mediated autophagy through
activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress and inhibition of
Akt/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 6:e18602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lv C, Kong H, Dong G, Liu L, Tong K, Sun
H, Chen B, Zhang C and Zhou M: Antitumor efficacy of α-solanine
against pancreatic cancer in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
9:e878682014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|