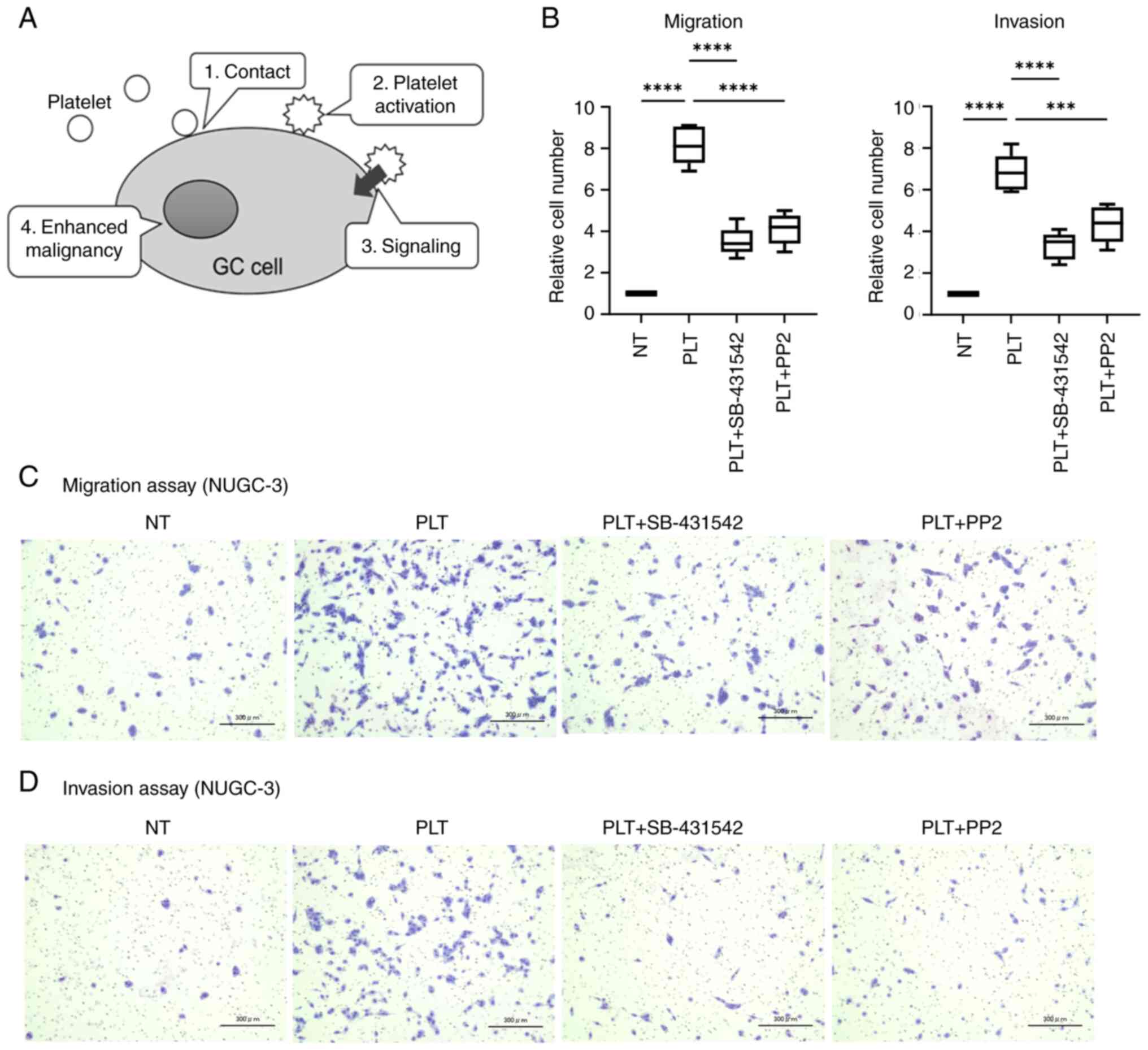
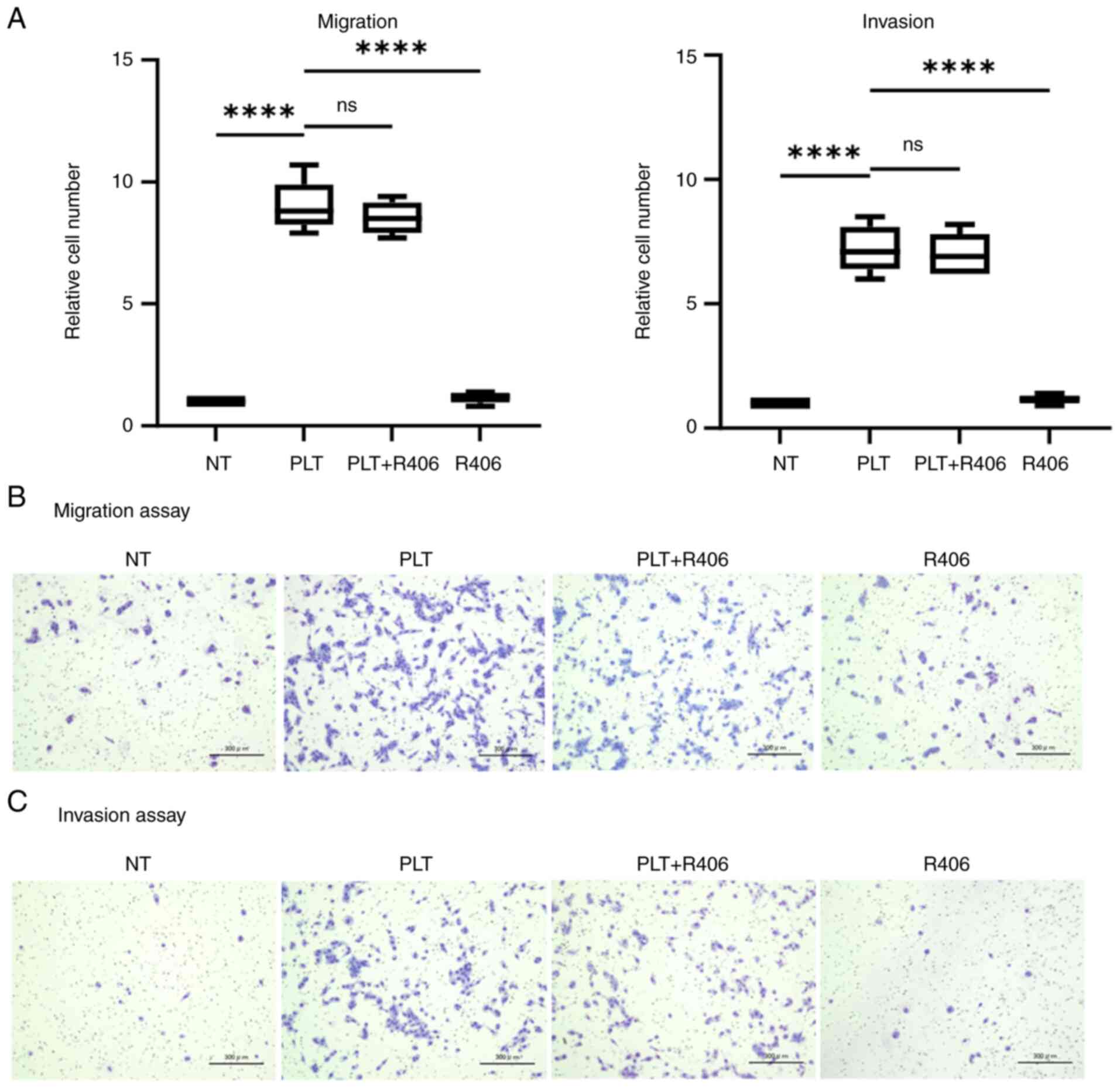
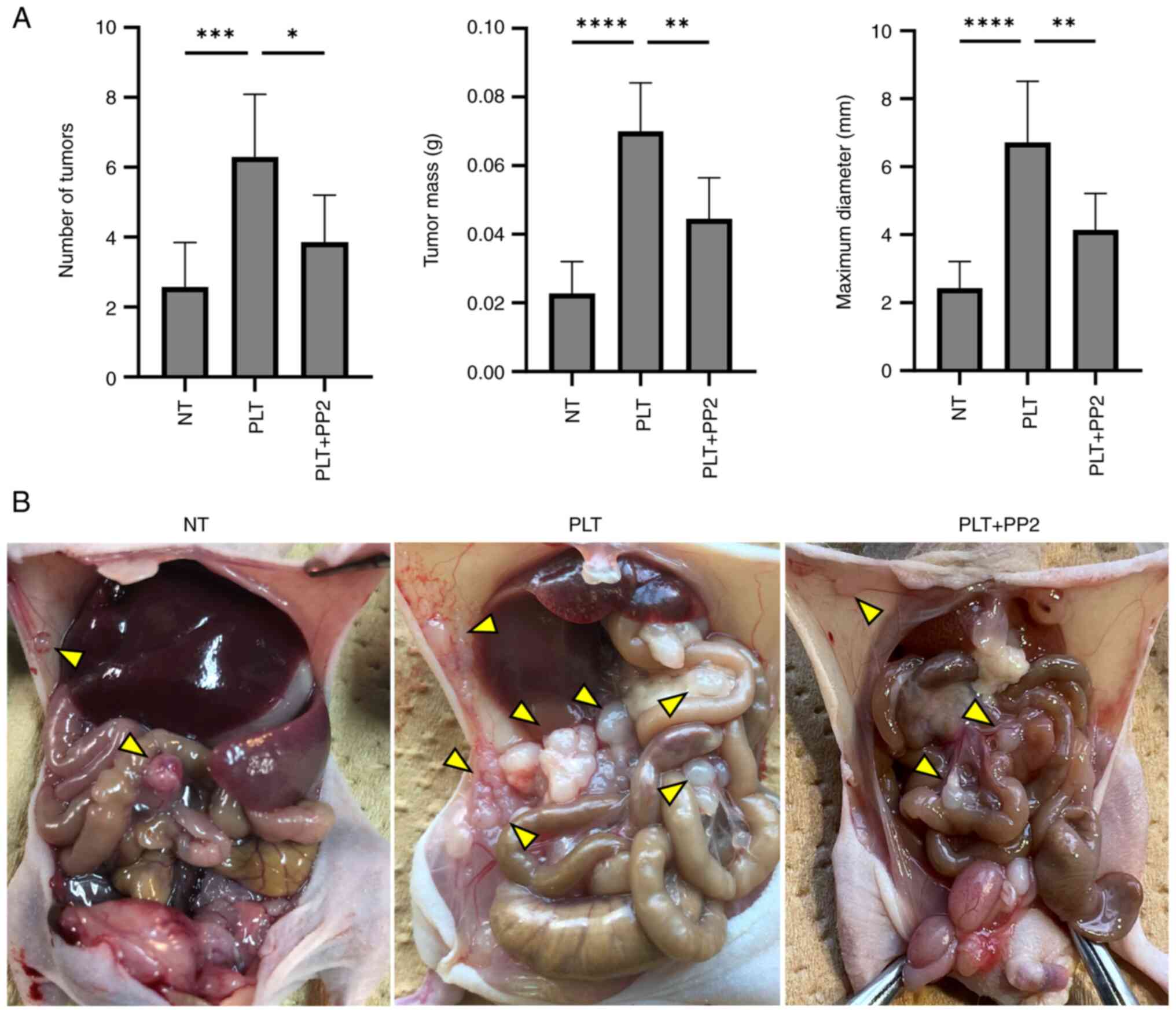
|
1
|
Arita T, Ichikawa D, Konishi H, Komatsu S,
Shiozaki A, Hiramoto H, Hamada J, Shoda K, Kawaguchi T, Hirajima S,
et al: Increase in peritoneal recurrence induced by intraoperative
hemorrhage in gastrectomy. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:758–764. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kamei T, Kitayama J, Yamashita H and
Nagawa H: Intraoperative blood loss is a critical risk factor for
peritoneal recurrence after curative resection of advanced gastric
cancer. World J Surg. 33:1240–1246. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Labelle M, Begum S and Hynes RO: Direct
signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an
epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis.
Cancer Cell. 20:576–590. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rothwell PM, Wilson M, Price JF, Belch JF,
Meade TW and Mehta Z: Effect of daily aspirin on risk of cancer
metastasis: A study of incident cancers during randomised
controlled trials. Lancet. 379:1591–1601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shirai T, Inoue O, Tamura S, Tsukiji N,
Sasaki T, Endo H, Satoh K, Osada M, Sato-Uchida H, Fujii H, et al:
C-type lectin-like receptor 2 promotes hematogenous tumor
metastasis and prothrombotic state in tumor-bearing mice. J Thromb
Haemost. 15:513–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Saito R, Shoda K, Maruyama S, Yamamoto A,
Takiguchi K, Furuya S, Hosomura N, Akaike H, Kawaguchi Y, Amemiya
H, et al: Platelets enhance malignant behaviours of gastric cancer
cells via direct contacts. Br J Cancer. 124:570–573. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Suzuki-Inoue K: Roles of the
CLEC-2-podoplanin interaction in tumor progression. Platelets. 1–7.
2018.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Suzuki-Inoue K, Fuller GL, García A, Eble
JA, Pöhlmann S, Inoue O, Gartner TK, Hughan SC, Pearce AC, Laing
GD, et al: A novel Syk-dependent mechanism of platelet activation
by the C-type lectin receptor CLEC-2. Blood. 107:542–549. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suzuki-Inoue K, Inoue O and Ozaki Y: Novel
platelet activation receptor CLEC-2: From discovery to prospects. J
Thromb Haemost. 9 (Suppl 1):S44–S55. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Breiteneder-Geleff S, Soleiman A, Kowalski
H, Horvat R, Amann G, Kriehuber E, Diem K, Weninger W, Tschachler
E, Alitalo K and Kerjaschki D: Angiosarcomas express mixed
endothelial phenotypes of blood and lymphatic capillaries:
Podoplanin as a specific marker for lymphatic endothelium. Am J
Pathol. 154:385–394. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fujita N and Takagi S: The impact of
Aggrus/podoplanin on platelet aggregation and tumour metastasis. J
Biochem. 152:407–413. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moroi M, Jung SM, Okuma M and Shinmyozu K:
A patient with platelets deficient in glycoprotein VI that lack
both collagen-induced aggregation and adhesion. J Clin Invest.
84:1440–1445. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sugiyama T, Okuma M, Ushikubi F, Sensaki
S, Kanaji K and Uchino H: A novel platelet aggregating factor found
in a patient with defective collagen-induced platelet aggregation
and autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 69:1712–1720. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mammadova-Bach E, Mangin P, Lanza F and
Gachet C: Platelets in cancer. From basic research to therapeutic
implications. Hamostaseologie. 35:325–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Derynck R, Turley SJ and Akhurst RJ: TGFβ
biology in cancer progression and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 18:9–34. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ishimoto T, Miyake K, Nandi T, Yashiro M,
Onishi N, Huang KK, Lin SJ, Kalpana R, Tay ST, Suzuki Y, et al:
Activation of transforming growth factor beta 1 signaling in
gastric cancer-associated fibroblasts increases their motility, via
expression of rhomboid 5 homolog 2, and ability to induce
invasiveness of gastric cancer cells. Gastroenterology.
153:191–204.e16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tauriello DVF, Palomo-Ponce S, Stork D,
Berenguer-Llergo A, Badia-Ramentol J, Iglesias M, Sevillano M,
Ibiza S, Cañellas A, Hernando-Momblona X, et al: TGFβ drives immune
evasion in genetically reconstituted colon cancer metastasis.
Nature. 554:538–543. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakayama T, Saito R, Furuya S, Shoda K,
Maruyma S, Takiguchi K, Shiraishi K, Akaike H, Kawaguchi Y, Amemiya
H, et al: Inhibition of cancer cell-platelet adhesion as a
promising therapeutic target for preventing peritoneal
dissemination of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 26:5382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Satoh K, Fukasawa I, Kanemaru K, Yoda S,
Kimura Y, Inoue O, Ohta M, Kinouchi H and Ozaki Y: Platelet
aggregometry in the presence of PGE(1) provides a reliable method
for cilostazol monitoring. Thromb Res. 130:616–621. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kawai S, Takagi Y, Kaneko S and Kurosawa
T: Effect of three types of mixed anesthetic agents alternate to
ketamine in mice. Exp Anim. 60:481–487. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Scala M, Nishikawa M, Ito H, Tabata H,
Khan T, Accogli A, Davids L, Ruiz A, Chiurazzi P, Cericola G, et
al: Variant-specific changes in RAC3 function disrupt
corticogenesis in neurodevelopmental phenotypes. Brain.
145:3308–3327. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Narikiyo K, Mizuguchi R, Ajima A, Shiozaki
M, Hamanaka H, Johansen JP, Mori K and Yoshihara Y: The claustrum
coordinates cortical slow-wave activity. Nat Neurosci. 23:741–753.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Olajide OJ, Gbadamosi IT, Yawson EO,
Arogundade T, Lewu FS, Ogunrinola KY, Adigun OO, Bamisi O, Lambe E,
Arietarhire LO, et al: Hippocampal degeneration and behavioral
impairment during alzheimer-like pathogenesis involves glutamate
excitotoxicity. J Mol Neurosci. 71:1205–1220. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. 8th
edition. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2011
|
|
26
|
Tashiro M and Tohei A: Recommended doses
of medetomidine-midazolam-butorphanol with atipamezole for
preventing hypothermia in mice. J Vet Med Sci. 84:445–453. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Estevez B and Du X: New concepts and
mechanisms of platelet activation signaling. Physiology (Bethesda).
32:162–177. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hwang BO, Park SY, Cho ES, Zhang X, Lee
SK, Ahn HJ, Chun KS, Chung WY and Song NY: Platelet
CLEC2-podoplanin axis as a promising target for oral cancer
treatment. Front Immunol. 12:8076002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sasaki T, Shirai T, Tsukiji N, Otake S,
Tamura S, Ichikawa J, Osada M, Satoh K, Ozaki Y and Suzuki-Inoue K:
Functional characterization of recombinant snake venom rhodocytin:
Rhodocytin mutant blocks CLEC-2/podoplanin-dependent platelet
aggregation and lung metastasis. J Thromb Haemost. 16:960–972.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suzuki-Inoue K: Platelets and
cancer-associated thrombosis: Focusing on the platelet activation
receptor CLEC-2 and podoplanin. Blood. 134:1912–1918. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mammadova-Bach E, Gil-Pulido J,
Sarukhanyan E, Burkard P, Shityakov S, Schonhart C, Stegner D,
Remer K, Nurden P, Nurden AT, et al: Platelet glycoprotein VI
promotes metastasis through interaction with cancer cell-derived
galectin-3. Blood. 135:1146–1160. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Saito M, Ichikawa J, Ando T, Schoenecker
JG, Ohba T, Koyama K, Suzuki-Inoue K and Haro H: Platelet-derived
TGF-β induces tissue factor expression via the Smad3 pathway in
osteosarcoma cells. J Bone Miner Res. 33:2048–2058. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Asazuma N, Ozaki Y, Satoh K, Yatomi Y,
Handa M, Fujimura Y, Miura S and Kume S: Glycoprotein Ib-von
Willebrand factor interactions activate tyrosine kinases in human
platelets. Blood. 90:4789–4798. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Poole A, Gibbins JM, Turner M, van Vugt
MJ, van de Winkel JG, Saito T, Tybulewicz VL and Watson SP: The Fc
receptor gamma-chain and the tyrosine kinase Syk are essential for
activation of mouse platelets by collagen. EMBO J. 16:2333–2341.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Suzuki-Inoue K, Wilde JI, Andrews RK,
Auger JM, Siraganian RP, Sekiya F, Rhee SG and Watson SP:
Glycoproteins VI and Ib-IX–V stimulate tyrosine phosphorylation of
tyrosine kinase Syk and phospholipase Cgamma2 at distinct sites.
Biochem J. 378:1023–1029. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Turner M, Schweighoffer E, Colucci F, Di
Santo JP and Tybulewicz VL: Tyrosine kinase SYK: Essential
functions for immunoreceptor signalling. Immunol Today. 21:148–154.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yanaga F, Poole A, Asselin J, Blake R,
Schieven GL, Clark EA, Law CL and Watson SP: Syk interacts with
tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins in human platelets activated by
collagen and cross-linking of the Fc gamma-IIA receptor. Biochem J.
311:471–478. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang B, Rouvelas I and Nilsson M: Gastric
and gastroesophageal junction cancer: Risk factors and prophylactic
treatments for prevention of peritoneal recurrence after curative
intent surgery. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 6:474–485. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kitayama J, Ishigami H, Yamaguchi H,
Sakuma Y, Horie H, Hosoya Y, Lefor AK and Sata N: Treatment of
patients with peritoneal metastases from gastric cancer. Ann
Gastroenterol Surg. 2:116–123. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cieśla S, Lisiecki R, Ławnicka A,
Kudliński B, Ostrowska P, Davì A, Veroux M and Murawa D: Clinical
significance of peritoneal fluid examination for free cancer cells
in patients qualified for surgery for gastric cancer. Front Surg.
8:6858682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kołomańska MM and Głuszek S: Free cancer
cells in gastric cancer-methods of detection, clinical and
prognostic importance (meta-analysis). Contemp Oncol (Pozn).
24:67–74. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Amo L, Tamayo-Orbegozo E, Maruri N,
Eguizabal C, Zenarruzabeitia O, Riñón M, Arrieta A, Santos S, Monge
J, Vesga MA, et al: Involvement of platelet-tumor cell interaction
in immune evasion. Potential role of podocalyxin-like protein 1.
Front Oncol. 4:2452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Labelle M and Hynes RO: The initial hours
of metastasis: The importance of cooperative host-tumor cell
interactions during hematogenous dissemination. Cancer Discov.
2:1091–1099. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Takemoto A, Okitaka M, Takagi S, Takami M,
Sato S, Nishio M, Okumura S and Fujita N: A critical role of
platelet TGF-β release in podoplanin-mediated tumour invasion and
metastasis. Sci Rep. 7:421862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schlesinger M: Role of platelets and
platelet receptors in cancer metastasis. J Hematol Oncol.
11:1252018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wiercinska E, Naber HPH, Pardali E, van
der Pluijm G, van Dam H and ten Dijke P: The TGF-β/Smad pathway
induces breast cancer cell invasion through the up-regulation of
matrix metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in a spheroid invasion model
system. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:657–666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Spalton JC, Mori J, Pollitt AY, Hughes CE,
Eble JA and Watson SP: The novel Syk inhibitor R406 reveals
mechanistic differences in the initiation of GPVI and CLEC-2
signaling in platelets. J Thromb Haemost. 7:1192–1199. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Manne BK, Badolia R, Dangelmaier C, Eble
JA, Ellmeier W, Kahn M and Kunapuli SP: Distinct pathways regulate
Syk protein activation downstream of immune tyrosine activation
motif (ITAM) and hemITAM receptors in platelets. J Biol Chem.
290:11557–11568. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
David CJ and Massagué J: Contextual
determinants of TGFβ action in development, immunity and cancer.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 19:419–435. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
De Kock L and Freson K: The (patho)biology
of SRC kinase in platelets and megakaryocytes. Medicina (Kaunas).
56:6332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
World Medical Association, . World medical
association declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Percie du Sert N, Ahluwalia A, Alam S,
Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl U,
Emerson M, et al: Reporting animal research: Explanation and
elaboration for the ARRIVE guidelines 2.0. PLoS Biol.
18:e30004112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|