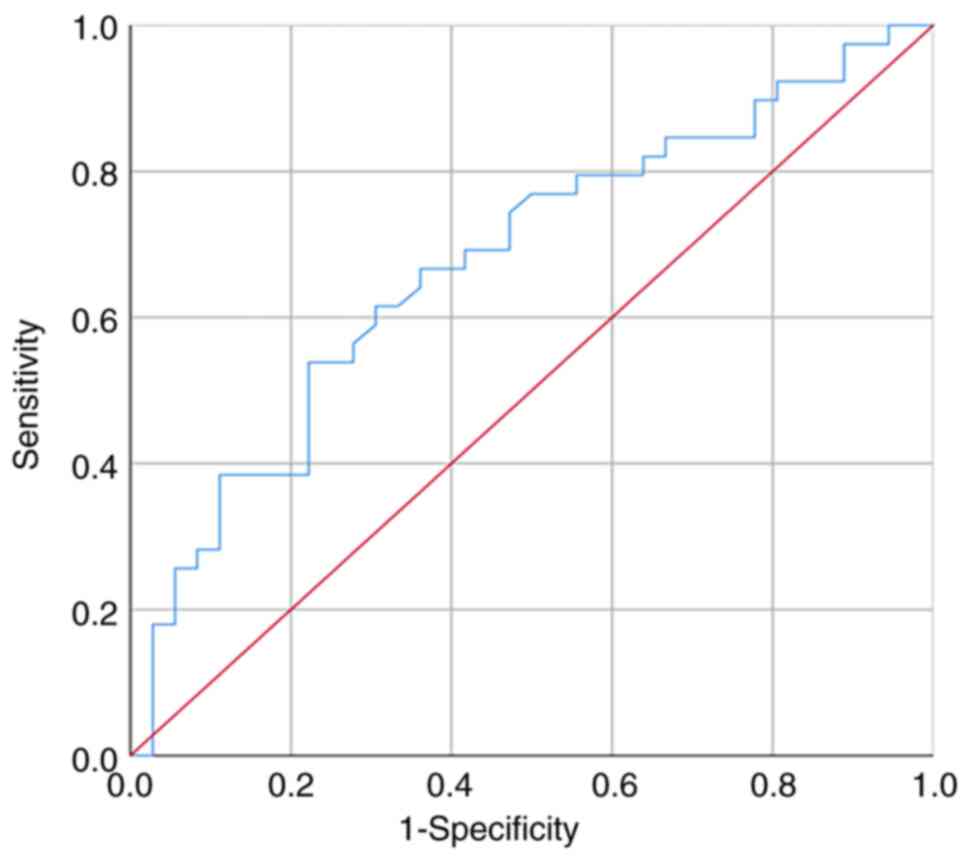
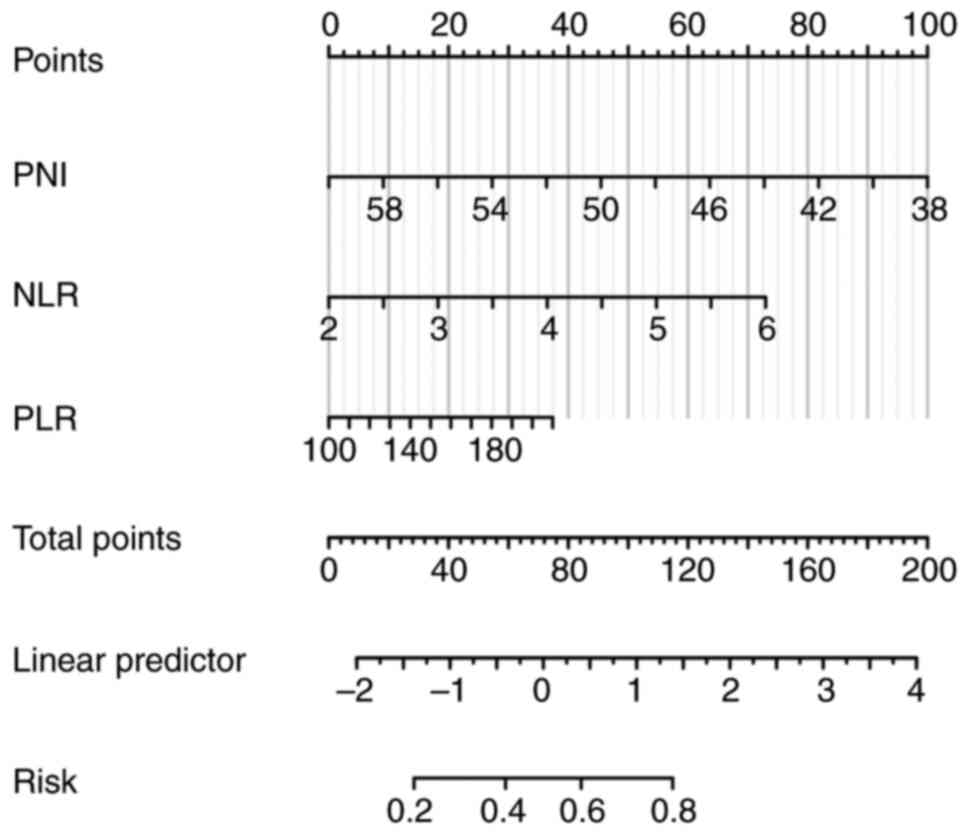
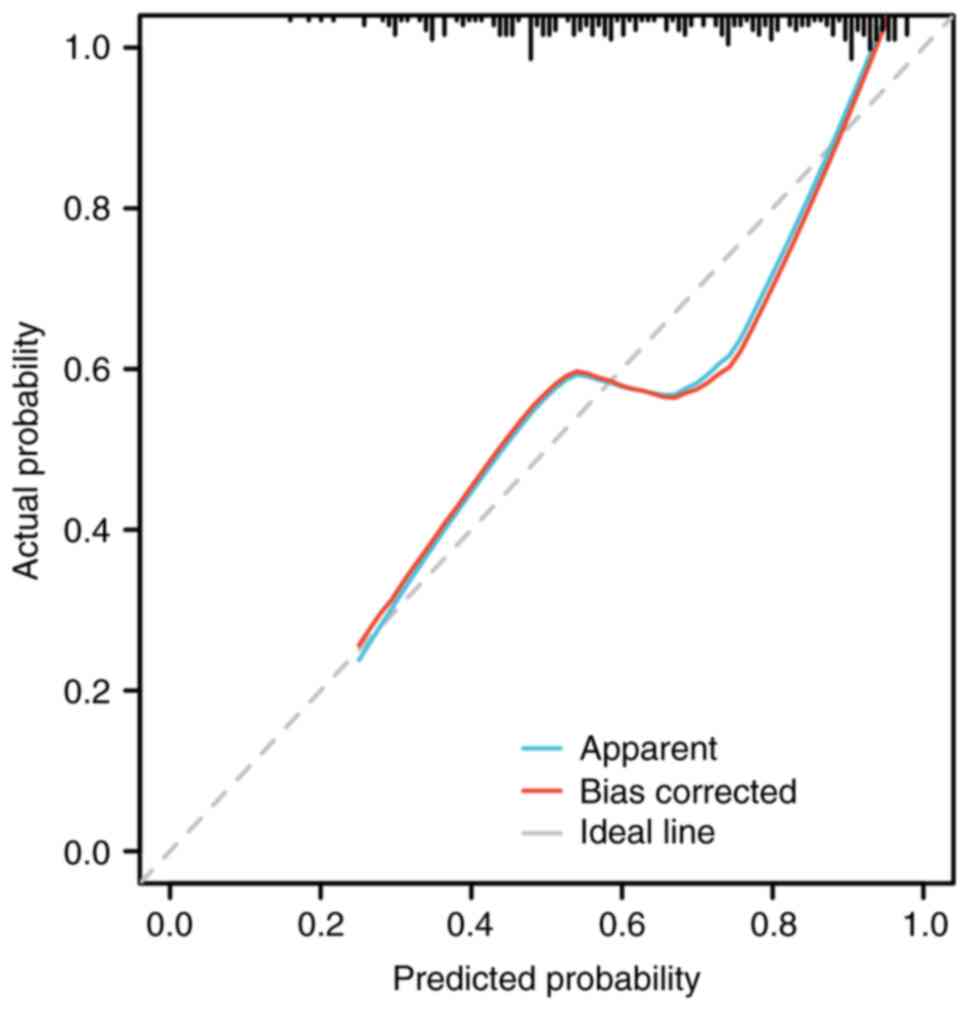
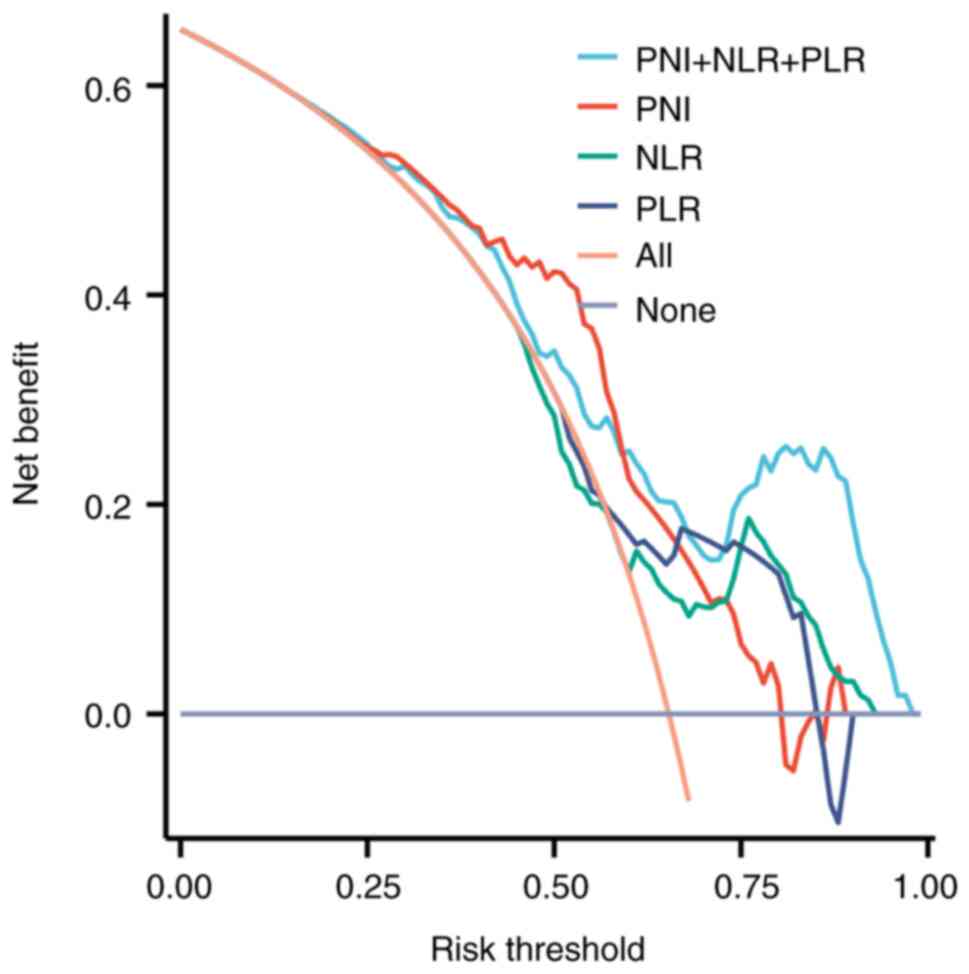
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhu H, Ma X, Ye T, Wang H, Wang Z, Liu Q
and Zhao K: Esophageal cancer in China: Practice and research in
the new era. Int J Cancer. 152:1741–1751. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li R, Sun J, Wang T, Huang L, Wang S, Sun
P and Yu C: Comparison of secular trends in esophageal cancer
mortality in China and Japan during 1990–2019: An age-period-cohort
analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 19:103022022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Tonoiso C, Ikushima H, Kubo A, Kawanaka T,
Funatani S, Kudo T, Yoshida T, Miyamoto H, Harada M, Takayama T and
Tangoku A: Clinical outcomes and prognostic factors of definitive
radiotherapy for esophageal cancer. J Med Invest. 66:99–105. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
de Groot C, Beukema JC, Langendijk JA, van
der Laan HP, van Luijk P, van Melle JP, Muijs CT and Prakken NHJ:
Radiation-Induced myocardial fibrosis in long-term esophageal
cancer survivors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 110:1013–1021.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Alizade-Harakiyan M, Jangjoo AG,
Jafari-Koshki T, Fatemi A and Mesbahi A: Radiobiological modeling
of acute esophagitis after radiation therapy of head, neck, and
thorax tumors: The influence of chemo-radiation. J Cancer Res Ther.
18:1706–1715. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Zhou P, Du Y, Zhang Y, Zhu M, Li T, Tian
W, Wu T and Xiao Z: Efficacy and safety in proton therapy and
photon therapy for patients with esophageal cancer: A
meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 6:e23281362023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zheng X, Guo W, Wang Y, Zhang J, Zhang Y,
Cheng C, Teng X, Lam S, Zhou T, Ma Z, et al: Multi-omics to predict
acute radiation esophagitis in patients with lung cancer treated
with intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Eur J Med Res.
28:1262023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang SA, Dai WS, Zhu JY, Gao B, Ren W and
Chen X: Nasogastric tube feeding improves nutritional status and
physical state in esophageal cancer patients during
chemoradiotherapy: A retrospective study. Support Care Cancer.
31:3412023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vidal-Casariego A, Calleja-Fernandez A,
Ballesteros-Pomar MD and Cano-Rodriguez I: Efficacy of glutamine in
the prevention of oral mucositis and acute radiation-induced
esophagitis: A retrospective study. Nutr Cancer. 65:424–429. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sui Q, Zhang X, Chen C, Tang J, Yu J, Li
W, Han K, Jiang W, Liao L, Kong L, et al: Inflammation promotes
resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in high microsatellite
instability colorectal cancer. Nat Commun. 13:73162022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Wang G, Jiang L, Wei
Q, Luo C, Chen L and Ying J: Systemic inflammatory markers of
resectable colorectal cancer patients with different mismatch
repair gene status. Cancer Manag Res. 13:2925–2935. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim HS and Ku JH: Systemic inflammatory
response based on neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic
marker in bladder cancer. Dis Markers. 2016:83452862016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rice TW, Blackstone EH and Rusch VW: 7th
edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual: Esophagus and
esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1721–1724. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL and
MacKenzie CR: A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in
longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J Chronic Dis.
40:373–383. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cox JD, Stetz J and Pajak TF: Toxicity
criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the
European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC).
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 31:1341–1346. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Beukema JC, van Luijk P, Widder J,
Langendijk JA and Muijs CT: Is cardiac toxicity a relevant issue in
the radiation treatment of esophageal cancer? Radiother Oncol.
114:85–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ishida N, Osawa S, Miyazu T, Kaneko M,
Tamura S, Tani S, Yamade M, Iwaizumi M, Hamaya Y, Furuta T and
Sugimoto K: Photodynamic therapy using talaporfin sodium for local
failure after chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy for esophageal
cancer: A single center experience. J Clin Med. 9:15092020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Danieli M and Gronchi A: Staging systems
and nomograms for soft tissue sarcoma. Curr Oncol. 30:3648–3671.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li S, Zhang H, Liao X, Yan X, Chen L, Lin
Y and Peng Y: The occurrence of early atrial fibrillation after
cardiac valve operation and the establishment of a nomogram model.
Front Cardiovasc Med. 10:10368882023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gu X, Shen H, Bai W, Xiang Z, Li X, Zhang
R, Shi F, Li H, Zhu G and Guo S: Endometrial cancer prognosis
prediction using correlation models based on CDK family genes.
Front Genet. 13:10216002022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang B, Jiang X, Tian D and Geng W:
Enteral nutritional support in patients undergoing
chemoradiotherapy for esophageal carcinoma. Future Oncol.
16:2949–2957. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Cao J, Xu H, Li W, Guo Z, Lin Y, Shi Y, Hu
W, Ba Y, Li S, Li Z, et al: Nutritional assessment and risk factors
associated to malnutrition in patients with esophageal cancer. Curr
Probl Cancer. 45:1006382021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Okadome K, Baba Y, Yagi T, Kiyozumi Y,
Ishimoto T, Iwatsuki M, Miyamoto Y, Yoshida N, Watanabe M and Baba
H: Prognostic nutritional index, tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes,
and prognosis in patients with esophageal cancer. Ann Surg.
271:693–700. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang Z, Wang Y, Zhang X and Zhang T:
Pretreatment prognostic nutritional index as a prognostic factor in
lung cancer: Review and meta-analysis. Clin Chim Acta. 486:303–310.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X and Wang Y: The prognostic
nutritional index is prognostic factor of gynecological cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 67:79–86. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yao J, Cui Q, Fan W, Ma Y, Chen Y, Liu T,
Zhang X, Xi Y, Wang C, Peng L, et al: Single-cell transcriptomic
analysis in a mouse model deciphers cell transition states in the
multistep development of esophageal cancer. Nat Commun.
11:37152020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
O'Sullivan KE, Phelan JJ, O'Hanlon C,
Lysaght J, O'Sullivan JN and Reynolds JV: The role of inflammation
in cancer of the esophagus. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
8:749–760. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shavakhi M, Nourigheimasi S, Dioso E,
Goutnik M, Lucke-Wold B, Khanzadeh S and Heidari F: Prognostic role
of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Can J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 2022:15540792022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Demirel ME and Akunal Turel C: The role of
the multi-inflammatory index as a novel predictor of hospital
mortality in acute ischemic stroke. Cureus. 15:e432582023.
|
|
31
|
Sun Y and Zhang L: The clinical use of
pretreatment NLR, PLR, and LMR in patients with esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag Res.
10:6167–6179. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ishibashi Y, Tsujimoto H, Einama T,
Mochizuki S, Kouzu K, Nomura S, Ito N, Harada M, Sugasawa H, Shinto
E, et al: Correlation between immunoinflammatory measures and
periostin expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A
single-center, retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg Oncol.
28:1228–1237. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|