Introduction
Lung cancer ranks among the highest in incidence and
mortality rates of common malignant tumors both in China and
worldwide (1,2). In 2018, it was estimated that there
were 2.1 million new cases of lung cancer and 1.8 million related
deaths globally, with China accounting for 37% of new cases and
39.2% of lung cancer related-deaths (1). Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), the
most common histological type of lung cancer, primarily comprises
squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma (3). Significant advancements in the
treatment of NSCLC, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation
therapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy, have been made,
particularly for patients with specific genetic mutations. However,
the overall prognosis improvement for the entire population of
patients with NSCLC varies due to individual differences, genetic
characteristics and responses to treatment (4,5).
The development of tumor immunotherapy has made a
major breakthrough in the treatment of tumors (6). Numerous studies have reported that
immunotherapy with immune-checkpoint inhibitors targeting
programmed death 1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) has
marked antitumor effects in several malignant tumors, such as
hepatocellular carcinoma (7),
melanoma (8), NSCLC (9) and head and neck cancer (10). However, the majority of patients
with NSCLC do not respond to this type of immunotherapy (11). This is due to the fact that cancer
cells can evade immune attack by manipulating immune surveillance
mechanisms (12). Therefore,
actively elucidating the mechanism of action may be a key
breakthrough in improving NSCLC immunotherapy.
PD-1 is an important immunosuppressive molecule
expressed on the surface of T cells. Once PD-L1 binds to PD-1 in
tumor cells, it transmits a ‘brake’ signal to T cells, inhibiting
the activation of T cells, thereby preventing the immune system
from killing cancer cells (13,14).
Studies have revealed that PD-L1 expression is elevated in a series
of malignant tumors, including NSCLC, and is associated with poor
prognosis and shortened patient survival (15,16).
Treatment that inhibits PD-1 or PD-L1 improves the survival of
patients with advanced NSCLC (17).
As an important non-coding RNA, circular (circ) RNA
can regulate the immune escape of tumors mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 in
several ways and promote further development of tumors. A previous
study reported that circCHST15 targeting microRNA (miR)-155-5p and
miR-194-5p up-regulated the expression of PD-L1, affected the
function of CD8+T cells and promoted the immune escape of lung
adenocarcinoma cells (18). Another
study reported that circHSP90A inhibited the progression of NSCLC
by regulating the signal transducer and activator of transcription
3 signaling and the PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint to activate antitumor
immunity (19). Such evidence
demonstrates the great potential of circRNA as an effective and
specific biomarker in the immunotherapeutic targeting of NSCLC.
CircENTPD7, a circRNA, is upregulated in
glioblastoma and targets the regulation of ROS proto-oncogene 1,
receptor tyrosine kinase expression to promote tumor progression
(20). Our previous study
demonstrated that upregulation of circENTPD7 expression in NSCLC
tissues and cells, along with high circENTPD7 levels, predicted a
lower survival rate of patients with NSCLC (21). However, the behavioral and
regulatory mechanisms of circENTPD7 in inducing immune responses
during NSCLC cell progression have not been fully elucidated.
Therefore, the present study aimed to elucidate the specific role
of circENTPD7 in NSCLC, particularly in the progression of immune
escape, and its potential relationship with PD-L1. Overall, the
results of the present study provide novel insights into the
mechanisms of NSCLC, providing a molecular basis for clinical
diagnosis and precision drug therapy.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Human normal lung epithelial BEAS-2B cells, human
NSCLC H1299 cells and human 293T cells were purchased from Wuhan
Elabscience Biotechnology Co., Ltd. BEAS-2B cells were grown in a
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Gibco; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.), whereas H1299 cells were grown in a Roswell Park
Memorial Institute 1640 complete medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). Activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells
(PBMCs) were purchased from IPHASE, Inc. (cat. no. 082A01.11).
PBMCs were grown in Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
special medium (cat. no. IMP-H022-1; Immocell; Xiamen Yimo
Biotechnology Co., Ltd.). All cells were cultured in a 5%
CO2 incubator at 37°C.
RNA interference and plasmid
transfection
Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. designed small interfering
(si)RNA (si-circENTPD7 and si-PD-L1) and lentivirus
pLV-eGFP-N-Puro-specifically targeting circENTPD7 or PD-L1
overexpression (OE)-insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2)
mRNA-binding protein 2 (IGF2BP2) expression vectors (OE-IGF2BP2)
and their negative control (NC) empty vectors (si-NC and OE-NC).
The lentiviral plasmid was transfected into H1299 cells using
Lipofectamine™ 3000 (Invitrogen™; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to the supplier's guidelines.
The concentration of nucleic acid used was 0.75 µg. Follow-up
experiments were performed 48 h after transfection in room
temperature. The siRNA-circENTPD7 and siRNA-PD-L1 sequences were as
follows: circENTPD7 siRNA-1 forward, 5′-UAUAUUGAUUCAAAAGGACCU-3′
and reverse, 3′-GUCCUUUUGAAUCAAUAUACA-5′; circENTPD7 siRNA-2
forward, 5′-UGUAUAUUGAUUCAAAAGGAC-3′ and reverse,
5′-CCUUUUGAAUCAAUAUACAAA-3′; circENTPD7 siRNA-3 forward,
5′-UUGUAUAUUGAUUCAAAAGGA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CUUUUGAAUCAAUAUACAAAG-3′; PD-L1 siRNA-1 forward,
5′-AUAAAGACAGCAAAUAUCCUC-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGAUAUUUGCUGUCUUUAUAU-3′; PD-L1 siRNA-2 forward,
5′-UAUAAAGACAGCAAAUAUCCU-3′ and reverse,
5′-GAUAUUUGCUGUCUUUAUAUU-3′; PD-L1 siRNA-3 forward,
5′-AGUUGUUGUGUUGAUUCUCAG-3′ and reverse,
5′-GAGAAUCAACACAACAACUAA-3′; si-NC forward,
5′-CACCGTTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTTTCAAGAGAACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAATTTTTTG-3′
and reverse,
5′-GATCCAAAAAATTCTCCGAACGTGTCACGTTCTCTTGAAACGTGACACGTTCGGAGAAC-3′.
Cell counting kit-8 assay for cell
viability
The viability of H1299 cells was assessed using the
Cell Counting Kit-8 proliferation assay kit (cat. no. CEB044Hu;
BIOSS). The duration of incubation with CCK-8 reagent was 2 h.
Absorption was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm, with all
procedures performed according to the kit manual.
Transwell assay
Cell migration and invasion were assessed in
Transwell Petri dishes with or without Matrigel (Corning, Inc.).
Briefly, transfected H1299 cells (2×105) were added to
100 µl serum-free medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
and seeded into the upper chamber, and then 500 µl DMEM containing
10% serum (Shanghai ExCell Biology, Inc.) was seeded into the lower
chamber. The cells in the upper chamber were incubated for 24 h in
a 5% CO2 incubator at 37°C and then fixed with 4%
paraformaldehyde (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) for 10 min
at room temperature. After cell staining with 0.2–0.5% crystal
violet (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 10 min at room temperature,
the cells were observed under an inverted optical microscope
(Shanghai Optical Instrument Factory) and statistically analyzed.
The migration assay was similar to the invasion assay, except that
Matrigel was not used.
Co-culture of H1299 cells and T
cells
Activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs)
were purchased from IPHASE, Inc. (cat. no. 082A01.11). First, CD4+
(CD3+ and CD4+) and CD8+ (CD3+ and CD8+) cells were purified from
human PBMCs using the EasySep™ Human T cell Isolation
Kit (cat. no. 17952; NovoBiotechnology). Subsequently, the % of
CD4+ and CD8+ cells in the total PBMC was analyzed using a FACScan
device. T cells were then stained with 5 µM FITC for 10 min, and
5×105 T cells were co-cultured with the treated H1299
cells in the medium. Subsequently, recombinant human lL-2 (20
IU/ml; cat. no. 90103ES60; Shanghai Yeasen Biotechnology Co. Ltd.),
anti-CD3 (2 µg/ml; cat no. ab16669; Abcam) and anti-CD28 (1 µg/ml;
cat. no. ab243228; Abcam) antibodies were added to the medium. T
cells were then collected and assessed using an Attune NxT flow
cytometer (Invitrogen; Themo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) after 48 h of
culture.
ELISA analysis
The culture medium supernatant of the co-culture
system was collected. According to the manufacturer's guidelines,
the human interferon-γ [IFN-γ; cat. no. EK180; Multi Sciences
(Lianke) Biotech Co., Ltd.], human IL-2 [cat. no. EK102; Multi
Sciences (Lianke) Biotech Co., Ltd.] and human transforming growth
factor β (TGF-β; cat. no. JL20082; Shanghai Future Industrial Co.,
Ltd.) ELISA kits were used to detect IFN-γ, IL-2 and TGF-β
concentrations in the H1299 cells, respectively.
Reverse transcription
(RT)-quantitative (q)PCR experiment
Total RNA was extracted from BEAS-2B and H1299 cells
using the FastPure Cell/Tissue Total RNA Isolation Kit V2 (cat. no.
RC112; Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.). RT of circRNA/mRNA was performed
using the HiScript III 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (cat. no.
R111-01/02; Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd.). The temperature protocol
used was as follows: 37°C for 15 min and 85°C for 5 sec. qPCR
(22) was performed using the Taq
Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix (cat. no. Q712; Vazyme Biotech
Co., Ltd.). The thermocycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for
10 sec, 60°C for 30 sec and 95°C for 15 sec. The relative
expression levels of the miRNAs were calculated using the
2−ΔΔCq method (23).
GAPDH was used as an internal reference for mRNA/circRNA. The
primers used are listed in Table
I.
 | Table I.Primer sequences. |
Table I.
Primer sequences.
| Gene | Direction | Primer sequence
(5′-3′) |
|---|
| CircENTPD7 | F |
ATGCCAGTGATTACCTTCGT |
|
| R |
CTTCAAGCTCCCCTACTC |
| IGF2BP2 | F |
AGAAAAGAGAACTCTGGAGCTG |
|
| R |
CAGCCAGCATATCATTTTCAAAGG |
| PD-L1 | F |
ACTTAAAAGGCCCAAGCACTG |
|
| R |
ACATGACAAGAAGACCTCACAG |
| GAPDH | F |
GGTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACA |
|
| R |
GTGAGGGTCTCTCTCTTCCT |
Western blotting
Protein was extracted from the BEAS-2B and H1299
cells using a radio-immunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer
(Biosharp Life Sciences). Protein quantification was determined by
the BCA method. Proteins with a volume of 10 µl and a mass of 20 µg
were then loaded onto an sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel
electrophoresis gel (10% separating gel and 5% compression gel,
BioFroxx; neoFroxx GmbH) and transferred to a polyvinylidene
fluoride membrane after electrophoresis. The membranes were blocked
by shaking at room temperature for 20–40 min using a rapid closure
solution (cat. no. P0252; 500 ml; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology). Subsequently, the membrane was incubated with the
following primary antibodies overnight at 4°C in a solution
containing 5% skim milk powder (BioFroxx; neoFroxx GmbH): EPR6741
(1:2,000; cat. no. ab124930; Abcam), anti-PD-L1 (1:1,000; cat. no.
ab205921; Abcam) and anti-GAPDH (1:10,000; cat. no. ab8245; Abcam).
The corresponding secondary antibodies Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L
(HRP; 1:20,000; cat. no. bs-0295G-HRP; Abcam) and Goat Anti-Mouse
IgG H&L (HRP; 1:20,000; cat. no. bs-0296G-HRP; Abcam) were then
added for another 2 h of incubation. Finally, an enhanced
chemiluminescence kit (cat. no. T15139; NCM Biotech) was used for
signal visualization, and the optical density values were analyzed
using ImageJ 1.8.0 software (National Institutes of Health).
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed and plotted using GraphPad Prism
9 (version 9.4.0; Dotmatics). The graph was organized using Adobe
Illustrator (version 2023; Adobe Systems, Inc.). All data are
expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical difference
between groups was assessed using an unpaired t-test. P<0.05 was
considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
High expression of circENTPD7, IGF2BP2
and PD-L1 in NSCLC cells
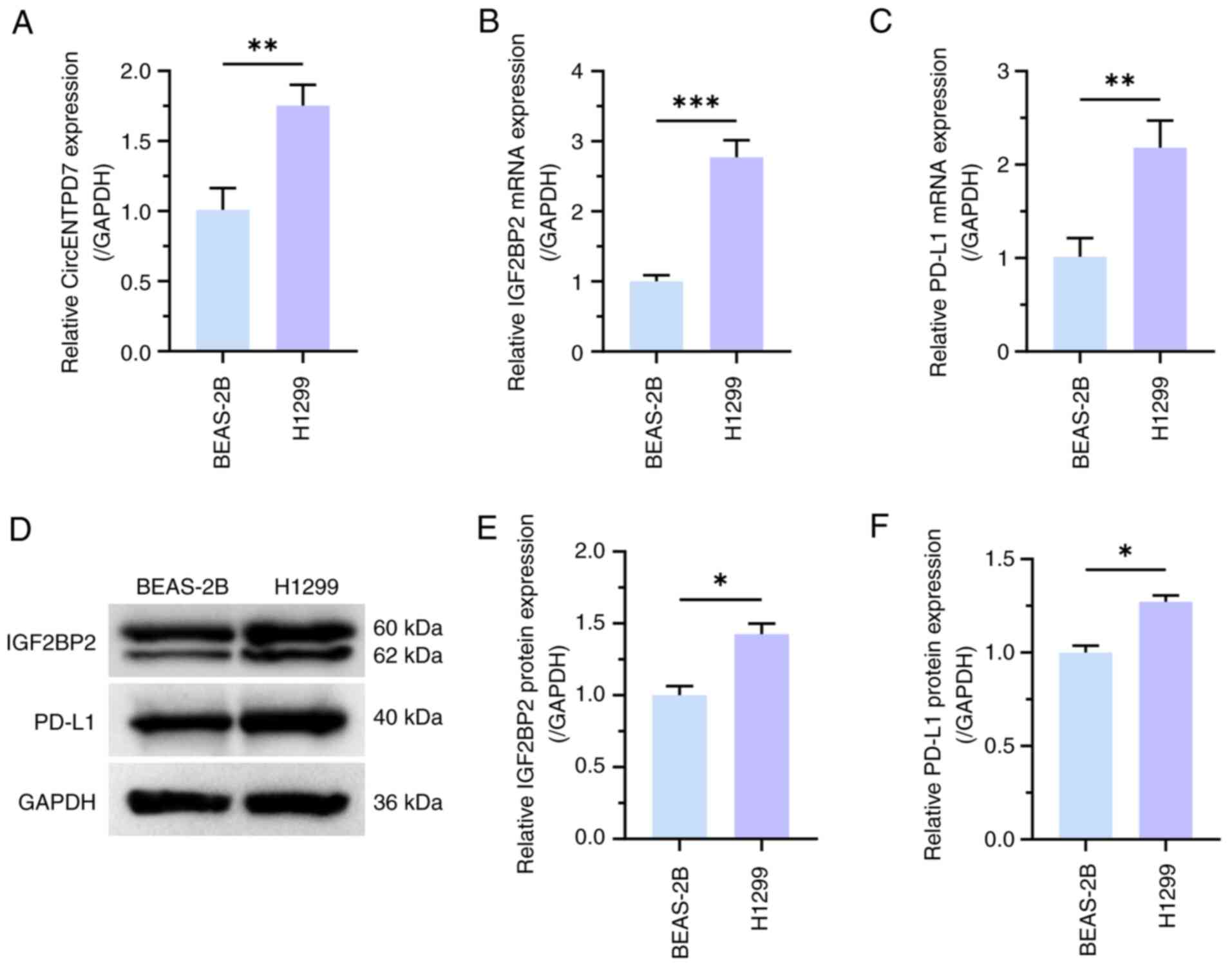
RT-qPCR was used to determine the expression
patterns of circENTPD7, IGF2BP2 and PD-L1 in normal lung epithelial
cells and NSCLC cell lines. RT-qPCR results revealed that
circENTPD7, IGF2BP2 and PD-L1 expression was significantly higher
in H1299 cells than in BEAS-2B cells (P<0.01; Fig. 1A-C). In addition, the results of
western blotting experiments also demonstrated that the expression
levels of IGF2BP2 and PD-L1 were significantly upregulated in H1299
cells, compared with in BEAS-2B cells (P<0.05; Fig. 1D-F).
CircENTPD7 knockdown suppresses the
malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells
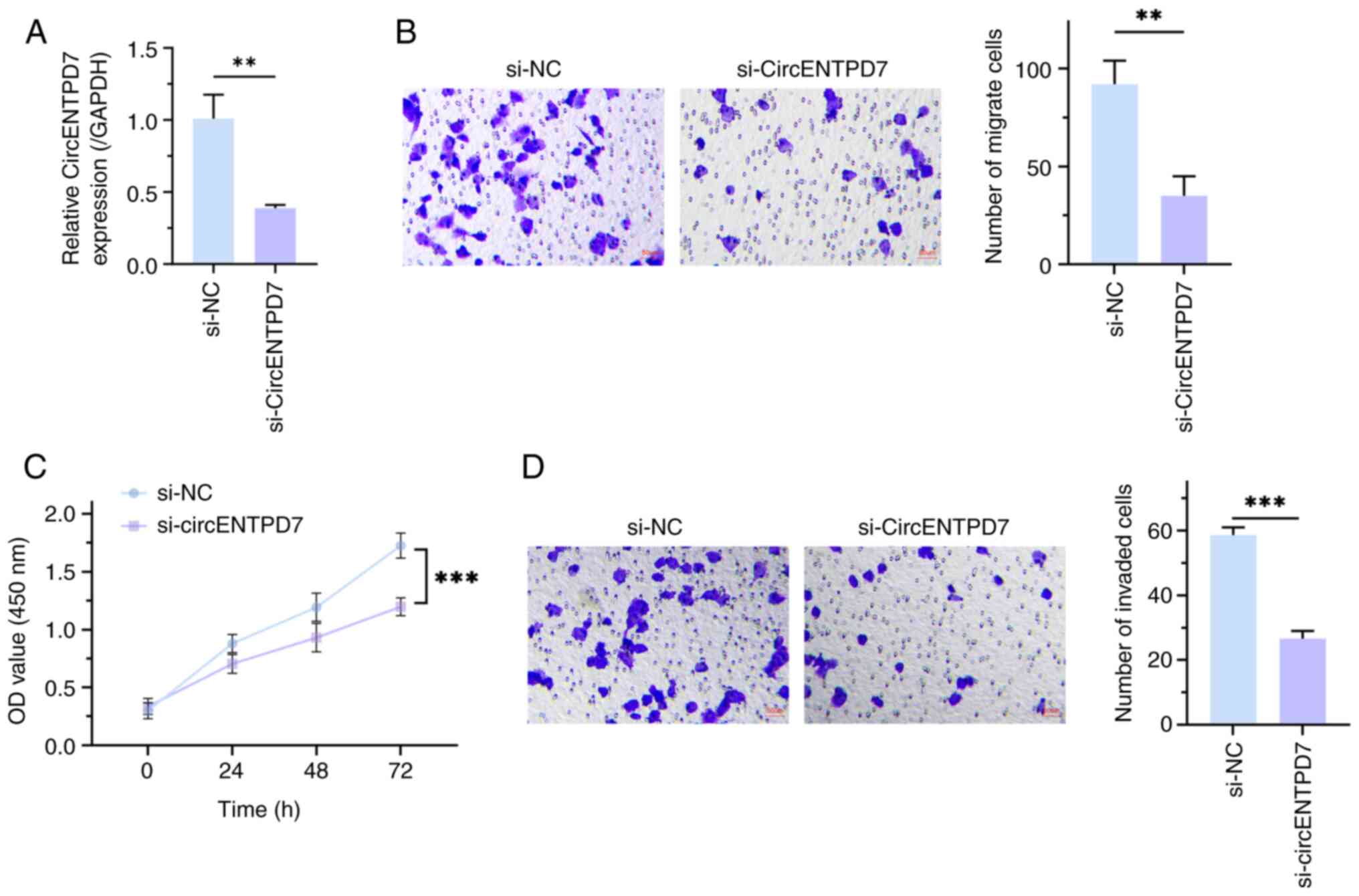
Subsequently, a circENTPD7 knockout function
experiment was performed to assess the biological function of
circENTPD7 in NSCLC cells, and RT-qPCR was used to detect
transfection efficiency. The results demonstrated that circENTPD7
expression was significantly reduced after transfection of
si-circENTPD7 into H1299 cells, compared with transfection with
si-NC (P<0.01; Fig. 2A).
Furthermore, Cell Counting Kit-8 analysis revealed that, compared
with the si-NC group, the proliferation of H1299 cells treated with
si-circENTPD7 was significantly suppressed (P<0.001; Fig. 2B). Furthermore, it was demonstrated
that downregulation of circENTPD7 significantly impeded H1299 cell
migration and invasion, in comparison with the control (P<0.01;
Fig. 2C and D). These data indicate
that knockdown of circENTPD7 could impede the proliferation,
migration and invasion of H1299 cells.
Overexpression of IGF2BP2 inhibits the
malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells by reversing circENTPD7
silencing
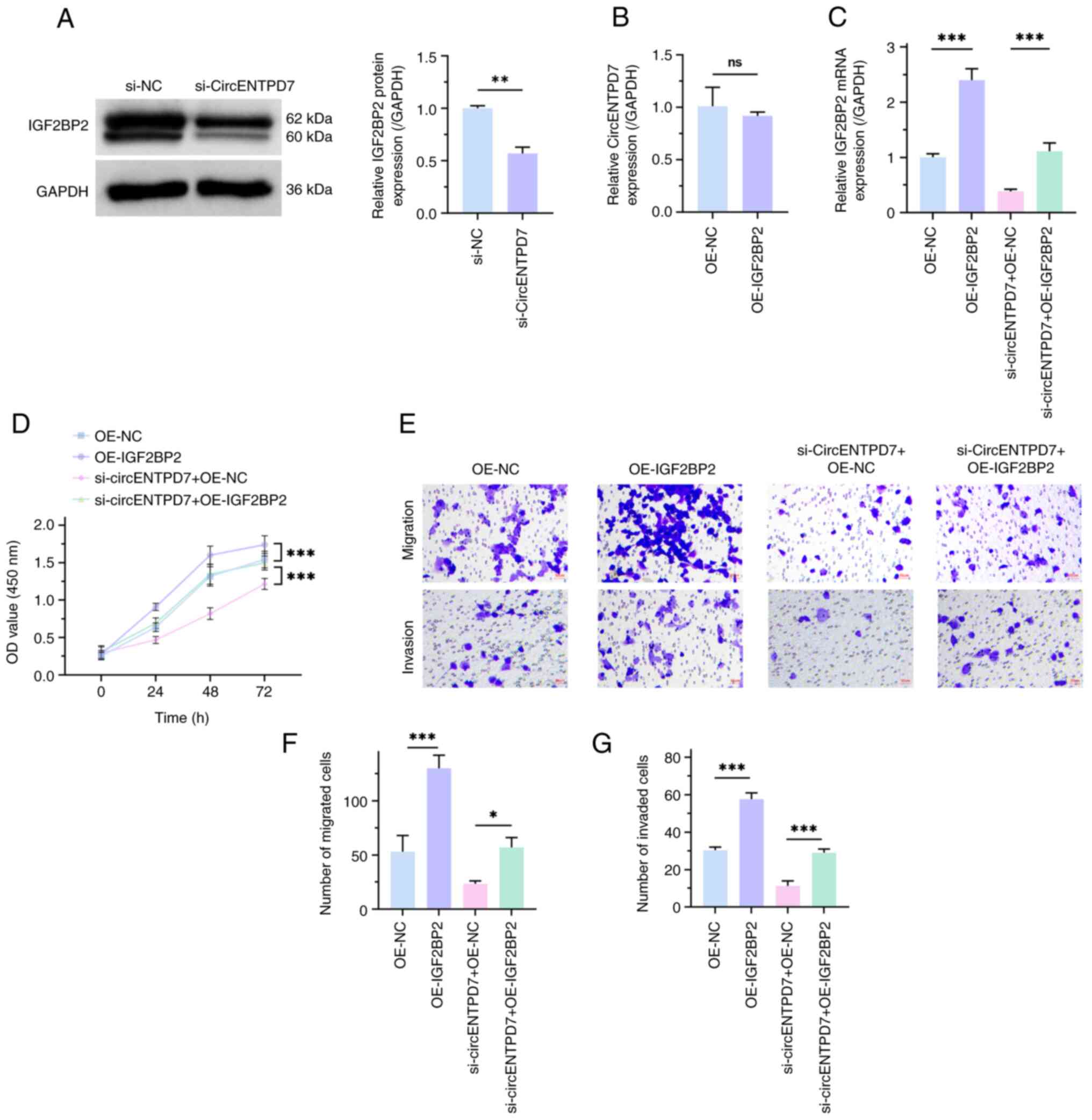
To evaluate the regulatory mechanism of circENTPD7
and IGF2BP2 in H1299 cells, the present study used western blotting
to assess the influence of downregulated circENTPD7 on IGF2BP2
expression in H1299 cells and then semi-quantified the results. The
results demonstrated that IGF2BP2 expression in the si-circENTPD7
group was significantly lower than that in the si-NC group
(P<0.01; Fig. 3A). However,
there was no significant difference in circENTPD7 expression
between the OE-IGF2BP2 and the OE-NC groups (P>0.05;
Fig. 3B). These results indicate
that circENTPD7 could positively regulate IGF2BP2, whereas IGF2BP2
could not negatively regulate circENTPD7. Subsequently, salvage
experiments were used to further assess the regulatory roles of
circENTPD7 and IGF2BP2 in NSCLC. Transfection efficiency was
determined (P<0.001; Fig. 3C).
In brief, transfection of the OE-IGF2BP2 plasmid in H1299 cells
significantly upregulated IGF2BP2 expression, and OE-IGF2BP2
significantly reversed the effect of si-circENTPD7 on IGF2BP2
expression, in comparison with the negative controls. At the same
time, biological function experiments revealed that overexpression
of IGF2BP2 could significantly accelerate the malignant behavior of
H1299 cells, in comparison with negative controls. Moreover,
overexpression of IGF2BP2 significantly reversed the inhibitory
effect of circENTPD7 silencing on the malignant behavior of H1299
cells, in comparison with negative controls (P<0.05; Fig. 3D-G). These data indicate that
circENTPD7 may accelerate the malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells by
upregulating IGF2BP2 expression.
IGF2BP2 overexpression upregulates
PD-L1 and promotes immune escape in NSCLC cells
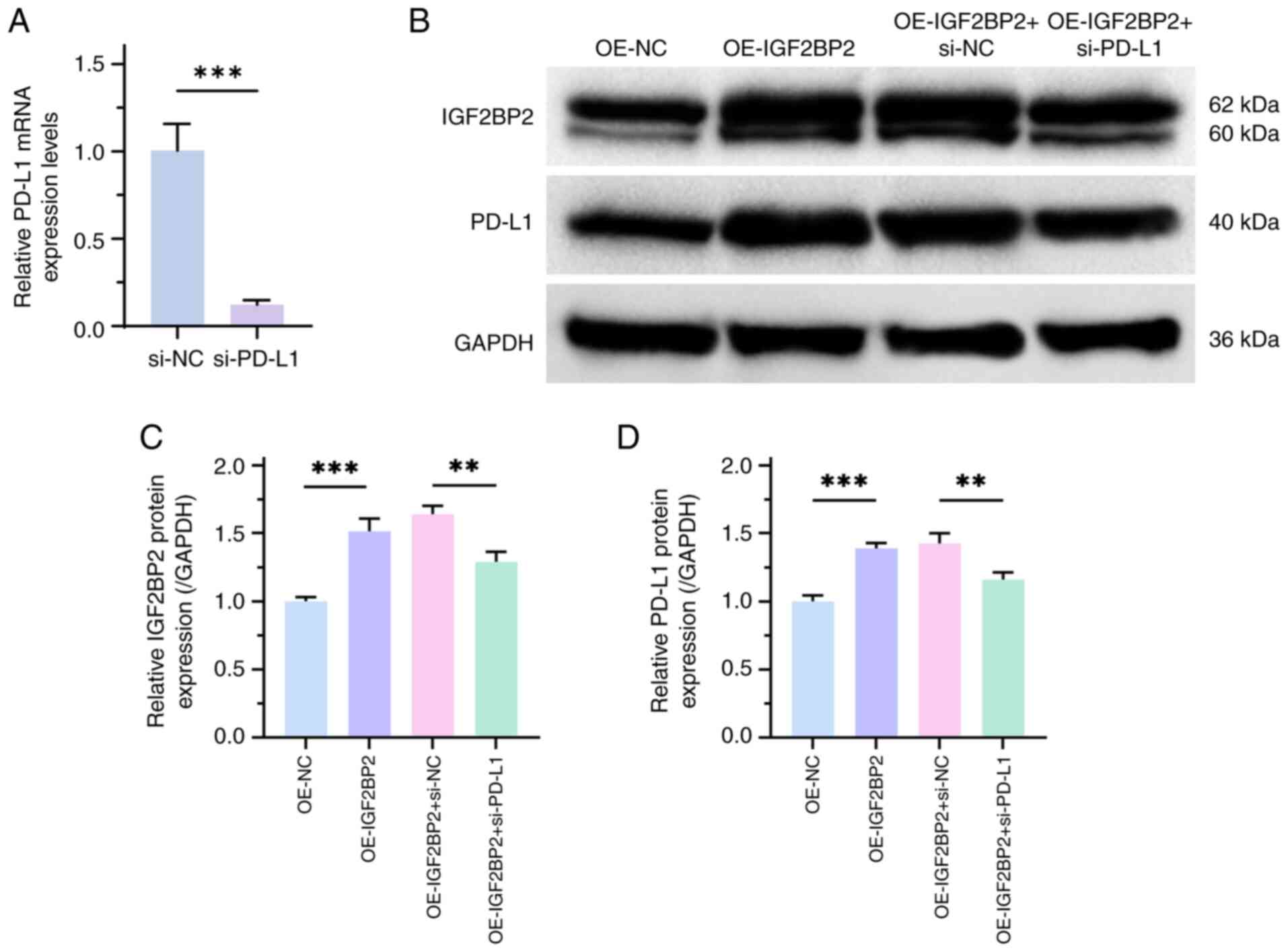
PD-1/PD-L1 is an important mechanism for tumor
immune escape (24). Therefore, the
present study assessed the effects of IGF2BP2 on PD-L1 expression.
RT-qPCR results demonstrated the transfection efficiency of
si-PD-L1 (P<0.001; Fig. 4A).
Furthermore, the results of western blotting revealed that the
protein expression levels of PD-L1 and IGF2BP2 were significantly
increased in the treatment group with high IGF2BP2 expression,
compared with negative controls. However, si-PD-L1 significantly
reversed the effects of high IGF2BP2 expression on PD-L1 and
IGF2BP2 expression levels, compared with negative controls,
suggesting an interaction between IGF2BP2 and PD-L1 (P<0.01;
Fig. 4B-D).
To further evaluate the effect of IGF2BP2
upregulation on PD-L1-mediated immune escape in NSCLC cells, CD8+
and CD4+T cells were first isolated and purified from human PBMC
cells and their purity was measured using flow cytometry (Fig. 5A). Subsequently, an in vitro
blocking experiment was performed. The experimental results
revealed that overexpression of IGF2BP2 significantly reduced CD4+
and CD8+T cell ratios, whilst blocking PD-L1 reversed this
phenomenon, in comparison with negative controls (P<0.001;
Fig. 5B-D). This indicates
increased proliferation of H1299 cells, suggesting immune evasion
by the tumor cells. In this scenario, the tumor cells could
potentially inhibit T cell activity by upregulating immune
checkpoint molecules such as PD-L1, promoting their own
proliferation. This decrease in the proportion of co-cultured CD4
and CD8 T cells may hinder their recognition of H1299 cells,
leading to a blocking effect. Furthermore, ELISA results
demonstrated that the inhibitory effect of IGF2BP2 overexpression
on the immune effectors IFN-γ and IL-2, as well as its promoting
effect on the immunosuppressive factor TGF-β, was significantly
reversed by blocking PD-L1, in comparison with negative controls
(P<0.001; Fig. 5E-G). These data
suggest that IGF2BP2 may drive NSCLC immune escape through
upregulation of PD-L1 expression.
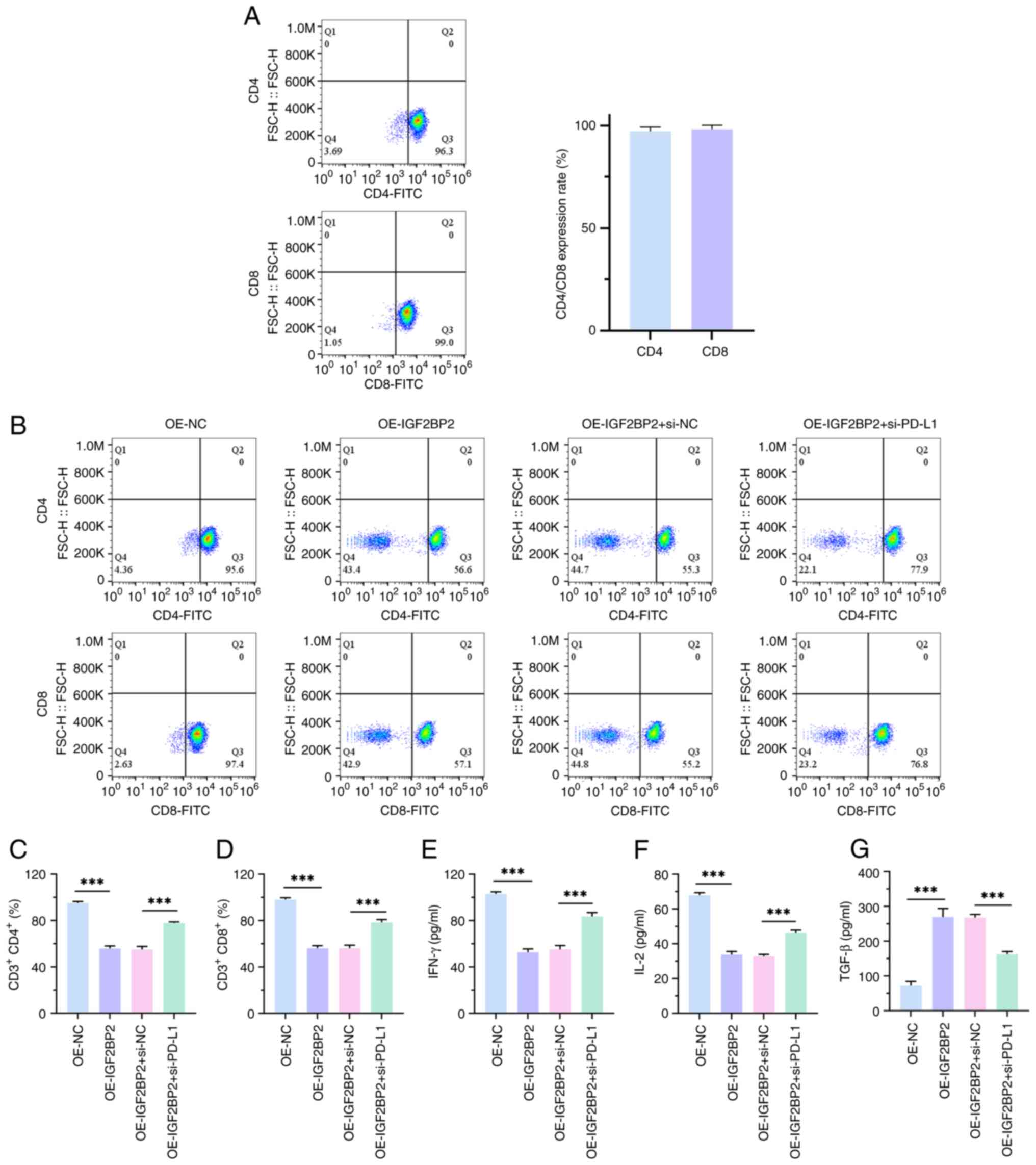 | Figure 5.Overexpression of IGF2BP2 promotes the
immune escape of non-small cell lung cancer cells. (A) CD8+ and
CD4+ T cells were isolated and purified from human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells using flow cytometry. (B) Flow cytometry was used
to assess the proportion of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the co-culture
system of T cells and H1299 cells. The lower-left quadrant
represent non-CD4+ or non-CD8+ T cells. (C) Bar chart of CD3+CD4+.
(D) Bar chart of CD3+CD8+. (E) IFN-γ production in T cell and H1299
cell co-culture system, assessed using ELISA. (F) IL-2 production
in T cell and H1299 cell co-culture system, assessed using ELISA.
(G) TGF-β production in T cell and H1299 cell co-culture system,
assessed using ELISA. n=3. ***P<0.001. IGF2BP2, insulin-like
growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2; IFN-γ, interferon-γ; IL,
interleukin; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β; OE,
overexpression; NC, negative control; si, small interfering. |
Discussion
Previous studies have reported that circENTPD7 acts
as an oncogene in NSCLC (20,21).
The results of the present study demonstrated that circENTPD7
expression in NSCLC cells was increased, consistent with the
previous conclusion. Loss-of-function experiments also confirmed
that circENTPD7 knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration
and invasion of NSCLC cells. These results revealed that circENTPD7
may serve a key role in the malignant progression of NSCLC as an
oncogene. However, the involvement of circENTPD7 in the immune
escape process of NSCLC remains unclear.
As the main ligand of PD-1, PD-L1 is mainly
expressed in T cells, B cells and other immune cells, and is highly
expressed in NSCLC (25). In normal
tissues, PD-L1 helps maintain immune homeostasis. However, in
cancer, PD-L1 facilitates immune escape by inhibiting the
activation, expansion and effector functions of antigen-specific
CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (26,27). In the present study, the
overexpression of IGF2BP2 upregulated PD-L1 expression in NSCLC
cells. Previous studies have reported that there is an interaction
between IGF2BP2 and PD-L1, and knockdown of IGF2BP2 can inhibit the
PD-1/PD-L1 pathway (28,29). Therefore, the present study assessed
the association between PD-L1 and IGF2BP2 and their role in the
immune escape of NSCLC. The results revealed that upregulation of
IGF2BP2 increased the number of T cells, whereas downregulation of
PD-L1 reversed the effect of IGF2BP2 on T cells. These results were
confirmed by key factors specific to T cell-mediated immune
responses (IL-2, TGF-β and IFN-γ). The aforementioned findings
indicate that IGF2BP2 regulates the immune escape process of NSCLC
cells by upregulating PD-L1 expression.
IGF2BP2 is an RNA-binding protein that regulates
several biological processes. Initially, IGF2BP2 was discovered as
a gene related to type 2 diabetes, whereas further studies have
reported its role in the occurrence and development of several
malignant tumors (30). Moreover,
IGF2BP2 is closely associated with cancer cell proliferation,
migration, adhesion, energy metabolism and immune response
(31–33). Notably, previous studies have
reported that IGF2BP2 acts as a tumor promoter in NSCLC cells, with
its high expression contributing to the growth and metastasis of
these cells (34,35). In the present study, IGF2BP2
contributed to the malignant phenotype of NSCLC cells, consistent
with previous reports.
In the present research, circENTPD7 positively
regulated the expression of IGF2BP2, whereas IGF2BP2 failed to
negatively regulate the expression of circENTPD7. In addition,
overexpression of IGF2BP2 could reverse the inhibitory effect of
circENTPD7 silencing on the malignant behavior of H1299 cells.
Therefore, it is hypothesized that circENTPD7 may promote
PD-L1-mediated immune escape by influencing the translation or
degradation of IGF2BP2 in NSCLC cells, thereby contributing to
tumor progression in NSCLC. However, more research is needed to
further explore these mechanisms. Additionally, future research
should involve animal experiments and detailed analysis of
functions and signaling pathways to elucidate the mechanisms by
which abnormal circENTPD7 expression promotes immune escape in
NSCLC via the IGF2BP2/PD-L1 axis. In addition, the expression of
circENTPD7 in the serum of patients with NSCLC should be tested in
the future to assess whether circENTPD7 can be used as a biomarker
for blood biopsies of patients with NSCLC. Despite initially
revealing that circENTPD7 positively regulates the expression of
IGF2BP2 and hypothesizing that this regulation may promote
PD-L1-mediated immune escape and tumor progression in NSCLC by
influencing the translation or degradation of IGF2BP2 within NSCLC
cells, the present study had several limitations. Firstly, it was
not possible to confirm a negative regulatory effect of IGF2BP2 on
circENTPD7, which hinders a comprehensive understanding of their
interaction mechanism. Secondly, although a hypothesis has been
proposed, the specific mechanism remains unclear, necessitating
further research to explore how circENTPD7 impacts the immune
escape of NSCLC through the IGF2BP2/PD-L1 axis. Additionally, the
present study primarily relies on cellular experiments, lacking
animal experiments and detailed functional and signaling pathway
analyses, which limits the broad applicability and persuasive power
of the findings. Lastly, although circENTPD7 holds potential as a
biomarker for blood biopsies in patients with NSCLC, its expression
in the serum of patients with NSCLC has not been detected in the
present study, and this potential application requires further
validation and clinical data support in future research.
In conclusion, the present study identified a novel
circRNA, circENTPD7, which exhibits oncogenic properties in NSCLC.
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that circENTPD7 inhibits the
proliferation and differentiation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells by
modulating the IGF2BP2/PD-L1 axis, thereby facilitating the immune
evasion of NSCLC cells. These findings suggest that circENTPD7 may
serve as a potential therapeutic target for immune escape in
NSCLC.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Guangzhou Health Science
and Technology General Guidance Project (grant no.
20221A010062).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
HY and TZ performed the conception and design of the
study. HY, YZ, RY, CX, ZL and TZ performed the investigation and
methodology. HY and TZ confirm the authenticity of all the raw
data. HY drafted the manuscript or figures preparation. All authors
have read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The use of the primary peripheral blood mononuclear
cells was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Cancer
Hospital and Institute of Guangzhou Medical University (Guangzhou,
China; approval no. KY-2023011010).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviation
Abbreviations:
|
NSCLC
|
non-small cell lung cancer
|
References
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
R, Torre L and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
de Groot PM, Wu CC, Carter BW and Munden
RF: The epidemiology of lung cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res.
7:220–233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng X, Liu D, Peng G, Liu J and Yang H:
MiroRNA-31-3p promotes the invasion and metastasis of
non-small-cell lung cancer cells by targeting forkhead box 1
(FOXO1). Comput Math Methods Med. 2022:45970872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alexander M, Kim SY and Cheng H: Update
2020: Management of Non-small cell lung cancer. Lung. 198:897–907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Duma N, Santana-Davila R and Molina JR:
Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, screening, diagnosis, and
treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:1623–1640. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sadreddini S, Baradaran B, Aghebati-Maleki
A, Sadreddini S, Shanehbandi D, Fotouhi A and Aghebati-Maleki L:
Immune checkpoint blockade opens a new way to cancer immunotherapy.
J Cell Physiol. 234:8541–8549. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sperandio RC, Pestana RC, Miyamura BV and
Kaseb AO: Hepato-cellular carcinoma immunotherapy. Annu Rev Med.
73:267–278. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kjeldsen JW, Lorentzen CL, Martinenaite E,
Ellebaek E, Donia M, Holmstroem RB, Klausen TW, Madsen CO, Ahmed
SM, Weis-Banke SE, et al: A phase 1/2 trial of an immune-modulatory
vaccine against IDO/PD-L1 in combination with nivolumab in
metastatic melanoma. Nat Med. 27:2212–2223. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Masuda K, Horinouchi H, Tanaka M,
Higashiyama R, Shinno Y, Sato J, Matsumoto Y, Okuma Y, Yoshida T,
Goto Y, et al: Efficacy of anti-PD-1 antibodies in NSCLC patients
with an EGFR mutation and high PD-L1 expression. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 147:245–251. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bhatia A and Burtness B: Treating head and
neck cancer in the age of immunotherapy: A 2023 update. Drugs.
83:217–248. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meyers DE, Bryan PM, Banerji S and Morris
DG: Targeting the PD-1/PD-L1 axis for the treatment of
non-small-cell lung cancer. Curr Oncol. 25:e324–e334. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Negrao MV, Skoulidis F, Montesion M,
Schulze K, Bara I, Shen V, Xu H, Hu S, Sui D, Elamin YY, et al:
Oncogene-specific differences in tumor mutational burden, PD-L1
expression, and outcomes from immunotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 9:e0028912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yokosuka T, Takamatsu M,
Kobayashi-Imanishi W, Hashimoto-Tane A, Azuma M and Saito T:
Programmed cell death 1 forms negative costimulatory microclusters
that directly inhibit T cell receptor signaling by recruiting
phosphatase SHP2. J Exp Med. 209:1201–1217. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor
immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 24:207–212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mu CY, Huang JA, Chen Y, Chen C and Zhang
XG: High expression of PD-L1 in lung cancer may contribute to poor
prognosis and tumor cells immune escape through suppressing tumor
infiltrating dendritic cells maturation. Med Oncol. 28:682–688.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rashed HE, Abdelrahman AE, Abdelgawad M,
Balata S and Shabrawy ME: Prognostic significance of programmed
cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1), CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
and p53 in non-small cell lung cancer: An immunohistochemical
study. Turk Patoloji Derg. 1:211–222. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lamberti G, Sisi M, Andrini E, Palladini
A, Giunchi F, Lollini PL, Ardizzoni A and Gelsomino F: The
mechanisms of PD-L1 regulation in non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Which are the involved players? Cancers (Basel).
12:31292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Jia Y, Wang B, Yang S, Du K, Luo
Y, Li Y and Zhu B: Circular RNA CHST15 sponges miR-155-5p and
miR-194-5p to promote the immune escape of lung cancer cells
mediated by PD-L1. Front Oncol. 11:5956092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lei J, Zhu J, Hui B, Jia C, Yan X, Jiang T
and Wang X: Circ-HSP90A expedites cell growth, stemness, and immune
evasion in non-small cell lung cancer by regulating STAT3 signaling
and PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 72:101–124.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu F, Cheng C, Qin H, Wang H and Yu H: A
novel circular RNA circENTPD7 contributes to glioblastoma
progression by targeting ROS1. Cancer Cell Int. 20:1182020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu H, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Yang R, Liao Z and
Zhou T: Circular RNA circENTPD7 suppresses the accumulation of PTEN
to promote cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Genet
Mol Biol. 45:e202200232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bong D, Sohn J and Lee SV: Brief guide to
RT-qPCR. Mol Cells. 47:1001412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang X, Wang J, Deng X, Xiong F, Ge J,
Xiang B, Wu X, Ma J, Zhou M, Li X, et al: Role of the tumor
microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol
Cancer. 18:102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jing H, Meng M, Ye M, Liu S, Cao X, Li K,
Liu Y, Zhang J and Wu Y: Integrin α2 promotes immune escape in
non-small-cell lung cancer by enhancing PD-L1 expression in
exosomes to inhibit CD8 + T-cell activity. J Investig Med.
72:57–66. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Attieh F, Chartouni A, Boutros M, Mouawad
A and Kourie HR: Tackling the immunotherapy conundrum: Advances and
challenges for operable non-small-cell lung cancer treatment.
Immunotherapy. 15:1415–1428. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jancewicz I, Szarkowska J, Konopinski R,
Stachowiak M, Swiatek M, Blachnio K, Kubala S, Oksinska P, Cwiek P,
Rusetska N, et al: PD-L1 overexpression, SWI/SNF complex
deregulation, and profound transcriptomic changes characterize
cancer-dependent exhaustion of persistently activated
CD4+ T cells. Cancers (Basel). 13:41482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang X and Liu J: Targeting PD-L1
(Programmed death-ligand 1) and inhibiting the expression of
IGF2BP2 (Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA-binding protein 2)
affect the proliferation and apoptosis of hypopharyngeal carcinoma
cells. Bioengineered. 12:7755–7764. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li Q, Xiao M, Shi Y, Hu J, Bi T, Wang C,
Yan L and Li X: eIF5B regulates the expression of PD-L1 in prostate
cancer cells by interacting with Wig1. BMC Cancer. 21:10222021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang J, Chen L and Qiang P: The role of
IGF2BP2, an m6A reader gene, in human metabolic diseases and
cancers. Cancer Cell Int. 21:992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu X, Yu Y, Zong K, Lv P and Gu Y:
Up-regulation of IGF2BP2 by multiple mechanisms in pancreatic
cancer promotes cancer proliferation by activating the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:4972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cui J, Tian J, Wang W, He T, Li X, Gu C,
Wang L, Wu J and Shang A: IGF2BP2 promotes the progression of
colorectal cancer through a YAP-dependent mechanism. Cancer Sci.
112:4087–4099. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Guan H, Tian K, Luo W and Li M:
m6A-modified circRNA MYO1C participates in the tumor
immune surveillance of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through
m6A/PD-L1 manner. Cell Death Dis. 14:1202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang RS, Zheng YL, Li C, Ding C, Xu C and
Zhao J: MicroRNA-485-5p suppresses growth and metastasis in
non-small cell lung cancer cells by targeting IGF2BP2. Life Sci.
199:104–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han L, Lei G, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Huang C and
Chen W: IGF2BP2 regulates MALAT1 by serving as an
N6-methyladenosine reader to promote NSCLC proliferation. Front Mol
Biosci. 8:7800892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|