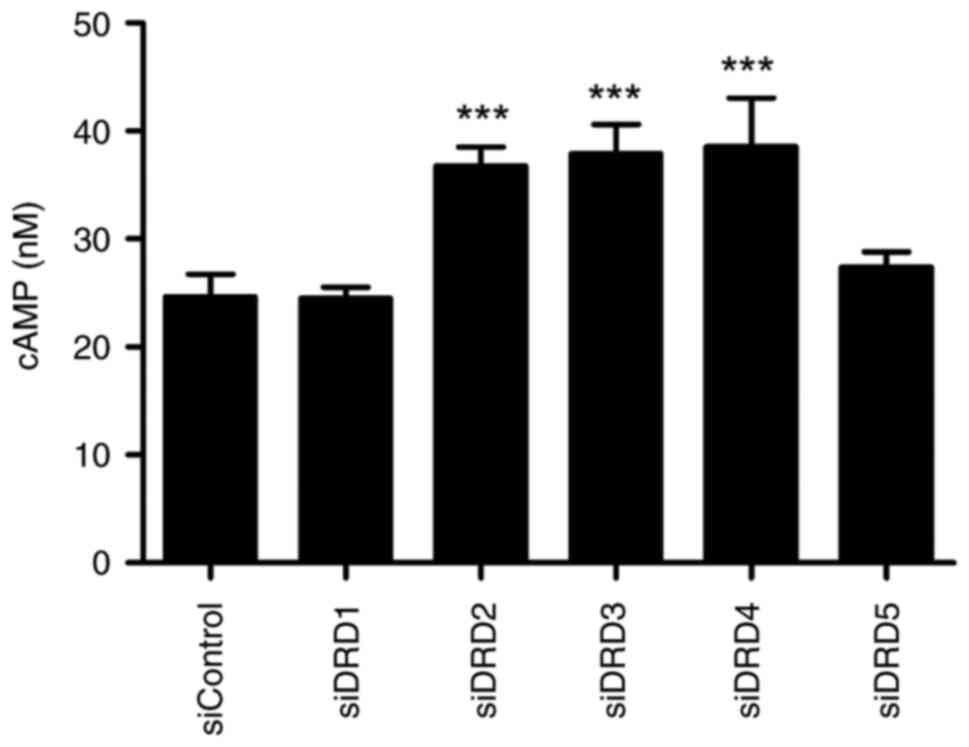
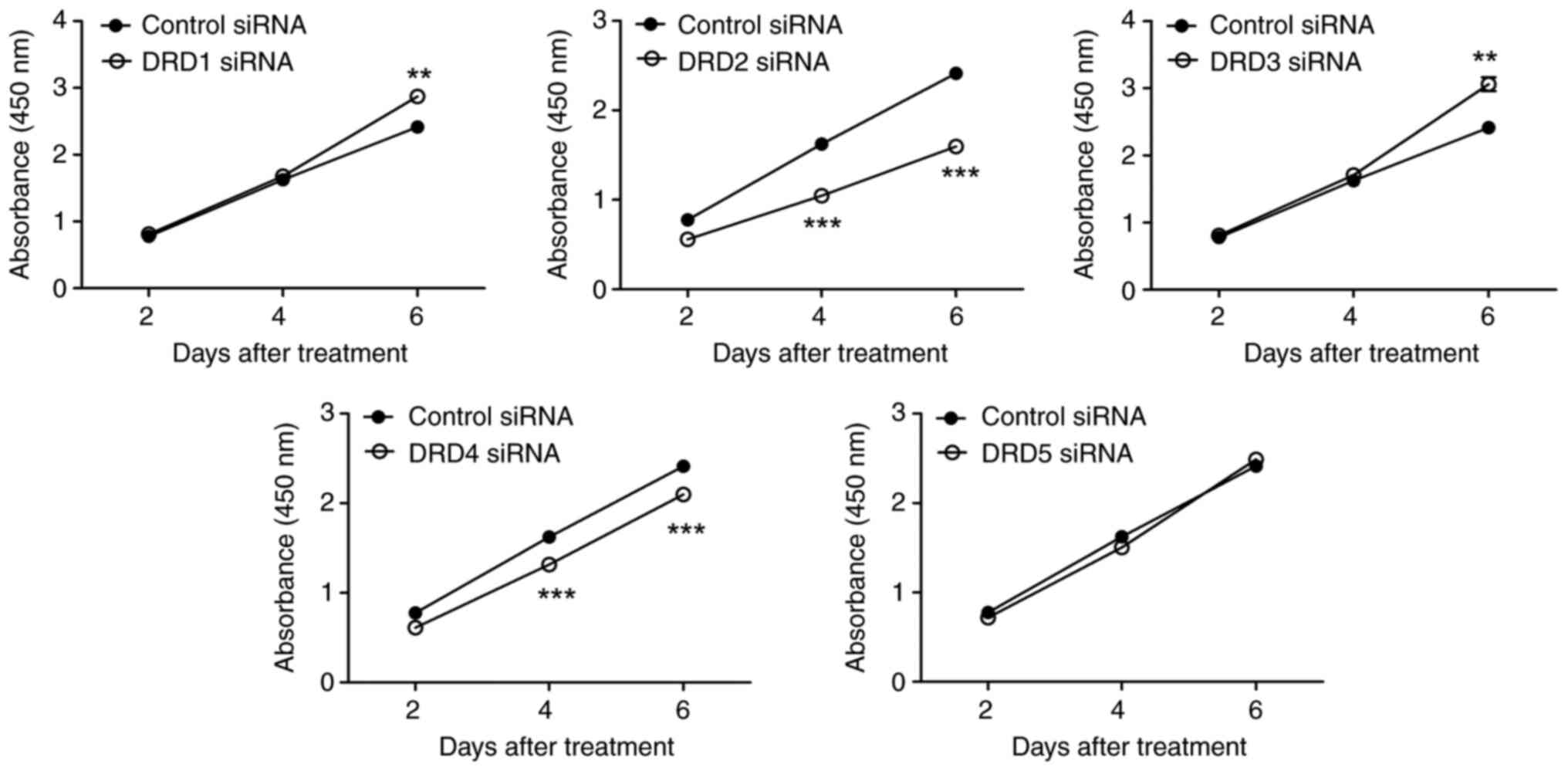
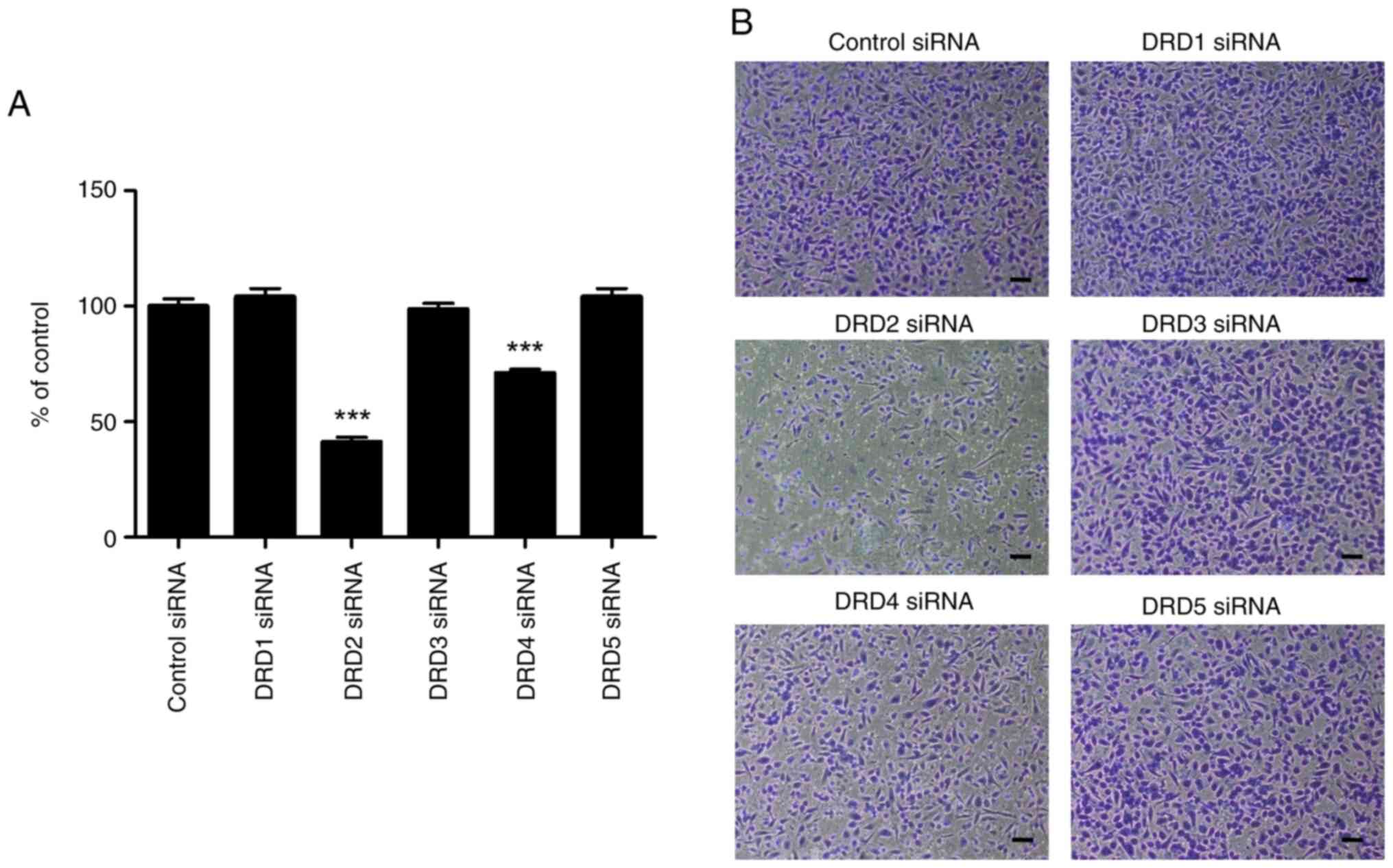
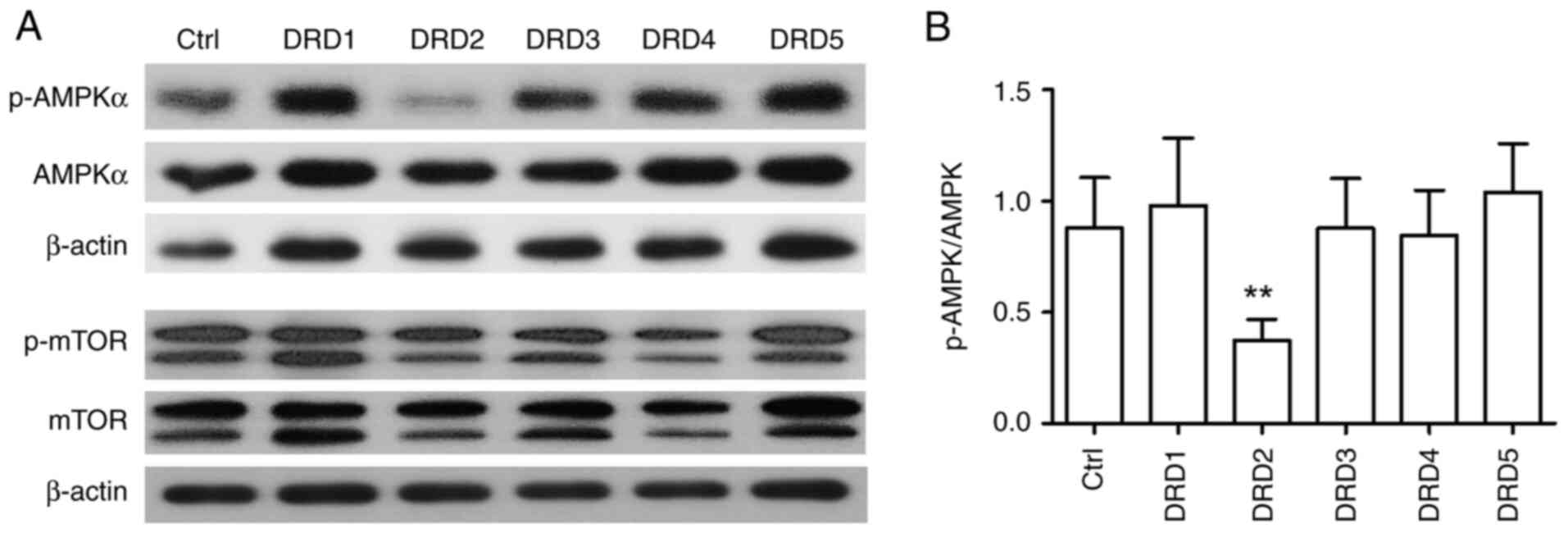
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Komura K, Sweeney CJ, Inamoto T, Ibuki N,
Azuma H and Kantoff PW: Current treatment strategies for advanced
prostate cancer. Int J Urol. 25:220–231. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sekhoacha M, Riet K, Motloung P, Gumenku
L, Adegoke A and Mashele S: Prostate cancer review: Genetics,
diagnosis, treatment options, and alternative approaches.
Molecules. 27:57302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Richardson GD, Robson CN, Lang SH, Neal
DE, Maitland NJ and Collins AT: CD133, a novel marker for human
prostatic epithelial stem cells. J Cell Sci. 117:3539–3545. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ
and Maitland NJ: Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate
cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 65:10946–10951. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Verma P, Shukla N, Kumari S, Ansari MS,
Gautam NK and Patel GK: Cancer stem cell in prostate cancer
progression, metastasis and therapy resistance. Biochim Biophys
Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gogola S, Rejzer M, Bahmad HF, Alloush F,
Omarzai Y and Poppiti R: Anti-cancer stem-cell-targeted therapies
in prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15:16212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
de Thé H: Differentiation therapy
revisited. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:117–127. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Enane FO, Saunthararajah Y and Korc M:
Differentiation therapy and the mechanisms that terminate cancer
cell proliferation without harming normal cells. Cell Death Dis.
9:9122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sachlos E, Risueño RM, Laronde S,
Shapovalova Z, Lee JH, Russell J, Malig M, McNicol JD, Fiebig-Comyn
A, Graham M, et al: Identification of drugs including a dopamine
receptor antagonist that selectively target cancer stem cells.
Cell. 149:1284–1297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rane JK, Pellacani D and Maitland NJ:
Advanced prostate cancer-a case for adjuvant differentiation
therapy. Nat Rev Urol. 9:595–602. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pérez G, López-Moncada F, Indo S, Torres
MJ, Castellón EA and Contreras HR: Knockdown of ZEB1 reverses
cancer stem cell properties in prostate cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
45:582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee Y, Yoon J, Ko D, Yu M, Lee S and Kim
S: TMPRSS4 promotes cancer stem-like properties in prostate cancer
cells through upregulation of SOX2 by SLUG and TWIST1. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 40:3722021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang N, Ke B, Hjort-Jensen K,
Iglesias-Gato D, Wang Z, Chang P, Zhao Y, Niu X, Wu T, Peng B, et
al: YAP1 regulates prostate cancer stem cell-like characteristics
to promote castration resistant growth. Oncotarget.
8:115054–115067. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roney MSI and Park SK: Antipsychotic
dopamine receptor antagonists, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Arch
Pharm Res. 41:384–408. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rosas-Cruz A, Salinas-Jazmín N and
Velázquez MAV: Dopamine receptors in cancer: Are they valid
therapeutic targets? Technol Cancer Res Treat.
20:153303382110279132021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee SI, Roney MSI, Park JH, Baek JY, Park
J, Kim SK and Park SK: Dopamine receptor antagonists induce
differentiation of PC-3 human prostate cancer cell-derived cancer
stem cell-like cells. Prostate. 79:720–731. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hill SJ and Young M: Antagonism of central
histamine H1 receptors by antipsychotic drugs. Eur J Pharmacol.
52:397–399. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Johnson DE, Nedza FM, Spracklin DK, Ward
KM, Schmidt AW, Iredale PA, Godek DM and Rollema H: The role of
muscarinic receptor antagonism in antipsychotic-induced hippocampal
acetylcholine release. Eur J Pharmacol. 506:209–219. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Richtand NM, Welge JA, Logue AD, Keck PE
Jr, Strakowski SM and McNamara RK: Dopamine and serotonin receptor
binding and antipsychotic efficacy. Neuropsychopharmacology.
32:1715–1726. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung HS, Lee SI, Kang SH, Wang JS, Yang
EH, Jeon B, Myung J, Baek JY and Park SK: Monoclonal antibodies
against autocrine motility factor suppress gastric cancer. Oncol
Lett. 13:4925–4932. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang MR, Park SK, Lee CW, Cho IJ, Jo YN,
Yang JW, Kim JA, Yun J, Lee KH, Kwon HJ, et al: Widdrol induces
apoptosis via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase in colon
cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 27:1407–1412. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Beaulieu JM and Gainetdinov RR: The
physiology, signaling, and pharmacology of dopamine receptors.
Pharmacol Rev. 63:182–217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Prabhu VV, Madhukar NS, Gilvary C, Kline
CLB, Oster S, El-Deiry WS, Elemento O, Doherty F, VanEngelenburg A,
Durrant J, et al: Dopamine receptor D5 is a modulator of tumor
response to dopamine receptor D2 antagonism. Clin Cancer Res.
25:2305–2313. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rosas-Cruz A, Salinas-Jazmín N,
Valdés-Rives A and Velasco-Velázquez MA: DRD1 and DRD4 are
differentially expressed in breast tumors and breast cancer stem
cells: Pharmacological implications. Transl Cancer Res.
11:3941–3950. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dolma S, Selvadurai HJ, Lan X, Lee L,
Kushida M, Voisin V, Whetstone H, So M, Aviv T, Park N, et al:
Inhibition of dopamine receptor D4 impedes autophagic flux,
proliferation, and survival of glioblastoma stem cells. Cancer
Cell. 29:859–873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bahmad HF, Cheaito K, Chalhoub RM, Hadadeh
O, Monzer A, Ballout F, El-Hajj A, Mukherji D, Liu YN, Daoud G and
Abou-Kheir W: Sphere-formation assay: Three-dimensional in vitro
culturing of prostate cancer stem/progenitor sphere-forming cells.
Front Oncol. 8:3472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hardie DG: Molecular pathways: Is AMPK a
friend or a foe in cancer? Clin Cancer Res. 21:3836–3840. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bonini MG and Gantner BN: The multifaceted
activities of AMPK in tumor progression-why the ‘one size fits all’
definition does not fit at all? IUBMB Life. 65:889–896. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gharibpoor F, Kamali Zonouzi S, Razi S and
Rezaei N: AMPK's double-faced role in advanced stages of prostate
cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 24:2064–2073. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim TH, Park JH, Park J, Son DM, Baek JY,
Jang HJ, Jung WK, Byun Y, Kim SK and Park SK: Stereospecific
inhibition of AMPK by (R)-crizotinib induced changes to the
morphology and properties of cancer and cancer stem cell-like
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 911:1745252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|