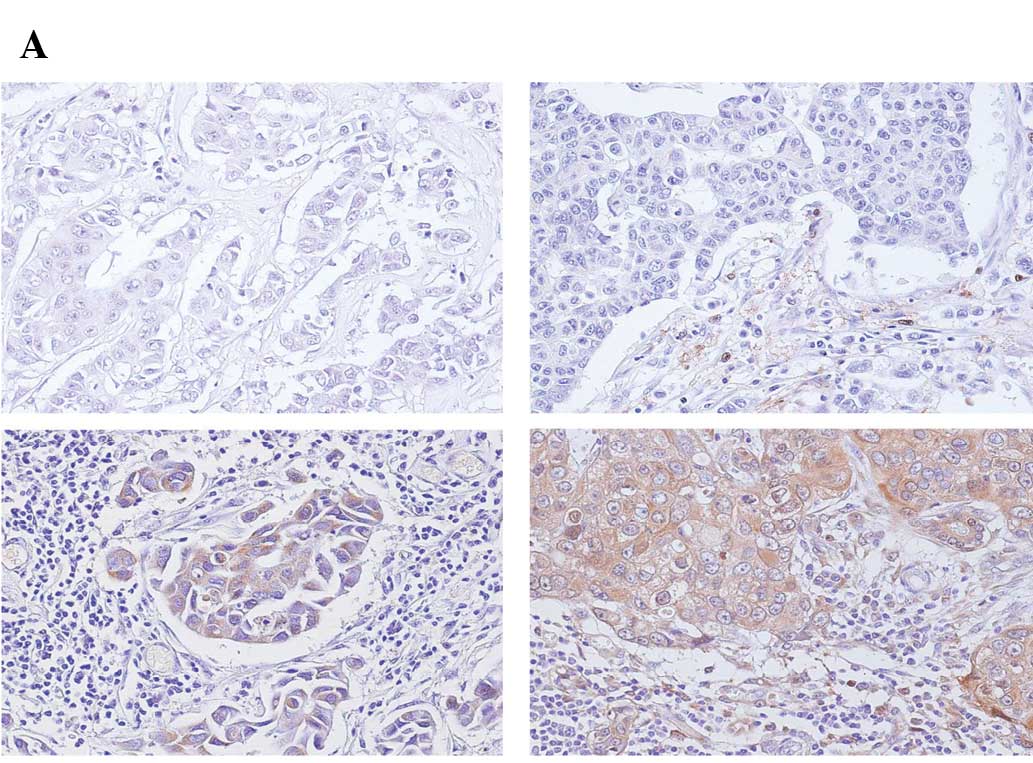
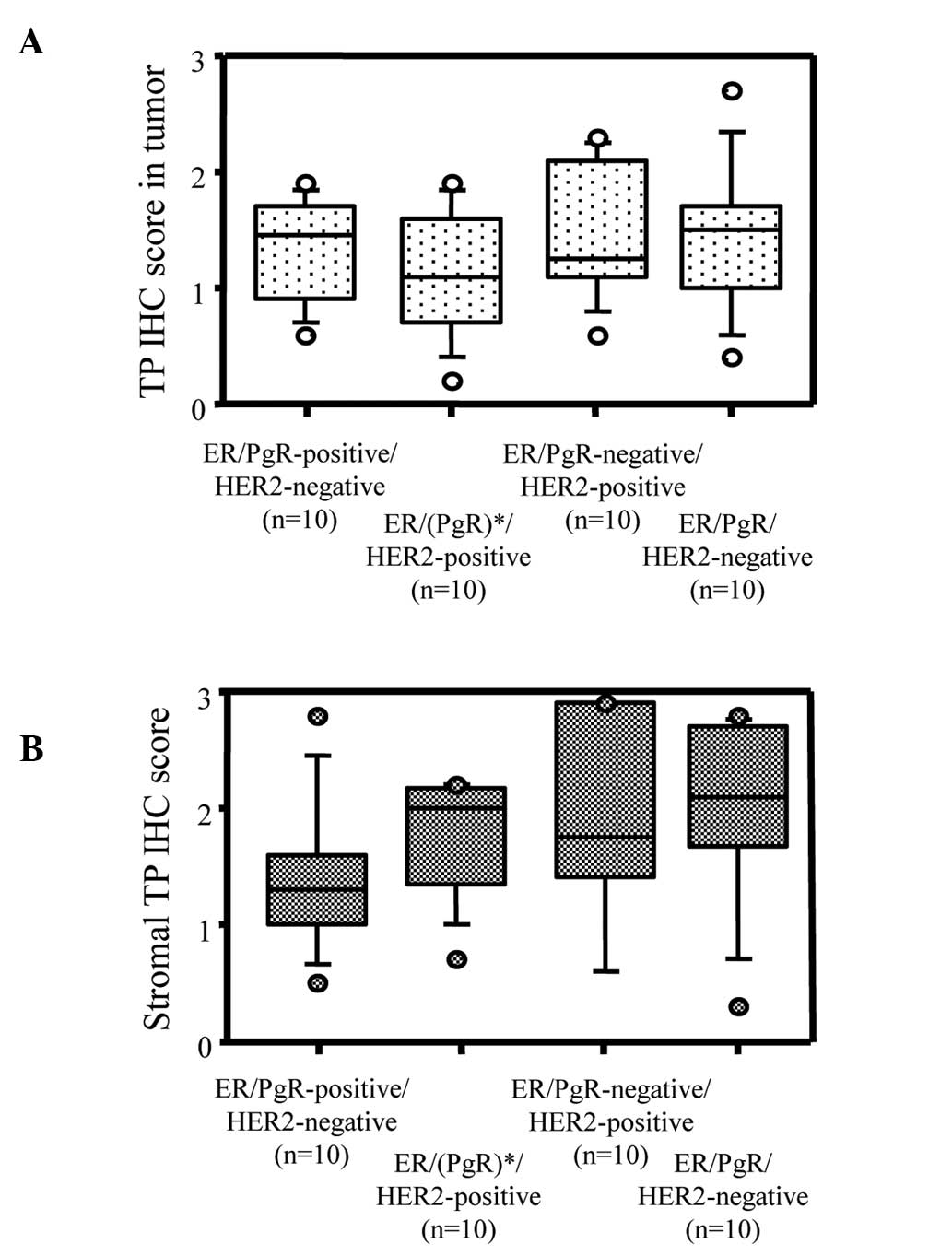
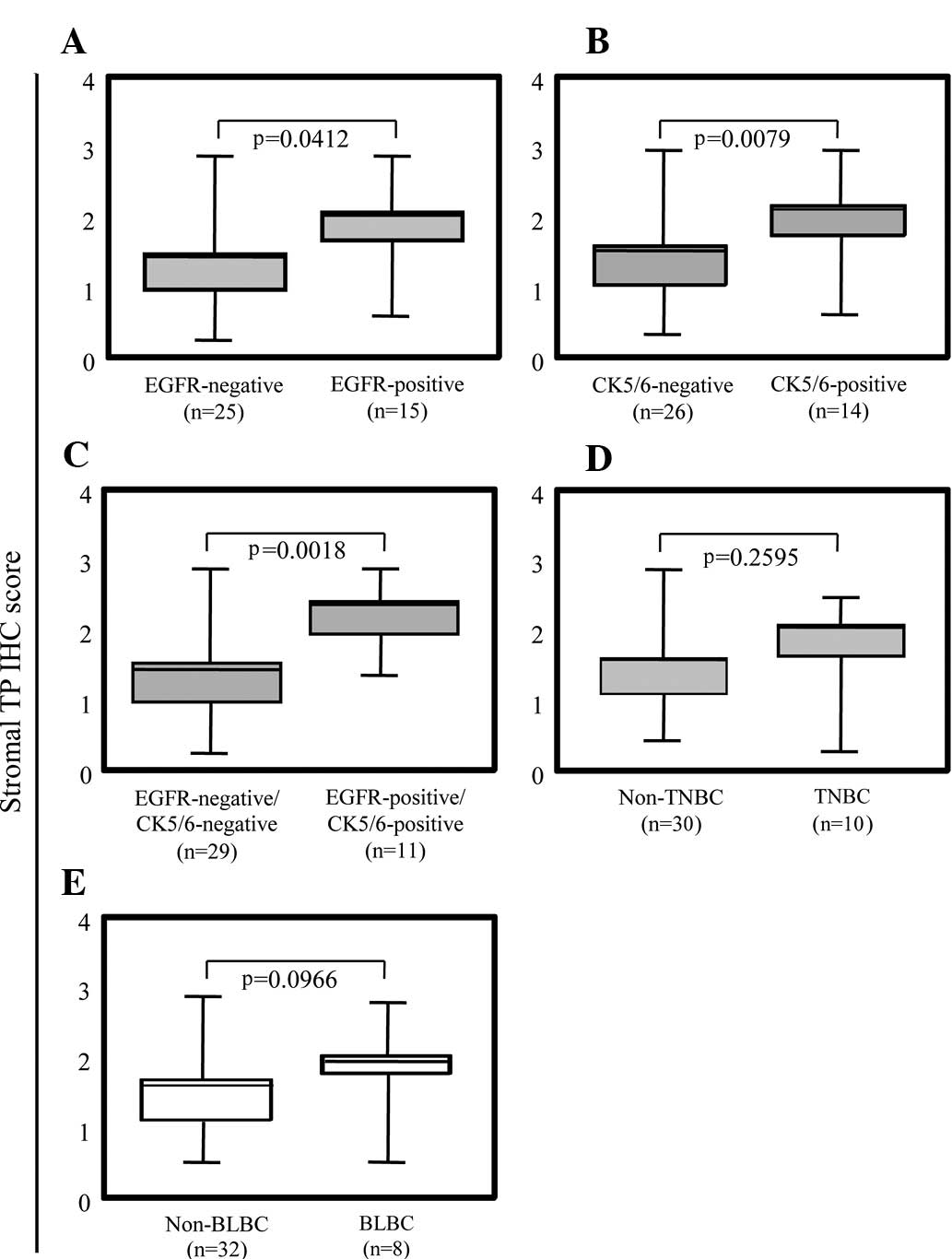
|
1
|
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, Coates
AS, Thurlimann B and Senn HJ: Panel members: Thresholds for
therapies: highlights of the St Gallen International expert
consensus on the primary therapy of early breast cancer 22009. Ann
Oncol. 20:1319–1329. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal
therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival:
an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 365:1687–1717.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, et al:
Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor
subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:10869–10874. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van’t Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, et
al: Gene expression profiling predicts clinical outcome of breast
cancer. Nature. 415:530–536. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, et al:
Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 406:747–752.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, et al:
Race, breast cancer subtypes and survival in the Carolina Breast
Cancer Study. JAMA. 295:2492–2502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Green AR, et al:
Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer.
109:25–32. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blum JL: Xeloda in the treatment of
metastatic breast cancer. Oncology. 57(Suppl 1): 16–20. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Miwa M, Ura M, Nishida M, et al: Design of
a novel oral fluoropyrimidine carbamate, capecitabine, which
generates 5-fluorouracil selectively in tumours by enzymes
concentrated in human liver and cancer tissue. Eur J Cancer.
34:1274–1281. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fiedkin M and Roberts D: The enzymatic
synthesis of nucleosides. I. Thymidine phosphorylase in mammalian
tissue. J Biol Chem. 207:245–256. 1954.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moghaddam A and Bicknell R: Expression of
platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor in Escherichia
coli and confirmation of its thymidine phosphorylase activity.
Biochemistry. 31:12141–12146. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Toi M, Atiqur Rahman M, Bando H, et al:
Thymidine phosphorylase (platelet-derived endothelial-cell growth
factor) in cancer biology and treatment. Lancet Oncol. 6:158–166.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ishikawa T, Sekiguchi F, Fukase Y, et al:
Positive correlation between the efficacy of capecitabine and
doxifluridine and the ration of thymidine phosphorylase to
dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase activities in tumors in human
cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 58:685–690. 1998.
|
|
14
|
Sawada Y, Fujii T, Takahashi H, et al: A
case of triple negative chest wall recurrent breast cancer treated
with capecitabine and docetaxel combination therapy (XT therapy).
Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 36:815–817. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hachisuka Y, Kamei Y, Umeoka T, et al: A
case of triple negative recurrent breast cancer successfully
treated with capecitabine + docetaxel combination chemotherapy. Gan
To Kagaku Ryoho. 35:475–458. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Umemura S, Shirane M, Takekoshi S, et al:
Overexpression of E2F-5 correlates with a pathological basal
phenotype and a worse clinical outcome. Br J Cancer. 100:764–771.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kono T, Nishida M, Inagaki N, et al:
Development and characterization of 1C6–203, a new monoclonal
antibody specific to human thymidine phosphorylase. J Histochem
Cytochem. 49:131–138. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Tsuda H, Akiyama F, Kurosumi M, et al:
Reproducible immuno-histochemical criteria based on multiple
raters’ judgments for expression of thymidine phosphorylase in
breast cancer tissue. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 86:215–223.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nielsen TO, Hsu FD, Jensen K, et al:
Immunohistochemical and clinical characterization of the basal-like
subtype of invasive breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5367–5374. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baselga J, Albanell J and Ruiz A: Phase II
and tumor pharmaco-dynamic study of gefitinib in patients with
advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:5323–5333. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shiu KK, Tan DS and Reis-Filho JS:
Development of therapeutic approaches to ‘triple negative’
phenotype breast cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:1123–1137.
2008.
|
|
22
|
Kim JB, Stein R and O’Hare MJ:
Tumour-stromal interactions in breast cancer: the role of stroma in
tumourigenesis. Tumour Biol. 26:173–185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Finak G, Bertos N, Pepin F, et al: Stromal
gene expression predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nat
Med. 14:518–527. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Evrard A, Cuq P, Ciccolini J, et al:
Increased cytotoxicity and bystander effect of 5-fluorouracil and
5-deoxy-5-fluorouridine in human colorectal cancer cells
transfected with thymidine phosphorylase. Br J Cancer.
80:1726–1733. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kato Y, Matsukawa S, Muraoka R, et al:
Enhancement of drug sensitivity and a bystander effect in PC-9
cells transfected with a platelet-derived endothelial cell growth
factor thymidine phosphorylase cDNA. Br J Cancer. 75:506–511. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eda H, Fujimoto K, Watanabe S, et al:
Cytokines induce thymidine phosphorylase expression in tumor cells
and make them more susceptible to 5′-deoxy-5-fluorouridine. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 32:333–338. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tripathy D: Capecitabine in combination
with novel targeted agents in the management of metastatic breast
cancer: underlying rationale and results of clinical trials.
Oncologist. 12:375–389. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fujimoto-Ouchi K, Sekiguchi F and Tanaka
Y: Antitumor activity of combinations of anti-HER-2 antibody
trastuzumab and oral fluoropyrimidines capecitabine/5′-dFUrd in
human breast cancer models. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 49:211–216.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mori K, Hasegawa M, Nishida M, et al:
Expression levels of thymidine phosphorylase and dihydropyrimidine
dehydrogenase in various human tumor tissues. Int J Oncol.
17:33–38. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|