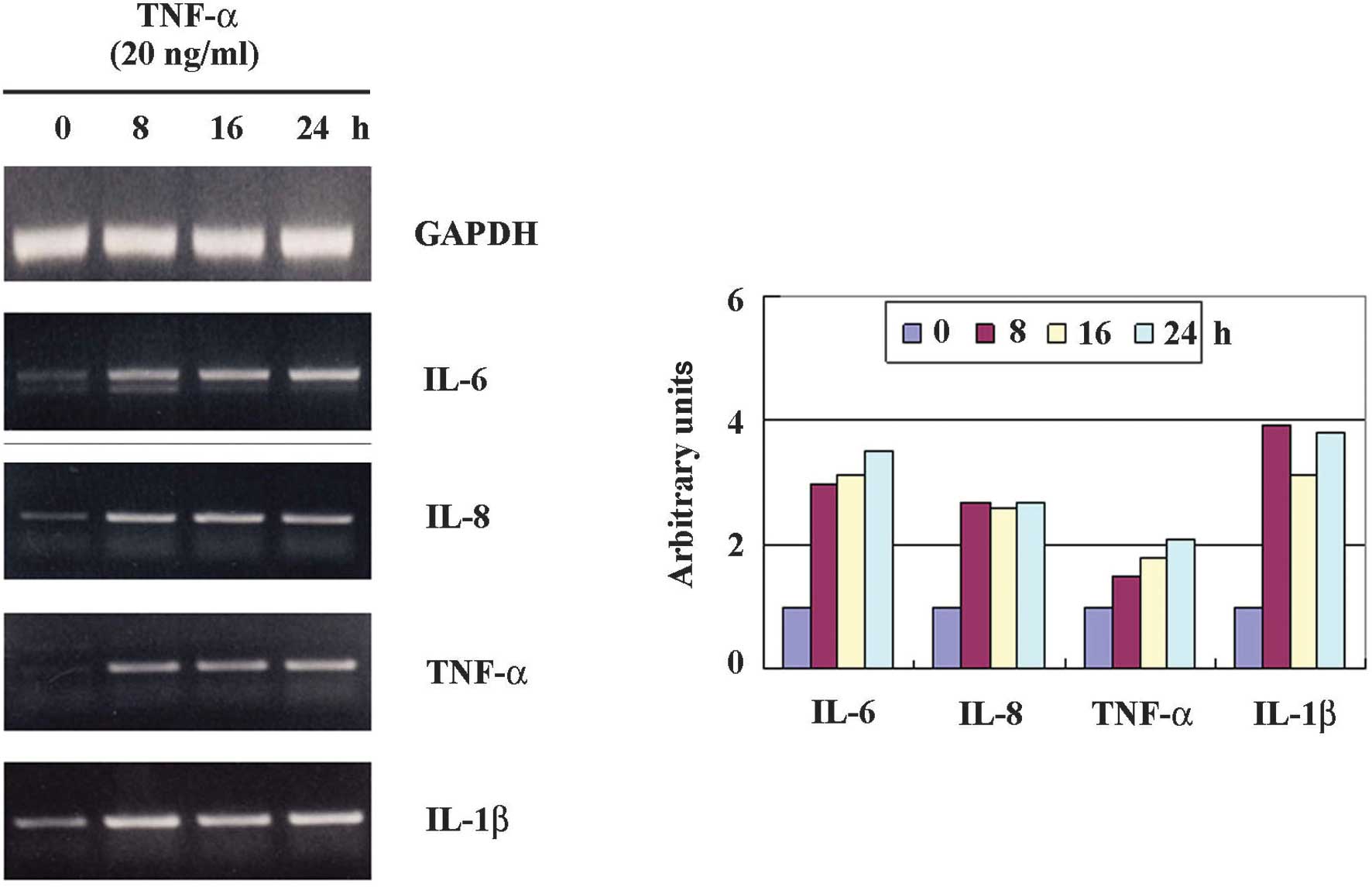
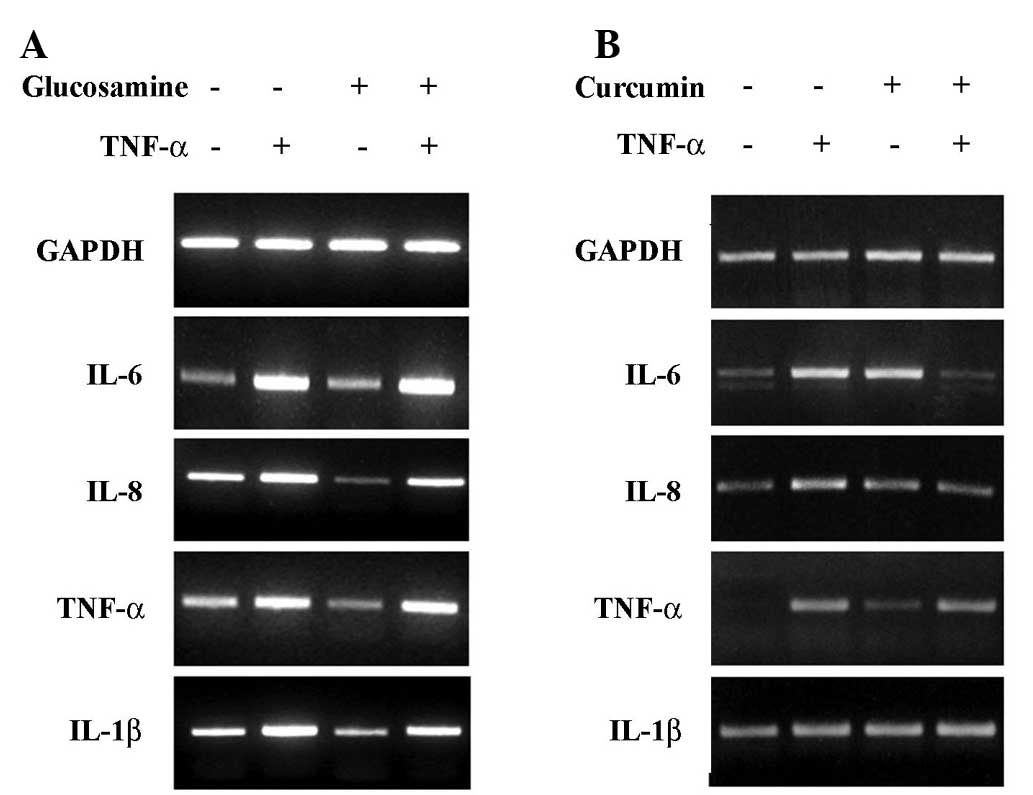
|
1
|
Damjanov N and Vojinovic J: Biologic
therapy of rheumatoid arthritis. Srp Arh Celok Lek. 137:205–210.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ding C, Cicuttini F, Li J and Jones G:
Targeting IL-6 in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune
diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 18:1457–1466. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kovarikova M, Hofmanova J, Soucek K and
Kozubik A: The effects of TNF-alpha and inhibitors of arachidonic
acid metabolism on human colon HT-29 cells depend on
differentiation status. Differentiation. 72:23–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carlsen H, Alexander G, Austenaa LM,
Ebihara K and Blomhoff R: Molecular imaging of the transcription
factor NF-kappaB, a primary regulator of stress response. Mutat
Res. 551:199–211. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Muthusamy V and Piva TJ: The UV response
of the skin: a review of the MAPK, NFkappaB and TNFalpha signal
transduction pathways. Arch Dermatol Res. Sep 16–2009.(Epub ahead
of print).
|
|
6
|
Leng H, Luo X, Ma L, Kang K and Zheng Z:
Reversal of ultraviolet B-induced immunosuppression by inhibition
of the extracellular signal-regulated mitogen-activated protein
kinase. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 25:264–269. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neves BM, Cruz MT, Francisco V,
Garcia-Rodriguez C, Silvestre R, Cordeiro-da-Silva A, Dinis AM,
Batista MT, Duarte CB and Lopes MC: Differential roles of
PI3-kinase, MAPKs and NF-kappaB on the manipulation of dendritic
cell T(h)1/T(h)2 cytokine/chemokine polarizing profile. Mol
Immunol. 46:2481–2492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ivanova IA, Nakrieko KA and Dagnino L:
Phosphorylation by p38 MAP kinase is required for E2F1 degradation
and keratinocyte differentiation. Oncogene. 28:52–62. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hong H, Park YK, Choi MS, Ryu NH, Song DK,
Suh SI, Nam KY, Park GY and Jang BC: Differential down-regulation
of COX-2 and MMP-13 in human skin fibroblasts by
glucosamine-hydrochloride. J Dermatol Sci. 56:43–50. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hwang SM, Chen CY, Chen SS and Chen JC:
Chitinous materials inhibit nitric oxide production by activated
RAW 264.7 macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 271:229–233.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xing D, Feng W, Not LG, Miller AP, Zhang
Y, Chen YF, Majid-Hassan E, Chatham JC and Oparil S: Increased
protein O-GlcNAc modification inhibits inflammatory and neointimal
responses to acute endoluminal arterial injury. Am J Physiol Heart
Circ Physiol. 295:335–342. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kneass ZT and Marchase RB: Protein
O-GlcNAc modulates motility-associated signaling intermediates in
neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 280:14579–14585. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sinha R, Anderson DE, McDonald SS and
Greenwald P: Cancer risk and diet in India. J Postgrad Med.
49:222–228. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pari L, Tewas D and Eckel J: Role of
curcumin in health and disease. Arch Physiol Biochem. 114:127–149.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jiang ZY, Zou L, Shi SS, Lu YR, Dong J,
Yang CH, Lu YC and Dai GK: Effects of curcumin on TNF-alpha and
TGF-beta1 in serum and lung tissue of SiO(2)-induced fibrosis in
mice. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 25:399–401.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reuter S, Charlet J, Juncker T, Teiten MH,
Dicato M and Diederich M: Effect of curcumin on nuclear factor
kappaB signaling pathways in human chronic myelogenous K562
leukemia cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1171:436–447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang SL, Li Y, Wen Y, Chen YF, Na LX, Li
ST and Sun CH: Curcumin, a potential inhibitor of up-regulation of
TNF-alpha and IL-6 induced by palmitate in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
through NF-kappaB and JNK pathway. Biomed Environ Sci. 22:32–39.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rafi MM, Yadav PN and Rossi AO:
Glucosamine inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 and iNOS expression in mouse
macrophage cells (RAW 264.7) by inhibition of p38-MAP kinase and
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Mol Nutr Food Res. 51:587–593.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chesnokov V, Sun C and Itakura K:
Glucosamine suppresses proliferation of human prostate carcinoma
DU145 cells through inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Cell Int.
9:25–28. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fox BA and Stephens MM:
Glucosamine/chondroitin/primorine combination therapy for
osteoarthritis. Drugs Today. 45:21–31. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonness S and Bieber T: Molecular basis of
atopic dermatitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 7:382–386. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Capon F, Trembath RC and Barker JN: An
update on the genetics of psoriasis. Dermatol Clin. 22:339–347.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Deane JA and Hickey MJ: Molecular
mechanisms of leukocyte trafficking in T-cell-mediated skin
inflammation: insights from intravital imaging. Expert Rev Mol Med.
11:e252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Escobar J, Pereda J, Arduini A, Sandoval
J, Sabater L, Aparisi L, Lopez-Rodas G and Sastre J: Cross-talk
between oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokines in acute
pancreatitis: a key role for protein phosphatases. Curr Pharm Des.
15:3027–3042. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|