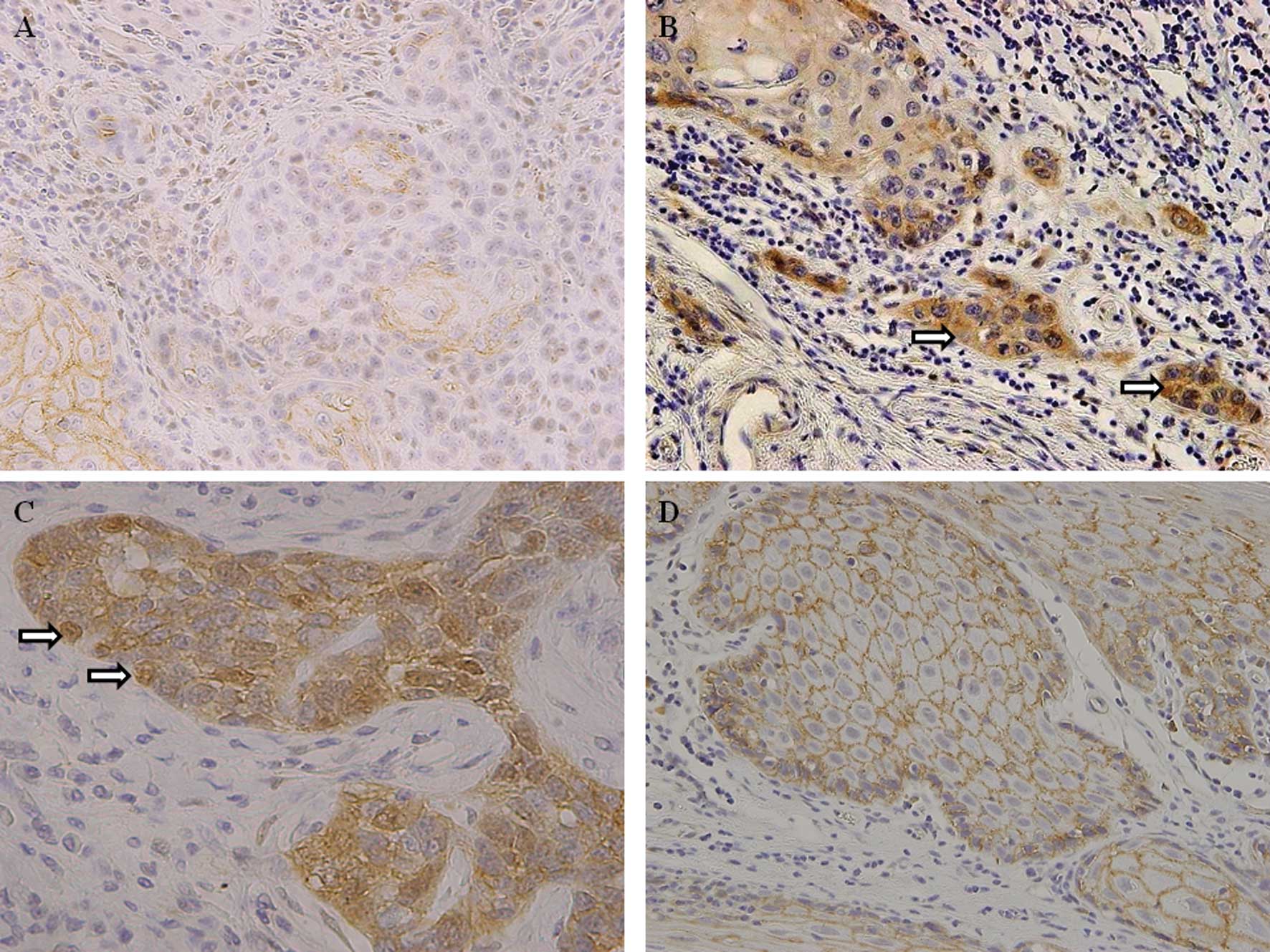
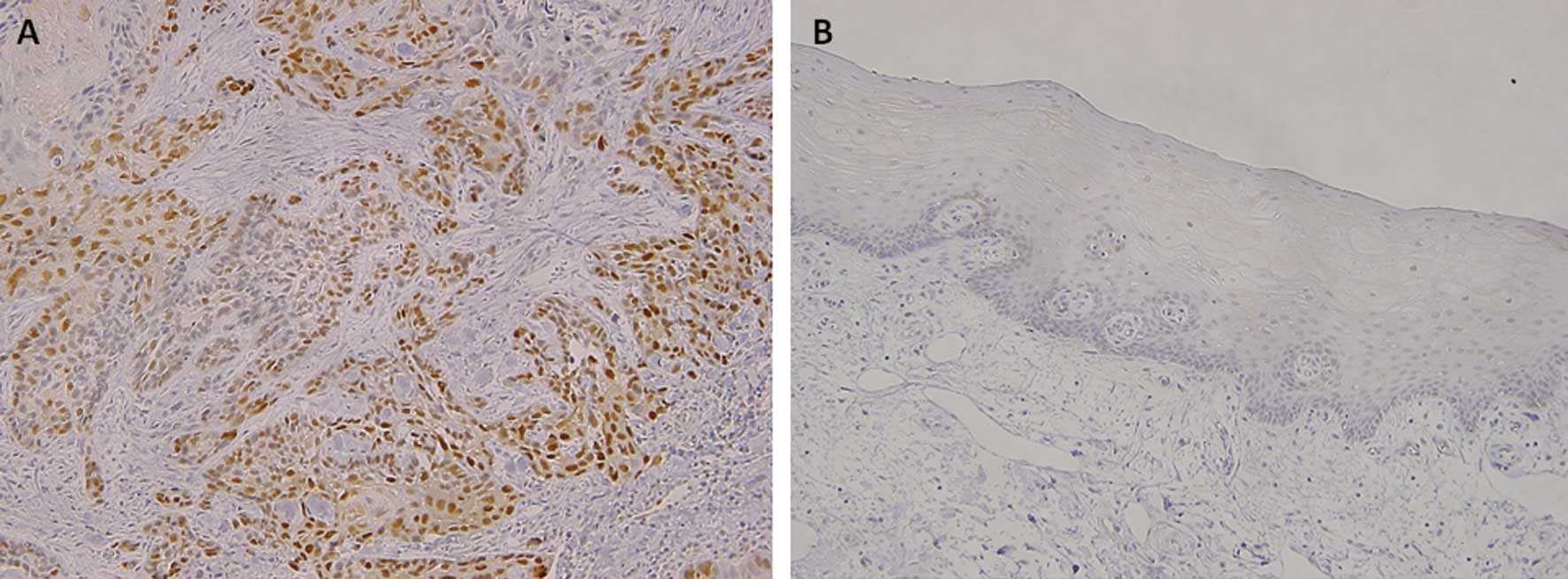
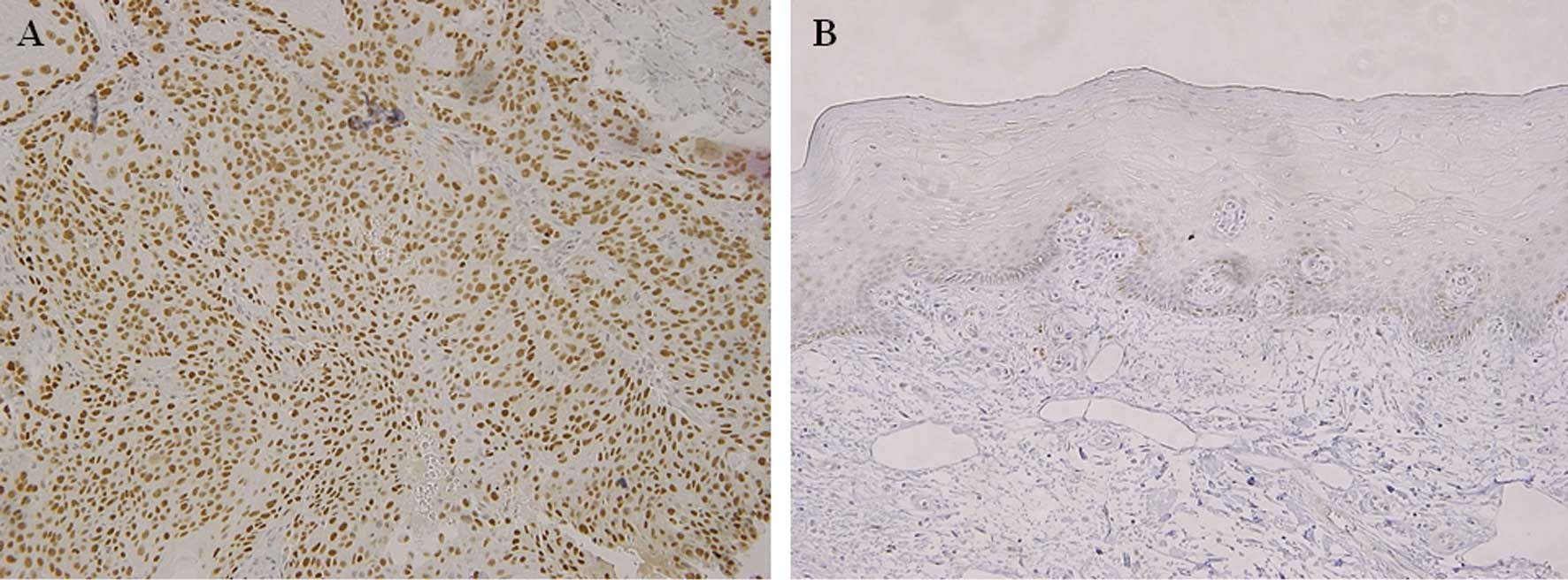
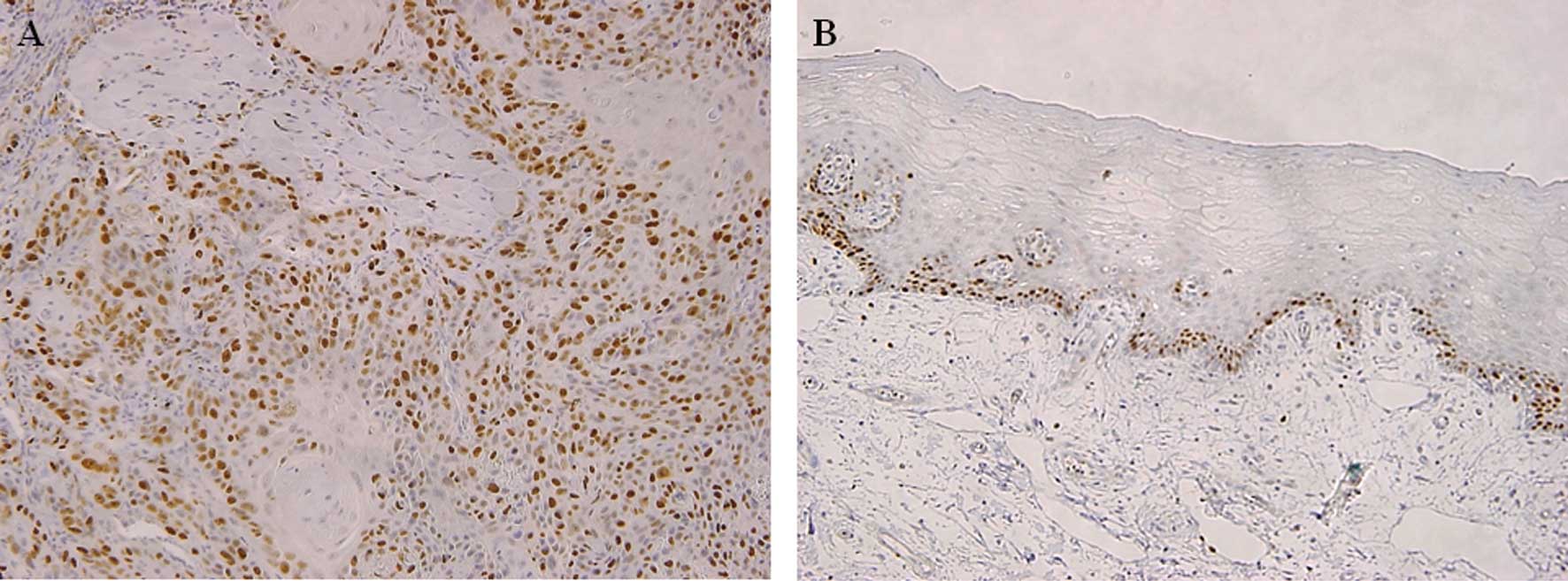
|
1
|
Ozawa M, Baribault H and Kemler R: The
cytoplasmic domain of the cell adhesion molecule uvomorulin
associates with three independent proteins structurally related in
different species. EMBO J. 8:1711–1717. 1989.
|
|
2
|
Hirohashi S: Inactivation of the
E-cadherin-mediated cell adhesion system in human cancers. Am J
Pathol. 153:333–339. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gumbiner BM: Cell adhesion: the molecular
basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 84:345–357.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Miller JR and Moon RT: Signal transduction
through beta-catenin and specification of cell fate during
embryogenesis. Genes Dev. 10:2527–2539. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shtutman M, Zhurinsky J, Simcha I,
Albanese C, D’Amico M, Pestell R and Ben-Ze’ev A: The cyclin D1
gene is a target of the beta-catenin/LEF-1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 96:5522–5527. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, et al:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brabletz T, Jung A, Dag S, Hlubek F and
Kirchner T: beta-catenin regulates the expression of the matrix
metalloproteinase-7 in human colorectal cancer. Am J Pathol.
155:1033–1038. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aberle H, Bauer A, Stappert J, Kispert A
and Kemler R: beta-catenin is a target for the ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway. EMBO J. 16:3797–3804. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Behrens J, von Kries JP, Kuhl M, Bruhn L,
Wedlich D, Grosschedl R and Birchmeier W: Functional interaction of
beta-catenin with the transcription factor LEF-1. Nature.
382:638–642. 1996. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tetsu O and McCormick F: Beta-catenin
regulates expression of cyclin D1 in colon carcinoma cells. Nature.
398:422–426. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin SY, Xia W, Wang JC, et al:
Beta-catenin, a novel prognostic marker for breast cancer: its
roles in cyclin D1 expression and cancer progression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:4262–4266. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiao Q, Ramadani M, Gansauge S, Gansauge
F, Leder G and Beger HG: Reduced membranous and ectopic cytoplasmic
expression of beta-catenin correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression
and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 95:194–197.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Damalas A, Ben-Ze’ev A, Simcha I, et al:
Excess beta-catenin promotes accumulation of transcriptionally
active p53. EMBO J. 18:3054–3063. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Damalas A, Kahan S, Shtutman M, Ben-Ze’ev
A and Oren M: Deregulated beta-catenin induces a p53- and
ARF-dependent growth arrest and cooperates with Ras in
transformation. EMBO J. 20:4912–4922. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsuzawa SI and Reed JC: Siah-1, SIP and
Ebi collaborate in a novel pathway for beta-catenin degradation
linked to p53 responses. Mol Cell. 7:915–926. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J, Stevens J, Rote CA, et al: Siah-1
mediates a novel beta-catenin degradation pathway linking p53 to
the adenomatous polyposis coli protein. Mol Cell. 7:927–936. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maruyama K, Ochiai A, Akimoto S, Nakamura
S, Baba S, Moriya Y and Hirohashi S: Cytoplasmic beta-catenin
accumulation as a predictor of hematogenous metastasis in human
colorectal cancer. Oncology. 59:302–309. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Karayiannakis AJ, Nakopoulou L,
Gakiopoulou H, Keramopoulos A, Davaris PS and Pignatelli M:
Expression patterns of beta-catenin in in situ and invasive breast
cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 27:31–36. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jawhari A, Jordan S, Poole S, Browne P,
Pignatelli M and Farthing MJ: Abnormal immunoreactivity of the
E-cadherin-catenin complex in gastric carcinoma: relationship with
patient survival. Gastroenterology. 112:46–54. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Papadavid E, Pignatelli M, Zakynthinos S,
Krausz T and Chu AC: Abnormal immunoreactivity of the
E-cadherin/catenin (alpha-, beta- and gamma-) complex in
premalignant and malignant non-melanocytic skin tumours. J Pathol.
196:154–162. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Endo K, Ueda T, Ueyama J, Ohta T and
Terada T: Immunoreactive E-cadherin, alpha-catenin, beta-catenin
and gamma-catenin proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma:
relationships with tumor grade, clinicopathologic parameters and
patients’ survival. Hum Pathol. 31:558–565. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pindborg JJ, Reichart PA, Smith CJ and van
der Waal I: World Health Organisation International Histological
Classification of Tumours. Histological Typing of Cancer and
Precancer of the Oral Mucosa (2nd edition). Springer. (Berlin).
1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lo Muzio L, Staibano S, Pannone G, et al:
Beta- and gamma-catenin expression in oral squamous cell
carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 19:3817–3826. 1999.
|
|
24
|
Ho CM, Lam KH, Wei WI, Lau SK and Lam LK:
Occult lymph node metastasis in small oral tongue cancers. Head
Neck. 14:359–363. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Johnson JT, Barnes EL, Myers EN, Schramm
VL Jr, Borochovitz D and Sigler BA: The extracapsular spread of
tumors in cervical node metastasis. Arch Otolaryngol. 107:725–729.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yamazaki H, Inoue T, Yoshida K, et al:
Lymph node metastasis of early oral tongue cancer after
interstitial radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
58:139–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Odajima T, Sasaki Y, Tanaka N, et al:
Abnormal beta-catenin expression in oral cancer with no gene
mutation: correlation with expression of cyclin D1 and epidermal
growth factor receptor, Ki-67 labeling index, and
clinicopathological features. Hum Pathol. 36:234–241. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ueda G, Sunakawa H, Nakamori K, et al:
Aberrant expression of beta- and gamma-catenin is an independent
prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral
Maxillofac Surg. 35:356–361. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Liu T, Nishioka M, Aguirre RL, Win
SS and Okada N: Activation of ERK1/2 and cyclin D1 expression in
oral tongue squamous cell carcinomas: relationship between
clinicopathological appearances and cell proliferation. Oral Oncol.
42:625–631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen TM and Defendi V: Functional
interaction of p53 with HPV18 E6, c-myc and H-ras in 3T3 cells.
Oncogene. 7:1541–1547. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Horak E, Smith K, Bromley L, LeJeune S,
Greenall M, Lane D and Harris AL: Mutant p53, EGF receptor and
c-erbB-2 expression in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 6:2277–2284.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xu J and Morris GF: p53-mediated
regulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in
cells exposed to ionizing radiation. Mol Cell Biol. 19:12–20.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chung GG, Zerkowski MP, Ocal IT, et al:
beta-catenin and p53 analyses of a breast carcinoma tissue
microarray. Cancer. 100:2084–2092. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Prange W, Breuhahn K, Fischer F, et al:
Beta-catenin accumulation in the progression of human
hepatocarcinogenesis correlates with loss of E-cadherin and
accumulation of p53, but not with expression of conventional WNT-1
target genes. J Pathol. 201:250–259. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D,
Vogelstein B and Craig RW: Participation of p53 protein in the
cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 51:6304–6311.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Polakis P: Wnt signaling and cancer. Genes
Dev. 14:1837–1851. 2000.
|
|
37
|
Gonzalez MV, Pello MF, Ablanedo P, Suarez
C, Alvarez V and Coto E: Chromosome 3p loss of heterozygosity and
mutation analysis of the FHIT and beta-cat genes in squamous cell
carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Pathol. 51:520–524. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Iwai S, Katagiri W, Kong C, Amekawa S,
Nakazawa M and Yura Y: Mutations of the APC, beta-catenin, and axin
1 genes and cytoplasmic accumulation of beta-catenin in oral
squamous cell carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 131:773–782.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|