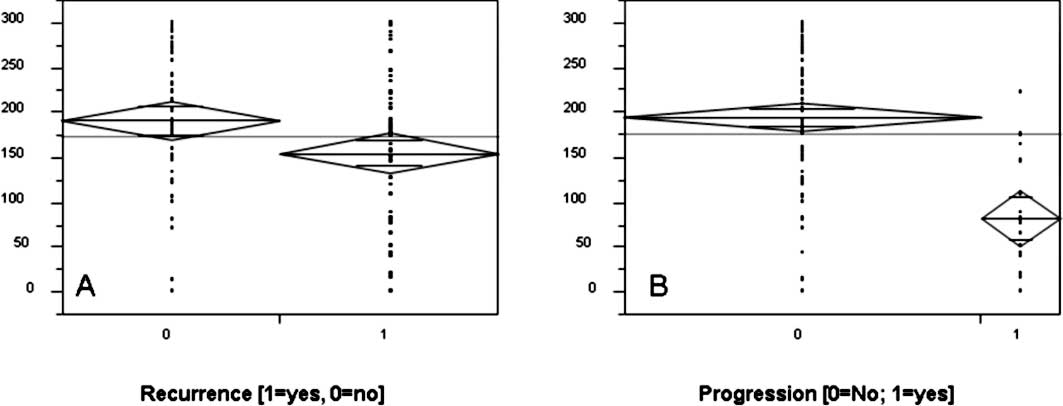
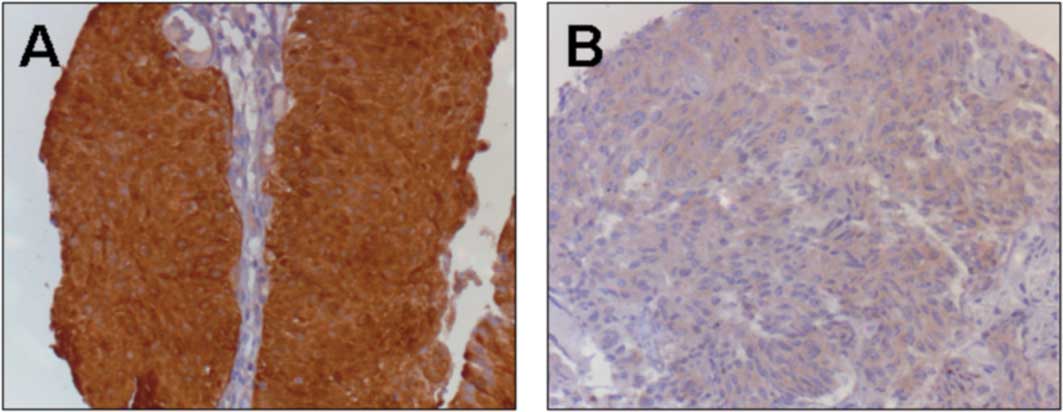
|
1
|
Landis SH, Murray T, Bolden S and Wingo
PA: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 49:8–31. 1999.
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J and
Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 59:225–249. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Guney S, Guney N, Canogullari Z and
Ergenekon E: TaT1 low and intermediate transitional cell carcinoma
of the bladder: recurrence rates and the timing of check
cystoscopies within the first year. Urol Int. 80:124–128.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Holmang S, Hedelin H, Anderstrom C,
Holmberg E, Busch C and Johansson SL: Recurrence and progression in
low grade papillary urothelial tumors. J Urol. 162:702–707. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herr HW: Tumor progression and survival of
patients with high grade, noninvasive papillary (TaG3) bladder
tumors: 15-year outcome. J Urol. 163:60–62. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Futscher BW, Oshiro MM, Wozniak RJ, et al:
Role for DNA methylation in the control of cell type specific
maspin expression. Nat Genet. 31:175–179. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao F, Shi HY, Daughty C, Cella N and
Zhang M: Maspin plays an essential embryonic development.
Development. 131:1479–1489. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang M, Volpert O, Shi YH and Bouck N:
Maspin is an angiogenesis inhibitor. Nat Med. 6:196–199. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Odero-Marah VA, Khalkhali-Ellis Z,
Chunthapong J, et al: Maspin regulates different signaling pathways
for motility and adhesion in aggressive breast cancer cells. Cancer
Biol Ther. 2:398–403. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McGowen R, Biliran H Jr, Sager R and Sheng
S: The surface of prostate carcinoma DU145 cells mediates the
inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by maspin.
Cancer Res. 60:4771–4778. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jiang N, Meng Y, Zhang S, Mensah-Osman E
and Sheng S: Maspin sensitizes breast carcinoma cells to induced
apoptosis. Oncogene. 21:4089–4098. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lockett J, Yin S, Li X, Meng Y and Sheng
S: Tumor suppressive maspin and epithelial homeostasis. J Cell
Biochem. 97:651–660. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Beecken WD, Engl T, Engels K, et al:
Clinical relevance of maspin expression in bladder cancer. World J
Urol. 24:338–344. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sugimoto S, Maass N, Takimoto Y, et al:
Expression and regulation of tumor suppressor gene maspin in human
bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 203:209–215. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Friedrich MG, Toma MI, Petri S, et al:
Expression of maspin in non-muscle invasive bladder carcinoma:
Correlation with tumor angiogenesis and prognosis. Eur Urol.
45:737–743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blandamura S, D’Alessandro E, Giacomelli
L, et al: Expression of maspin in papillary Ta/T1 bladder
neoplasms. Anticancer Res. 28:471–478. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kramer MW, Kuczyk MA, Hennenlotter J, et
al: Decreased expression of galectin-3 predicts tumour recurrence
in pTa bladder cancer. Oncol Rep. 20:1403–1408. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mostofi FK, Sorbin L and Torloni H:
Histological typing of urinary bladder tumours International
classification of tumours. World Health Organisation. Geneva:
1973.
|
|
19
|
Kramer MW, Merseburger AS, Hennenlotter J
and Kuczyk M: Tissue microarrays in clinical urology – technical
considerations. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 41:478–484. 2007.
|
|
20
|
Merseburger AS, Anastasiadis AG,
Hennenlotter J, et al: Tissue microarrays: applications in
urological cancer research. World J Urol. 24:579–584. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Merseburger AS, Kramer MW, Hennenlotter J,
et al: Loss of galectin-3 expression correlates with clear cell
renal carcinoma progression and reduced survival. World J Urol.
26:637–642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ngamkitidechakul C, Burke JM, O’Brien WJ
and Twining SS: Maspin: synthesis by human cornea and regulation of
in vitro stromal cell adhesion to extracellular matrix. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 42:3135–3141. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Reis-Filho JS, Milanezi F, Silva P and
Schmitt FC: Maspin expression in myoepithelial tumors of the
breast. Pathol Res Pract. 197:817–821. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Reis-Filho JS, Torio B, Albergaria A and
Schmitt FC: Maspin expression in normal skin and usual cutaneous
carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 441:551–558. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mohsin SK, Zhang M, Clark GM and Craig
Allred D: Maspin expression in invasive breast cancer: Association
with other prognostic factors. J Pathol. 199:432–435. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sood AK, Fletcher MS, Gruman LM, et al:
The paradoxical expression of maspin in ovarian carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 8:2924–2932. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Heighway J, Knapp T, Boyce L, et al:
Expression profiling of primary non-small cell lung cancer for
target identification. Oncogene. 21:7749–7763. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|