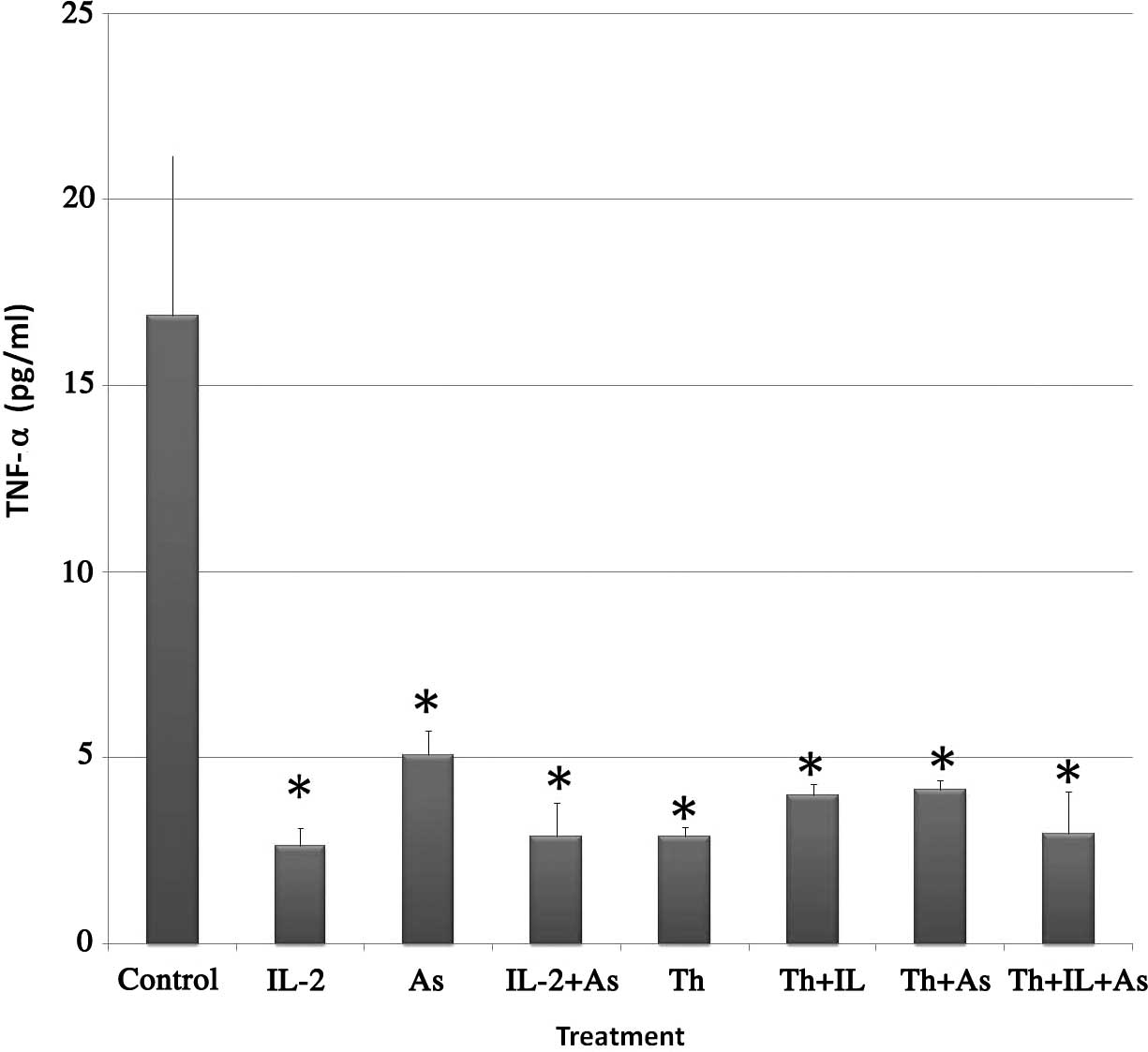
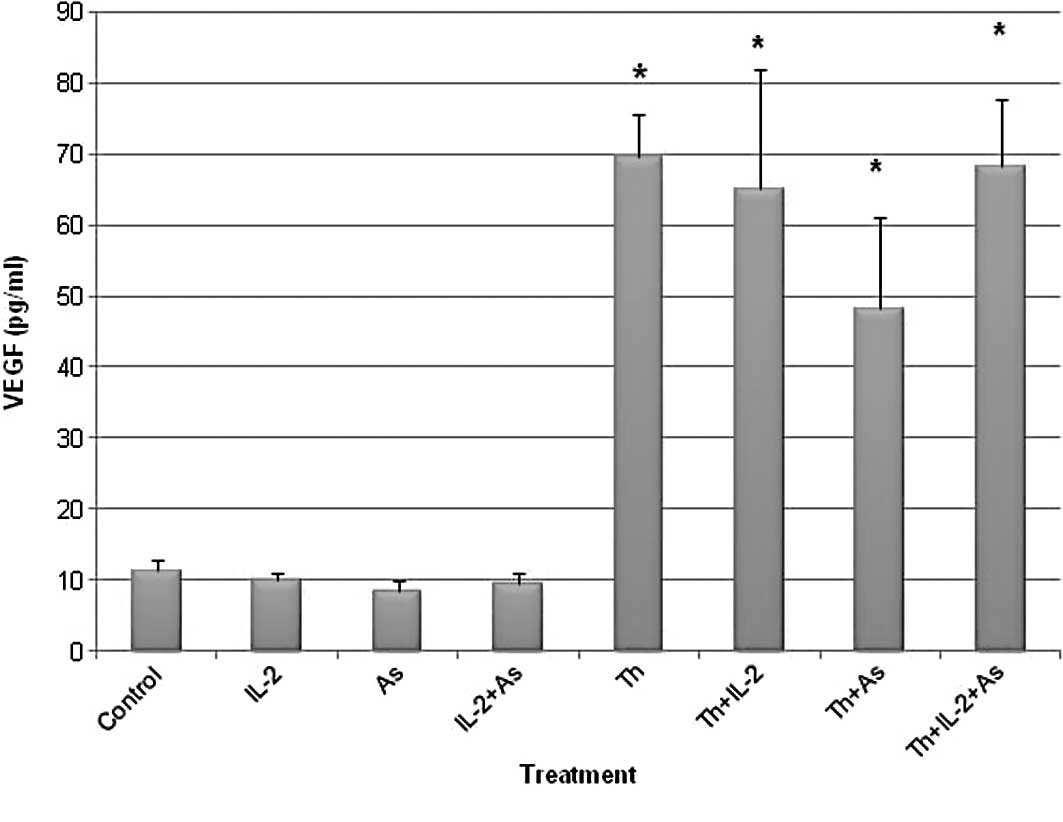
|
1
|
McGeehan GM and Uhl J: TNF-α in human
diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 2:662–667. 1996.
|
|
2
|
Snoeck HW, Weekx S, Moulijn A, et al:
Tumor necrosis factor alpha is a potent synergistic factor for the
proliferation of primitive human hematopoietic progenitor cells and
induces resistance to transforming growth factor beta but not to
interferon gamma. J Exp Med. 183:705–710. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Girardin E, Grau GE, Dayer JM,
Roux-Lombard P and Lambert PH: Tumor necrosis factor and
interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious
purpura. N Eng J Med. 319:397–400. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tracey KJ, Wei H, Manogue KR, et al:
Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces cachexia, anemia and
inflammation. J Exp Med. 167:1211–1227. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sampaio EP, Sarno EN, Galilly R, Cohn ZA
and Kaplan G: Thalidomide selectively inhibits tumor necrosis
factor alpha production by stimulated human monocytes. J Exp Med.
173:699–703. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Minchinton AL, Fryer KH, Wendt KR, Clow KA
and Hayes MM: The effect of thalidomide on experimental tumors and
metastases. Anticancer Drugs. 7:339–343. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kruse FF, Joussen AM, Rohrschneider K,
Becker MD and Volcker HE: Thalidomide inhibits corneal angiogenesis
induced by vascular endothelial growth factor. Graefes Arch Clin
Exp Ophthalmol. 236:461–466. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E and
Folkman J: Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 91:4082–4085. 1994.
|
|
9
|
Lu C and Hassan HT: Human stem cell
factor-antibody (anti-SCF) enhances chemotherapy cytotoxicity in
human CD34+ resistant myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 30:296–302.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Renauld AE and Spengler RN: Tumor necrosis
factor expressed by primary hippocampal neurons and SH-SY5Y cells
is regulated by α2-adrenergic receptor activation. J Neurosci Res.
67:264–274. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ogasawara T, Narita C and Kawauchi K:
Production of vascular endothelial growth factor in T-cell
prolymphocytic leukemia. Leuk Res. 31:403–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: mechanistic
insights, neovascular diseases in cancer, rheumatoid and other
disease. Nature Med. 1:27–31. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aguayo A, Estey E, Kantarjian H, et al:
Cellular vascular endothelial growth factor is a predictor of
outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
94:3717–3721. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fiedler W, Graeven U, Ergun S, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor, a possible paracrine growth
factor in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 89:1870–1875.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Koch HP: Thalidomide and congeners as
anti-inflammatory agents. Prog Med Chem. 22:165–242. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Moreira AL, Sampaio EP, Zmuidzinas A,
Frindt P, Smith KA and Kaplan G: Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory
action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA
degradation. J Exp Med. 177:1675–1680. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sampaio EP, Kaplan G, Miranda A, Nery JA,
Miguel CP, Viana SM and Sarno EN: The influence of thalidomide on
the clinical and immunologic manifestation of erythema nodosum
leprosum. J Infect Dis. 168:408–414. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shannon EJ, Morales MJ and Sandoval F:
Immunomodulatory assays to study structure-activity relationships
of thalidomide. Immunopharmacology. 35:203–212. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tavares JL, Wangoo A, Dilworth P, Marshall
B, Kotecha S and Shaw RJ: Thalidomide reduces tumor necrosis factor
alpha production by human alveolar macrophages. Respir Med.
91:31–39. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brieger J, Schroeder P, Gosepath J and
Mann WJ: Vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast
growth factor are released by squamous cell carcinoma cells after
irradiation and increase resistance to subsequent irradiation. Intl
J Mol Med. 16:159–164. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Shintani S, Kiyota A, Mihara M, Nakahara
Y, Terakado N, Ueyama Y and Matsumura T: Association of
preoperative radiation effect with tumor angiogenesis and vascular
endothelial growth factor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Jpn J
Cancer. 91:1051–1057. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Sirvidis
E, Simopoulos K, Pissakas G, Gatter KC and Harris AL: Squamous cell
head and neck cancer: evidence of angiogenic regeneration during
radiotherapy. Anticancer Res. 2:4301–4309. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Geng L, Donnelly E, McMahon G, Lin PC,
Sierra-River E, Oshinka H and Hallahan DE: Inhibition of vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor signaling leads to reversal of
tumor resistance to radiotherapy. Cancer Res. 61:2413–2419.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|