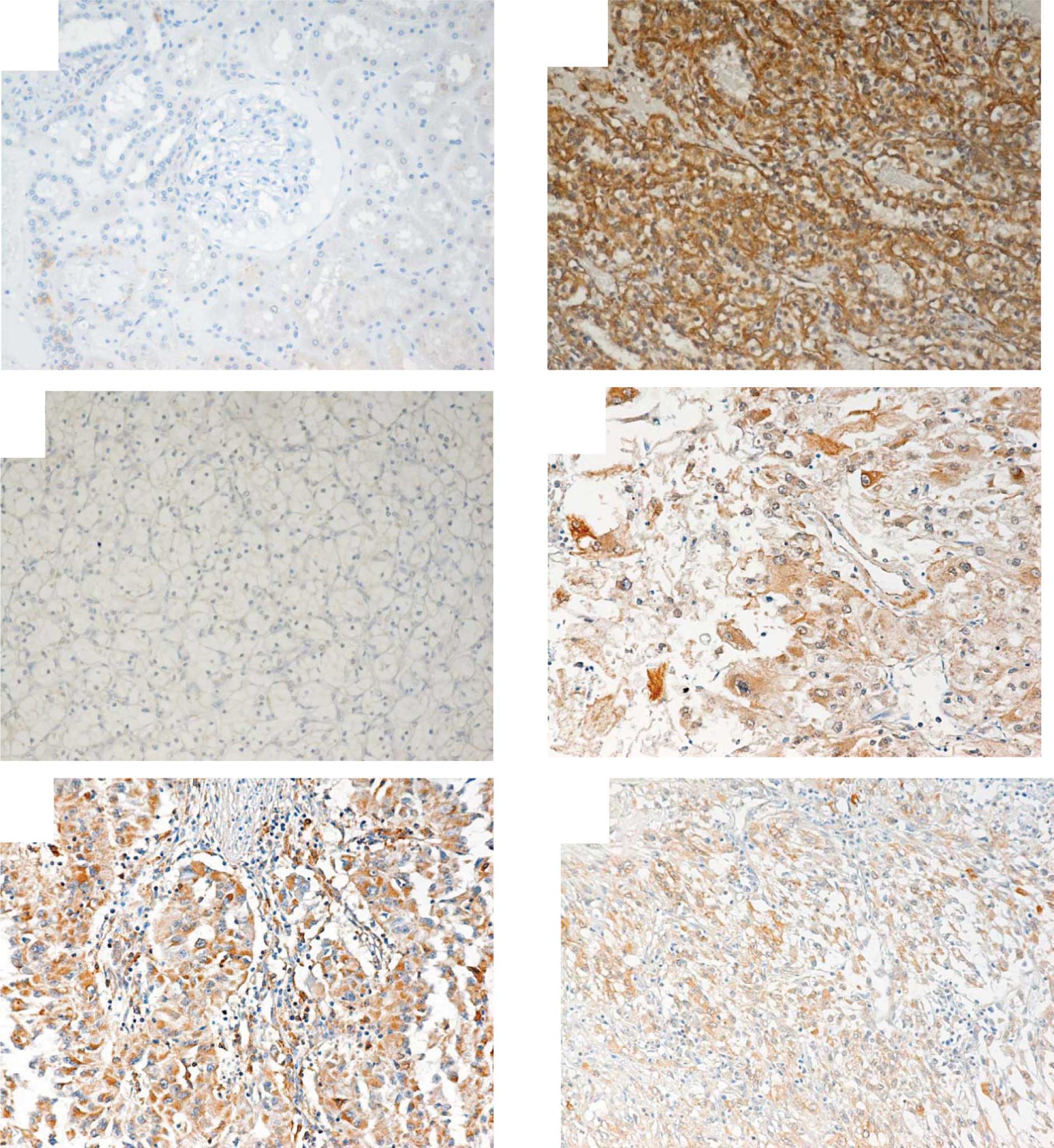
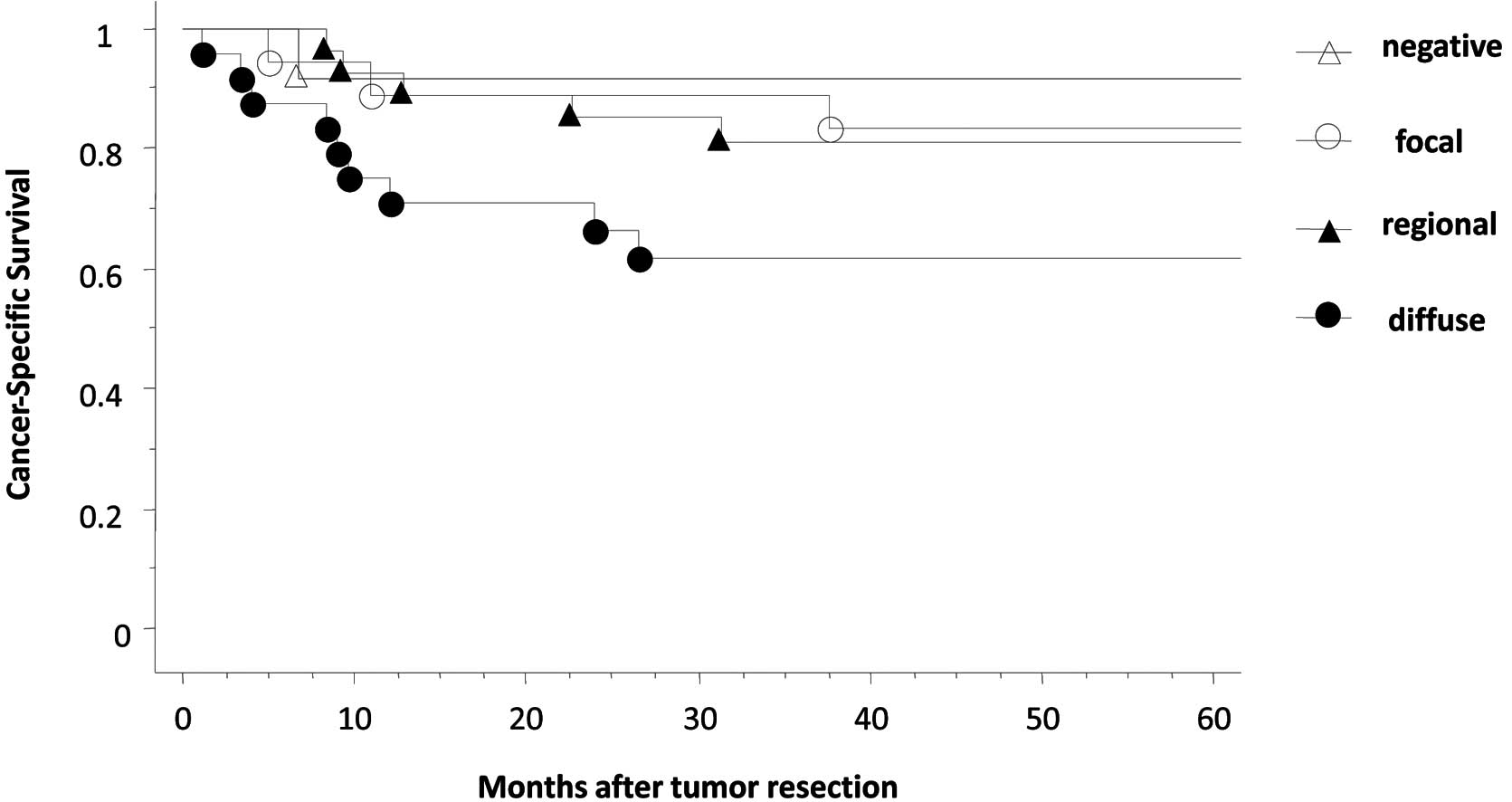
|
1
|
Weis RH and Lin PY: Kidney cancer:
identification of novel targets for therapy. Kidney Int.
69:224–232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson D, Bukowski M, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C,
Kim ST, Chen I, Bycott PW, Baum CM and Figlin RA: Sunitinib vs.
interferon alpha in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim HL, Seligson D, Liu X, Janzen N, Bui
MHT, Yu H, Shi T, Figlin RA, Horvath S and Belldegrun AS: Using
protein expression to predict survival in clear cell renal
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5464–5471. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Motzer RJ and Bukowski RM: Targeted
therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
24:5601–5608. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Patel PH, Chadalavada RSV, Chaganti RSK
and Motzer RJ: Targeting von Hippel-Lindau pathway in renal cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 12:7215–7220. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Klatte T, Seligson DB, Riggs SB, Leppert
JT, Berkman MK, Kleid MD, Hong Yu, Kabbinavar FF, Pantuck AJ and
Belldegrun AS: Hypoxia-inducible factor α in clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:7388–7393. 2007.
|
|
7
|
Togashi A, Katagiri T, Ashida S, Fujioka
T, Maruyama O, Wakumoto Y, Sakamoto Y, Fujime M, Kawachi Y, Shuin T
and Nakamura Y: Hypoxia-inducible protein2 (HIG2), a novel
diagnostic marker for renal cell carcinoma and potential target for
molecular therapy. Cancer Res. 65:4817–4826. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Patard JJ, Fergelot P, Karakiewicz PI,
Klatte T, Trinh QD, Rioux-Leclecq N, Said JW, Belldegrun AS and
Pantuck AJ: Low CAIX expression and absence of VHL gene mutation
are associated with tumor aggressiveness and poor survival of clear
cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 123:395–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao M, Yoshida M, Kishida T, Nakaigawa N,
Baba M, Kobayashi K, Miura T, Moriyama M, Nagashima Y, Nakatani Y,
Kubota Y and Kondo K: VHL tumor suppressor gene alterations
associated with good prognosis in sporadic clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:1569–1575. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mizutani Y: Recent advances in molecular
targeted therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Int J Urol.
16:444–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tozawa K, Okamoto T, Kawai N, Hashimoto Y,
Hayashi Y and Kohri K: Positive correlation between sialyl Lewis X
expression and pathologic findings in renal cell carcinoma. Kidney
Int. 67:1391–1396. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liao SY, Aurelio ON, Jan K, Zavada J and
Stanbridge EJ: Identification of the MN/CA9 protein as a reliable
diagnostic biomarker of clear cell carcinoma of the kidney. Cancer
Res. 57:2827–2831. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wykoff CC, Beasley NJP, Watson PH, Turner
KJ, Pastrek J, Sibtain A, Wilson GD, Turley H, Talks KL, Maxwell
PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ and Harris AL: Hypoxia-inducible
expression of tumor-associated carbonic anhydrases. Cancer Res.
60:7075–7083. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uemura H, Fujumoto K, Tanaka M, Yoshikawa
M, Hirano Y, Uejima S, Yoshikawa K and Itoh K: A phase I trial of
vaccination of CA9-derived peptides for HLA-A24-positive patients
with cytokine-refractory metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:1768–1775. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Davis ID, Wiseman GA, Lee FT, Gansen DN,
Hopkins W, Papenfuss AT, Liu Z, Moynihan TJ, Croghan GA, Adjei AA,
Hoffman EW, Ingle JN, Old LJ and Scott AM: A phase 1 multiple dose,
dose escalation study of cG250 monoclonal antibody in patients with
advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immun. 7:132007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leibovich BC, Sheinin Y, Lohse CM,
Thompson RH, Cheville JC, Zavada J and Kwon ED: Carbonic anhydrase
IX is not an independent predictor of outcome for patients with
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 25:4757–4764. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|