Spandidos Publications style
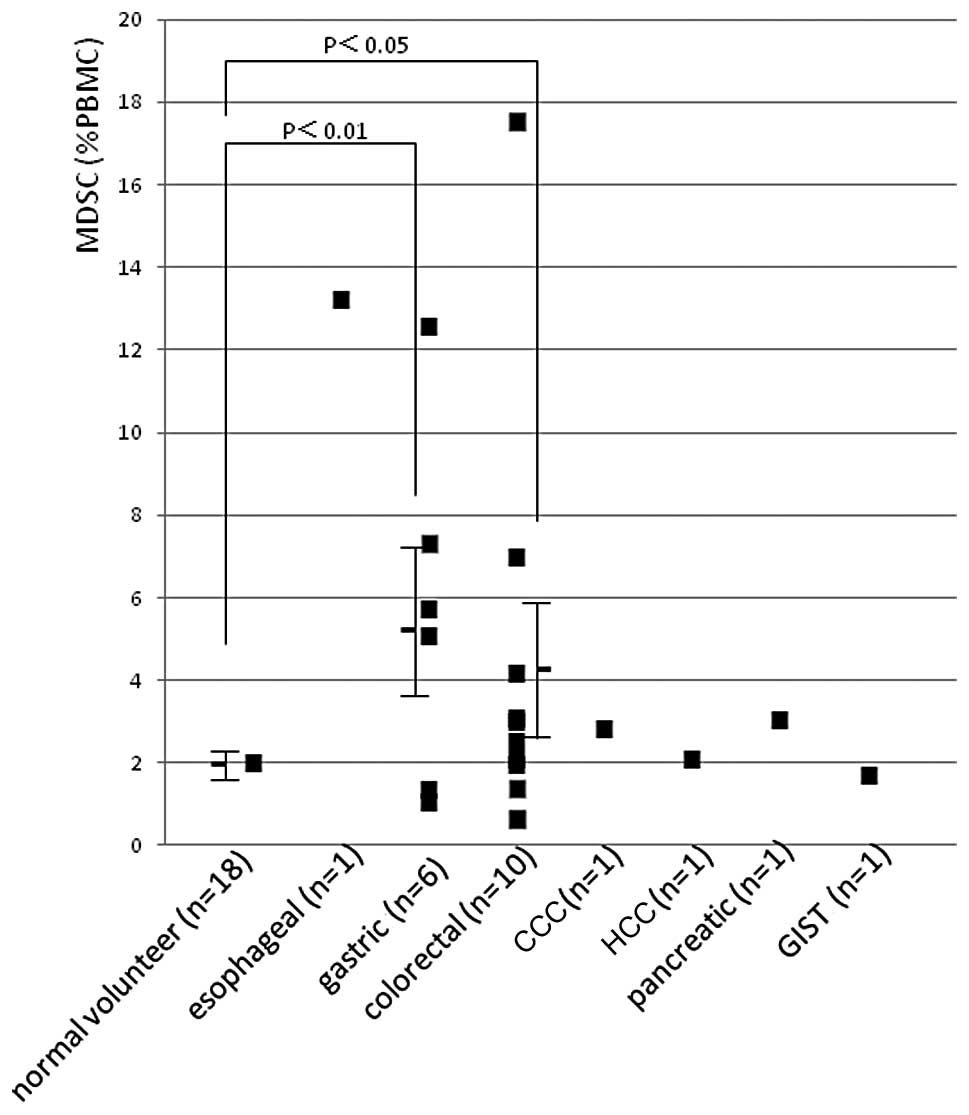
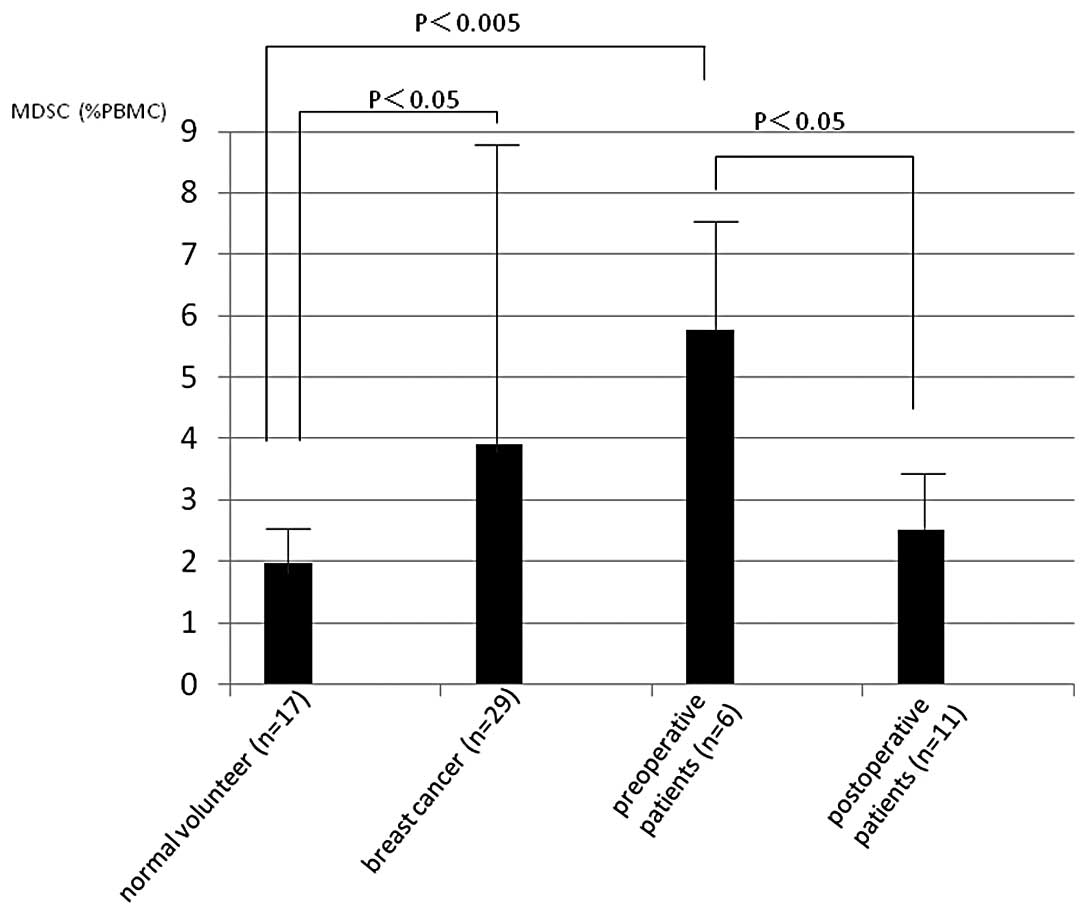
Ohki S, Shibata M, Gonda K, Machida T, Shimura T, Nakamura I, Ohtake T, Koyama Y, Suzuki S, Ohto H, Ohto H, et al: Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer. Oncol Rep 28: 453-458, 2012.
APA
Ohki, S., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Shimura, T., Nakamura, I. ... Takenoshita, S. (2012). Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer. Oncology Reports, 28, 453-458. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1812
MLA
Ohki, S., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Shimura, T., Nakamura, I., Ohtake, T., Koyama, Y., Suzuki, S., Ohto, H., Takenoshita, S."Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer". Oncology Reports 28.2 (2012): 453-458.
Chicago
Ohki, S., Shibata, M., Gonda, K., Machida, T., Shimura, T., Nakamura, I., Ohtake, T., Koyama, Y., Suzuki, S., Ohto, H., Takenoshita, S."Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased and correlate to immune suppression, inflammation and hypoproteinemia in patients with cancer". Oncology Reports 28, no. 2 (2012): 453-458. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1812