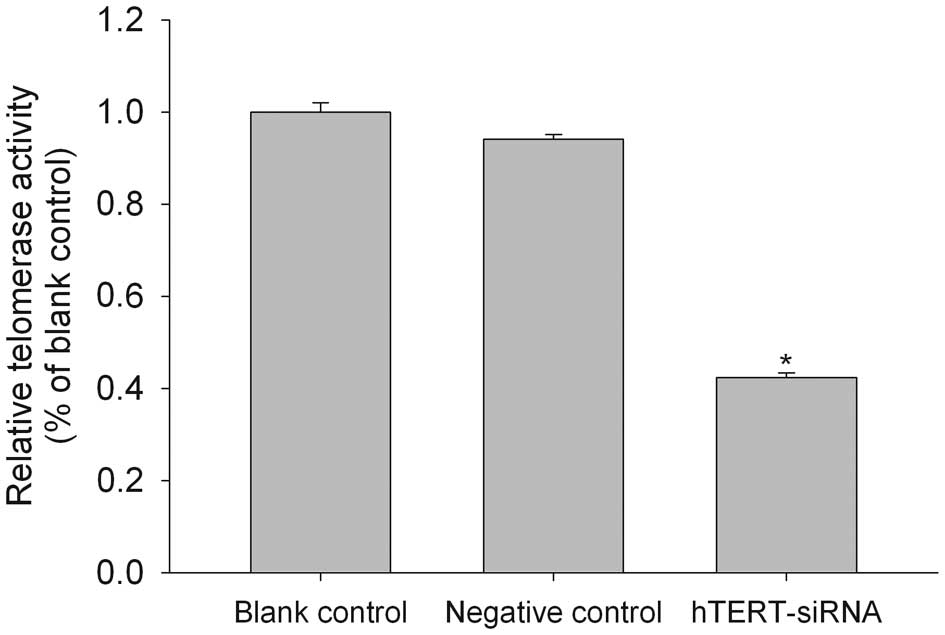
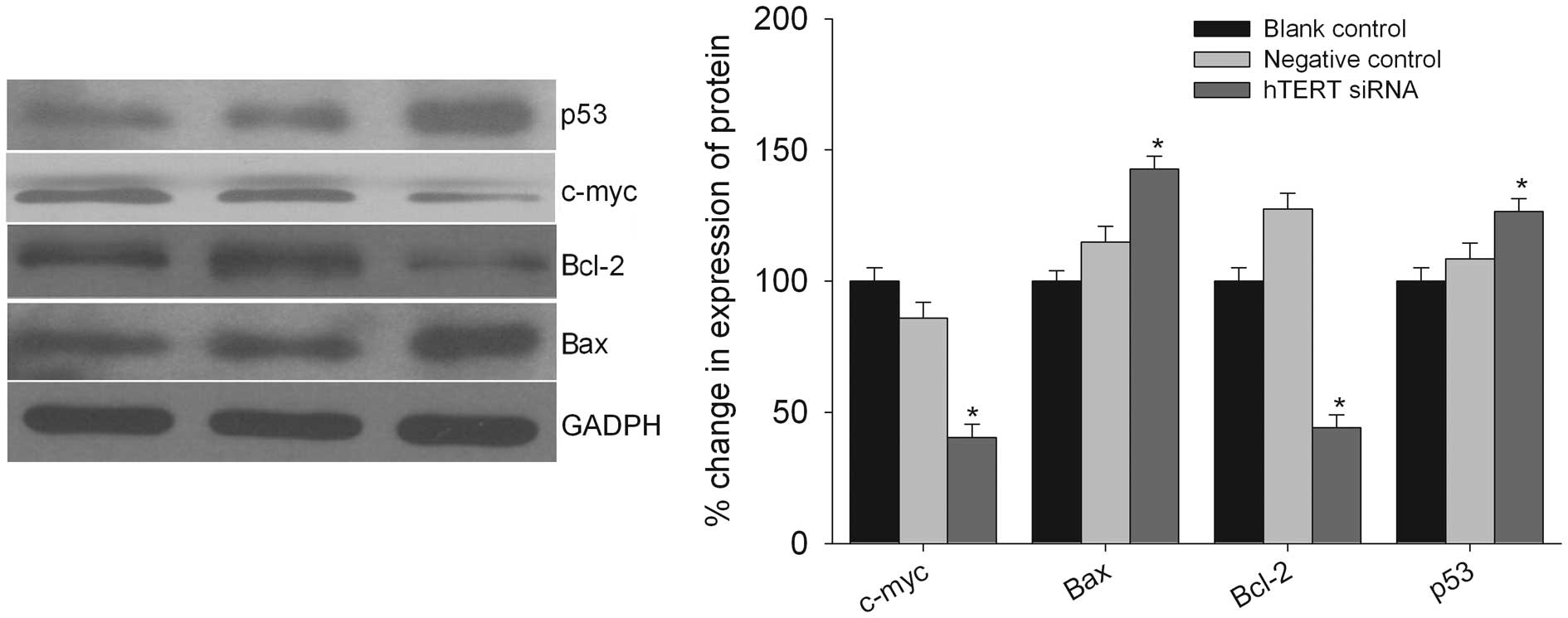
|
1
|
Lino MM and Merlo A: PI3Kinase signaling
in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 103:417–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao P, Wang C, Fu Z, et al: Lentiviral
vector mediated siRNA knock-down of hTERT results in diminished
capacity in invasiveness and in vivo growth of human glioma
cells in a telomere length-independent manner. Int J Oncol.
31:361–368. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li C, Zhou C, Wang S, et al: Sensitization
of glioma cells to tamoxifen-induced apoptosis by Pl3-kinase
inhibitor through the GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway.
PLoS One. 6:e270532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Prados MD and Levin V: Biology and
treatment of malignant glioma. Semin Oncol. 27:1–10. 2000.
|
|
5
|
Ponnala S, Chetty C, Veeravalli KK, Dinh
DH, Klopfenstein JD and Rao JS: MMP-9 silencing regulates hTERT
expression via beta1 integrin-mediated FAK signaling and induces
senescence in glioma xenograft cells. Cell Signal. 23:2065–2075.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shervington A, Cruickshanks N, Wright H,
et al: Glioma: what is the role of c-Myc, hsp90 and telomerase? Mol
Cell Biochem. 283:1–9. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Feng J, Funk WD, Wang SS, et al: The RNA
component of human telomerase. Science. 269:1236–1241. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Harrington L, McPhail T, Mar V, et al: A
mammalian telomerase-associated protein. Science. 275:973–977.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakayama JI, Saito M, Nakamura H, Matsuura
A and Ishikawa F: TLP1: a gene encoding a protein component of
mammalian telomerase is a novel member of WD repeats family. Cell.
88:875–884. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Meyerson M, Counter CM, Eaton EN, et al:
hEST2, the putative human telomerase catalytic subunit gene, is
up-regulated in tumor cells and during immortalization. Cell.
90:785–795. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kondo S, Kanzawa T, Germano IM, Kondo Y,
Ito H and Kyo S: Inhibition of telomerase activity in malignant
glioma cells correlates with their sensitivity to temozolomide. Br
J Cancer. 89:922–929. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferguson SD: Malignant gliomas: diagnosis
and treatment. Dis Mon. 57:558–569. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Furnari FB, Fenton T, Bachoo RM, et al:
Malignant astrocytic glioma: genetics, biology, and paths to
treatment. Genes Dev. 21:2683–2710. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 apoptotic
switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene. 26:1324–1337.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xue Y, Li L, Zhang D, et al: Telomerase
suppression initiates PML-dependent p53 activation to inhibit
bladder cancer cell growth. Oncol Rep. 24:1551–1559.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang Y, Cheng Y, Zhang L, et al:
Inhibition of eEF-2 kinase sensitizes human glioma cells to TRAIL
and down-regulates Bcl-xL expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
414:129–134. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
George J, Banik NL and Ray SK: Knockdown
of hTERT and concurrent treatment with interferon-gamma inhibited
proliferation and invasion of human glioblastoma cell lines. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 42:1164–1173. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shammas MA, Koley H, Batchu RB, et al:
Telomerase inhibition by siRNA causes senescence and apoptosis in
Barrett's adenocarcinoma cells: mechanism and therapeutic
potential. Mol Cancer. 4:242005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen CH and Chen RJ: Prevalence of
telomerase activity in human cancer. J Formos Med Assoc.
110:275–289. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shay JW and Wright WE: Role of telomeres
and telomerase in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 21:349–353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
George J, Banik NL and Ray SK: Combination
of hTERT knockdown and IFN-gamma treatment inhibited angiogenesis
and tumor progression in glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res.
15:7186–7195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YF, Wang DL, Shi GS and Huang H:
Expressions of hTERT, HIF-1alpha and CD105 in gliomas and their
clinical significance. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 35:681–682.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Packham G and Cleveland JL: c-Myc and
apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1242:11–28. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lutz W, Leon J and Eilers M: Contributions
of Myc to tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1602:61–71.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
von Bueren AO, Shalaby T, Oehler-Janne C,
et al: RNA interference-mediated c-MYC inhibition prevents cell
growth and decreases sensitivity to radio- and chemotherapy in
childhood medulloblastoma cells. BMC Cancer. 9:102009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Louis DN: The p53 gene and protein in
human brain tumors. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 53:11–21. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Levine AJ, Hu W and Feng Z: The P53
pathway: what questions remain to be explored? Cell Death Differ.
13:1027–1036. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Krakstad C and Chekenya M: Survival
signalling and apoptosis resistance in glioblastomas: opportunities
for targeted therapeutics. Mol Cancer. 9:1352010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|