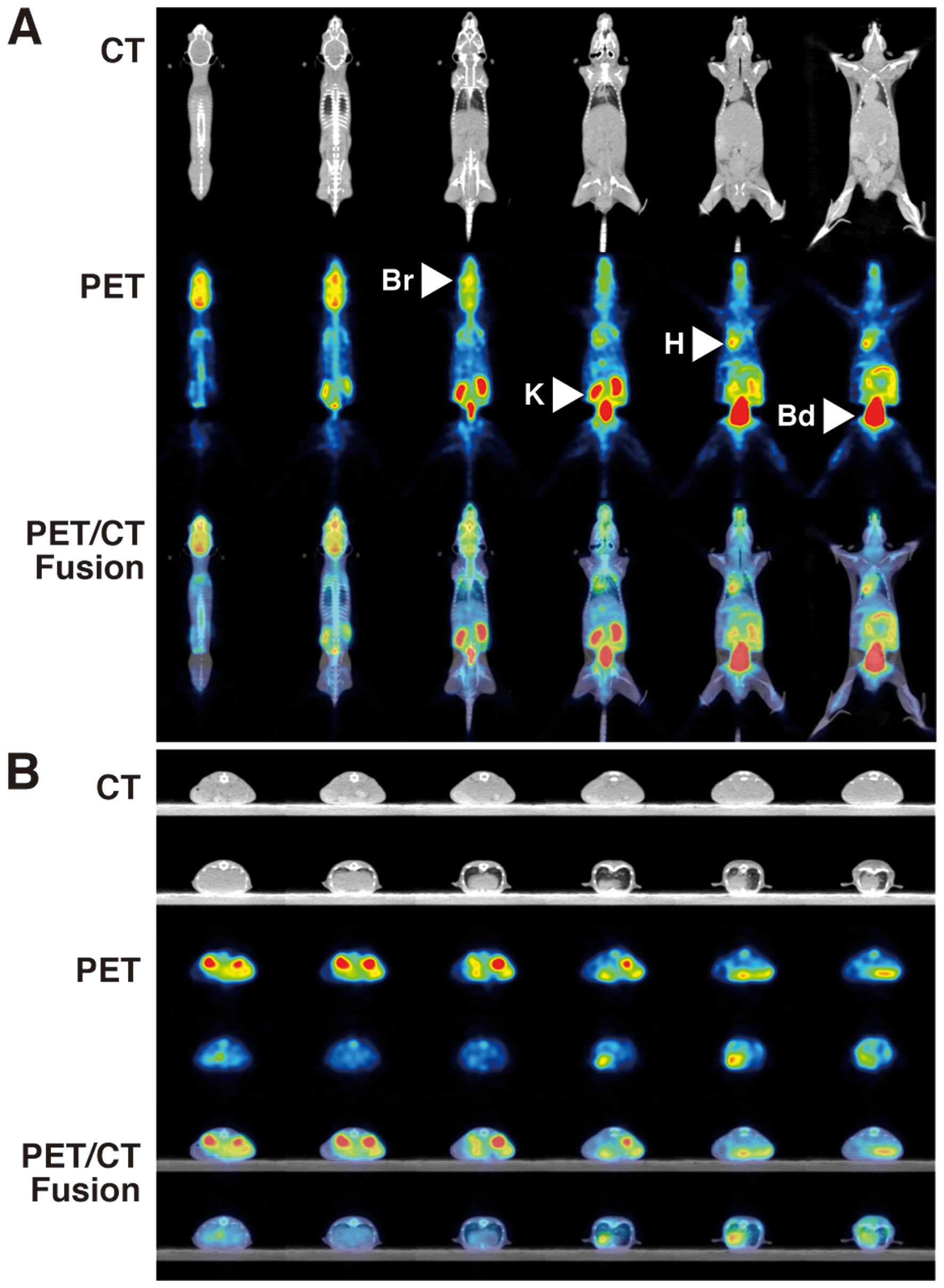
|
1
|
O’Connor ES, Greenblatt DY, LoConte NK, et
al: Adjuvant chemotherapy for stage II colon cancer with poor
prognostic features. J Clin Oncol. 29:3381–3388. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karoui M, Roudot-Thoraval F, Mesli F, et
al: Primary colectomy in patients with stage IV colon cancer and
unresectable distant metastases improves overall survival: results
of a multicentric study. Dis Colon Rectum. 54:930–938. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Tokunaga T, Oshika Y, Abe Y, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) mRNA isoform expression
pattern is correlated with liver metastasis and poor prognosis in
colon cancer. Br J Cancer. 77:998–1002. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tokunaga T, Nakamura M, Oshika Y, et al:
Thrombospondin 2 expression is correlated with inhibition of
angiogenesis and metastasis of colon cancer. Br J Cancer.
79:354–359. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun L, Hu H, Peng L, et al: P-cadherin
promotes liver metastasis and is associated with poor prognosis in
colon cancer. Am J Pathol. 179:380–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka M, Hashiguchi Y, Ueno H, Hase K and
Mochizuki H: Tumor budding at the invasive margin can predict
patients at high risk of recurrence after curative surgery for
stage II, T3 colon cancer. Dis Colon Rectum. 46:1054–1059. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sato T, Ueno H, Mochizuki H, et al:
Objective criteria for the grading of venous invasion in colorectal
cancer. Am J Surg Pathol. 34:454–462. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cronin CG, Swords R, Truong MT, et al:
Clinical utility of PET/CT in lymphoma. Am J Roentgenol.
194:W91–W103. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ueda S, Saeki T, Shigekawa T, et al:
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography
optimizes neoadjuvant chemotherapy for primary breast cancer to
achieve pathological complete response. Int J Clin Oncol.
17:276–282. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xie L, Saynak M, Veeramachaneni NK, et al:
Non-small cell lung cancer: prognostic importance of positive FDG
PET findings in the mediastinum for patients with N0–N1 disease at
pathologic analysis. Radiology. 261:226–234. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abe Y, Tamura K, Sakata I, et al: Clinical
implications of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission
tomography/computed tomography at delayed phase for diagnosis and
prognosis of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Oncol Rep. 27:333–338.
2012.
|
|
12
|
Mori S and Oguchi K: Application of
(18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography to detection
of proximal lesions of obstructive colorectal cancer. Jpn J Radiol.
28:584–590. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ducreux M and Dromain C: Non-invasive
imaging tools in colorectal cancer. Rev Prat. 60:1071–1073.
2010.(In French).
|
|
14
|
Treglia G, Calcagni ML, Rufini V, et al:
Clinical significance of incidental focal colorectal
(18)F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake: our experience and a review of the
literature. Colorectal Dis. 14:174–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kubota R, Kubota K, Yamada S, Tada M, Ido
T and Tamahashi N: Microautoradiographic study for the
differentiation of intratumoral macrophages, granulation tissues
and cancer cells by the dynamics of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose
uptake. J Nucl Med. 35:104–112. 1994.
|
|
16
|
Abe Y, Nakamura M, Ohnishi Y, Inaba M,
Ueyama Y and Tamaoki N: Multidrug resistance gene (MDR1) expression
in human tumor xenografts. Int J Oncol. 5:1285–1292.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abe Y, Ohnishi Y, Yoshimura M, et al:
P-glycoprotein-mediated acquired multidrug resistance of human lung
cancer cells in vivo. Br J Cancer. 74:1929–1934. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suto R, Abe Y, Nakamura M, et al:
P-glycoprotein-mediated acquired multidrug resistance of human
osteosarcoma xenografts in vivo. Int J Oncol. 12:287–291.
1998.
|
|
19
|
Fujimori S, Abe Y, Nishi M, et al: The
subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase enhance cisplatin resistance
in human non-small cell lung cancer xenografts in vivo. Int
J Oncol. 25:413–418. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miyakawa Y, Ohnishi Y, Tomisawa M, et al:
Establishment of a new model of human multiple myeloma using
NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) (NOG) mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
313:258–262. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ikoma N, Yamazaki H, Abe Y, et al: S100A4
expression with reduced E-cadherin expression predicts distant
metastasis of human malignant melanoma cell lines in the
NOD/SCID/γCnull (NOG) mouse model. Oncol Rep.
14:633–637. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hamada K, Monnai M, Kawai K, et al: Liver
metastasis models of colon cancer for evaluation of drug efficacy
using NOD/Shi-scid IL2Rγnull (NOG) mice. Int J Oncol.
32:153–159. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chijiwa T, Abe Y, Ikoma N, et al:
Thrombospondin 2 inhibits metastasis of human malignant melanoma
through microenvironment-modification in
NOD/SCID/γCnull (NOG) mice. Int J Oncol.
34:5–13. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ito M, Hiramatsu H, Kobayashi K, et al:
NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mouse: an excellent recipient mouse model
for engraftment of human cells. Blood. 100:3175–3182. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hiramatsu H, Nishikomori R, Heike T, et
al: Complete reconstitution of human lymphocytes from cord blood
CD34+ cells using the NOD/SCID/gamma(c)(null) mice
model. Blood. 102:873–880. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suemizu H, Monnai M, Ohnishi Y, Ito M,
Tamaoki N and Nakamura M: Identification of a key molecular
regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma using a
novel quantitative model of metastasis in
NOD/SCID/γcnull (NOG) mice. Int J Oncol.
31:741–751. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kubo A, Ohmura M, Wakui M, et al:
Semi-quantitative analyses of metabolic systems of human colon
cancer metastatic xenografts in livers of superimmunodeficient NOG
mice. Anal Bioanal Chem. 400:1895–1904. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Deroose CM, De A, Loening AM, et al:
Multimodality imaging of tumor xenografts and metastases in mice
with combined small-animal PET, small-animal CT, and
bioluminescence imaging. J Nucl Med. 48:295–303. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oberdorfer F, Hull WE, Traving BC and
Maier-Borst W: Synthesis and purification of
2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-glucose and
2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-D-mannose: characterization of products by
1H- and 19F-NMR spectroscopy. Int J Rad Appl Instrum A. 37:695–701.
1986.
|
|
30
|
Mizuta T, Kitamura K, Iwata H, et al:
Performance evaluation of a high-sensitivity large-aperture
small-animal PET scanner: ClairvivoPET. Ann Nucl Med. 22:447–455.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ueda S, Tsuda H, Asakawa H, et al:
Clinicopathological and prognostic relevance of uptake level using
18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed
tomography fusion imaging (18F-FDG PET/CT) in primary breast
cancer. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 38:250–258. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Abe Y, Tamura K, Sakata I, et al:
Usefulness of 18F-FDG positron emission
tomography/computed tomography for the diagnosis of
pyothorax-associated lymphoma: a report of three cases. Oncol Lett.
1:833–836. 2010.
|
|
33
|
Abe Y, Tamura K, Sakata I, et al: Unique
intense uptake demonstrated by 18F-FDG positron emission
tomography/computed tomography in primary pancreatic lymphoma: a
case report. Oncol Lett. 1:605–607. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ozeki Y, Abe Y, Kita H, et al: A case of
primary lung cancer lesion demonstrated by F-18 FDG positron
emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) one year after the
detection of metastatic brain tumor. Oncol Lett. 2:621–623.
2011.
|
|
35
|
Takamiya Y, Abe Y, Tanaka Y, et al: Murine
P-glycoprotein on stromal vessels mediates multidrug resistance in
intracerebral human glioma xenografts. Br J Cancer. 76:445–450.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hatanaka H, Oshika Y, Abe Y, et al:
Vascularization is decreased in pulmonary adenocarcinoma expressing
brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1). Int J Mol Med.
5:181–183. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pantaleo MA, Nicoletti G, Nanni C, et al:
Preclinical evaluation of KIT/PDGFRA and mTOR inhibitors in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors using small animal FDG PET. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 29:1732010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Moroz MA, Kochetkov T, Cai S, et al:
Imaging colon cancer response following treatment with AZD1152: a
preclinical analysis of [18F]fluoro-2-deoxyglucose and
3′-deoxy-3′-[18F]fluorothymidine imaging. Clin Cancer Res.
17:1099–1110. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kubota K, Nakamoto Y, Tamaki N, et al:
FDG-PET for the diagnosis of fever of unknown origin: a Japanese
multi-center study. Ann Nucl Med. 25:355–364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tsukada H, Sato K, Fukumoto D, Nishiyama
S, Harada N and Kakiuchi T: Evaluation of D-isomers of O-11C-methyl
tyrosine and O-18F-fluoromethyl tyrosine as tumor-imaging agents in
tumor-bearing mice: comparison with L- and D-11C-methionine. J Nucl
Med. 47:679–688. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsukada H, Sato K, Fukumoto D and Kakiuchi
T: Evaluation of D-isomers of O-18F-fluoromethyl, O-18F-fluoroethyl
and O-18F-fluoropropyl tyrosine as tumour imaging agents in mice.
Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 33:1017–1024. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Perk LR, Stigter-van Walsum M, Visser GW,
et al: Quantitative PET imaging of Met-expressing human cancer
xenografts with 89Zr-labelled monoclonal antibody DN30. Eur J Nucl
Med Mol Imaging. 35:1857–1867. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang H, Liu B, Tian JH, et al: Monitoring
early responses to irradiation with dual-tracer micro-PET in
dual-tumor bearing mice. World J Gastroenterol. 16:5416–5423. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|