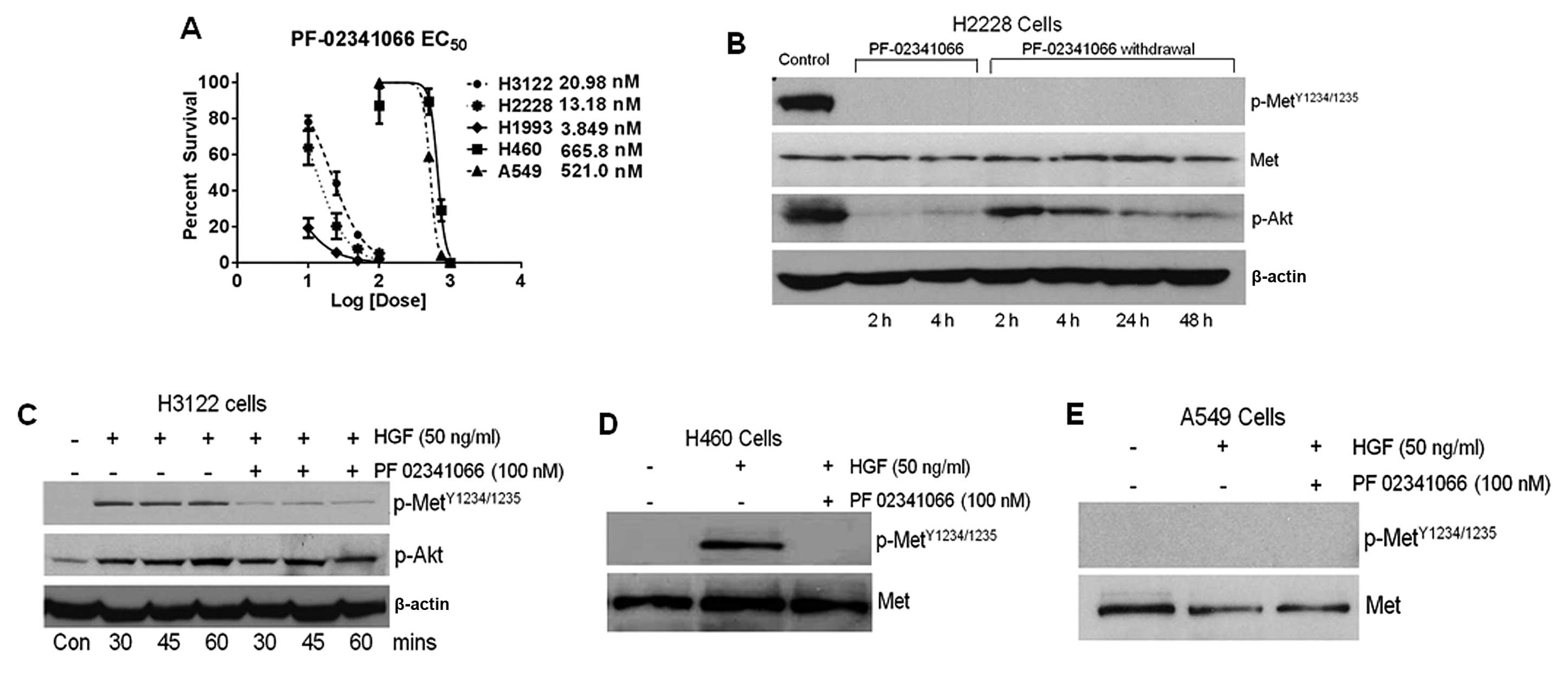
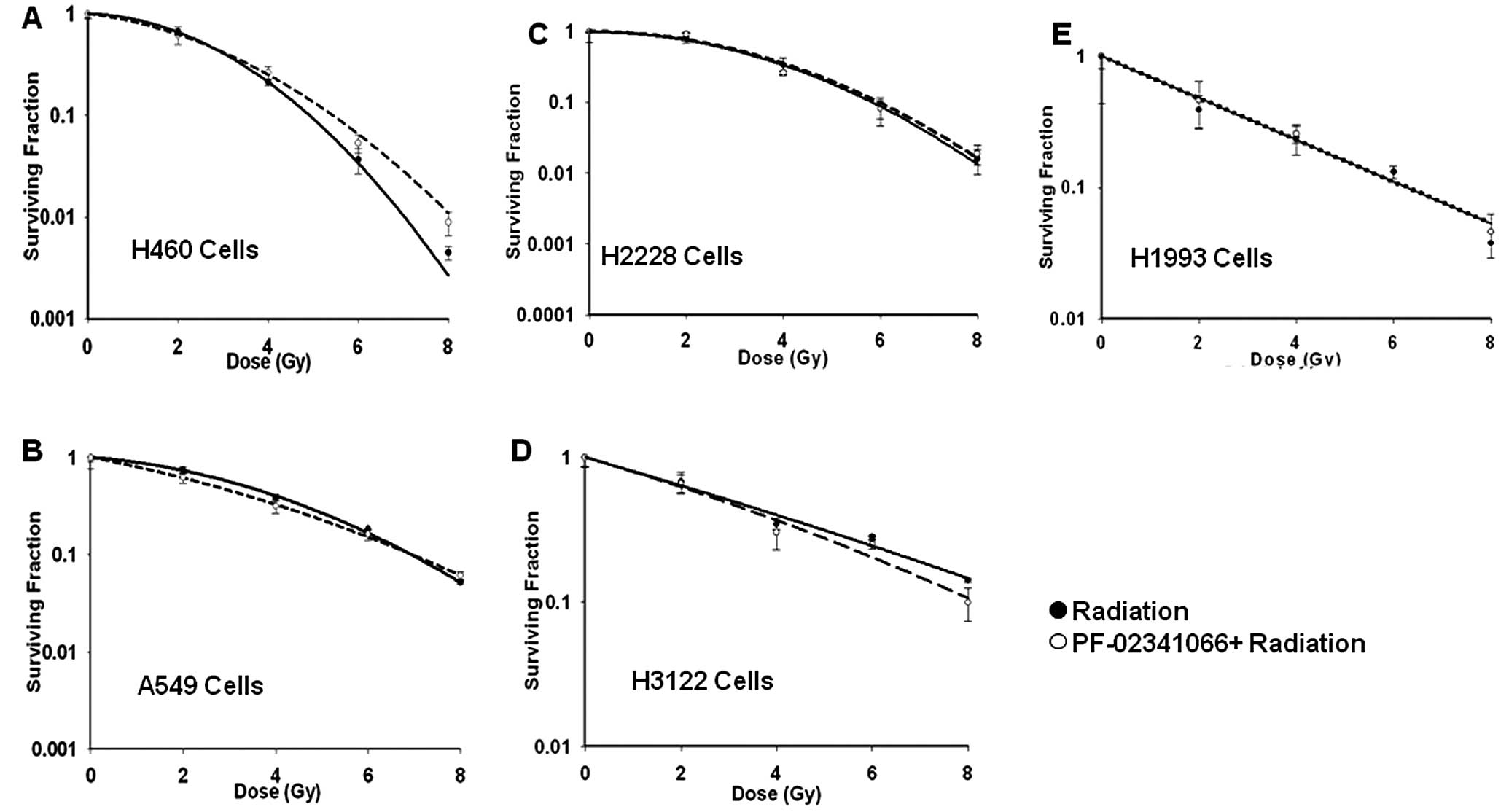
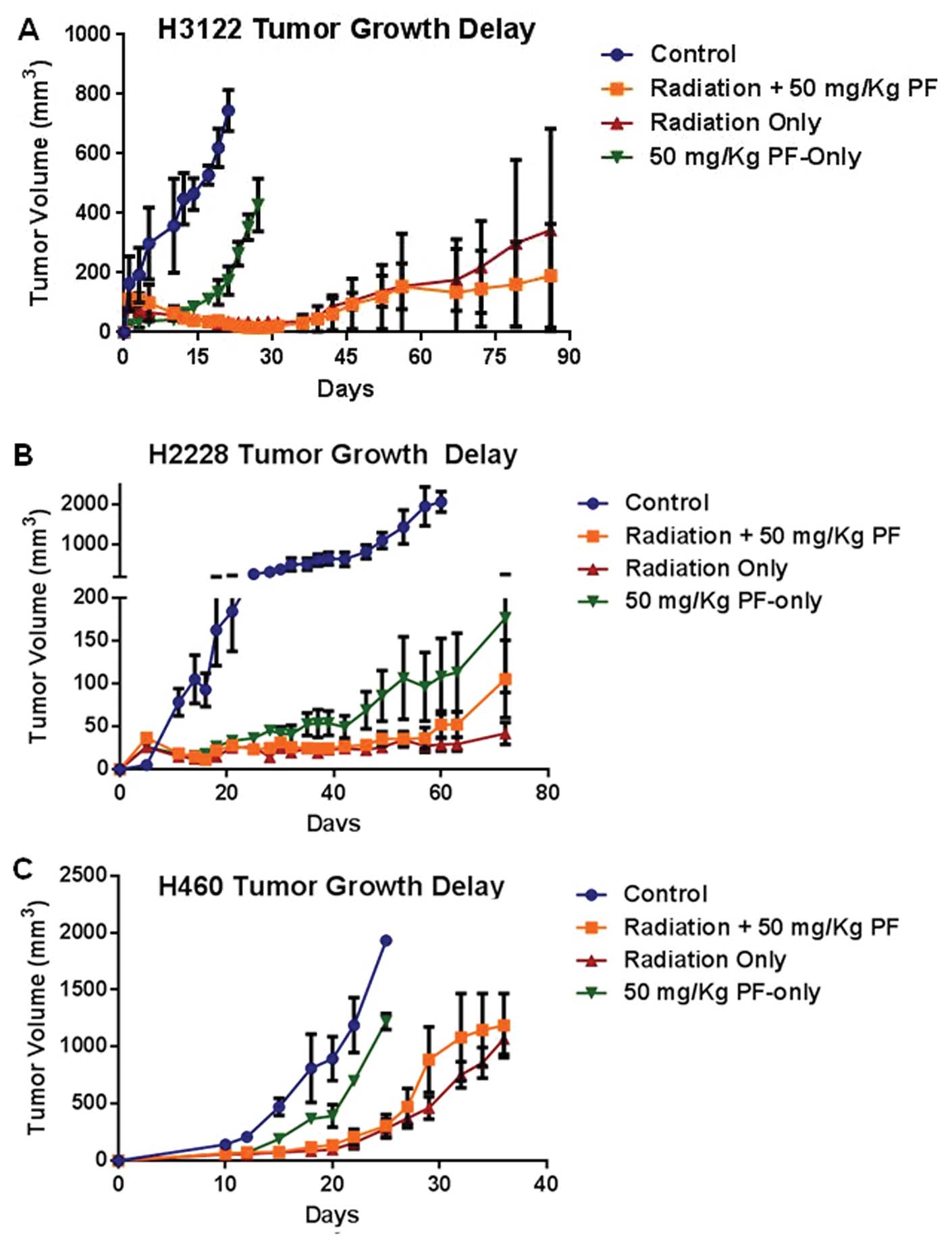
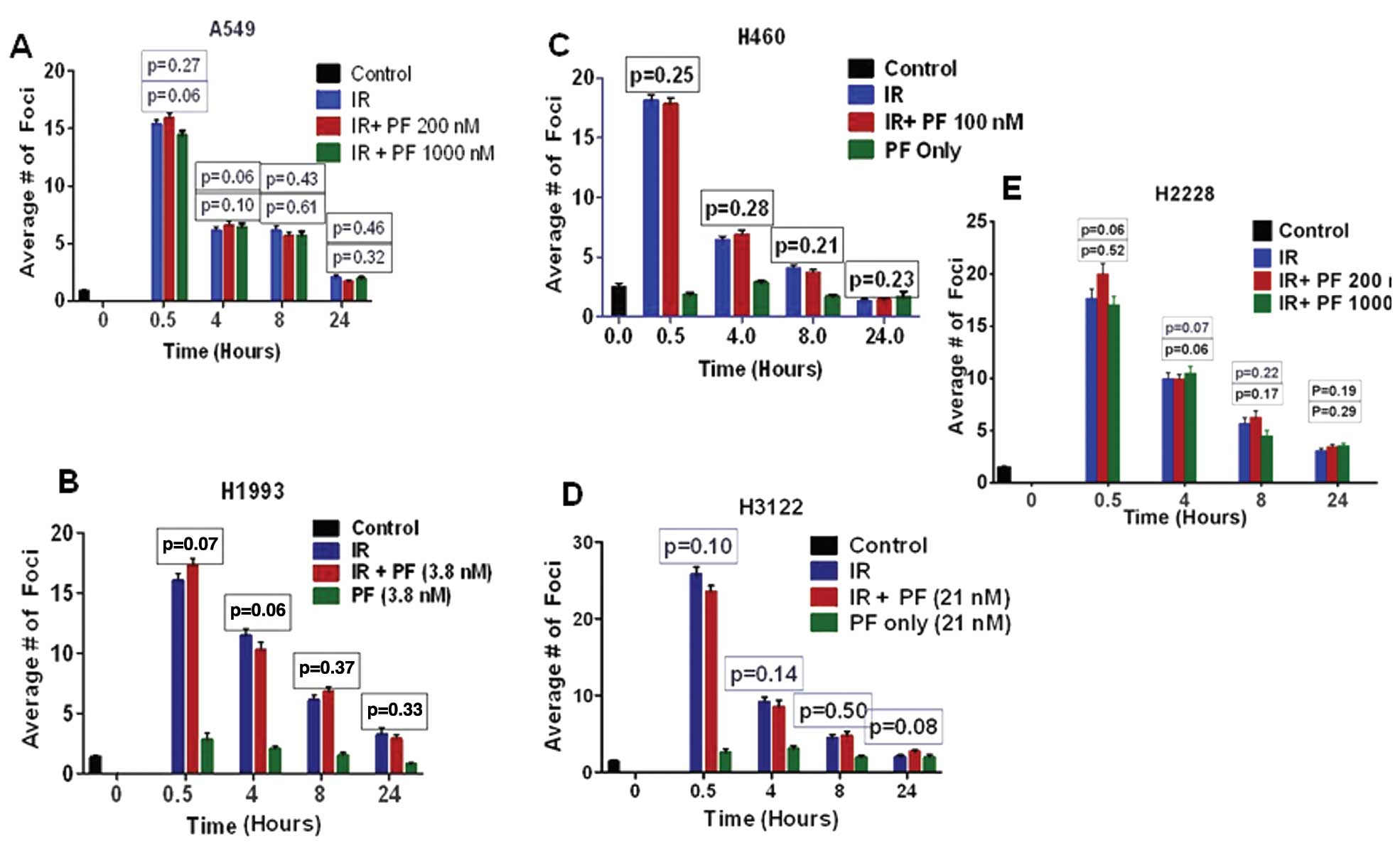
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al:
Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in
non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, et al:
Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged lung
adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5216–5223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi YL, Takeuchi K, Soda M, et al:
Identification of novel isoforms of the EML4-ALK transforming gene
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 68:4971–4976. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Soda M, Takada S, Takeuchi K, et al: A
mouse model for EML4-ALK-positive lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 105:19893–19897. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamazaki S, Vicini P, Shen Z, et al:
Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic modeling of crizotinib for
anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition and antitumor efficacy in
human tumor xenograft mouse models. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
340:549–557. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lin E, Li L, Guan Y, et al: Exon array
profiling detects EML4-ALK fusion in breast, colorectal, and
non-small cell lung cancers. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1466–1476. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kodym E, Kodym R, Reis AE, Habib AA, Story
MD and Saha D: The small-molecule CDK inhibitor, SNS-032, enhances
cellular radiosensitivity in quiescent and hypoxic non-small cell
lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 66:37–47. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kong Z, Raghavan P, Xie D, et al:
Epothilone B confers radiation dose enhancement in DAB2IP gene
knock-down radioresistant prostate cancer cells. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 78:1210–1218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim JC, Saha D, Cao Q and Choy H:
Enhancement of radiation effects by combined docetaxel and
flavopiridol treatment in lung cancer cells. Radiother Oncol.
71:213–221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ou SH: Crizotinib: a novel and
first-in-class multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the
treatment of anaplastic lymphoma kinase rearranged non-small cell
lung cancer and beyond. Drug Des Devel Ther. 5:471–485.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bai RY, Ouyang T, Miething C, Morris SW,
Peschel C and Duyster J: Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase
associated with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma activates the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt antiapoptotic signaling pathway.
Blood. 96:4319–4327. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Z, Sasaki T, Tan X, et al: Inhibition
of ALK, PI3K/MEK, and HSP90 in murine lung adenocarcinoma induced
by EML4-ALK fusion oncogene. Cancer Res. 70:9827–9836. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fan S, Ma YX, Gao M, et al: The
multisubstrate adapter Gab1 regulates hepatocyte growth factor
(scatter factor)-c-Met signaling for cell survival and DNA repair.
Mol Cell Biol. 21:4968–4984. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Christensen JG, Zou HY, Arango ME, et al:
Cytoreductive antitumor activity of PF-2341066, a novel inhibitor
of anaplastic lymphoma kinase and c-Met, in experimental models of
anaplastic large-cell lymphoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:3314–3322. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Bacco F, Luraghi P, Medico E, et al:
Induction of MET by ionizing radiation and its role in
radioresistance and invasive growth of cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
103:645–661. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aebersold DM, Kollar A, Beer KT, Laissue
J, Greiner RH and Djonov V: Involvement of the hepatocyte growth
factor/scatter factor receptor c-met and of Bcl-xL in the
resistance of oropharyngeal cancer to ionizing radiation. Int J
Cancer. 96:41–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y and Dennis PA:
Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell
lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to
chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res. 61:3986–3997.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McDermott U, Iafrate AJ, Gray NS, et al:
Genomic alterations of anaplastic lymphoma kinase may sensitize
tumors to anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res.
68:3389–3395. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|