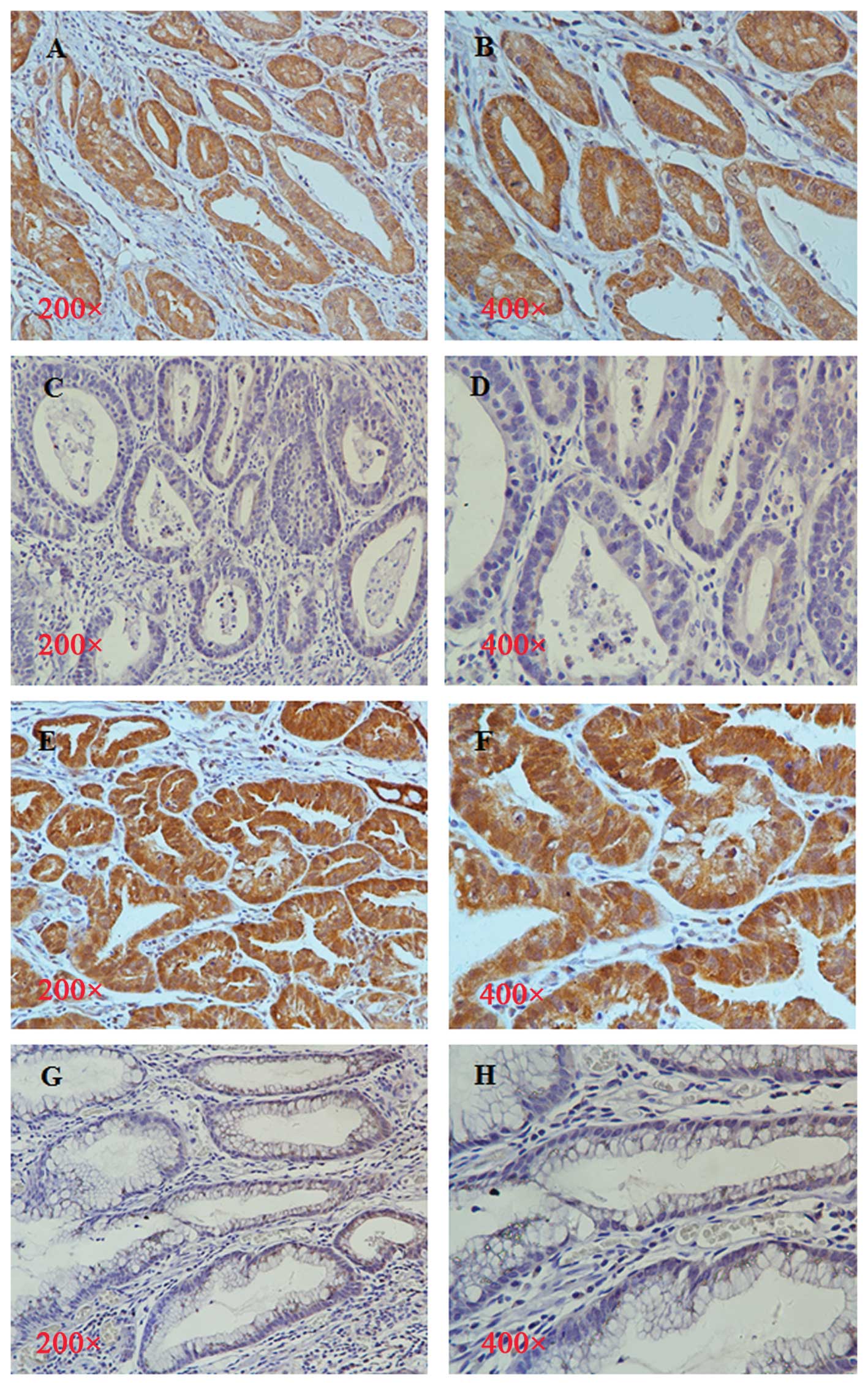
|
1
|
Avdulov S, Li S, Michalek V, et al:
Activation of translation complex eIF4F is essential for the
genesis and maintenance of the malignant phenotype in human mammary
epithelial cells. Cancer Cell. 5:553–563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chen CN, Hsieh FJ, Cheng YM, Lee PH and
Chang KJ: Expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in gastric
adenocarcinoma and its association with clinical outcome. J Surg
Oncol. 86:22–27. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
De Benedetti A and Graff JR: eIF-4E
expression and its role in malignancies and metastases. Oncogene.
23:3189–3199. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dong K, Wang R, Wang X, et al:
Tumor-specific RNAi targeting eIF4E suppresses tumor growth,
induces apoptosis and enhances cisplatin cytotoxicity in human
breast carcinoma cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 113:443–456.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choi CH, Lee JS, Kim SR, et al: Direct
inhibition of eIF4E reduced cell growth in endometrial
adenocarcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:463–469. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Herbert TP, Fahraeus R, Prescott A, Lane
DP and Proud CG: Rapid induction of apoptosis mediated by peptides
that bind initiation factor eIF4E. Curr Biol. 10:793–796. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ge Y, Cheng R, Zhou Y, et al:
Cryptotanshinone induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of
multidrug resistant human chronic myeloid leukemia cells by
inhibiting the activity of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Mol
Cell Biochem. 368:17–25. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou FF, Yan M, Guo GF, et al: Knockdown
of eIF4E suppresses cell growth and migration, enhances
chemosensitivity and correlates with increase in Bax/Bcl-2 ratio in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Med Oncol. 28:1302–1307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gills JJ and Dennis PA: Perifosine: update
on a novel Akt inhibitor. Curr Oncol Rep. 11:102–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elrod HA, Lin YD, Yue P, et al: The
alkylphospholipid perifosine induces apoptosis of human lung cancer
cells requiring inhibition of Akt and activation of the extrinsic
apoptotic pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 6:2029–2038. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Papa V, Tazzari PL, Chiarini F, et al:
Proapoptotic activity and chemosensitizing effect of the novel Akt
inhibitor perifosine in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leukemia.
22:147–160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tazzari PL, Tabellini G, Ricci F, et al:
Synergistic proapoptotic activity of recombinant TRAIL plus the Akt
inhibitor perifosine in acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer
Res. 68:9394–9403. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Leighl NB, Dent S, Clemons M, et al: A
Phase 2 study of perifosine in advanced or metastatic breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 108:87–92. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ghobrial IM, Roccaro A, Hong F, et al:
Clinical and translational studies of a phase II trial of the novel
oral Akt inhibitor perifosine in relapsed or relapsed/refractory
Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1033–1041.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Cho DC, Hutson TE, Samlowski W, et al: Two
phase 2 trials of the novel Akt inhibitor perifosine in patients
with advanced renal cell carcinoma after progression on vascular
endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Cancer. 118:6055–6062.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma Z, Zhu L, Luo X, Zhai S, Li P and Wang
X: Perifosine enhances mTORC1-targeted cancer therapy by activation
of GSK3β in NSCLC cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1009–1017.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang S, Rosenwald IB, Hutzler MJ, et al:
Expression of the eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E and
2alpha in non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Am J Pathol. 155:247–255. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Muta D, Makino K, Nakamura H, Yano S, Kudo
M and Kuratsu J: Inhibition of eIF4E phosphorylation reduces cell
growth and proliferation in primary central nervous system lymphoma
cells. J Neurooncol. 101:33–39. 2011.
|
|
19
|
Soni A, Akcakanat A, Singh G, et al: eIF4E
knockdown decreases breast cancer cell growth without activating
Akt signaling. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1782–1788. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Fan SQ, Ramalingam SS, Kauh J, Xu ZH,
Khuri FR and Sun SY: Phosphorylated eukaryotic translation
initiation factor 4 (eIF4E) is elevated in human cancer tissues.
Cancer Biol Ther. 8:1463–1469. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wheater MJ, Johnson PW and Blaydes JP: The
role of MNK proteins and eIF4E phosphorylation in breast cancer
cell proliferation and survival. Cancer Biol Ther. 10:728–735.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fischer PM: Cap in hand: targeting eIF4E.
Cell Cycle. 8:2535–2541. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jia Y, Polunovsky V, Bitterman PB and
Wagner CR: Cap-dependent translation initiation factor eIF4E: an
emerging anticancer drug target. Med Res Rev. 32:786–814. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hideshima T, Catley L, Yasui H, et al:
Perifosine, an oral bioactive novel alkylphospholipid, inhibits Akt
and induces in vitro and in vivo cytotoxicity in human multiple
myeloma cells. Blood. 107:4053–4062. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yoshizawa A, Fukuoka J, Shimizu S, et al:
Overexpression of phospho-eIF4E is associated with survival through
AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:240–248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|