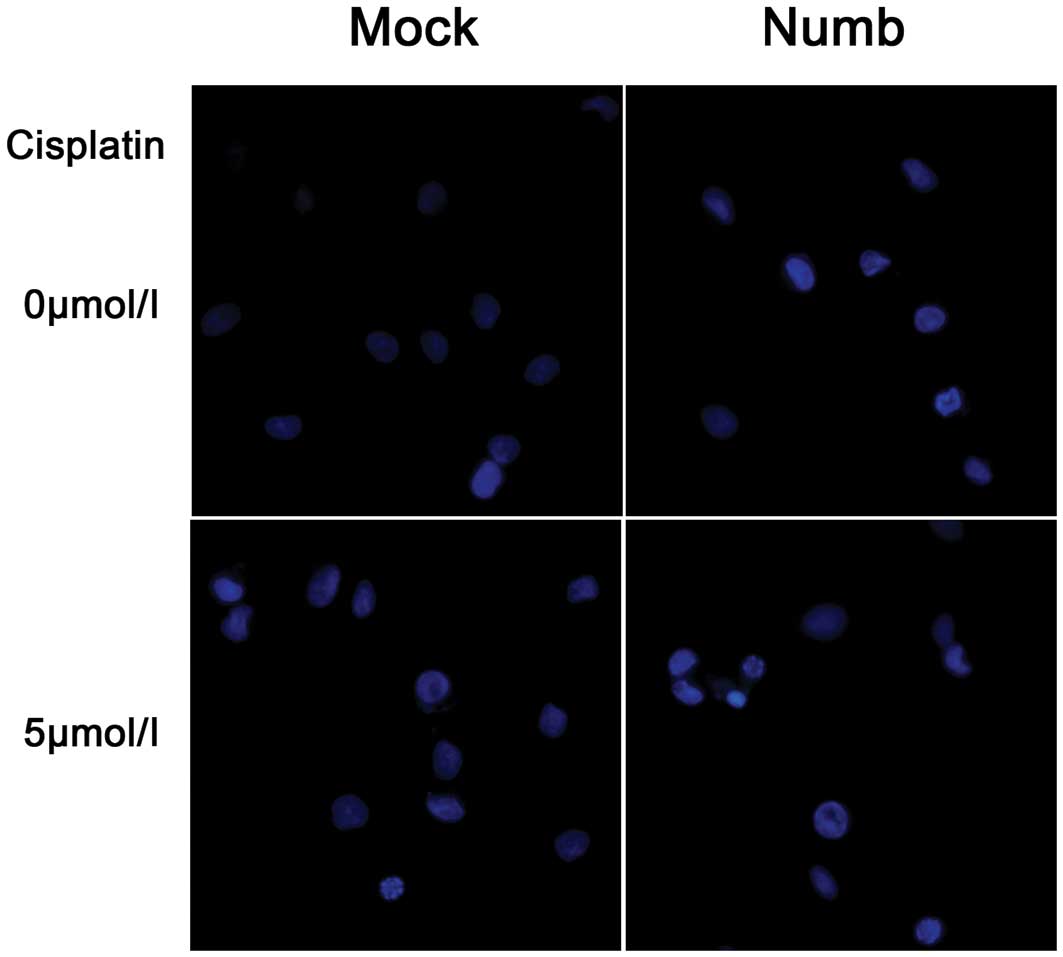
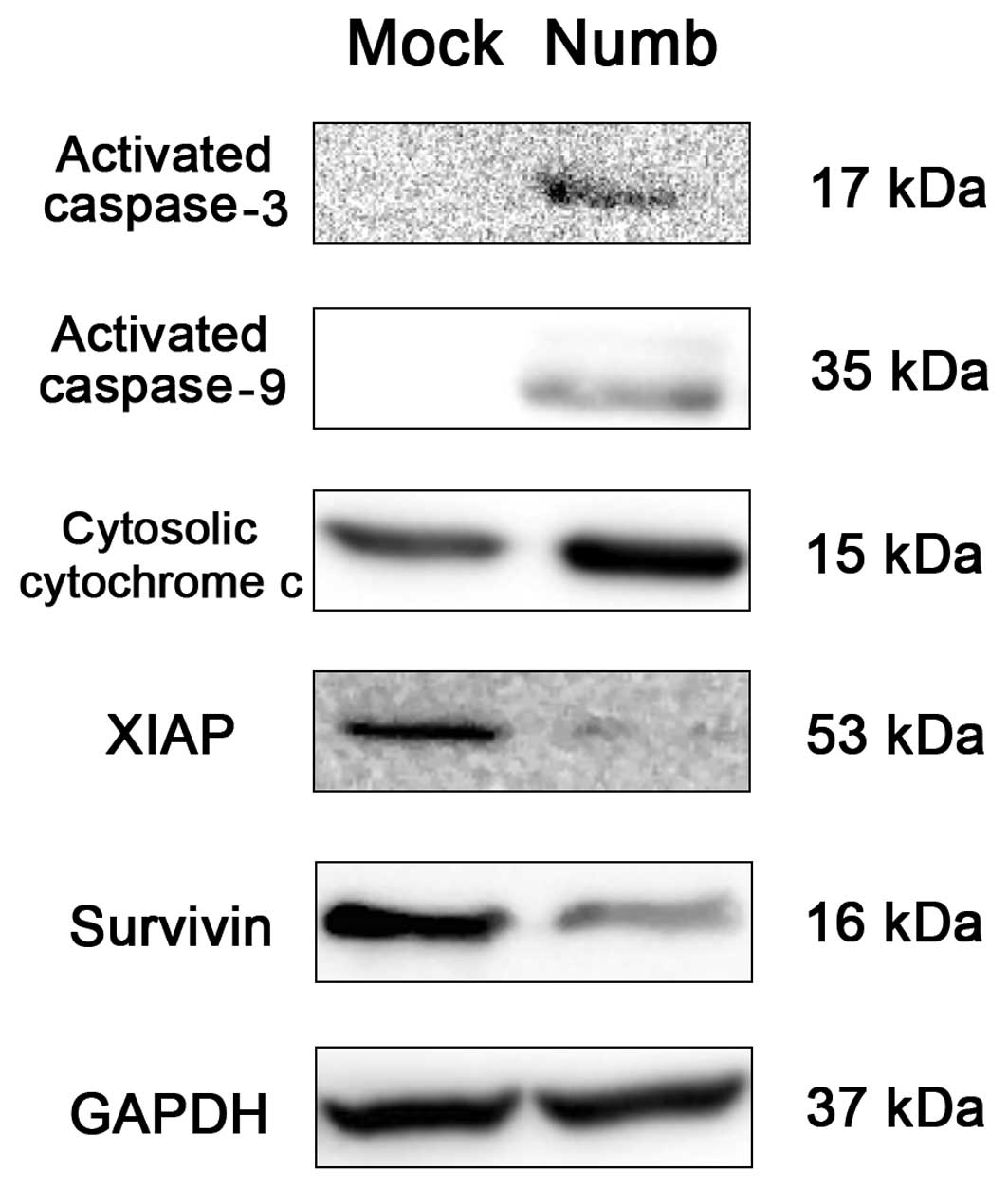
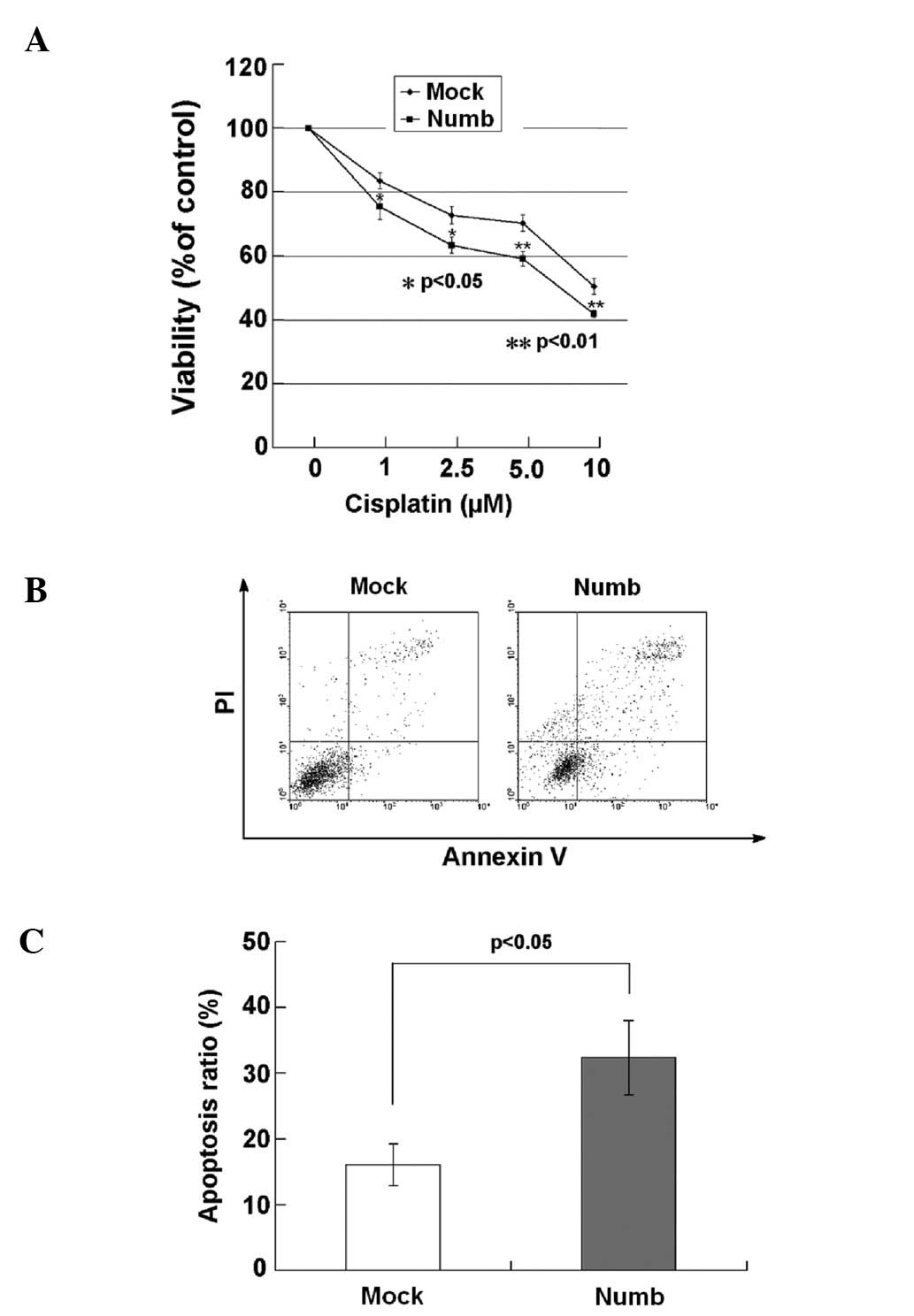
|
1
|
Peto J, Decarli A, La Vecchia C, Levi F
and Negri E: The European mesothelioma epidemic. Br J Cancer.
79:666–672. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bianchi C and Bianchi T: Malignant
mesothelioma: global incidence and relationship with asbestos. Ind
Health. 45:379–387. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robinson BWS, Musk AW and Lake RA:
Malignant mesothelioma. Lancet. 366:397–408. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Beachy PA, Karhadkar SS and Berman DM:
Tissue repair and stem cell renewal in carcinogenesis. Nature.
432:324–331. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Uemura T, Shepherd S, Ackerman L, Jan LY
and Jan YN: numb, a gene required in determination of cell
fate during sensory organ formation in Drosophila embryos.
Cell. 58:349–360. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rhyu MS, Jan LY and Jan YN: Asymmetric
distribution of numb protein during division of the sensory organ
precursor cell confers distinct fates to daughter cells. Cell.
76:477–491. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morrison SJ and Spradling AC: Stem cells
and niches: mechanisms that promote stem cell maintenance
throughout life. Cell. 132:598–611. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rašin MR, Gazula VR, Breunig JJ, et al:
Numb and Numbl are required for maintenance of cadherin-based
adhesion and polarity of neural progenitors. Nat Neurosci.
10:819–827. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nishimura T and Kaibuchi K: Numb controls
integrin endocytosis for directional cell migration with aPKC and
PAR-3. Dev Cell. 13:15–28. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McGill MA and McGlade CJ: Mammalian numb
proteins promote Notch1 receptor ubiquitination and degradation of
the Notch1 intracellular domain. J Biol Chem. 278:23196–23203.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Di Marcotullio L, Ferretti E, Greco A, et
al: Numb is a suppressor of Hedgehog signalling and targets Gli1
for Itch-dependent ubiquitination. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1415–1423.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Colaluca IN, Tosoni D, Nuciforo P, et al:
NUMB controls p53 tumour suppressor activity. Nature. 451:76–80.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pece S, Confalonieri S, Romano PR and Di
Fiore PP: NUMB-ing down cancer by more than just a NOTCH. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1815:26–43. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Singh A and Settleman J: EMT, cancer stem
cells and drug resistance: an emerging axis of evil in the war on
cancer. Oncogene. 29:4741–4751. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RYJ and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lanzetti L and Di Fiore PP: Endocytosis
and cancer: an ‘insider’ network with dangerous liaisons. Traffic.
9:2011–2021. 2008.
|
|
17
|
Vaccari T and Bilder D: At the crossroads
of polarity, proliferation and apoptosis: the use of
Drosophila to unravel the multifaceted role of endocytosis
in tumor suppression. Mol Oncol. 3:354–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goldstein B and Macara IG: The PAR
proteins: fundamental players in animal cell polarization. Dev
Cell. 13:609–622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Aranda V, Nolan ME and Muthuswamy SK: Par
complex in cancer: a regulator of normal cell polarity joins the
dark side. Oncogene. 27:6878–6887. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pece S, Serresi M, Santolini E, et al:
Loss of negative regulation by Numb over Notch is relevant to human
breast carcinogenesis. J Cell Biol. 167:215–221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D’Ario G, et al:
Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:22293–22298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caussinus E and Gonzalez C: Induction of
tumor growth by altered stem-cell asymmetric division in
Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Genet. 37:1125–1129. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bric A, Miething C, Bialucha CU, et al:
Functional identification of tumor-suppressor genes through an in
vivo RNA interference screen in a mouse lymphoma model. Cancer
Cell. 16:324–335. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
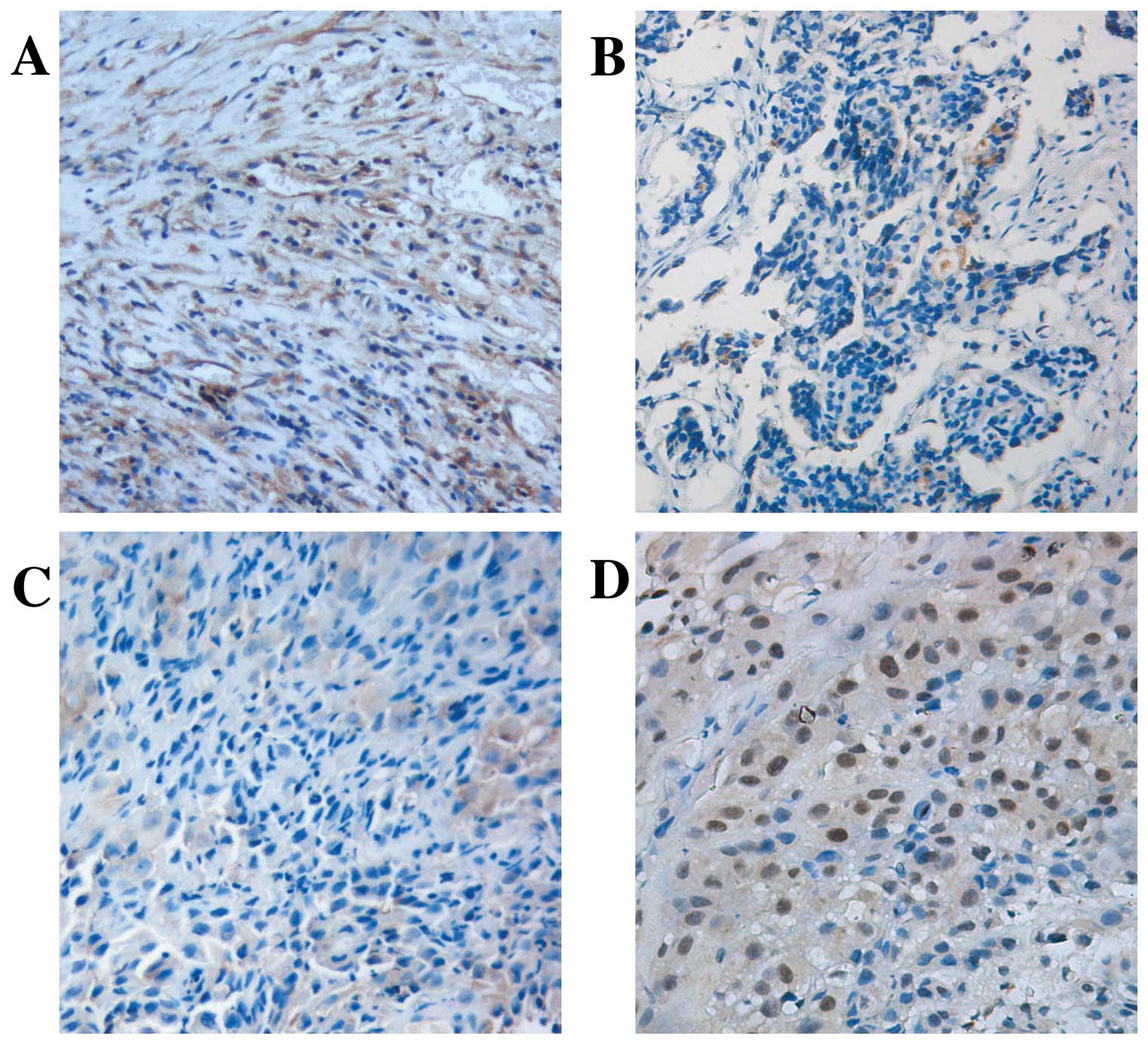
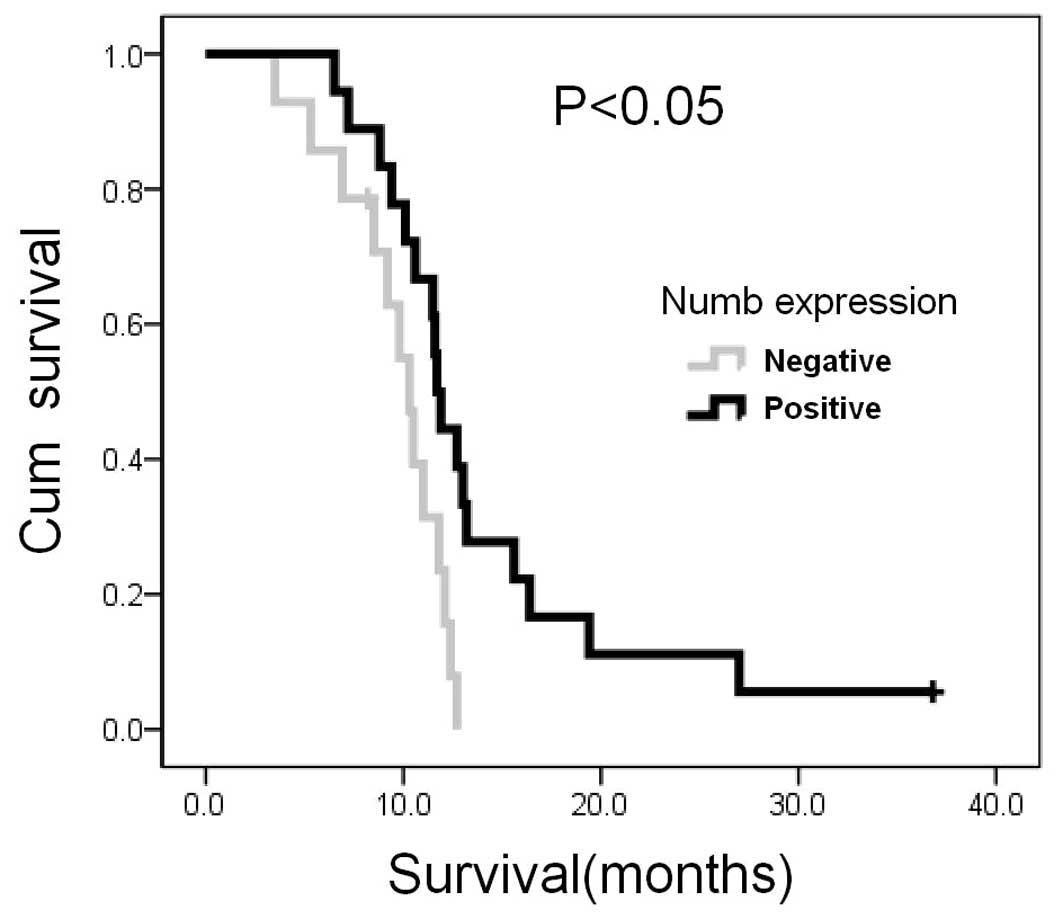
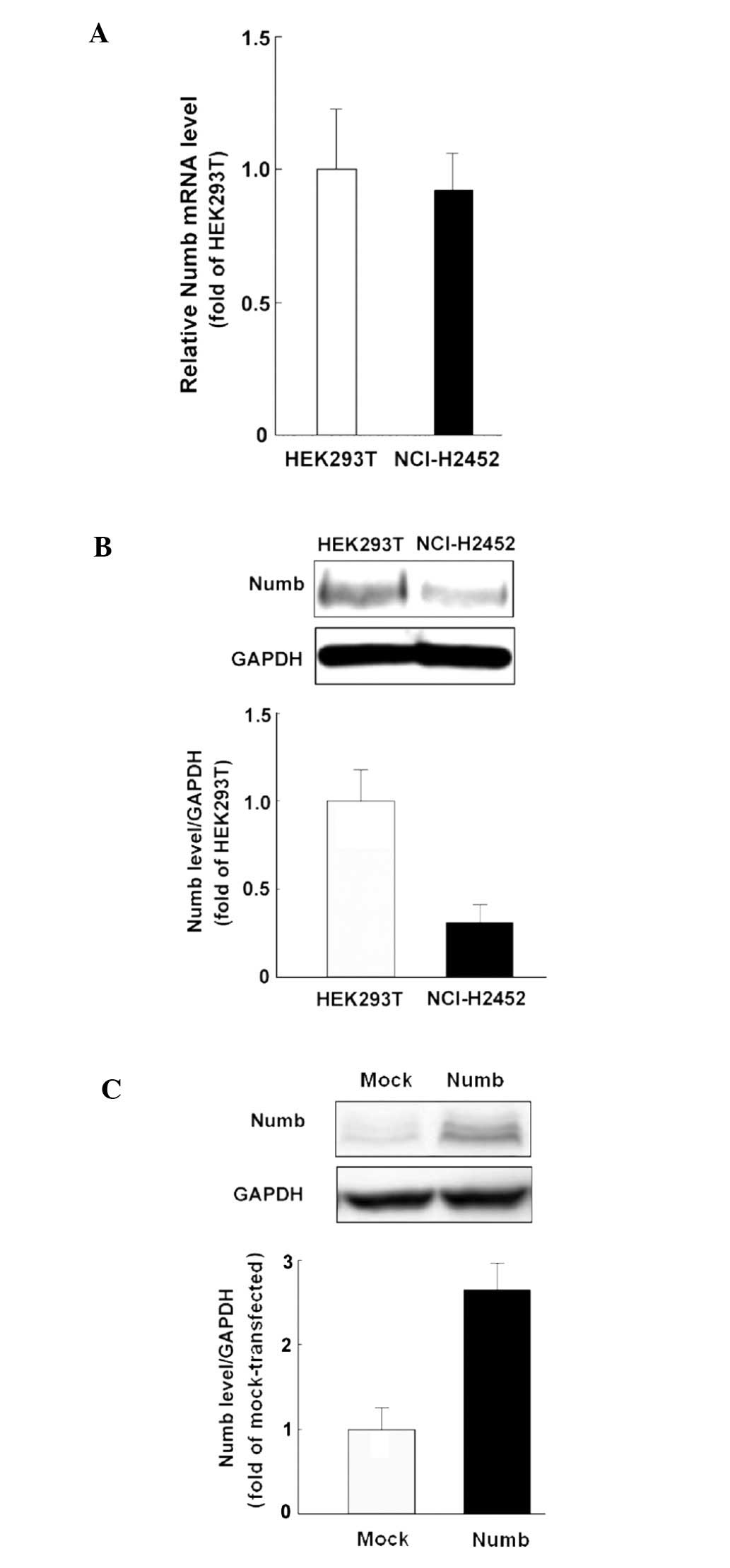
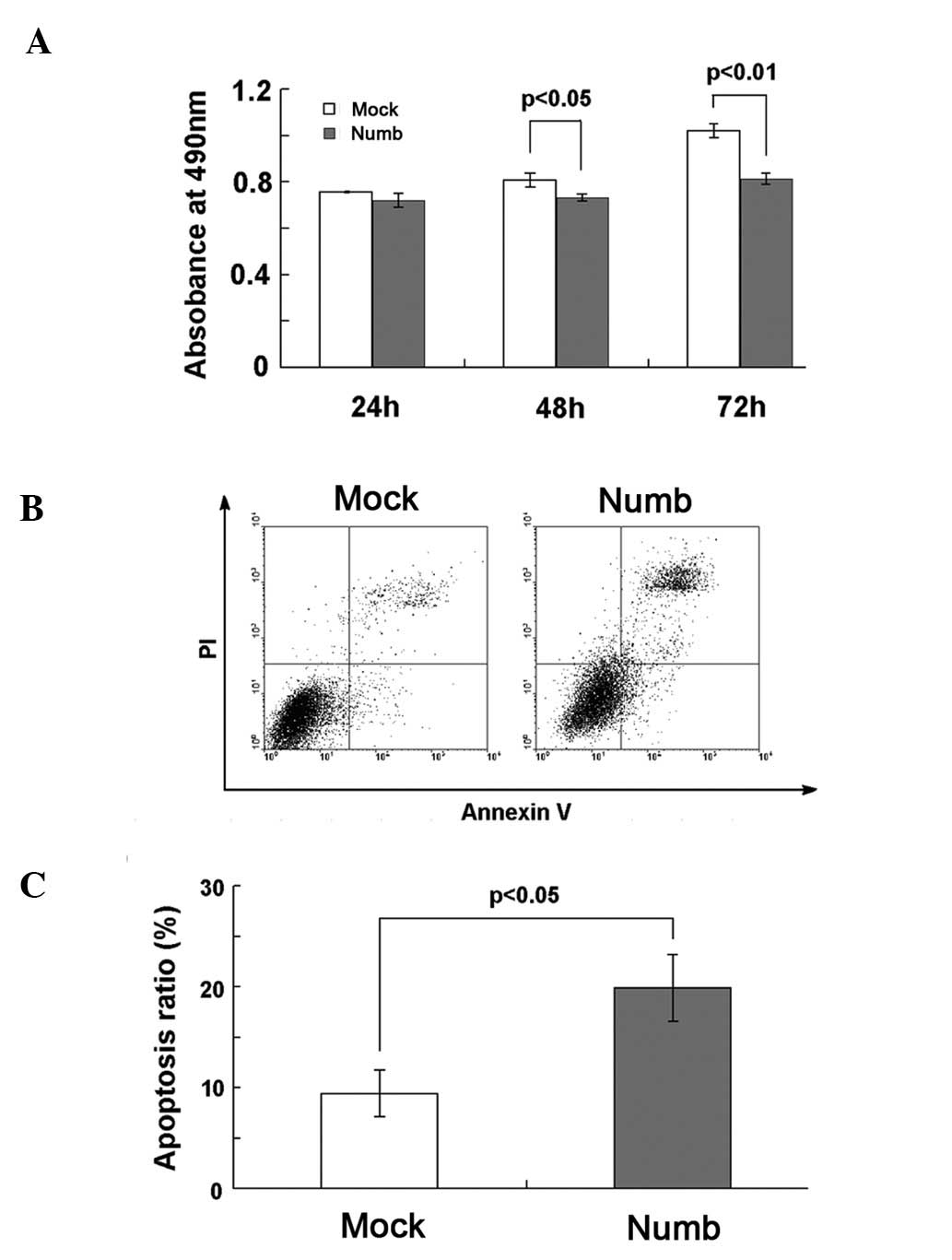
Maiorano E, Favia G, Pece S, et al:
Prognostic implications of NUMB immunoreactivity in salivary gland
carcinomas. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 20:779–789.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Marino S: Medulloblastoma: developmental
mechanisms out of control. Trends Mol Med. 11:17–22. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yan B, Omar FM, Das K, et al:
Characterization of Numb expression in astrocytomas.
Neuropathology. 28:479–484. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Travis W, Brambilla E, Muller-Hermelink H
and Harris C; World Health Organization Classification of Tumours.
Pathology & Genetics. Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and
Heart. IARC Press; Lyon: 2004
|
|
28
|
Heidebrecht H, Buck F, Endl E, Kruse M,
Adam K and Andresen K: Ki-67-Mcm6, a new MoAb specific to Mcm6:
comparison of the distribution profile of Mcm6 and Ki-67 antigen.
Lab Invest. 81:1163–1165. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Adams JM and Cory S: The Bcl-2 protein
family: arbiters of cell survival. Science. 281:1322–1326. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kleinberg L, Lie AK, Flørenes VA, Nesland
JM and Davidson B: Expression of inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein
family members in malignant mesothelioma. Hum Pathol. 38:986–994.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu M, Yuan S, Szporn AH, Gan L, Shtilbans
V and Burstein DE: Immunocytochemical detection of XIAP in body
cavity effusions and washes. Mod Pathol. 18:1618–1622.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gordon G, Mani M, Mukhopadhyay L, et al:
Expression patterns of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins in malignant
pleural mesothelioma. J Pathol. 211:447–454. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gordon G, Mani M, Mukhopadhyay L, et al:
Inhibitor of apoptosis proteins are regulated by tumour necrosis
factor-α in malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Pathol. 211:439–446.
2007.
|
|
34
|
Hmeljak J, Erčulj N, Dolžan V, Kern I and
Cör A: BIRC5 promoter SNPs do not affect nuclear survivin
expression and survival of malignant pleural mesothelioma patients.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:1641–1651. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, et al:
IAP-family protein survivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis
induced by Fas (CD95), Bax, caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer
Res. 58:5315–5320. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi K, Hatano M, Otaki M, Ogasawara
T and Tokuhisa T: Expression of a murine homologue of the inhibitor
of apoptosis protein is related to cell proliferation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:1457–1462. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kim KW, Mutter RW, Willey CD, et al:
Inhibition of survivin and aurora B kinase sensitizes mesothelioma
cells by enhancing mitotic arrests. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
67:1519–1525. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia C, Xu Z, Yuan X, et al: Induction of
apoptosis in mesothelioma cells by antisurvivin oligonucleotides.
Mol Cancer Ther. 1:687–694. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Rabik CA and Dolan ME: Molecular
mechanisms of resistance and toxicity associated with platinating
agents. Cancer Treat Rev. 33:9–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Boulikas T and Vougiouka M: Cisplatin and
platinum drugs at the molecular level (Review). Oncol Rep.
10:663–682. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ikuta K, Takemura K, Kihara M, et al:
Defects in apoptotic signal transduction in cisplatin-resistant
non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 13:1229–1234.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Okouoyo S, Herzer K, Ucur E, et al: Rescue
of death receptor and mitochondrial apoptosis signaling in
resistant human NSCLC in vivo. Int J Cancer. 108:580–587. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yang X, Zheng F, Xing H, et al: Resistance
to chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via decreased caspase-3 activity
and overexpression of antiapoptotic proteins in ovarian cancer. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 130:423–428. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mueller T, Voigt W, Simon H, et al:
Failure of activation of caspase-9 induces a higher threshold for
apoptosis and cisplatin resistance in testicular cancer. Cancer
Res. 63:513–521. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|