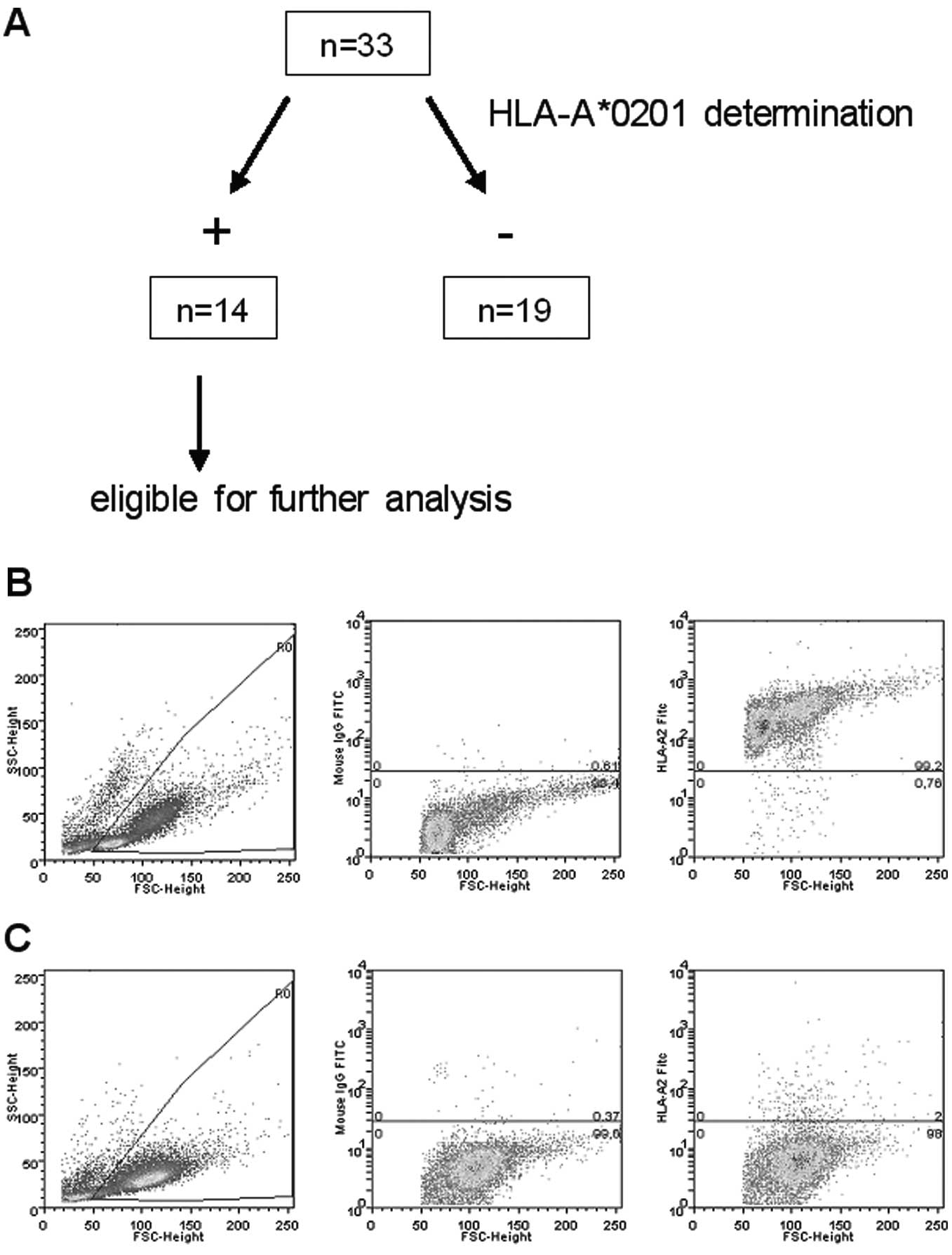
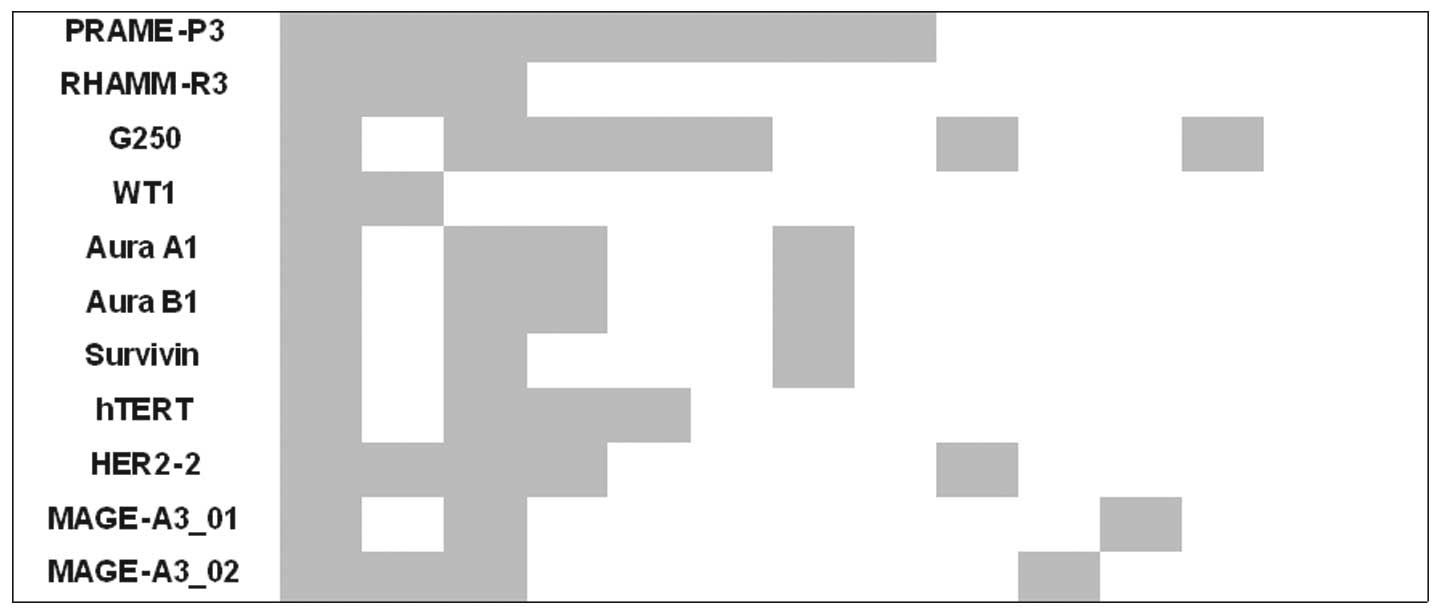
|
1
|
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, et al:
Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:2542–2550. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, et al:
Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3
study. Lancet Oncol. 11:521–529. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kwak EL, Bang YJ, Camidge DR, et al:
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase inhibition in non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1693–1703. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Raez LE, Fein S and Podack ER: Lung cancer
immunotherapy. Clin Med Res. 3:221–228. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lynch TJ, Bondarenko I, Luft A, et al:
Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as
first-line treatment in stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer:
results from a randomized, double-blind, multicenter phase II
study. J Clin Oncol. 30:2046–2054. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Topalian SL, Hodi FS, Brahmer JR, et al:
Safety, activity, and immune correlates of anti-PD-1 antibody in
cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:2443–2454. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Marigo I, Dolcetti L, Serafini P,
Zanovello P and Bronte V: Tumor-induced tolerance and immune
suppression by myeloid derived suppressor cells. Immunol Rev.
222:162–179. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pardoll D: Does the immune system see
tumors as foreign or self? Annu Rev Immunol. 21:807–839. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Novellino L, Castelli C and Parmiani G: A
listing of human tumor antigens recognized by T cells: March 2004
update. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 54:187–207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Greiner J, Bullinger L, Guinn BA, Döhner H
and Schmitt M: Leukemia-associated antigens are critical for the
proliferation of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Clin Cancer Res.
14:7161–7166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Greiner J, Schmitt M, Li L, et al:
Expression of tumor-associated antigens in acute myeloid leukemia:
implications for specific immunotherapeutic approaches. Blood.
108:4109–4117. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ribas A, Butterfield LH, Glaspy JA and
Economou JS: Current developments in cancer vaccines and cellular
immunotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 21:2415–2432. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosenberg SA: Development of effective
immunotherapy for the treatment of patients with cancer. J Am Coll
Surg. 198:685–696. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Banchereau J and Steinman RM: Dendritic
cells and the control of immunity. Nature. 392:245–252. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kelly RJ, Gulley JL and Giaccone G:
Targeting the immune system in non-small-cell lung cancer: bridging
the gap between promising concept and therapeutic reality. Clin
Lung Cancer. 11:228–237. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gridelli C, Rossi A, Maione P, Ferrara ML,
Castaldo V and Sacco PC: Vaccines for the treatment of non-small
cell lung cancer: a renewed anticancer strategy. Oncologist.
14:909–920. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bolonaki I, Kotsakis A, Papadimitraki E,
et al: Vaccination of patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer with an optimized cryptic human telomerase reverse
transcriptase peptide. J Clin Oncol. 25:2727–2734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Peled N, Oton AB, Hirsch FR and Bunn P:
MAGE A3 antigen-specific cancer immunotherapeutic. Immunotherapy.
1:19–25. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tyagi P and Mirakhur B: MAGRIT: the
largest-ever phase III lung cancer trial aims to establish a novel
tumor-specific approach to therapy. Clin Lung Cancer. 10:371–374.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eaton KD and Martins RG: Maintenance
chemotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
8:815–821. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Walter S, Weinschenk T, Stenzl A, et al:
Multipeptide immune response to cancer vaccine IMA901 after
single-dose cyclophosphamide associates with longer patient
survival. Nat Med. 18:1254–1261. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmitt M, Schmitt A, Rojewski MT, et al:
RHAMM-R3 peptide vaccination in patients with acute myeloid
leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome, and multiple myeloma elicits
immunologic and clinical responses. Blood. 111:1357–1365. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Greiner J, Li L, Ringhoffer M, et al:
Identification and characterization of epitopes of the receptor for
hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM/CD168) recognized by
CD8+ T cells of HLA-A2-positive patients with acute
myeloid leukemia. Blood. 106:938–945. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Greiner J, Dohner H and Schmitt M: Cancer
vaccines for patients with acute myeloid leukemia - definition of
leukemia-associated antigens and current clinical protocols
targeting these antigens. Haematologica. 91:1653–1661. 2006.
|
|
25
|
Bellantuono I, Gao L, Parry S, et al: Two
distinct HLA-A0201-presented epitopes of the Wilms tumor antigen 1
can function as targets for leukemia-reactive CTL. Blood.
100:3835–3837. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parkhurst MR, Riley JP, Igarashi T, Li Y,
Robbins PF and Rosenberg SA: Immunization of patients with the
hTERT:540–548 peptide induces peptide-reactive T lymphocytes that
do not recognize tumors endogenously expressing telomerase. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:4688–4698. 2004.
|
|
27
|
Greiner J, Schmitt A, Giannopoulos K, et
al: High-dose RHAMM-R3 peptide vaccination for patients with acute
myeloid leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome and multiple myeloma.
Haematologica. 95:1191–1197. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Swinson DE, Jones JL, Richardson D, et al:
Carbonic anhydrase IX expression, a novel surrogate marker of tumor
hypoxia, is associated with a poor prognosis in non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 21:473–482. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vermylen P, Roufosse C, Burny A, et al:
Carbonic anhydrase IX antigen differentiates between preneoplastic
malignant lesions in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Eur Respir J.
14:806–811. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
ClinicalTrials.gov. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/.
H-Cg. NCT00003102.
|
|
31
|
Siebels M, Rohrmann K, Oberneder R, et al:
A clinical phase I/II trial with the monoclonal antibody cG250
(RENCAREX®) and interferon-alpha-2a in metastatic renal
cell carcinoma patients. World J Urol. 29:121–126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Epping MT, Wang L, Edel MJ, Carlée L,
Hernandez M and Bernards R: The human tumor antigen PRAME is a
dominant repressor of retinoic acid receptor signaling. Cell.
122:835–847. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Oberthuer A, Hero B, Spitz R, Berthold F
and Fischer M: The tumor-associated antigen PRAME is universally
expressed in high-stage neuroblastoma and associated with poor
outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 10:4307–4313. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kessler JH, Beekman NJ, Bres-Vloemans SA,
et al: Efficient identification of novel
HLA-A*0201-presented cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes in
the widely expressed tumor antigen PRAME by proteasome-mediated
digestion analysis. J Exp Med. 193:73–88. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schmitt A, Barth TF, Beyer E, et al: The
tumor antigens RHAMM and G250/CAIX are expressed in head and neck
squamous cell carcinomas and elicit specific CD8+ T cell
responses. Int J Oncol. 34:629–639. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Albanell J, Lonardo F, Rusch V, et al:
High telomerase activity in primary lung cancers: association with
increased cell proliferation rates and advanced pathologic stage. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 89:1609–1615. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang L, Soria JC, Kemp BL, Liu DD, Mao L
and Khuri FR: hTERT expression is a prognostic factor of survival
in patients with stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:2883–2889. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fujita Y, Fujikane T, Fujiuchi S, et al:
The diagnostic and prognostic relevance of human telomerase reverse
transcriptase mRNA expression detected in situ in patients with
nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer. 98:1008–1013. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gure AO, Chua R, Williamson B, et al:
Cancer-testis genes are coordinately expressed and are markers of
poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:8055–8062. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Eifuku R, Takenoyama M, Yoshino I, et al:
Analysis of MAGE-3 derived synthetic peptide as a human lung cancer
antigen recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Int J Clin Oncol.
6:34–39. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Vansteenkiste J, Zielinski M, Linder A,
Dahabre J, Esteban E, Malinowski W, Jassem J, Passlick B, Lehmann F
and Brichard VG: Final results of a multi-center, double-blind,
randomized, placebo-controlled phase II study to assess the
efficacy of MAGE-A3 immunotherapeutic as adjuvant therapy in stage
IB/II non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J Clin Oncol.
25:75542007.
|
|
42
|
Lo Iacono M, Monica V, Saviozzi S, et al:
Aurora Kinase A expression is associated with lung cancer
histological-subtypes and with tumor de-differentiation. J Transl
Med. 9:1002011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S and Venkitaraman
AR: AURORA-A amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly
checkpoint, inducing resistance to Taxol. Cancer Cell. 3:51–62.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Smith SL, Bowers NL, Betticher DC, et al:
Overexpression of aurora B kinase (AURKB) in primary non-small cell
lung carcinoma is frequent, generally driven from one allele, and
correlates with the level of genetic instability. Br J Cancer.
93:719–729. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Linder A, Budihardjo-Welim H, Velehorschi
W, Coche T, Gruselle O, D'Agostino D, Louahed J, Lehmann F and
Brichard VG; Lungenklinik Hemer, Hemer Nordrhein-Westfalen,
Germany; Praxis für Pathologie Hemer, Hemer, Germany;
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals, Rixensart, Belgium. Prognostic value
of MAGE-A3 and PRAME gene expression in non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC). J Clin Oncol. 30:70562012.
|
|
46
|
Gautschi O, Heighway J, Mack PC, Purnell
PR, Lara PN Jr and Gandara DR: Aurora kinases as anticancer drug
targets. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1639–1648. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fu J, Bian M, Jiang Q and Zhang C: Roles
of Aurora kinases in mitosis and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res.
5:1–10. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|