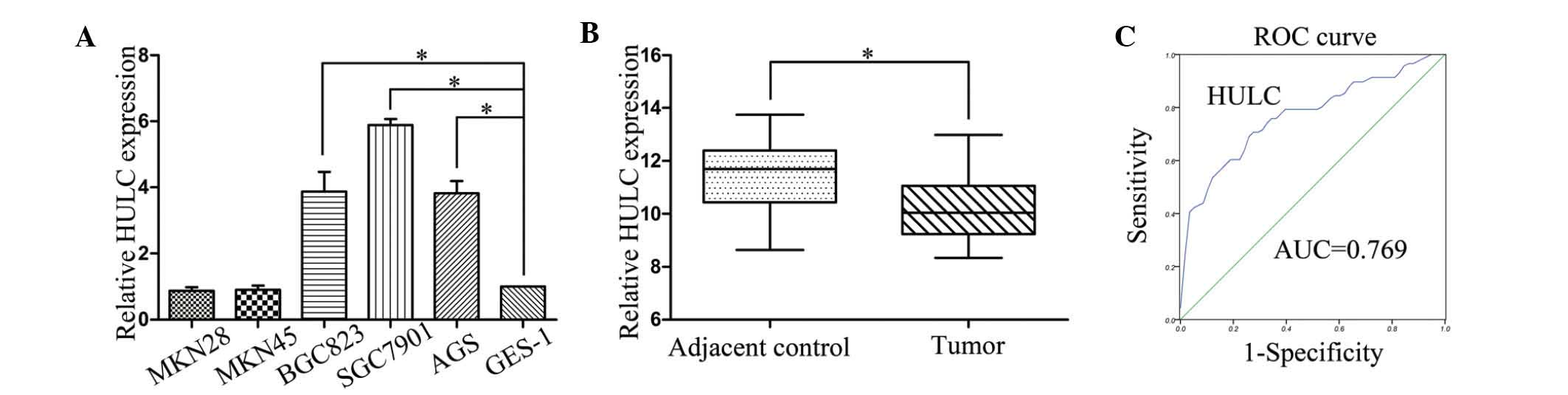
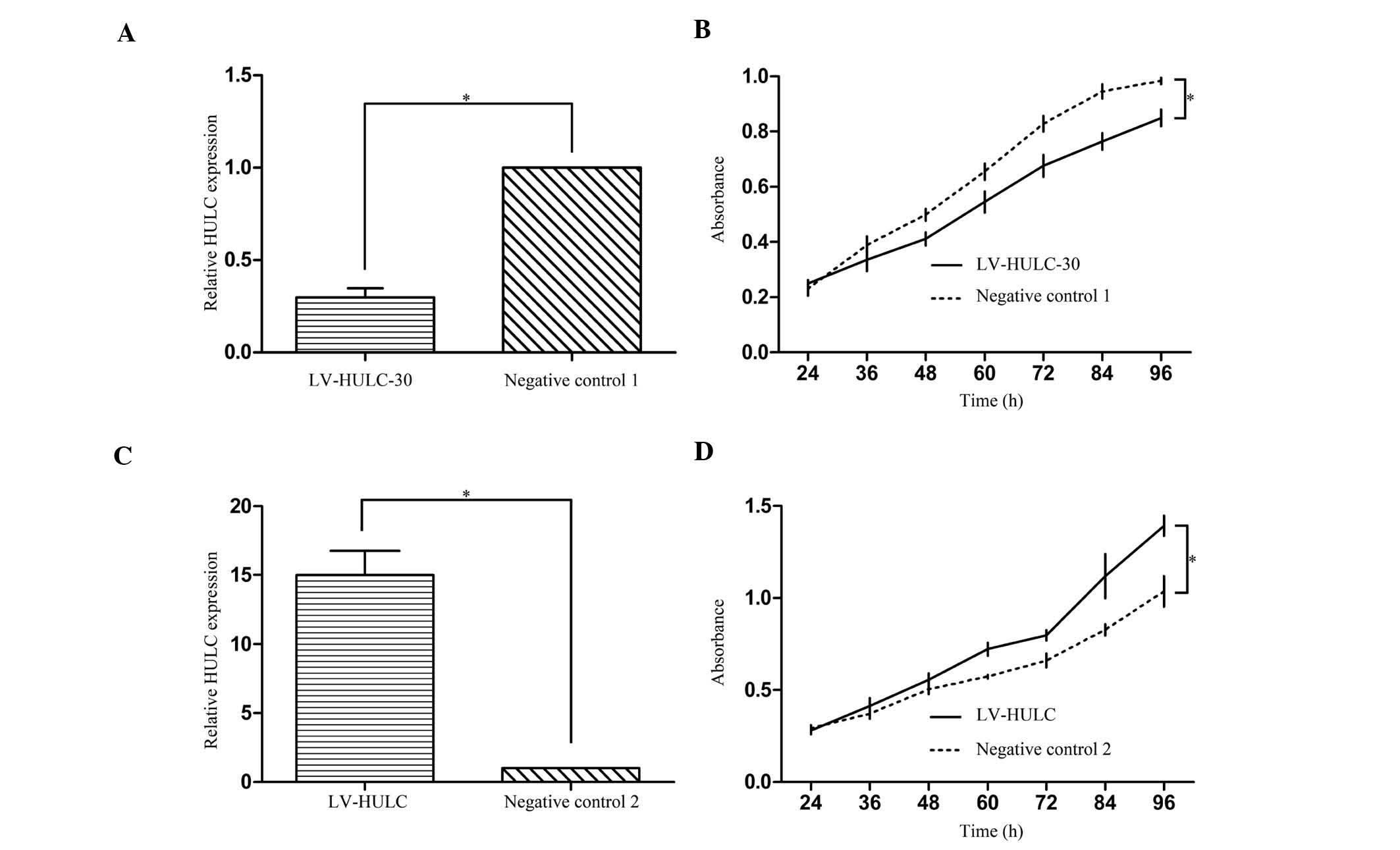
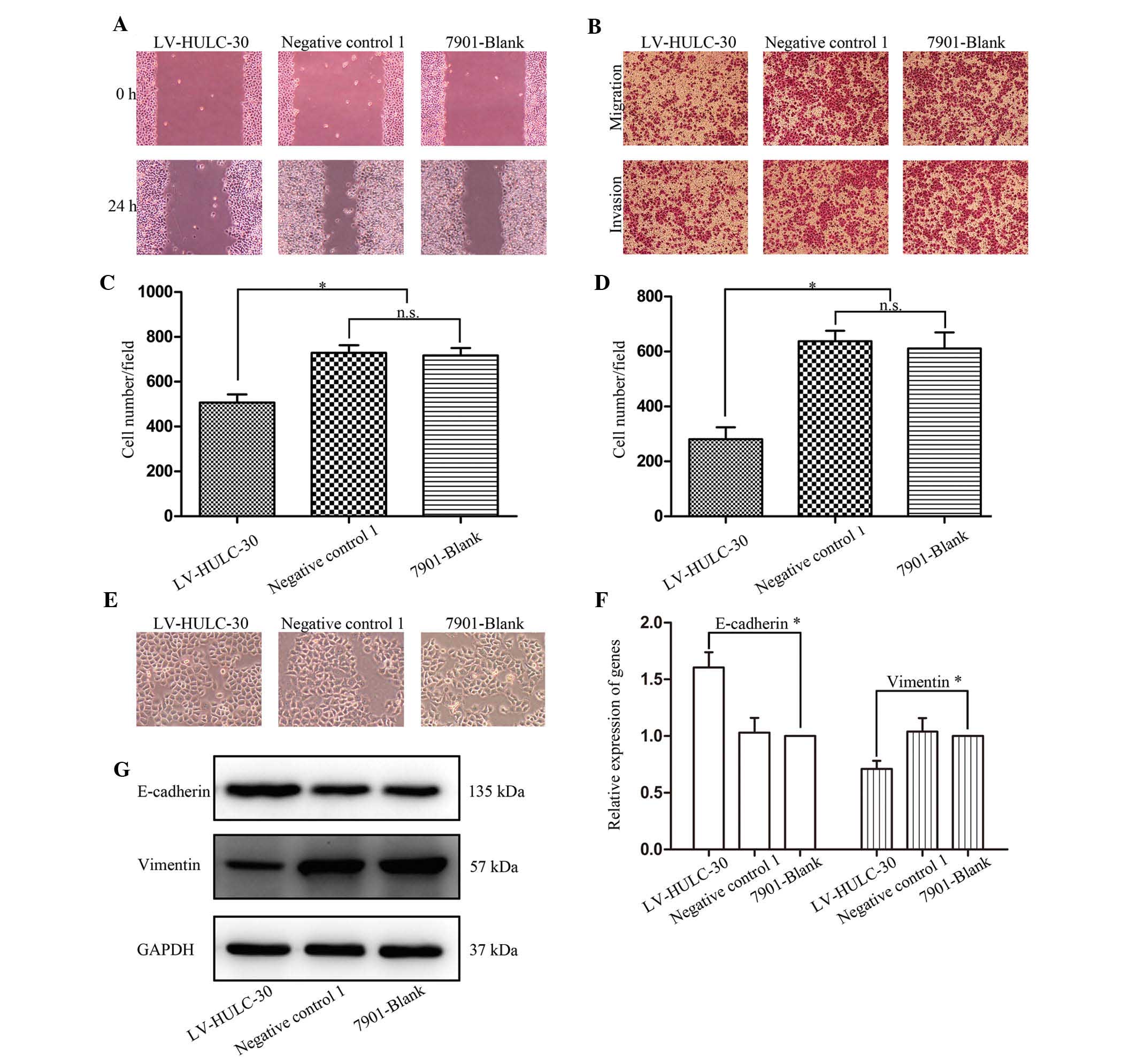
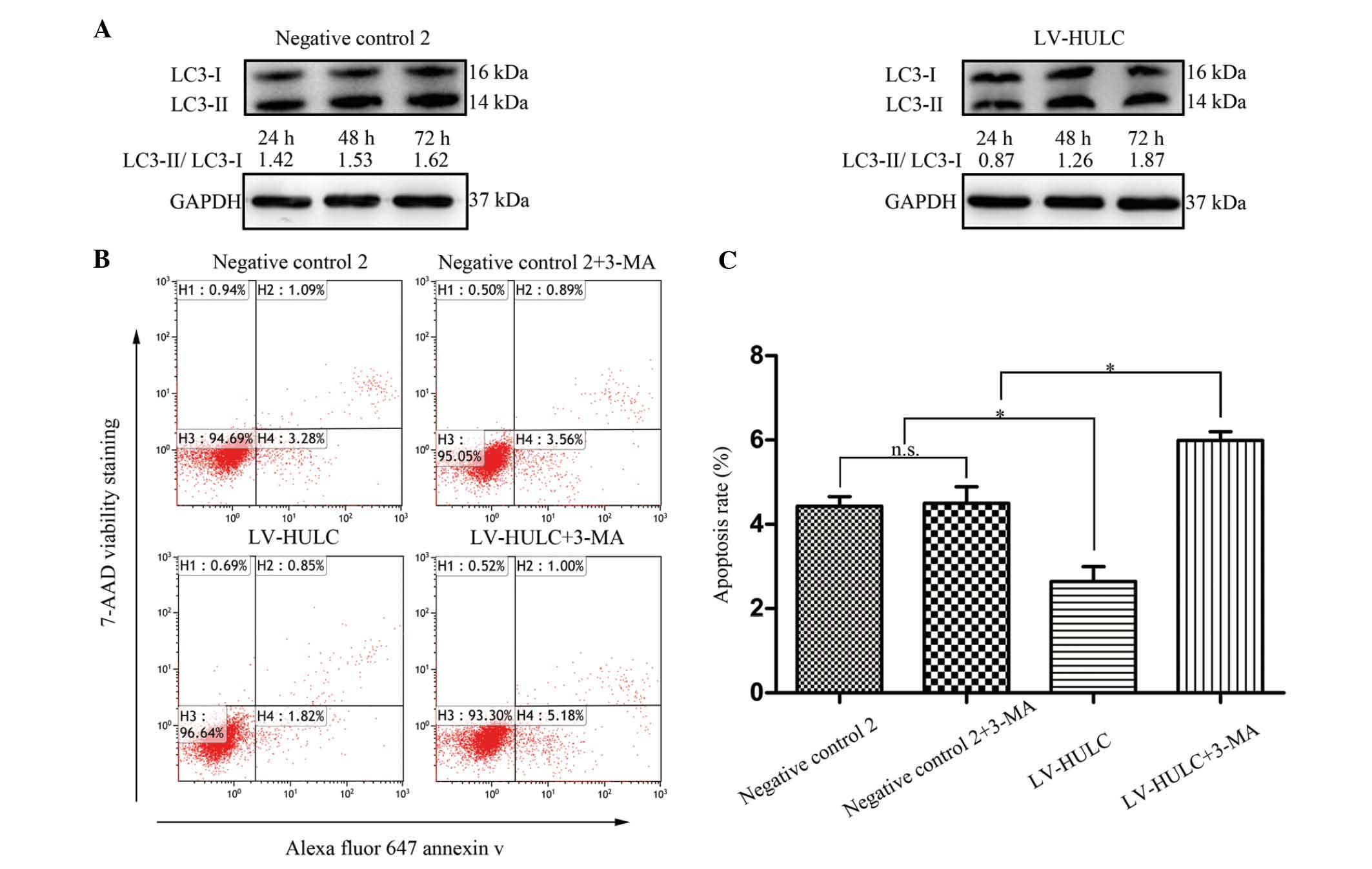
|
1
|
Konishi H, Ichikawa D, Komatsu S, et al:
Detection of gastric cancer-associated microRNAs on microRNA
microarray comparing pre- and post-operative plasma. Br J Cancer.
106:740–747. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cheng Y, Jin Z, Agarwal R, et al: LARP7 is
a potential tumor suppressor gene in gastric cancer. Lab Invest.
92:1013–1019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Costa FF: Non-coding RNAs: new players in
eukaryotic biology. Gene. 357:83–94. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Panzitt K, Tschernatsch MM, Guelly C, et
al: Characterization of HULC, a novel gene with striking
up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma, as noncoding RNA.
Gastroenterology. 132:330–342. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu D, Yang F, Yuan JH, et al: Long
noncoding RNAs associated with liver regeneration 1 accelerates
hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration by activating
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Hepatology. 58:739–751. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, et al: CREB
up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through
interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
38:5366–5383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matouk IJ, Abbasi I, Hochberg A, Galun E,
Dweik H and Akkawi M: Highly upregulated in liver cancer noncoding
RNA is overexpressed in hepatic colorectal metastasis. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:688–692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Yang B, Zhou Q, et al: Autophagy
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion through activation
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Carcinogenesis. 34:1343–1351.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ledford H: Cancer theory faces doubts.
Nature. 472:2732011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Enomoto M, Tsuchida A, Miyazawa K, et al:
Vitamin K2-induced cell growth inhibition via autophagy formation
in cholangiocellular carcinoma cell lines. Int J Mol Med.
20:801–808. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lv Q, Hua F and Hu ZW: DEDD, a novel tumor
repressor, reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating
selective autophagy. Autophagy. 8:1675–1676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Akalay I, Janji B, Hasmim M, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in
breast carcinoma promote escape from T-cell-mediated lysis. Cancer
Res. 73:2418–2427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nie Y, Liu X, Qu S, Song E, Zou H and Gong
C: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker
for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and survival. Cancer Sci.
104:458–464. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang F, Bi J, Xue X, et al: Up-regulated
long non-coding RNA H19 contributes to proliferation of gastric
cancer cells. FEBS J. 279:3159–3165. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang H, Zhong Y, Xie H, et al: Induction
of the liver cancer-down-regulated long noncoding RNA uc002mbe.2
mediates trichostatin-induced apoptosis of liver cancer cells.
Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1761–1769. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wahlestedt C: Targeting long non-coding
RNA to therapeutically upregulate gene expression. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 12:433–446. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu Q, Huang J, Zhou N, et al: LncRNA
loc285194 is a p53-regulated tumor suppressor. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:4976–4987. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lv Q, Wang W, Xue J, et al: DEDD interacts
with PI3KC3 to activate autophagy and attenuate
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 72:3238–3250. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shin NR, Jeong EH, Choi CI, et al:
Overexpression of Snail is associated with lymph node metastasis
and poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. BMC Cancer.
12:5212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin X, Shang X, Manorek G and Howell SB:
Regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition by claudin-3
and claudin-4. PLoS One. 8:e674962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Davidson B, Trope CG and Reich R:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in ovarian carcinoma. Front
Oncol. 2:332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R and Kondo S:
The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to
therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:726–734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Levine B and Yuan J: Autophagy in cell
death: an innocent convict? J Clin Invest. 115:2679–2688. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He H, Zang LH, Feng YS, et al: Physalin A
induces apoptotic cell death and protective autophagy in HT1080
human fibrosarcoma cells. J Nat Prod. 76:880–888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ye L, Zhao X, Lu J, Qian G, Zheng JC and
Ge S: Knockdown of TIGAR by RNA interference induces apoptosis and
autophagy in HepG2 hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 437:300–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh SY, Choi SJ, Kim KH, Cho EY, Kim JH and
Roh CR: Autophagy-related proteins, LC3 and Beclin-1, in placentas
from pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia. Reprod Sci.
15:912–920. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mann SS and Hammarback JA: Molecular
characterization of light chain 3. A microtubule binding subunit of
MAP1A and MAP1B. J Biol Chem. 269:11492–11497. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lang T, Schaeffeler E, Bernreuther D,
Bredschneider M, Wolf DH and Thumm M: Aut2p and Aut7p, two novel
microtubule-associated proteins are essential for delivery of
autophagic vesicles to the vacuole. EMBO J. 17:3597–3607. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A,
Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, GABARAP and
GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II
formation. J Cell Sci. 117:2805–2812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ying L, Huang Y, Chen H, et al:
Downregulated MEG3 activates autophagy and increases cell
proliferation in bladder cancer. Mol Biosyst. 9:407–411. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|