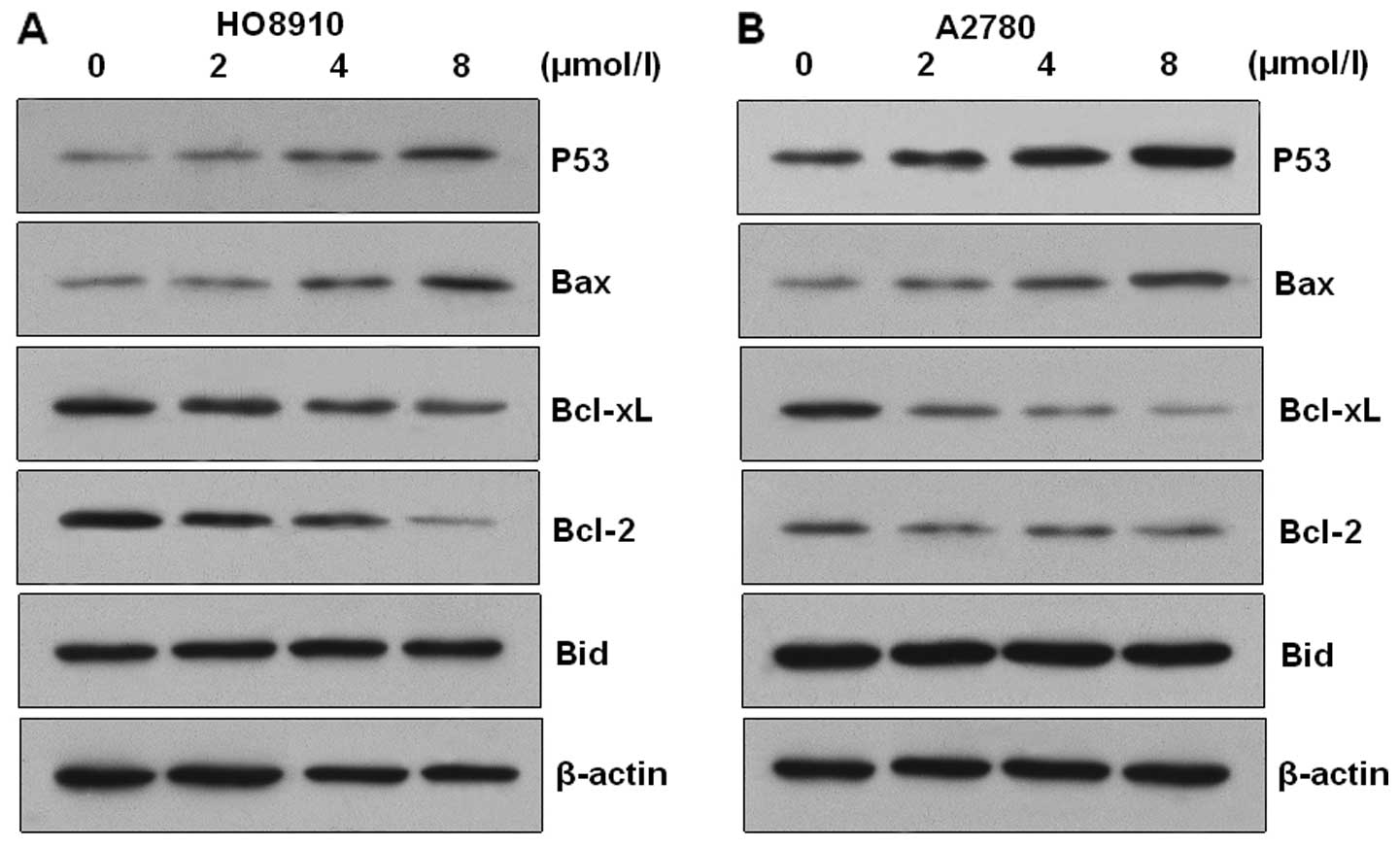
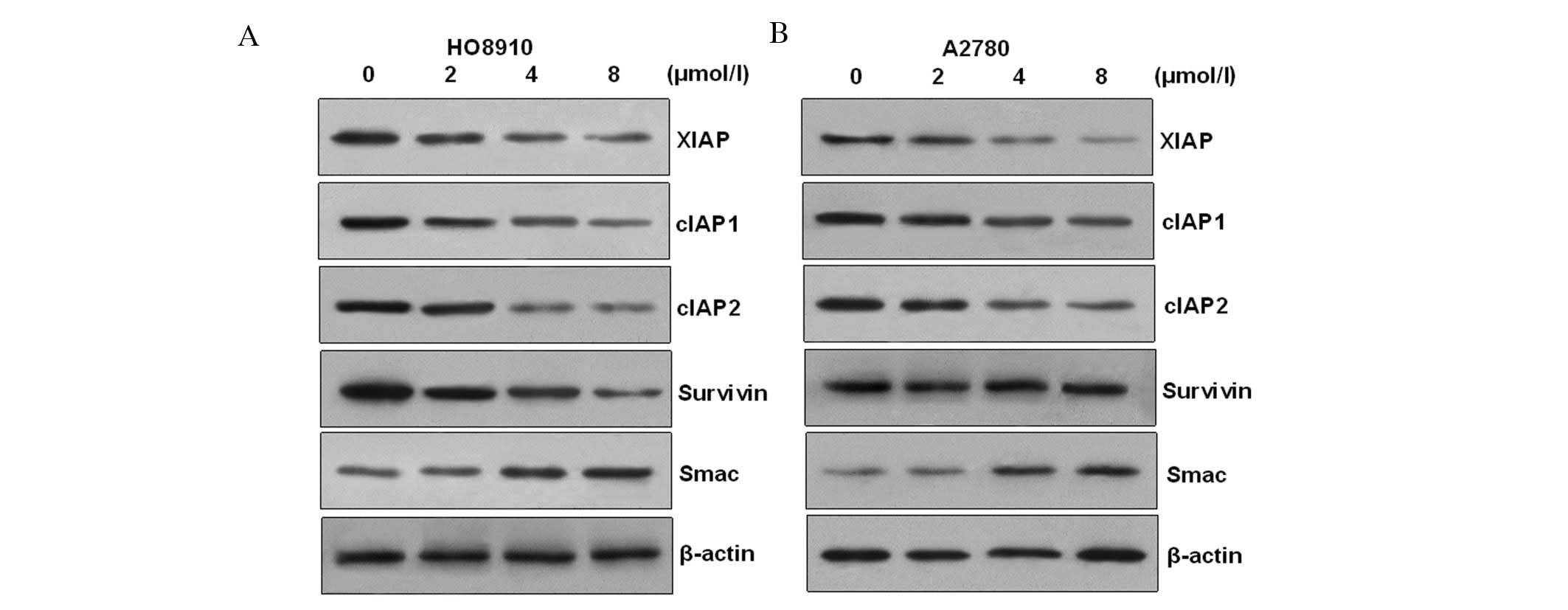
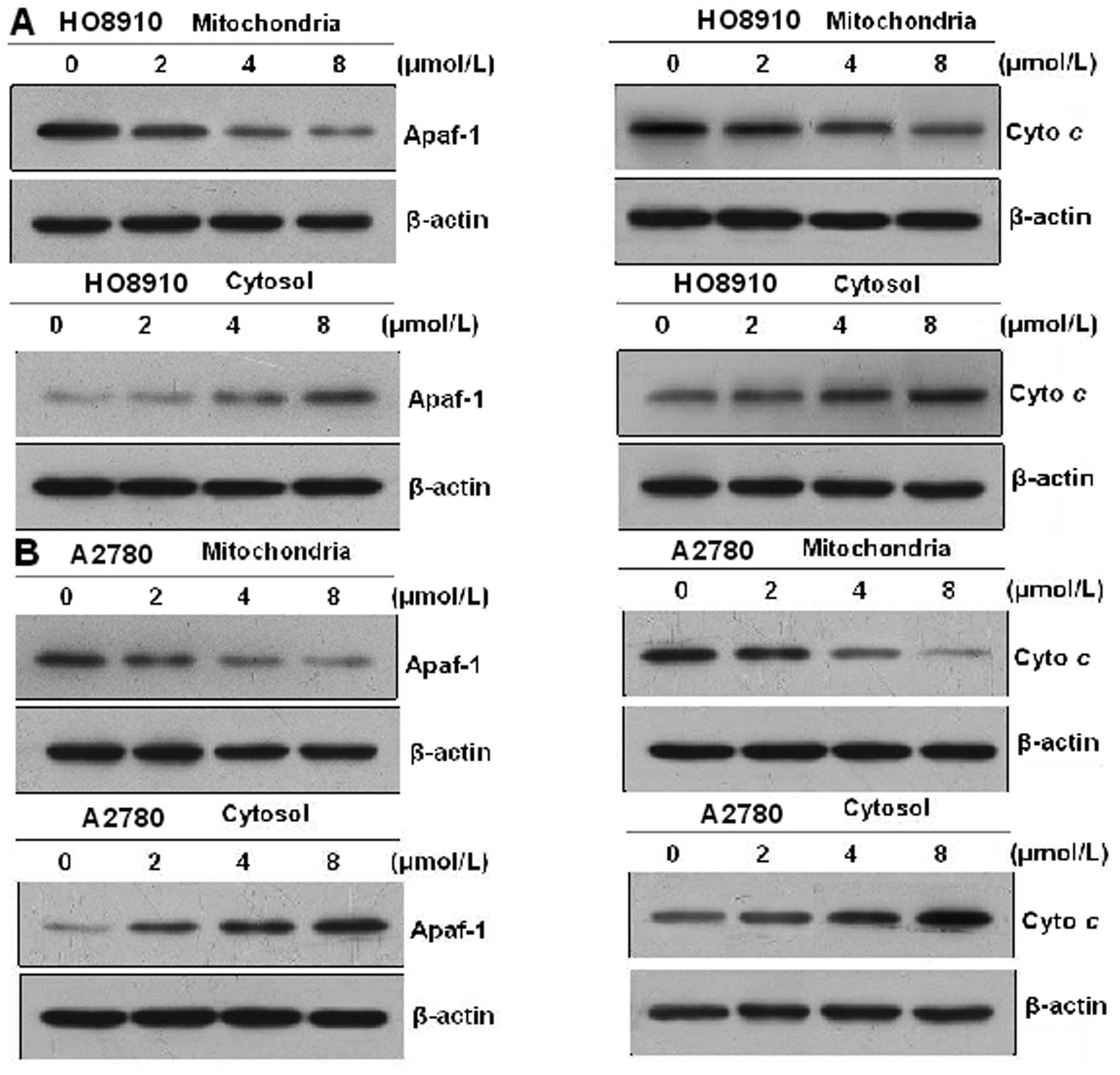
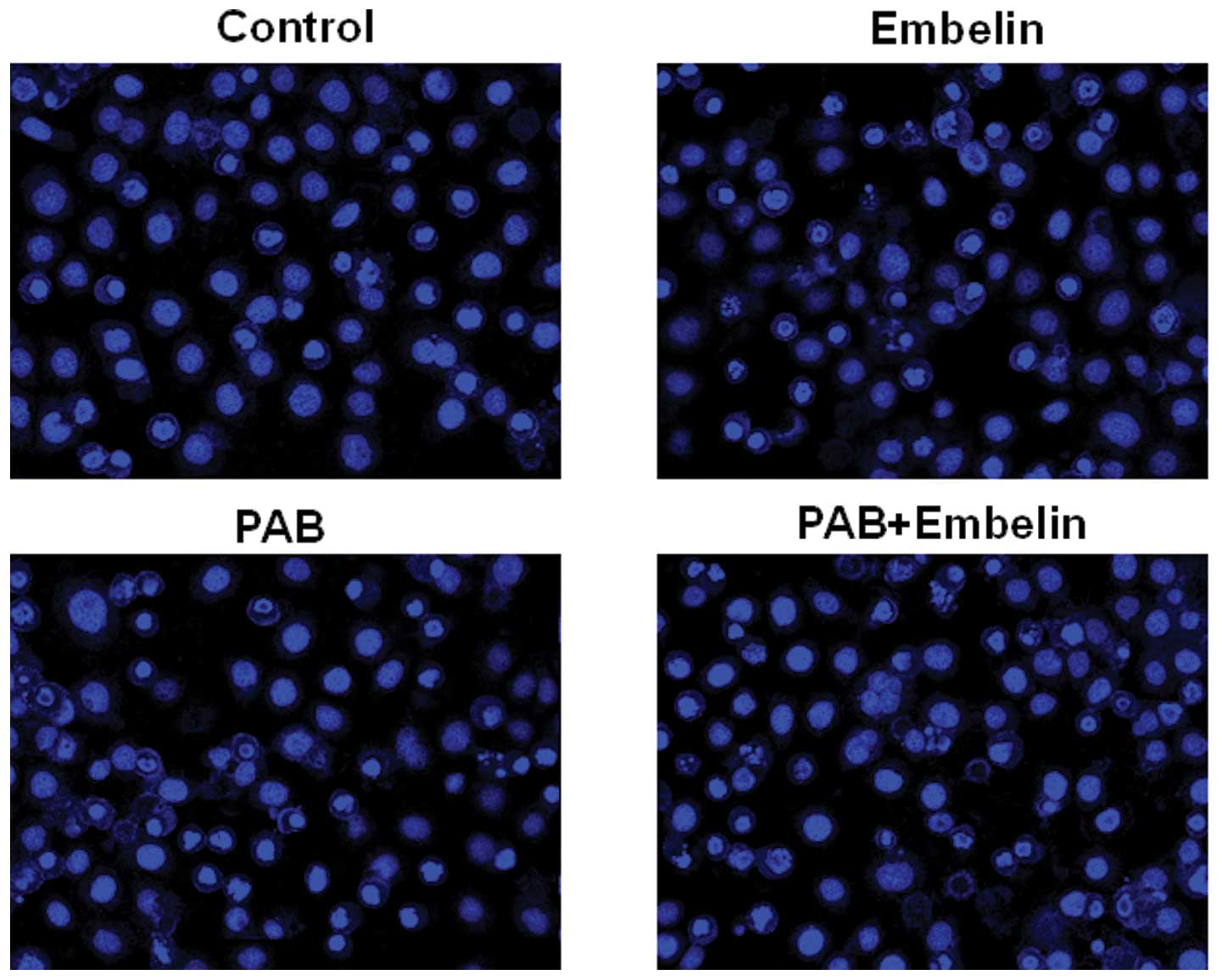
|
1
|
Yin F, Liu X, Li D, Wang Q, Zhang W and Li
L: Tumor suppressor genes associated with drug resistance in
ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:3–10. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kodigepalli KM, Dutta PS, Bauckman KA and
Nanjundan M: SnoN/SkiL expression is modulated via arsenic
trioxide-induced activation of the PI3K/AKT pathway in ovarian
cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 587:5–16. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ishii T, Kira N, Yoshida T and Narahara H:
Cucurbitacin D induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and
apoptosis in human endometrial and ovarian cancer cells. Tumour
Biol. 34:285–291. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yu JH, Liu CY, Zheng GB, et al:
Pseudolaric acid B induced cell cycle arrest, autophagy and
senescence in murine fibrosarcoma l929 cell. Int J Med Sci.
10:707–718. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ma G, Chong L, Li XC, Khan IA, Walker LA
and Khan SI: Selective inhibition of human leukemia cell growth and
induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by pseudolaric acid B.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1333–1340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Thompson CB: Apoptosis in the pathogenesis
and treatment of disease. Science. 267:1456–1462. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fulda S: Apoptosis pathways and their
therapeutic exploitation in pancreatic cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
7:1221–1227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Varfolomeev E and Vucic D: Inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins: fascinating biology leads to attractive tumor
therapeutic targets. Future Oncol. 7:633–648. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tong J, Yin S, Dong Y, Guo X, Fan L, Ye M
and Hu H: Pseudolaric acid B induces caspase-dependent apoptosis
and autophagic cell death in prostate cancer cells. Phytother Res.
27:885–891. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qi M, Yao G, Fan S, Cheng W, Tashiro S,
Onodera S and Ikejima T: Pseudolaric acid B induces mitotic
catastrophe followed by apoptotic cell death in murine fibrosarcoma
L929 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 683:16–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khan M, Zheng B, Yi F, et al: Pseudolaric
acid B induces caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis
in u87 glioblastoma cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2012:9575682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carter BZ, Mak DH, Wang Z, Ma W, Mak PY,
Andreeff M and Davis RE: XIAP downregulation promotes
caspase-dependent inhibition of proteasome activity in AML. Leuk
Res. 37:974–979. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao Z, Zhang R, Li J, et al: X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis protein (XIAP) regulation of cyclin D1
protein expression and cancer cell anchorage-independent growth via
its E3 ligase-mediated protein phosphatase 2A/c-Jun axis. J Biol
Chem. 288:20238–20247. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yao SQ, Rojanasakul LW, Chen ZY, et al:
Fas/FasL pathway-mediated alveolar macrophage apoptosis involved in
human silicosis. Apoptosis. 16:1195–1204. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Supiot S, Gouraud W, Campion L, et al:
Early dynamic transcriptomic changes during preoperative
radiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer: a feasibility study.
World J Gastroenterol. 19:3249–3254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fulda S: Tumor resistance to apoptosis.
Int J Cancer. 124:511–515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fulda S: Inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP)
proteins as therapeutic targets for radiosensitization of human
cancers. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:760–766. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paramasivam A, Sambantham S, Shabnam J, et
al: Anti-cancer effects of thymoquinone in mouse neuroblastoma
(Neuro-2a) cells through caspase-3 activation with down-regulation
of XIAP. Toxicol Lett. 213:151–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Galluzzi L, Morselli E, Kepp O, et al:
Mitochondrial gateways to cancer. Mol Aspects Med. 31:1–20. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu CX, Jin H and Cho MH: Apoptosis and
apoptosis-based therapy in lung cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
9:952–957. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang C, Chen X, Guo B, et al: Induction
of apoptosis by Icariside II through extrinsic and intrinsic
signaling pathways in human breast cancer MCF7 cells. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 76:1322–1328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zeng C, Ke Z, Song Y, et al: Annexin A3 is
associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer and participates
in the modulation of apoptosis in vitro by affecting the Bcl-2/Bax
balance. Exp Mol Pathol. 95:23–31. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang C and Youle RJ: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. Annu Rev Genet. 43:95–118. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Du C, Fang M, Li Y, Li L and Wang X: Smac,
a mitochondrial protein that promotes cytochrome c-dependent
caspase activation by eliminating IAP inhibition. Cell. 102:33–42.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Verhagen AM, Ekert PG, Pakusch M, et al:
Identification of DIABLO, a mammalian protein that promotes
apoptosis by binding to and antagonizing IAP proteins. Cell.
102:43–53. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Adrain C, Creagh EM and Martin SJ:
Apoptosis-associated release of Smac/DIABLO from mitochondria
requires active caspases and is blocked by Bcl-2. EMBO J.
20:6627–6636. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chipuk JE and Green DR: How do BCL-2
proteins induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization?
Trends Cell Biol. 18:157–164. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fulda S and Vucic D: Targeting IAP
proteins for therapeutic intervention in cancer. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 11:109–124. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Salvesen GS and Duckett CS: Apoptosis: IAP
proteins: blocking the road to death’s door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:401–410. 2002.
|
|
31
|
Ahn KS, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB: Embelin,
an inhibitor of X chromosome-linked inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein,
blocks nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling pathway leading to
suppression of NF-κB-regulated antiapoptotic and metastatic gene
products. Mol Pharmacol. 71:209–219. 2007.
|