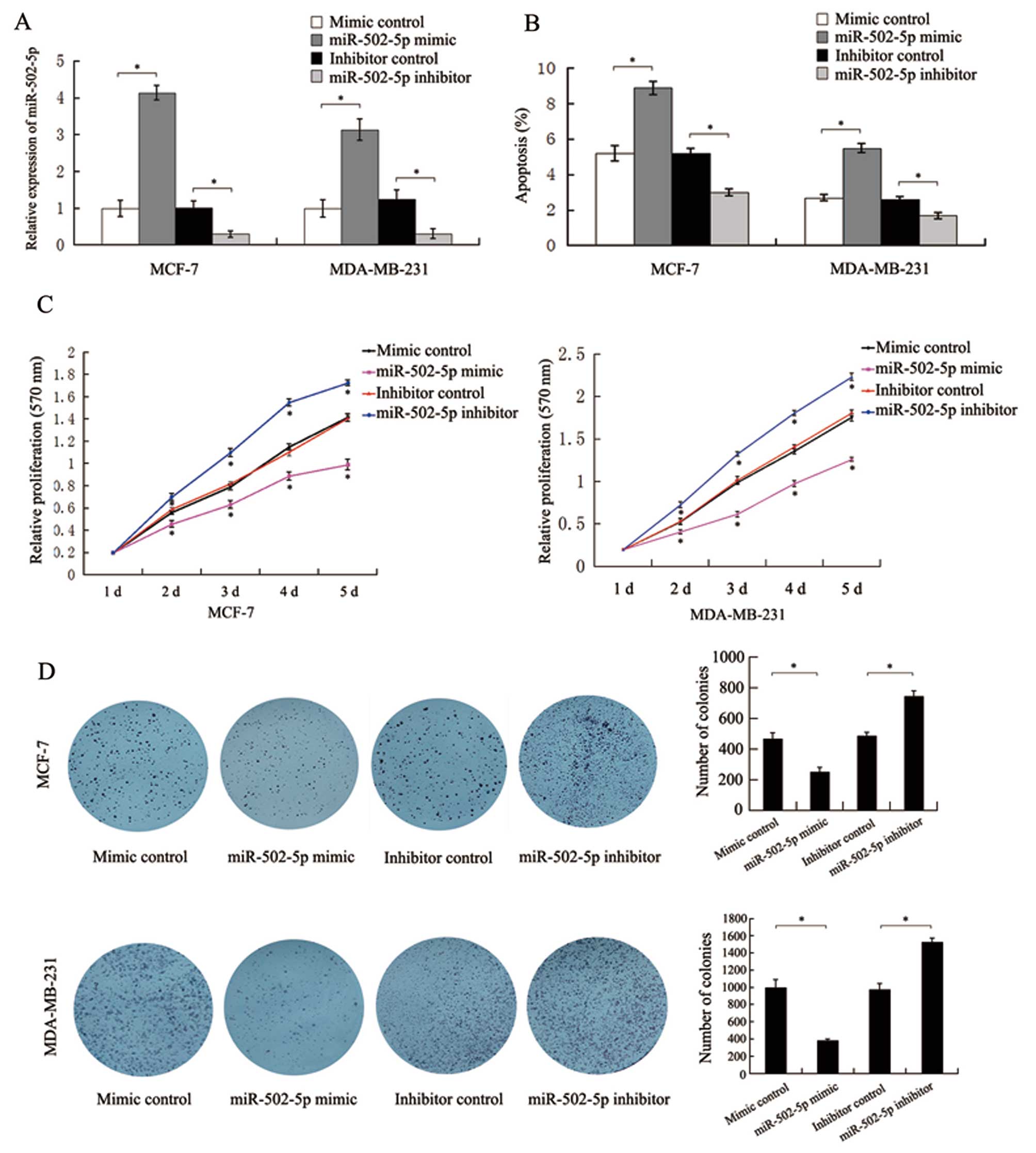
|
1
|
Chung JY, Park YC, Ye H and Wu H: All
TRAFs are not created equal: common and distinct molecular
mechanisms of TRAF-mediated signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
115:679–688. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xia ZP and Chen ZJ: TRAF2: a double-edged
sword? Sci STKE. 2005:pe72005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arch RH and Thompson CB: 4-1BB and Ox40
are members of a tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-nerve growth factor
receptor subfamily that bind TNF receptor-associated factors and
activate nuclear factor κB. Mol Cell Biol. 18:558–565.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Duckett CS, Gedrich RW, Gilfillan MC and
Thompson CB: Induction of nuclear factor kappaB by the CD30
receptor is mediated by TRAF1 and TRAF2. Mol Cell Biol.
17:1535–1542. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hsu H, Shu HB, Pan MG and Goeddel DV:
TRADD-TRAF2 and TRADD-FADD interactions define two distinct TNF
receptor 1 signal transduction pathways. Cell. 82:299–308. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Reinhard C, Shamoon B, Shyamala V and
Williams LT: Tumor necrosis factor α-induced activation of c-jun
N-terminal kinase is mediated by TRAF2. EMBO J. 16:1080–1092.
1997.
|
|
7
|
Rothe M, Sarma V, Dixit VM and Goeddel DV:
TRAF2-mediated activation of NF-kappa B by TNF receptor 2 and CD40.
Science. 269:1424–1427. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takeuchi M, Rothe M and Goeddel DV:
Distinct domains for nuclear factor-κB activation and association
with tumor necrosis factor signaling proteins. J Biol Chem.
271:19935–19942. 1996.
|
|
9
|
Liu ZG, Hsu H, Goeddel DV and Karin M:
Dissection of TNF receptor 1 effector functions: JNK activation is
not linked to apoptosis while NF-κB activation prevents cell death.
Cell. 87:565–576. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Natoli G, Costanzo A, Ianni A, Templeton
DJ, Woodgett JR, Balsano C and Levrero M: Activation of SAPK/JNK by
TNF receptor 1 through a noncytotoxic TRAF2-dependent pathway.
Science. 275:200–203. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cao Z, Henzel WJ and Gao X: IRAK: a kinase
associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science. 271:1128–1131.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song HY, Regnier CH, Kirschning CJ,
Goeddel DV and Rothe M: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase
cascades: bifurcation of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-jun N-terminal
kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:9792–9796. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jing Q, Huang S, Guth S, et al:
Involvement of microRNA in AU-rich element-mediated mRNA
instabiliby. Cell. 120:623–634. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lecellier CH, Dunoyer P, Arar K, et al: A
cellular microRNA mediates antiviral defense in human cells.
Science. 308:557–560. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sullivan CS, Grundhoff AT, Tevethia S,
Pipas JM and Ganem D: SV40-encoded microRNAs regulate viral gene
expression and reduce susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells. Nature.
435:682–686. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pallante P, Visone R, Ferracin M, et al:
MicroRNA deregulation in human thyroid papillary carcinomas. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 13:497–508. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang B, Pan X, Cobb GP and Anderson TA:
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev Biol. 302:1–12.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen CZ: MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor
suppressors. N Engl Med. 353:1768–1771. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang S, Mi X, Liu N, Fang C, Teng Y and
Zhao R: Expression of TRAF2 and its relationship with invasion in
breast cancer. J China Med Univ. 37:52008.
|
|
24
|
Zhang X, Wen Z, Sun L, Wang J, Song M,
Wang E and Mi X: TRAF2 regulates the cytoplasmic/nuclear
distribution of TRAF4 and its biological function in breast cancer
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 436:344–348. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Haghighat S, Akbari ME, Ghaffari S and
Yavari P: Standardized breast cancer mortality rate compared to the
general female population of Iran. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
13:5525–5528. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blondal T, Jensby Nielsen S, Baker A,
Andreasen D, Mouritzen P, Wrang Teilum M and Dahlsveen IK:
Assessing sample and miRNA profile quality in serum and plasma or
other biofluids. Methods. 59:S1–S6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lorenzen JM and Thum T: Circulating and
urinary microRNAs in kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.
7:1528–1533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhai H, Song B, Xu X, Zhu W and Ju J:
Inhibition of autophagy and tumor growth in colon cancer by
miR-502. Oncogene. 32:1570–1579. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ding C, Li R, Peng J, Li S and Guo Z: A
polymorphism at the miR-502 binding site in the 3′ untranslated
region of the SET8 gene is associated with the outcome of
small-cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 3:689–692. 2012.
|