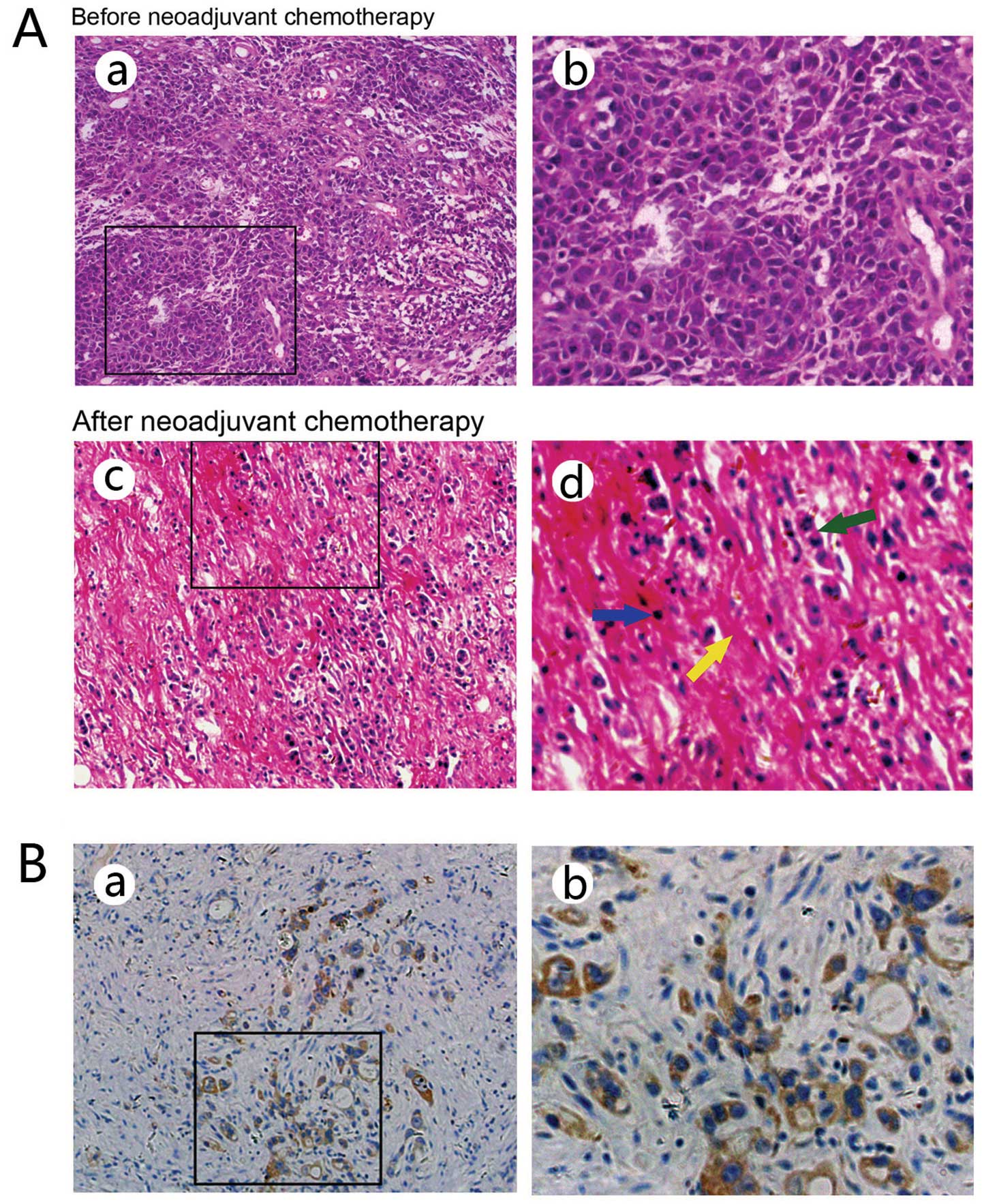
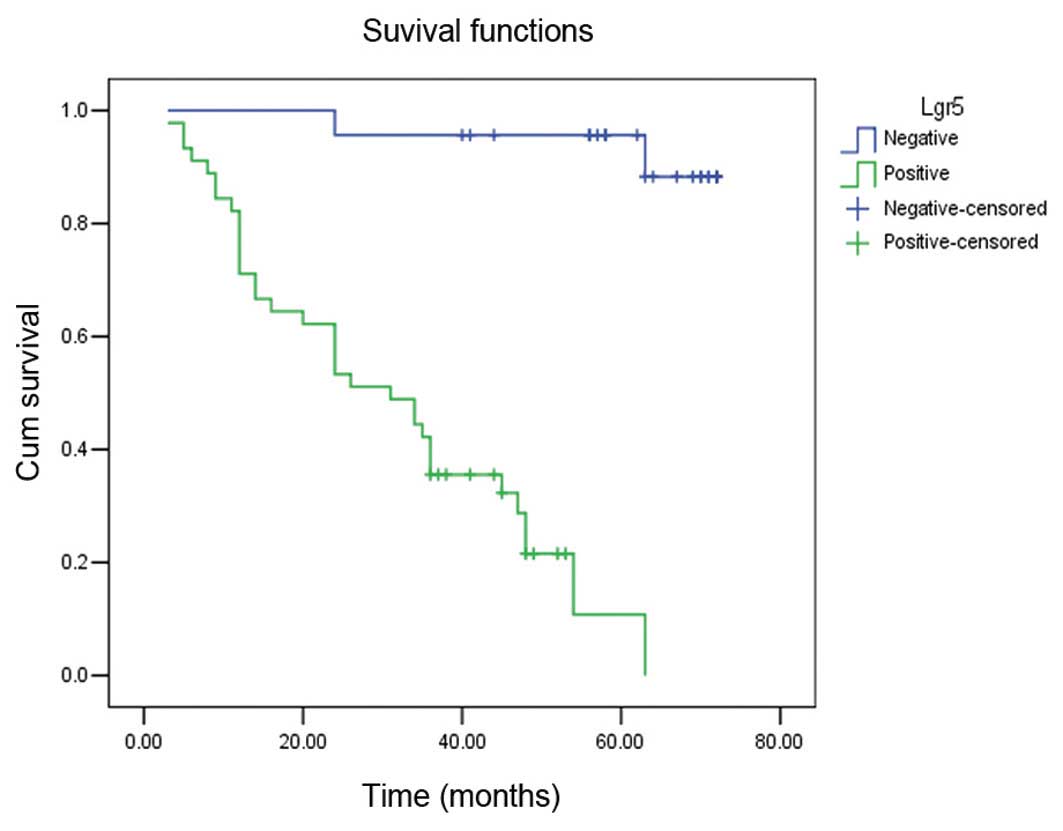
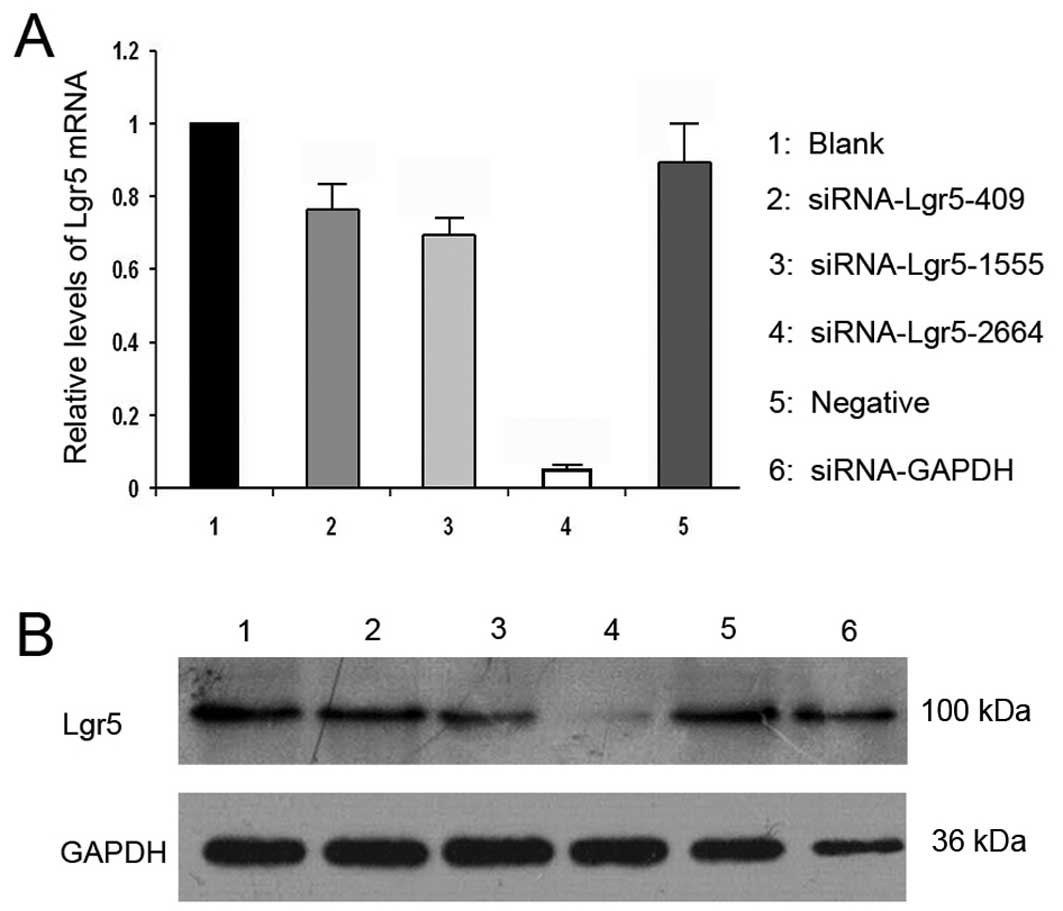
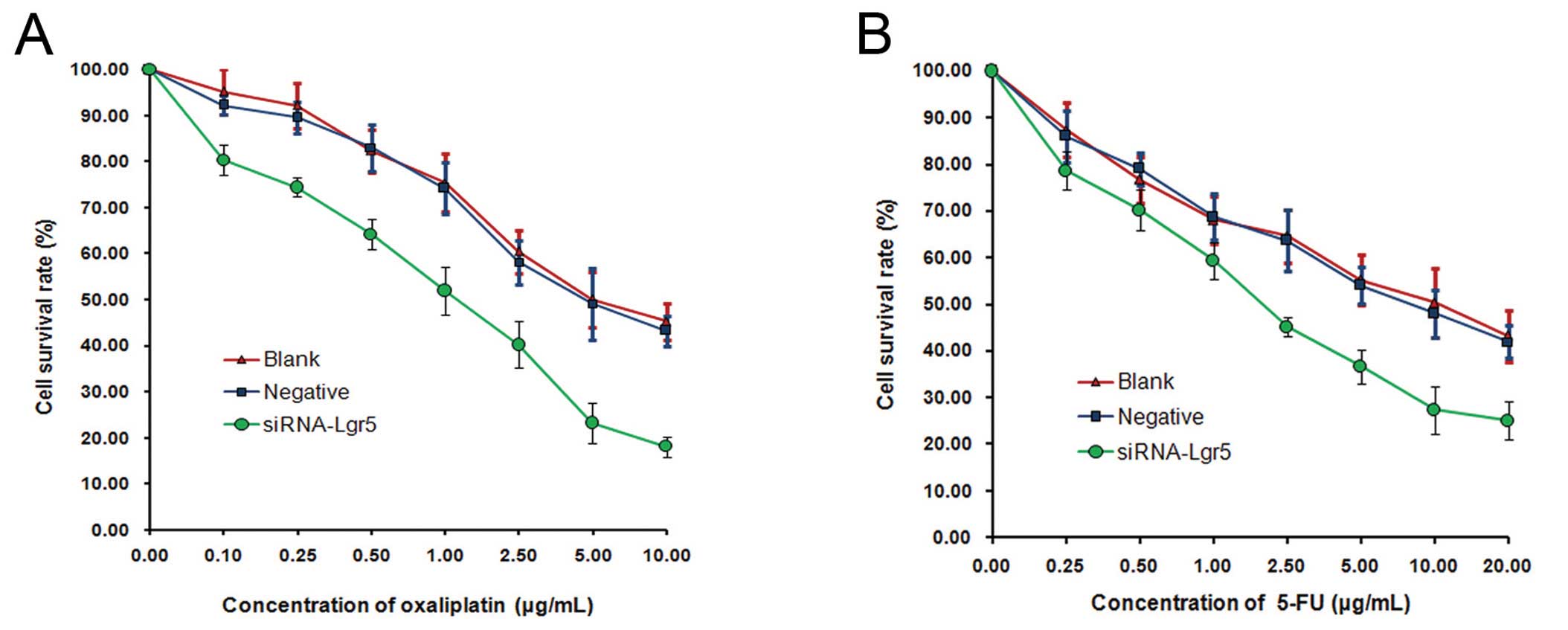
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thun MJ, DeLancey JO, Center MM, Jemal A
and Ward EM: The global burden of cancer: priorities for
prevention. Carcinogenesis. 31:100–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cunningham D, Allum WH, Stenning SP, et
al: Perioperative chemotherapy versus surgery alone for resectable
gastroesophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 355:11–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Becker K, Langer R, Reim D, et al:
Significance of histopathological tumor regression after
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric adenocarcinomas: a summary of
480 cases. Ann Surg. 253:934–939. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Van der Flier LG, Sabates-Bellver J, Oving
I, et al: The intestinal Wnt/TCF signature. Gastroenterology.
132:628–632. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Segditsas S, Sieber O, Deheragoda M, et
al: Putative direct and indirect Wnt targets identified through
consistent gene expression changes in APC-mutant intestinal
adenomas from humans and mice. Hum Mol Genet. 17:3864–3875. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamamoto Y, Sakamoto M, Fujii G, et al:
Overexpression of orphan G-protein-coupled receptor, Gpr49, in
human hepatocellular carcinomas with beta-catenin mutations.
Hepatology. 37:528–533. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carmon KS, Lin Q, Gong X, Thomas A and Liu
Q: LGR5 interacts and cointernalizes with Wnt receptors to modulate
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2054–2064.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, et al:
Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker
gene Lgr5. Nature. 449:1003–1007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jaks V, Barker N, Kasper M, et al: Lgr5
marks cycling, yet long-lived, hair follicle stem cells. Nat Genet.
40:1291–1299. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barker N, Huch M, Kujala P, et al:
Lgr5(+ve) stem cells drive self-renewal in the stomach and build
long-lived gastric units in vitro. Cell Stem Cell. 6:25–36.
2010.
|
|
12
|
Simon E, Petke D, Boger C, et al: The
spatial distribution of LGR5+ cells correlates with
gastric cancer progression. PLoS One. 7:e354862012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takahashi H, Ishii H, Nishida N, et al:
Significance of Lgr5(+ve) cancer stem cells in the colon and
rectum. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1166–1174. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Kemper K, Prasetyanti PR, De Lau W,
Rodermond H, Clevers H and Medema JP: Monoclonal antibodies against
Lgr5 identify human colorectal cancer stem cells. Stem Cells.
30:2378–2386. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu XS, Xi HQ and Chen L: Lgr5 is a
potential marker of colorectal carcinoma stem cells that correlates
with patient survival. World J Surg Oncol. 10:2442012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
McClanahan T, Koseoglu S, Smith K, et al:
Identification of overexpression of orphan G protein-coupled
receptor GPR49 in human colon and ovarian primary tumors. Cancer
Biol Ther. 5:419–426. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tanese K, Fukuma M, Yamada T, et al:
G-protein-coupled receptor GPR49 is up-regulated in basal cell
carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation and tumor formation. Am J
Pathol. 173:835–843. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Becker L, Huang Q and Mashimo H: Lgr5, an
intestinal stem cell marker, is abnormally expressed in Barrett’s
esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 23:168–174.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakata S, Campos B, Bageritz J, et al:
LGR5 is a marker of poor prognosis in glioblastoma and is required
for survival of brain cancer stem-like cells. Brain Pathol.
23:60–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vermeulen L, Todaro M, de Sousa Mello F,
et al: Single-cell cloning of colon cancer stem cells reveals a
multi-lineage differentiation capacity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:13427–13432. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Becker L, Huang Q and Mashimo H:
Immunostaining of Lgr5, an intestinal stem cell marker, in normal
and premalignant human gastrointestinal tissue.
ScientificWorldJournal. 8:1168–1176. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saigusa S, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, et al:
Clinical significance of LGR5 and CD44 expression in locally
advanced rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Int J
Oncol. 41:1643–1652. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Saigusa S, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, et al:
Significant correlation between LKB1 and LGR5 gene expression and
the association with poor recurrence-free survival in rectal cancer
after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
139:131–138. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ozkan M, Akbudak IH, Deniz K, et al:
Prognostic value of excision repair cross-complementing gene 1
expression for cisplatin-based chemotherapy in advanced gastric
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 11:181–185. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, et al:
Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology
Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Becker K, Mueller JD, Schulmacher C, et
al: Histomorphology and grading of regression in gastric carcinoma
treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cancer. 98:1521–1530. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B and Chen L: Aberrant
expression of EphA3 in gastric carcinoma: correlation with tumor
angiogenesis and survival. J Gastroenterol. 47:785–794. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xi HQ, Zhao P and Han WD:
Clinicopathological significance and prognostic value of LRP16
expression in colorectal carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol.
16:1644–1648. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Matsubara J, Yamada Y, Nakajima TE, et al:
Clinical significance of insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor
and epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with advanced
gastric cancer. Oncology. 74:76–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wood LD, Calhoun ES, Silliman N, et al:
Somatic mutations of GUCY2F, EPHA3, and NTRK3 in human cancers. Hum
Mutat. 27:1060–1061. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2−ΔΔCT
method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lordick F, Stein HJ, Peschel C and Siewert
JR: Neoadjuvant therapy for oesophagogastric cancer. Br J Surg.
91:540–551. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Al-Hajj M: Cancer stem cells and oncology
therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol. 19:61–64. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dirks PB: Cancer: stem cells and brain
tumours. Nature. 444:687–688. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Setoguchi T, Taga T and Kondo T: Cancer
stem cells persist in many cancer cell lines. Cell Cycle.
3:414–415. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Haq R and Zanke B: Inhibition of apoptotic
signaling pathways in cancer cells as a mechanism of chemotherapy
resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 17:233–239. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gu L, Findley HW, Zhu N and Zhou M:
Endogenous TNFalpha mediates cell survival and chemotherapy
resistance by activating the PI3K/Akt pathway in acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 20:900–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mahon KL, Henshall SM, Sutherland RL and
Horvath LG: Pathways of chemotherapy resistance in
castration-resistant prostate cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
18:R103–R123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cui J, Jiang W, Wang S, Wang L and Xie K:
Role of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in drug resistance of pancreatic
cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 18:2464–2471. 2012.
|
|
40
|
Zhang H, Zhang X, Wu X, et al:
Interference of Frizzled 1 (FZD1) reverses multidrug resistance in
breast cancer cells through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Cancer Lett.
323:106–113. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|