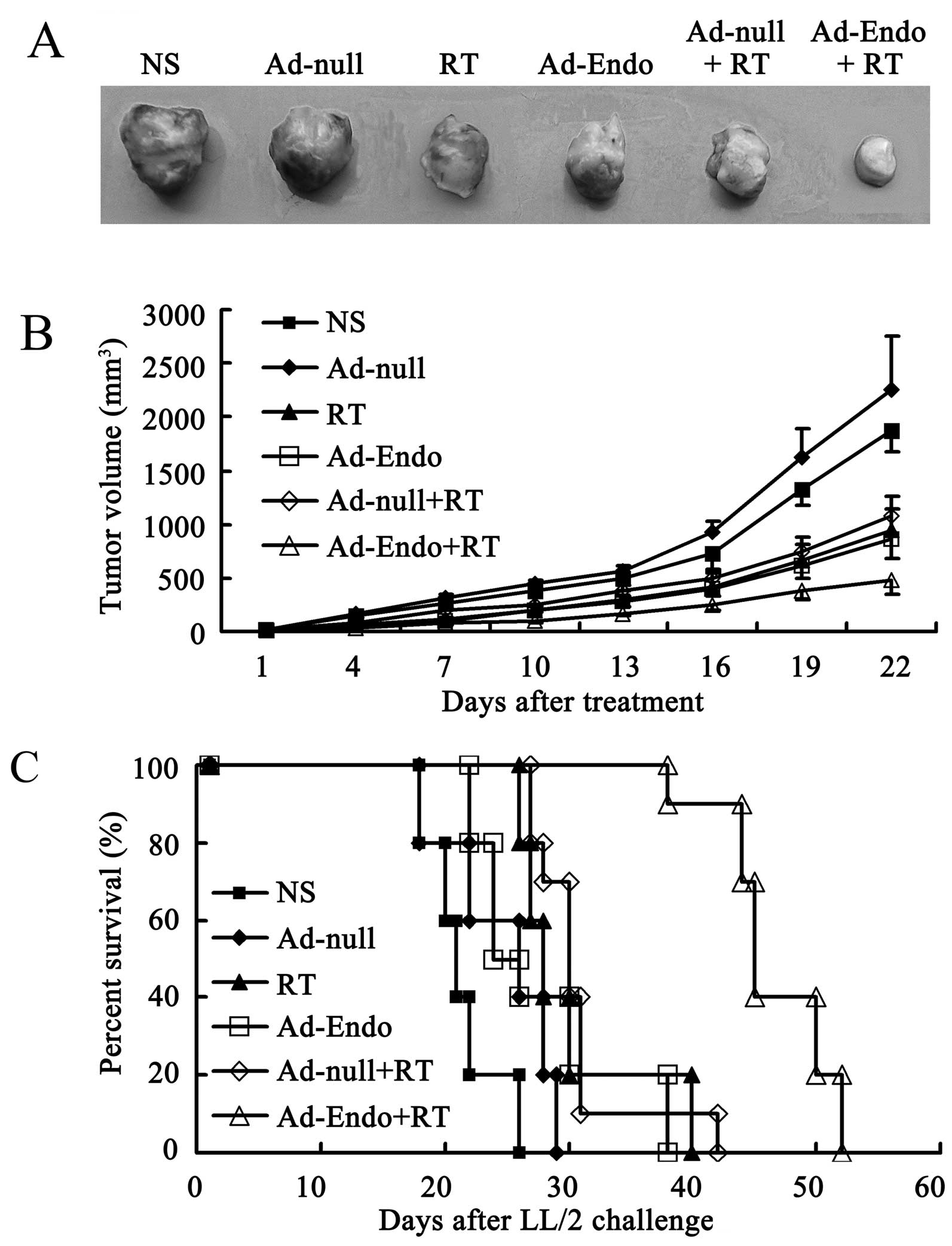
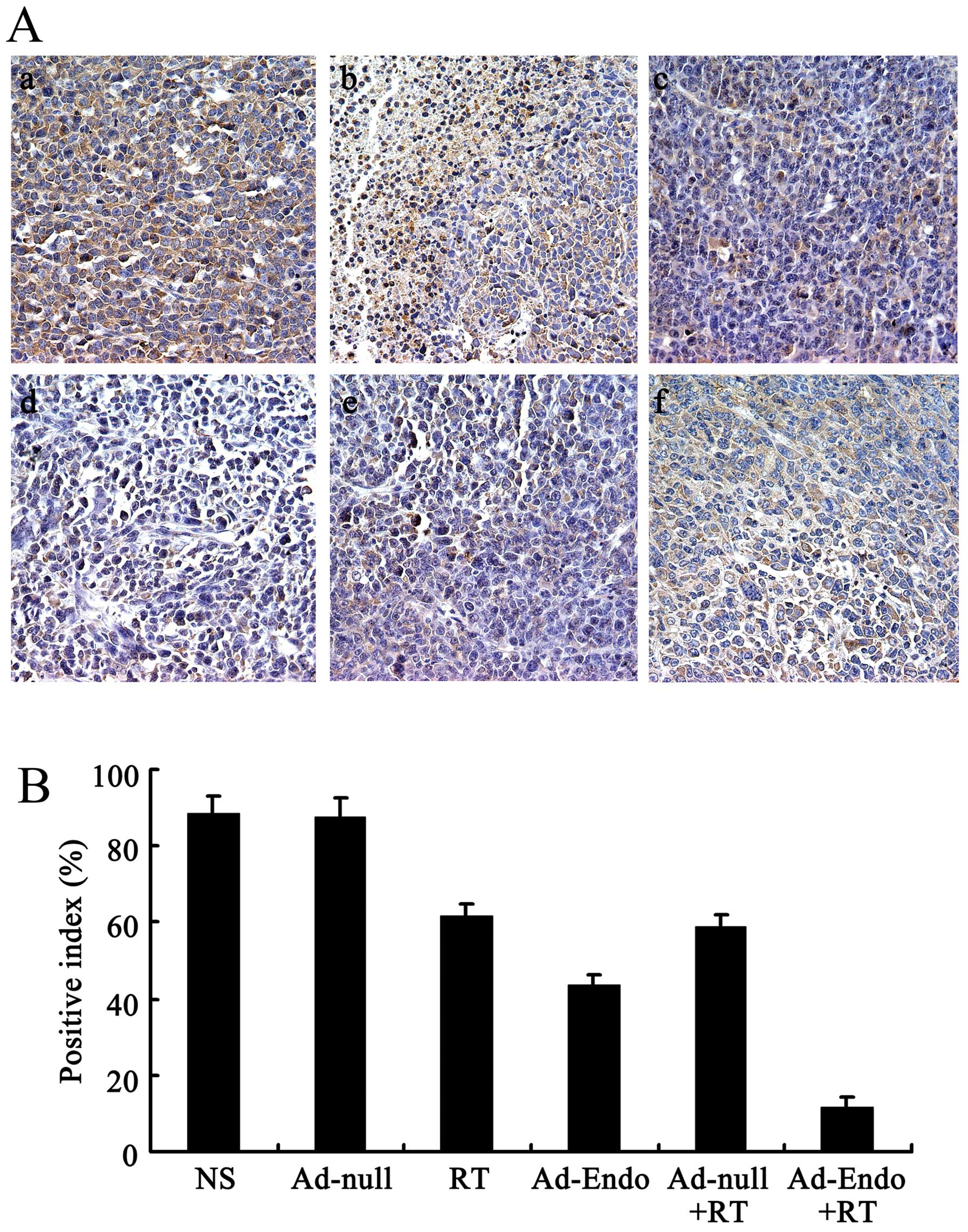
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2006. CA Cancer J Clin. 56:106–130. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ning T, Yan X, Lu ZJ, et al: Gene therapy
with the angiogenesis inhibitor endostatin in an orthotopic lung
cancer murine model. Hum Gene Ther. 20:103–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhuang HQ and Yuan ZY: Process in the
mechanisms of endostatin combined with radiotherapy. Cancer Lett.
282:9–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Govindan R, Bogart J and Vokes EE: Locally
advanced non-small cell lung cancer: the past, present, and future.
J Thorac Oncol. 3:917–928. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bunn PA Jr and Thatcher N: Systemic
treatment for advanced (stage IIIb/IV) non-small cell lung cancer:
more treatment options; more things to consider. Conclusion
Oncologist. 13(Suppl 1): 37–46. 2008.
|
|
6
|
Bayman NA, Blackhall F, Jain P, Lee L,
Thatcher N and Faivre-Finn C: Management of unresectable stage III
non-small-cell lung cancer with combined-modality therapy: a review
of the current literature and recommendations for treatment. Clin
Lung Cancer. 9:92–101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang HL, Yuan C, Zhang DM, et al: A novel
combined conjugate vaccine: enhanced immunogenicity of bFGF with
CRM197 as a carrier protein. Mol Med Rep. 4:857–863.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis in cancer,
vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med. 1:27–31. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hahnfeldt P, Panigrahy D, Folkman J and
Hlatky L: Tumor development under angiogenic signaling: a dynamical
theory of tumor growth, treatment response, and postvascular
dormancy. Cancer Res. 59:4770–4775. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shi HS, Yang LP, Wei W, et al:
Systemically administered liposome-encapsulated Ad-PEDF potentiates
the anti-cancer effects in mouse lung metastasis melanoma. J Transl
Med. 11:862013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, et al:
Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997.
|
|
13
|
Oh SP, Warman ML, Seldin MF, et al:
Cloning of cDNA and genomic DNA encoding human type XVIII collagen
and localization of the α1(XVIII) collagen gene to mouse chromosome
10 and human chromosome 21. Genomics. 19:494–499. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wenzel D, Schmidt A, Reimann K, et al:
Endostatin, the proteolytic fragment of collagen XVIII, induces
vasorelaxation. Circ Res. 98:1203–1211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dhanabal M, Ramchandran R, Waterman MJ, et
al: Endostatin induces endothelial cell apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
274:11721–11726. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Skovseth DK, Veuger MJ, Sorensen DR, De
Angelis PM and Haraldsen G: Endostatin dramatically inhibits
endothelial cell migration, vascular morphogenesis, and
perivascular cell recruitment in vivo. Blood. 105:1044–1051. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu DS, Wu CM, Huang TH and Xie QD:
Combined effects of radiotherapy and endostatin gene therapy in
melanoma tumor model. Radiat Environ Biophys. 47:285–291. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Blezinger P, Wang J, Gondo M, et al:
Systemic inhibition of tumor growth and tumor metastases by
intramuscular administration of the endostatin gene. Nat
Biotechnol. 17:343–348. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
You ZY, Zhao Y, Liu F, Zhang YD and Wang
JJ: The radiosensitization effects of Endostar on human lung
squamous cancer cells H-520. Cancer Cell Int. 10:172010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui R, Ohashi R, Takahashi F, et al:
Signal transduction mediated by endostatin directly modulates
cellular function of lung cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Sci.
98:830–837. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thomas JP, Arzoomanian RZ, Alberti D, et
al: Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of
recombinant human endostatin in patients with advanced solid
tumors. J Clin Oncol. 21:223–231. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li XP, Li CY, Li X, et al: Inhibition of
human nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and metastasis in mice by
adenovirus-associated virus-mediated expression of human
endostatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:1290–1298. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Malecki M, Kolsut P and Proczka R:
Angiogenic and antiangiogenic gene therapy. Gene Ther. 12(Suppl 1):
S159–S169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sauter BV, Martinet O, Zhang WJ, Mandeli J
and Woo SL: Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of endostatin in
vivo results in high level of transgene expression and
inhibition of tumor growth and metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:4802–4807. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mellon MJ, Ahn M, Jimenez JA, Kao C and
Gardner TA: Anti-angiogenic gene therapy for metastatic renal cell
carcinoma produces tumor growth suppression in an athymic nude
mouse model. J Urol. 179:737–742. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kerbel RS, Yu J, Tran J, et al: Possible
mechanisms of acquired resistance to anti-angiogenic drugs:
implications for the use of combination therapy approaches. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 20:79–86. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis - correlation in invasive
breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu Y, Yang L, Hu B, et al: Synergistic
anti-tumor effect of recombinant human endostatin adenovirus
combined with gemcitabine. Anticancer Drugs. 16:551–557. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis and tissue
factor. Nat Med. 2:167–168. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J
and Hanahan D: Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage
carcinogenesis in mice. Science. 284:808–812. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Algire GH, Chalkley HW, Earle WE, et al:
Vascular reactions of normal and malignant tissues in vivo. III
Vascular reactions’ of mice to fibroblasts treated in vitro with
methylcholanthrene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 11:555–580. 1950.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Folkman J, Merler E, Abernathy C and
Williams G: Isolation of a tumor factor responsible for
angiogenesis. J Exp Med. 133:275–288. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Risau W: Mechanisms of angiogenesis.
Nature. 386:671–674. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Folkman J and Kalluri R: Cancer without
disease. Nature. 427:7872004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shi W, Teschendorf C, Muzyczka N and
Siemann DW: Gene therapy delivery of endostatin enhances the
treatment efficacy of radiation. Radiother Oncol. 66:1–9. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ehrmann RL and Knoth M: Choriocarcinoma.
Transfilter stimulation of vasoproliferation in the hamster cheek
pouch Studied by light and electron microscopy. J Natl Cancer Inst.
41:1329–1341. 1968.
|
|
38
|
Huang G and Chen L: Recombinant human
endostatin improves anti-tumor efficacy of paclitaxel by
normalizing tumor vasculature in Lewis lung carcinoma. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 136:1201–1211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wickstrom SA, Alitalo K and Keski-Oja J:
Endostatin associates with integrin α5β1 and
caveolin-1, and activates Src via a tyrosyl phosphatase-dependent
pathway in human endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 62:5580–5589.
2002.
|
|
40
|
Lan KL, Ou-Yang F, Yen SH, Shih HL and Lan
KH: Cationic liposome coupled endostatin gene for treatment of
peritoneal colon cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:307–318. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boehm T, Pirie-Shepherd S, Trinh LB,
Shiloach J and Folkman J: Disruption of the KEX1 gene in Pichia
pastoris allows expression of full-length murine and human
endostatin. Yeast. 15:563–572. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Griscelli F, Li H, Bennaceur-Griscelli A,
et al: Angiostatin gene transfer: inhibition of tumor growth in
vivo by blockage of endothelial cell proliferation associated
with a mitosis arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:6367–6372.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin P, Buxton JA, Acheson A, et al:
Antiangiogenic gene therapy targeting the endothelium-specific
receptor tyrosine kinase Tie2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:8829–8834. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Regulier E, Paul S, Marigliano M, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated delivery of antiangiogenic genes as an
antitumor approach. Cancer Gene Ther. 8:45–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bai RZ, Wu Y, Liu Q, et al: Suppression of
lung cancer in murine model: treated by combination of recombinant
human endostsatin adenovirus with low-dose cisplatin. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 28:312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Liao Z, Huang C, Zhou F, et al: Radiation
enhances suicide gene therapy in radioresistant laryngeal squamous
cell carcinoma via activation of a tumor-specific promoter. Cancer
Lett. 283:20–28. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Durand RE and LePard NE: Contribution of
transient blood flow to tumour hypoxia in mice. Acta Oncol.
34:317–323. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Bussink J, Kaanders JH and van der Kogel
AJ: Tumor hypoxia at the micro-regional level: clinical relevance
and predictive value of exogenous and endogenous hypoxic cell
markers. Radiother Oncol. 67:3–15. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cousins C and Sharp C: Medical
interventional procedures-reducing the radiation risks. Clin
Radiol. 59:468–473. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lee CG, Heijn M, di Tomaso E, et al:
Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor treatment augments tumor
radiation response under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Cancer
Res. 60:5565–5570. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Teicher BA, Holden SA, Ara G, et al:
Potentiation of cytotoxic cancer therapies by TNP-470 alone and
with other anti-angiogenic agents. Int J Cancer. 57:920–925. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor vasculature
with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination
therapy. Nat Med. 7:987–989. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|