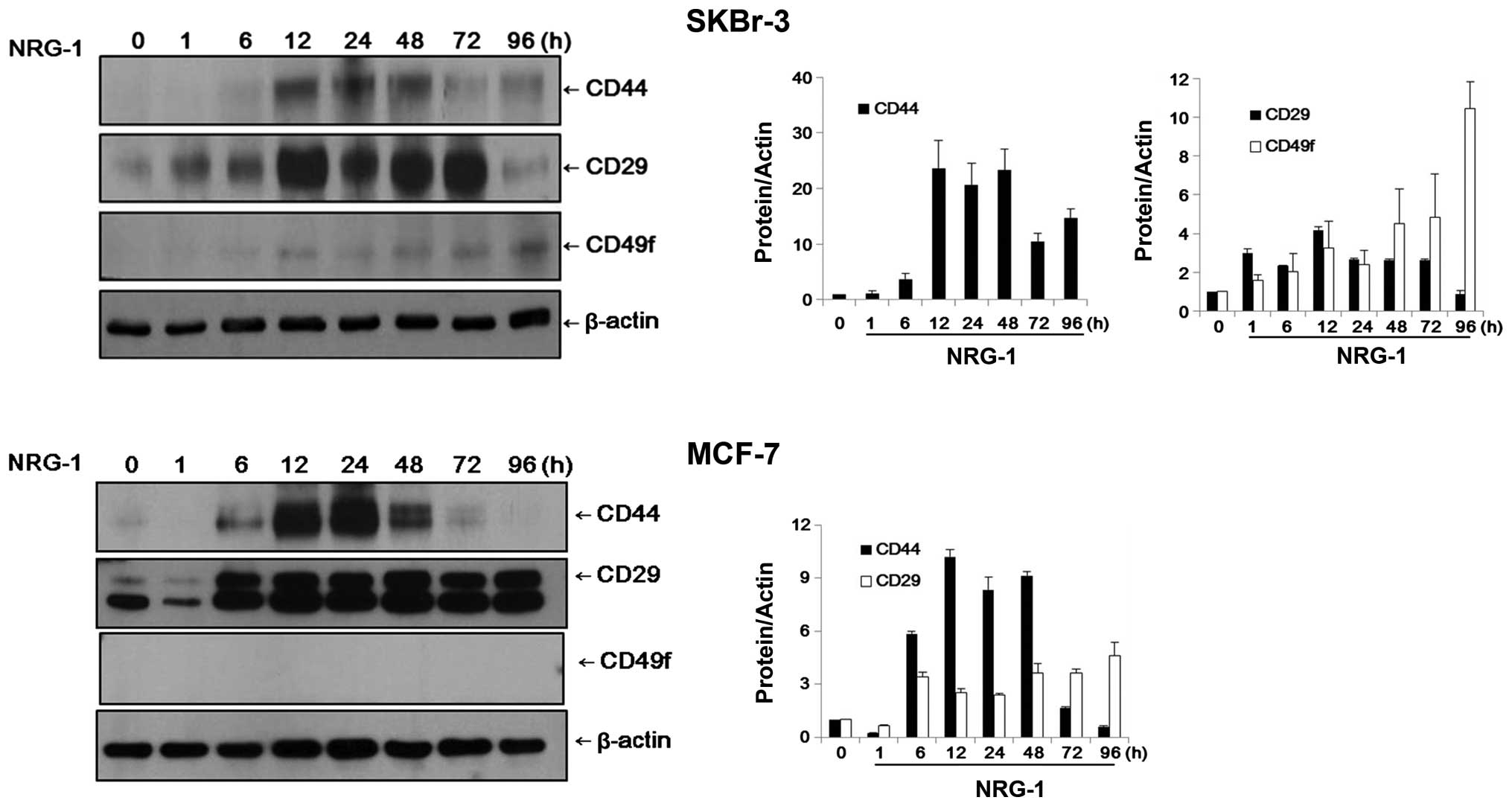
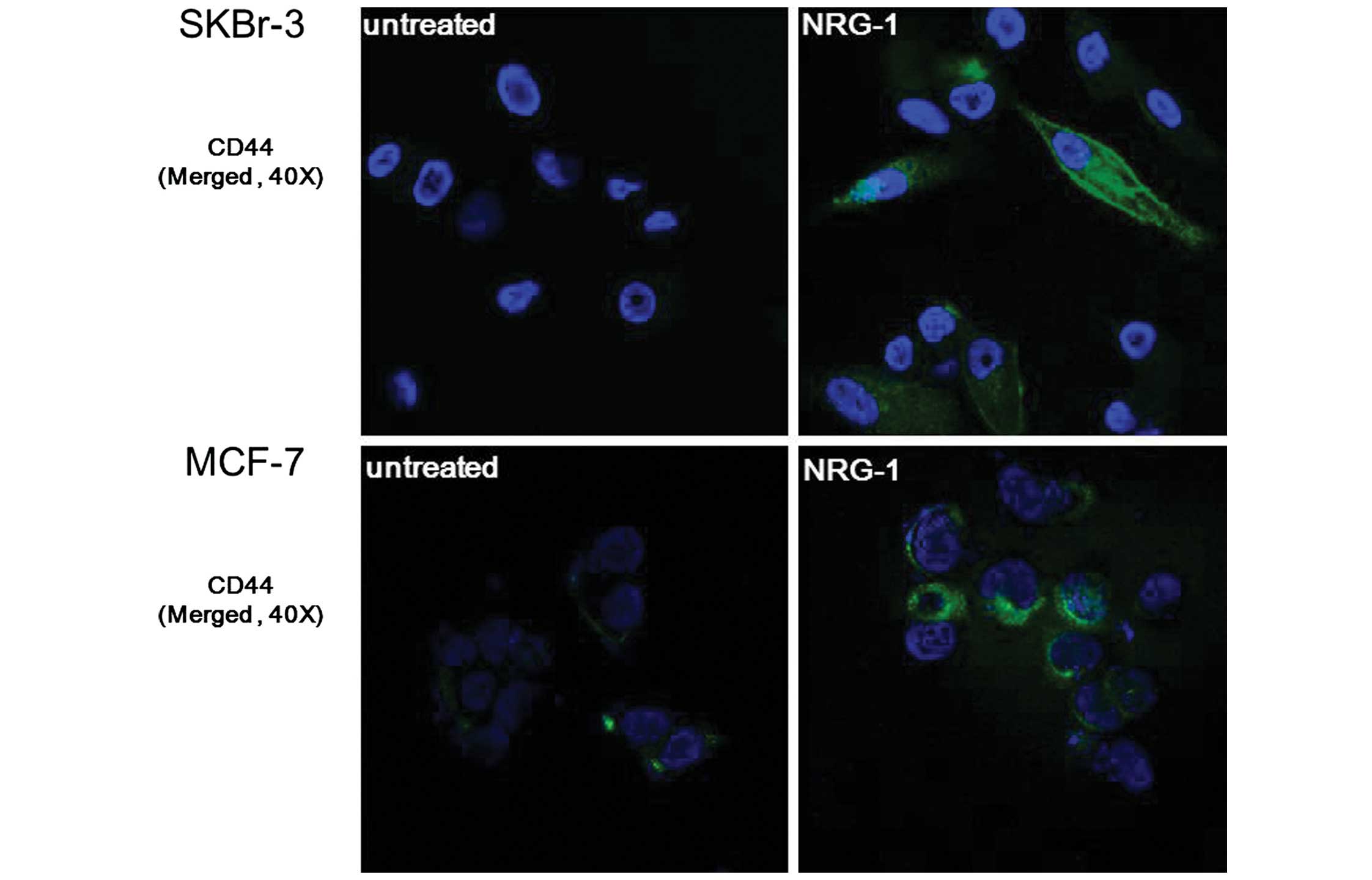
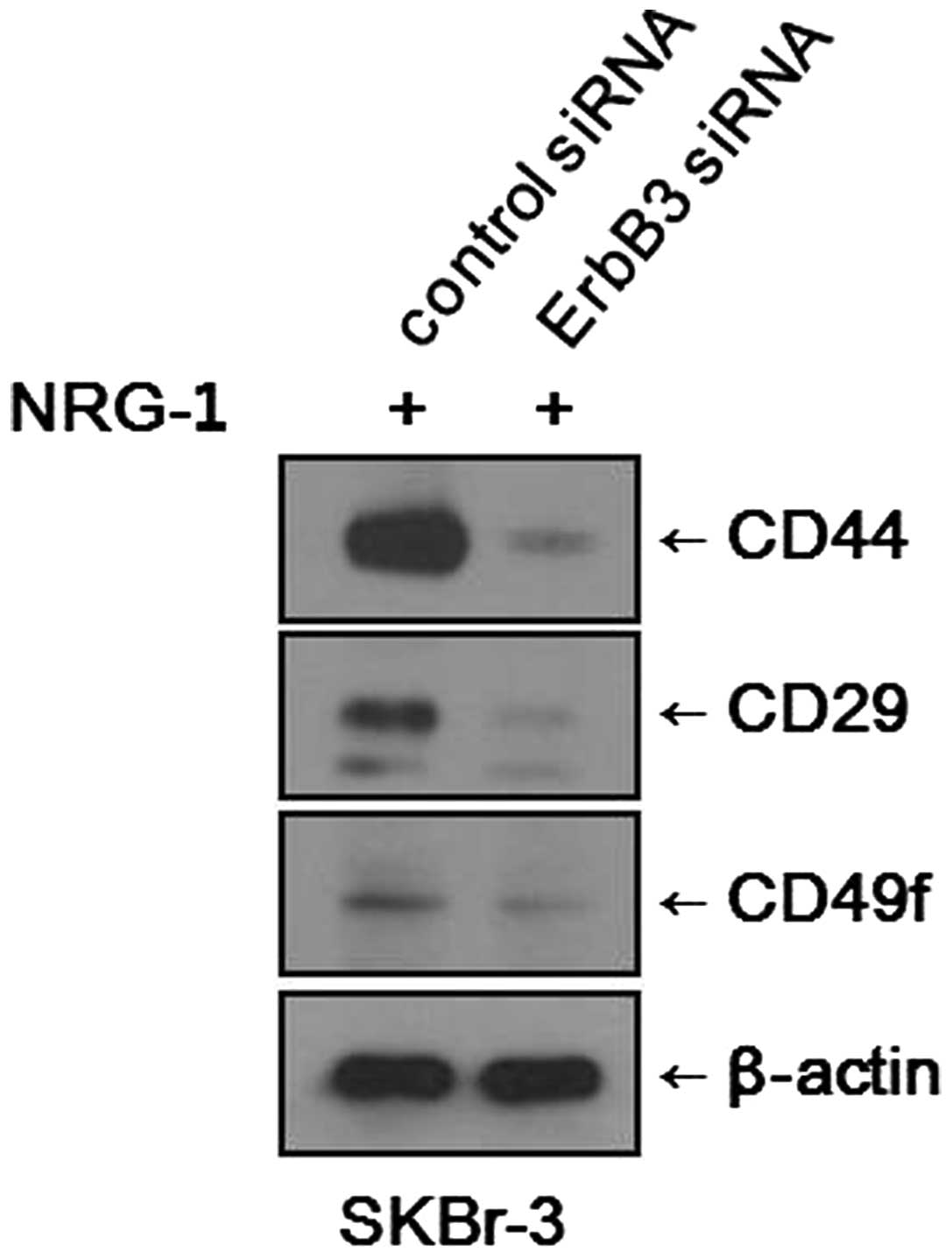
|
1
|
Holmes WE, Sliwkowski MX, Akita RW, et al:
Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2.
Science. 256:1205–1210. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Britsch S: The neuregulin-I/ErbB signaling
system in development and disease. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol.
190:1–65. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Atlas E, Cardillo M, Mehmi I,
Zahedkargaran H, Tang C and Lupu R: Heregulin is sufficient for the
promotion of tumorigenicity and metastasis of breast cancer cells
in vivo. Mol Cancer Res. 1:165–175. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vijapurkar U, Kim MS and Koland JG: Roles
of mitogen-activated protein kinase and phosphoinositide 3′-kinase
in ErbB2/ErbB3 coreceptor-mediated heregulin signaling. Exp Cell
Res. 284:291–302. 2003.
|
|
5
|
Hsieh AC and Moasser MM: Targeting HER
proteins in cancer therapy and the role of the non-target HER3. Br
J Cancer. 97:453–457. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Olayioye MA, Neve RM, Lane HA and Hynes
NE: The ErbB signaling network: receptor heterodimerization in
development and cancer. EMBO J. 19:3159–3167. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lupu R, Cardillo M, Cho C, et al: The
significance of heregulin in breast cancer tumor progression and
drug resistance. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 38:57–66. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hijazi MM, Thompson EW, Tang C, et al:
Heregulin regulates the actin cytoskeleton and promotes invasive
properties in breast cancer cell lines. Int J Oncol. 17:629–641.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng L, Zha Z, Lang B, Liu J and Yao X:
Heregulin-beta1 promotes metastasis of breast cancer cell line
SKBr-3 through upregulation of Snail and induction of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Lett. 280:50–60. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan G, Qian L, Song L, et al:
Heregulin-beta promotes matrix metalloproteinase-7 expression via
HER2-mediated AP-1 activation in MCF-7 cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
318:73–79. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cho SJ, Chae MJ, Shin BK, Kim HK and Kim
A: Akt- and MAPK-mediated activation and secretion of MMP-9 into
stroma in breast cancer cells upon heregulin treatment. Mol Med
Rep. 1:83–88. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial- mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kokkinos MI, Wafai R, Wong MK, Newgreen
DF, Thompson EW and Waltham M: Vimentin and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer - observations in vitro and in
vivo. Cells Tissues Organs. 185:191–203. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Micalizzi DS, Farabaugh SM and Ford HL:
Epithelial- mesenchymal transition in cancer: parallels between
normal development and tumor progression. J Mammary Gland Biol
Neoplasia. 15:117–134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ebben JD, Treisman DM, Zorniak M, Kutty
RG, Clark PA and Kuo JS: The cancer stem cell paradigm: a new
understanding of tumor development and treatment. Expert Opin Ther
Targets. 14:621–632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Blick T, Hugo H, Widodo E, et al:
Epithelial mesenchymal transition traits in human breast cancer
cell lines parallel the CD44(hi/)CD24(lo/-) stem cell phenotype in
human breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:235–252.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Creighton CJ, Chang JC and Rosen JM:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in tumor-initiating cells
and its clinical implications in breast cancer. J Mammary Gland
Biol Neoplasia. 15:253–260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mani SA, Guo W, Liao MJ, et al: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties
of stem cells. Cell. 133:704–715. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
May CD, Sphyris N, Evans KW, Werden SJ,
Guo W and Mani SA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
stem cells: a dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression.
Breast Cancer Res. 13:2022011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Almqvist PM, Mah R, Lendahl U, Jacobsson B
and Hendson G: Immunohistochemical detection of nestin in pediatric
brain tumors. J Histochem Cytochem. 50:147–158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dahlstrand J, Collins VP and Lendahl U:
Expression of the class VI intermediate filament nestin in human
central nervous system tumors. Cancer Res. 52:5334–5341.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyazono K: Transforming growth
factor-beta signaling in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
progression of cancer. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci.
85:314–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Taylor MA, Parvani JG and Schiemann WP:
The pathophysiology of epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by
transforming growth factor-beta in normal and malignant mammary
epithelial cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:169–190. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang H, Wu J, Zhang Y, et al: Transforming
growth factor β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition increases
cancer stem-like cells in the PANC-1 cell line. Oncol Lett.
3:229–233. 2012.
|
|
25
|
Hardy KM, Booth BW, Hendrix MJ, Salomon DS
and Strizzi L: ErbB/EGF signaling and EMT in mammary development
and breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:191–199.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim J, Jung J, Lee SJ, Lee JS and Park MJ:
Cancer stem-like cells persist in established cell lines through
autocrine activation of EGFR signaling. Oncol Lett. 3:607–612.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Y and Laterra J: Cancer stem cells:
distinct entities or dynamically regulated phenotypes? Cancer Res.
72:576–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Levenson AS and Jordan VC: MCF-7: the
first hormone-responsive breast cancer cell line. Cancer Res.
57:3071–3078. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lacroix M and Leclercq G: Relevance of
breast cancer cell lines as models for breast tumours: an update.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 83:249–289. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A,
Morrison SJ and Clarke MF: Prospective identification of
tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:3983–3988. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cariati M, Naderi A, Brown JP, et al:
Alpha-6 integrin is necessary for the tumourigenicity of a stem
cell-like subpopulation within the MCF-7 breast cancer cell line.
Int J Cancer. 122:298–304. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shackleton M, Vaillant F, Simpson KJ, et
al: Generation of a functional mammary gland from a single stem
cell. Nature. 439:84–88. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Taddei I, Deugnier MA, Faraldo MM, et al:
Beta1 integrin deletion from the basal compartment of the mammary
epithelium affects stem cells. Nat Cell Biol. 10:716–722. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
White DE, Kurpios NA, Zuo D, et al:
Targeted disruption of beta1-integrin in a transgenic mouse model
of human breast cancer reveals an essential role in mammary tumor
induction. Cancer Cell. 6:159–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sarrio D, Rodriguez-Pinilla SM, Hardisson
D, Cano A, Moreno-Bueno G and Palacios J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer relates to the basal-like phenotype.
Cancer Res. 68:989–997. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jeong H, Ryu YJ, An J, Lee Y and Kim A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer correlates with
high histological grade and triple-negative phenotype.
Histopathology. 60:E87–E95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kim S, Choi JH, Lim HI, et al: EGF-induced
MMP-9 expression is mediated by the JAK3/ERK pathway, but not by
the JAK3/STAT-3 pathway in a SKBr-3 breast cancer cell line. Cell
Signal. 21:892–898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park S, Jung HH, Park YH, Ahn JS and Im
YH: ERK/MAPK pathways play critical roles in EGFR ligands-induced
MMP1 expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 407:680–686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Frogne T, Benjaminsen RV, Sonne-Hansen K,
et al: Activation of ErbB3, EGFR and Erk is essential for growth of
human breast cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to
fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 114:263–275. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Garrett JT, Olivares MG, Rinehart C, et
al: Transcriptional and posttranslational up-regulation of HER3
(ErbB3) compensates for inhibition of the HER2 tyrosine kinase.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5021–5026. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sergina NV, Rausch M, Wang D, et al:
Escape from HER-family tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy by the
kinase-inactive HER3. Nature. 445:437–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|