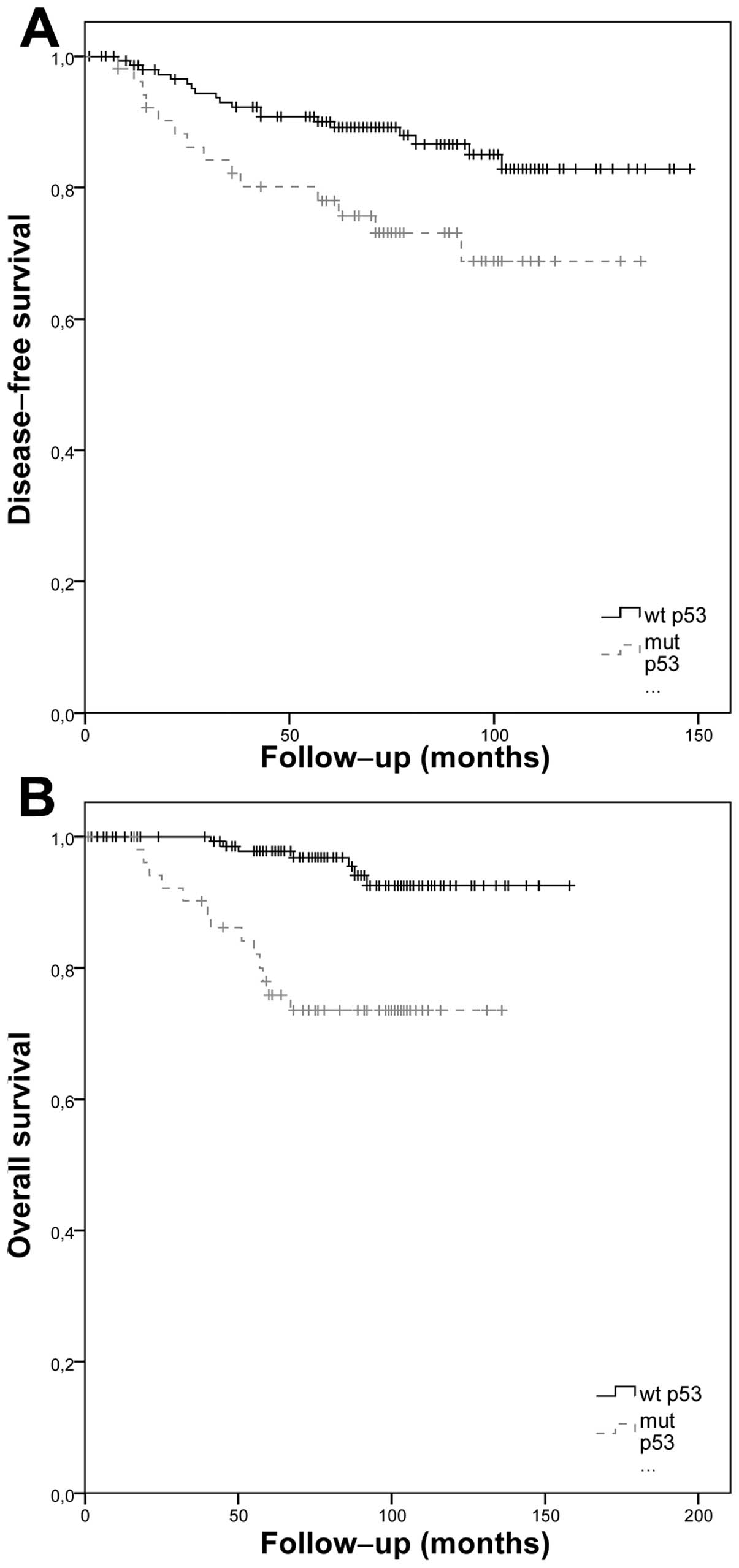
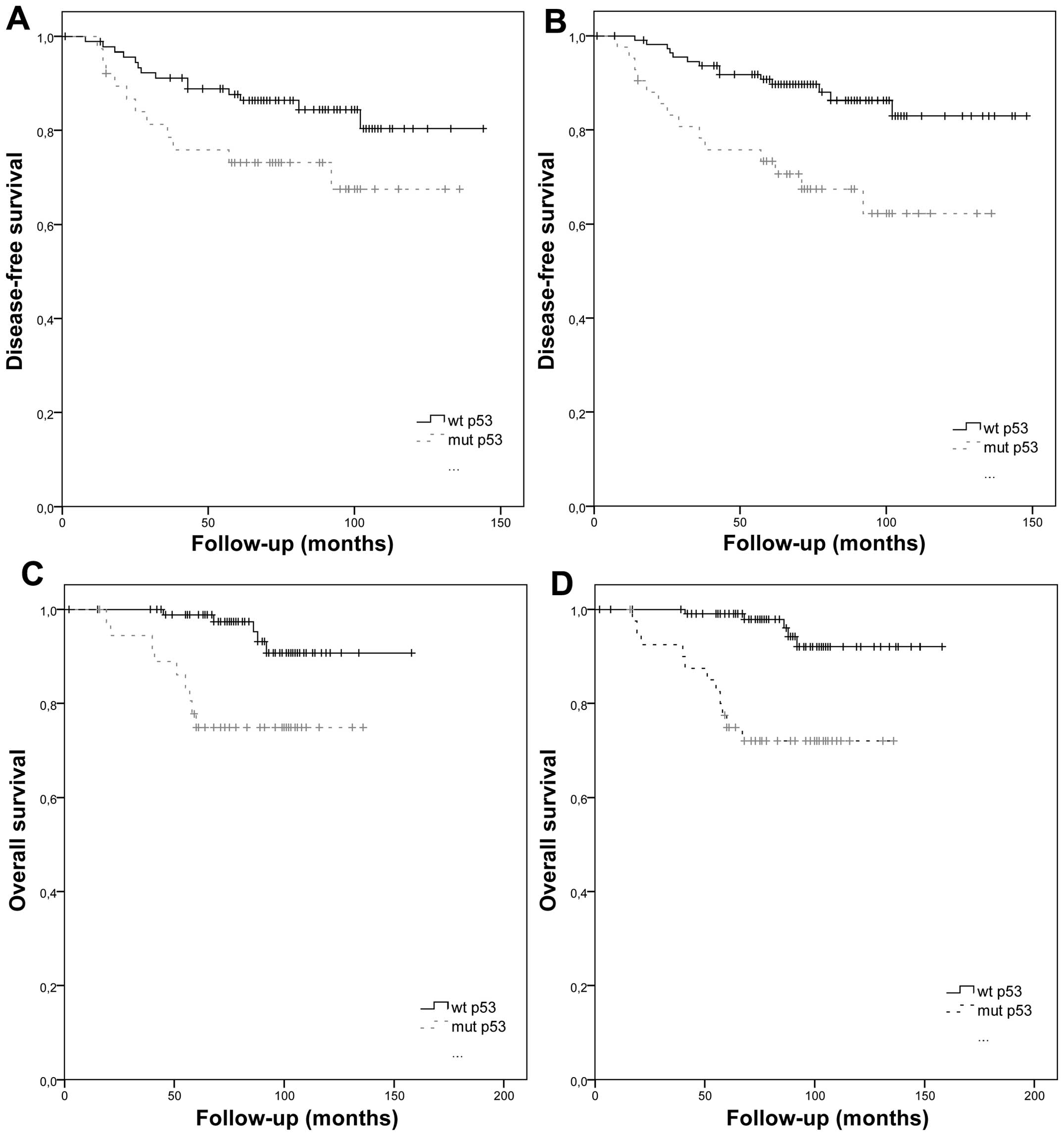
|
1
|
Dušek L, Mužík J, Gelnarová E, Fínek J,
Vyzula R and Abrahámová J: Cancer incidence and mortality in the
Czech Republic. Klin Onkol. 23:311–324. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Cancer Research UK. www.cancerresearchuk.orghttps://www.cancerresearchuk.org.
Accessed March, 2013
|
|
3
|
Kastan MB, Canman CE and Leonard CJ: P53,
cell cycle control and apoptosis: implications for cancer. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 14:3–15. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kastan MB, Onyekwere O, Sidransky D,
Vogelstein B and Craig RW: Participation of p53 protein in the
cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 51:6304–6311.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Soussi T and Béroud C: Assessing
TP53 status in human tumours to evaluate clinical outcome.
Nat Rev Cancer. 1:233–239. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Greenblatt M, Bennett W, Hollstein M and
Harris C: Mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene: clues
to cancer etiology and molecular pathogenesis. Cancer Res.
54:4855–4878. 1994.
|
|
7
|
Caron de Fromentel C and Soussi T: TP53
tumor suppressor gene: a model for investigating human mutagenesis.
Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 4:1–15. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brosh R and Rotter V: When mutants gain
new powers: news from the mutant p53 field. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:701–713. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho Y, Gorina S, Jeffrey PD and Pavletich
NP: Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex:
understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science. 265:346–355. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bertheau P, Espié M, Turpin E, et al:
TP53 status and response to chemotherapy in breast cancer.
Pathobiology. 75:132–139. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Harris CC and Hollstein M: Clinical
implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med.
329:1318–1327. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Olivier M, Langerød A, Carrieri P, et al:
The clinical value of somatic TP53 gene mutations in 1,794 patients
with breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 12:1157–1167. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Poeta ML, Manola J, Goldwasser MA, et al:
TP53 mutations and survival in squamous-cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 357:2552–2561. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hrstka R, Beranek M, Klocova K, Nenutil R
and Vojtesek B: Intronic polymorphisms in TP53 indicate lymph node
metastasis in breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 22:1205–1211.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elston C and Ellis I: Assessment of
histological grade. The Breast. 13. Churchill Livingstone;
Edinburgh, New York: pp. 356–384. 1998
|
|
16
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, et al: The
genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours
reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Geisler S, Lønning PE, Aas T, et al:
Influence of TP53 gene alterations and c-erbB-2 expression
on the response to treatment with doxorubicin in locally advanced
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 61:2505–2512. 2001.
|
|
18
|
Chrisanthar R, Knappskog S, Løkkevik E, et
al: CHEK2 mutations affecting kinase activity together with
mutations in TP53 indicate a functional pathway associated
with resistance to epirubicin in primary breast cancer. PLoS One.
3:e30622008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wahl AF, Donaldson KL, Faircnild C, et al:
Loss of normal p53 function confers sensitization to Taxol by
increasing G2/M arrest and apoptosis. Nat Med. 2:72–79. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chrisanthar R, Knappskog S, Løkkevik E, et
al: Predictive and prognostic impact of TP53 mutations and
MDM2 promoter genotype in primary breast cancer patients
treated with epirubicin or paclitaxel. PLoS One.
6:e192492011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonnefoi H, Piccart M, Bogaerts J, et al:
TP53 status for prediction of sensitivity to taxane versus
non-taxane neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer (EORTC
10994/BIG 1–00): a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
12:527–539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Geisler S, Børresen-Dale AL, Johnsen H, et
al: TP53 gene mutations predict the response to neoadjuvant
treatment with 5-fluorouracil and mitomycin in locally advanced
breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5582–5588. 2003.
|
|
23
|
Powell B, Soong R, Iacopetta B, Seshadri R
and Smith DR: Prognostic significance of mutations to different
structural and functional regions of the p53 gene in breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 6:443–451. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fernández-Cuesta L, Oakman C,
Falagan-Lotsch P, et al: Prognostic and predictive value of
TP53 mutations in nodepositive breast cancer patients
treated with anthracycline-or anthracycline/taxane-based adjuvant
therapy: results from the BIG 02–98 phase III trial. Breast Cancer
Res. 14:R702012.
|
|
25
|
Lai H, Ma F, Trapido E, Meng L and Lai S:
Spectrum of p53 tumor suppressor gene mutations and breast cancer
survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 83:57–66. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|