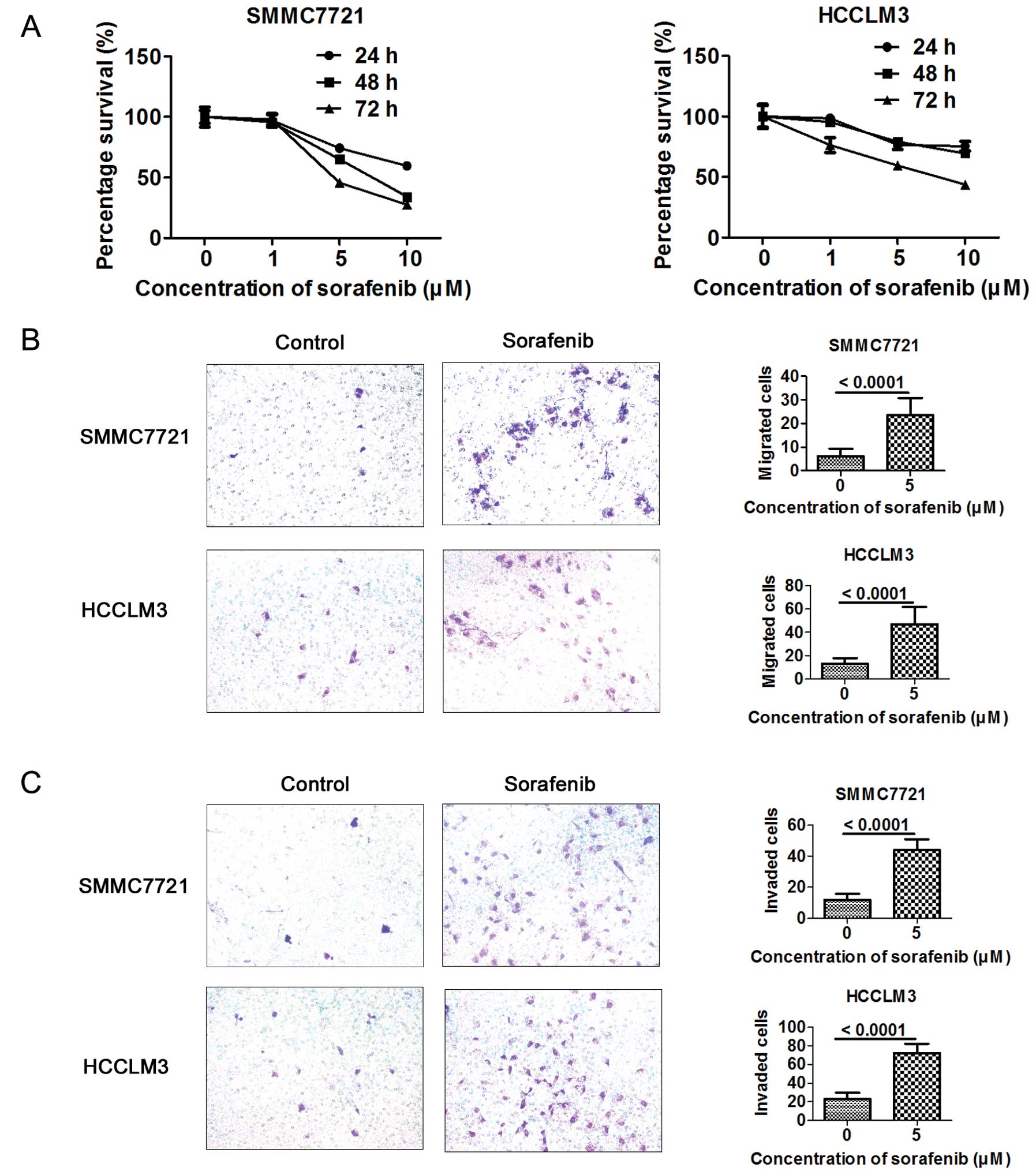
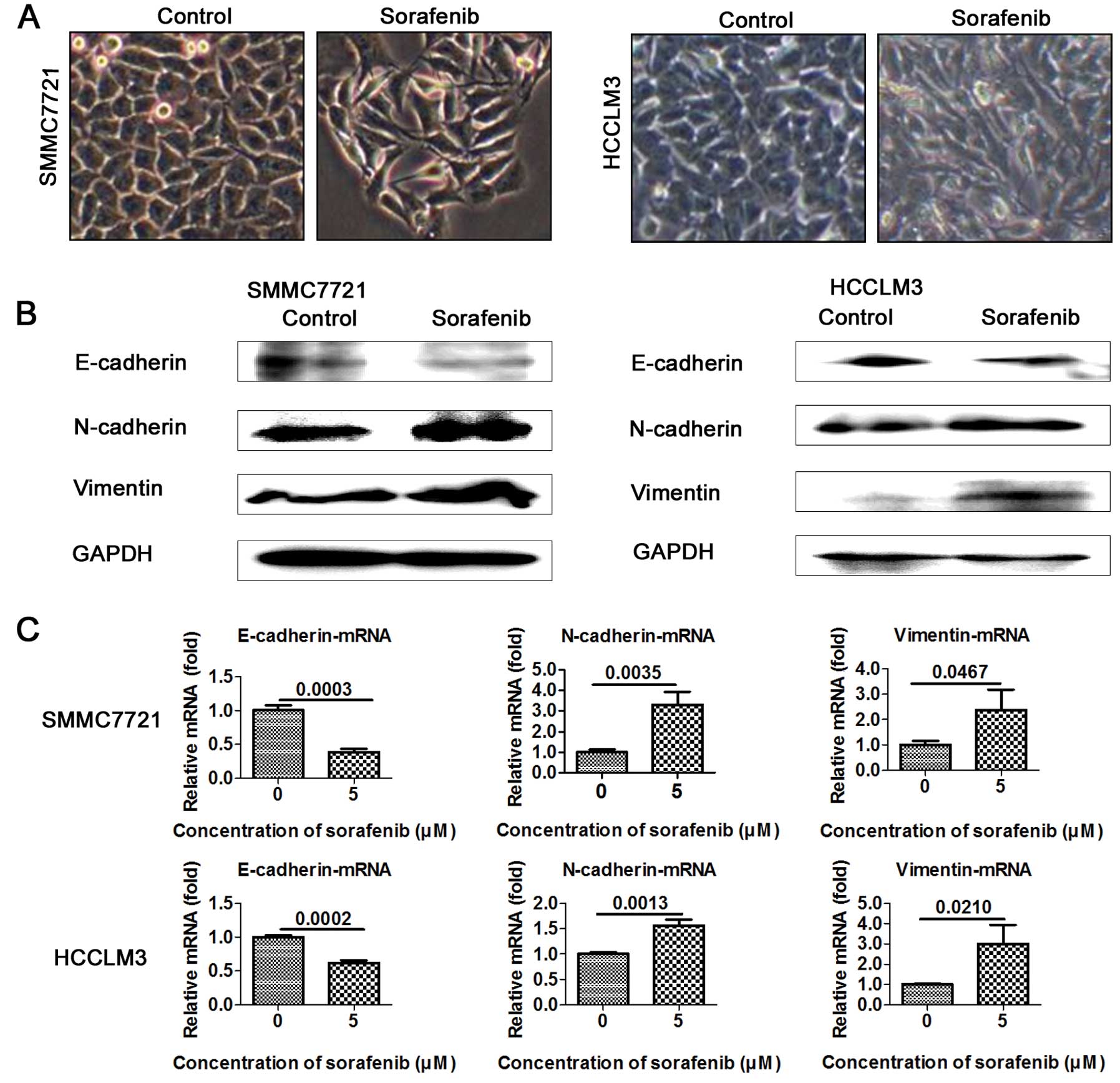
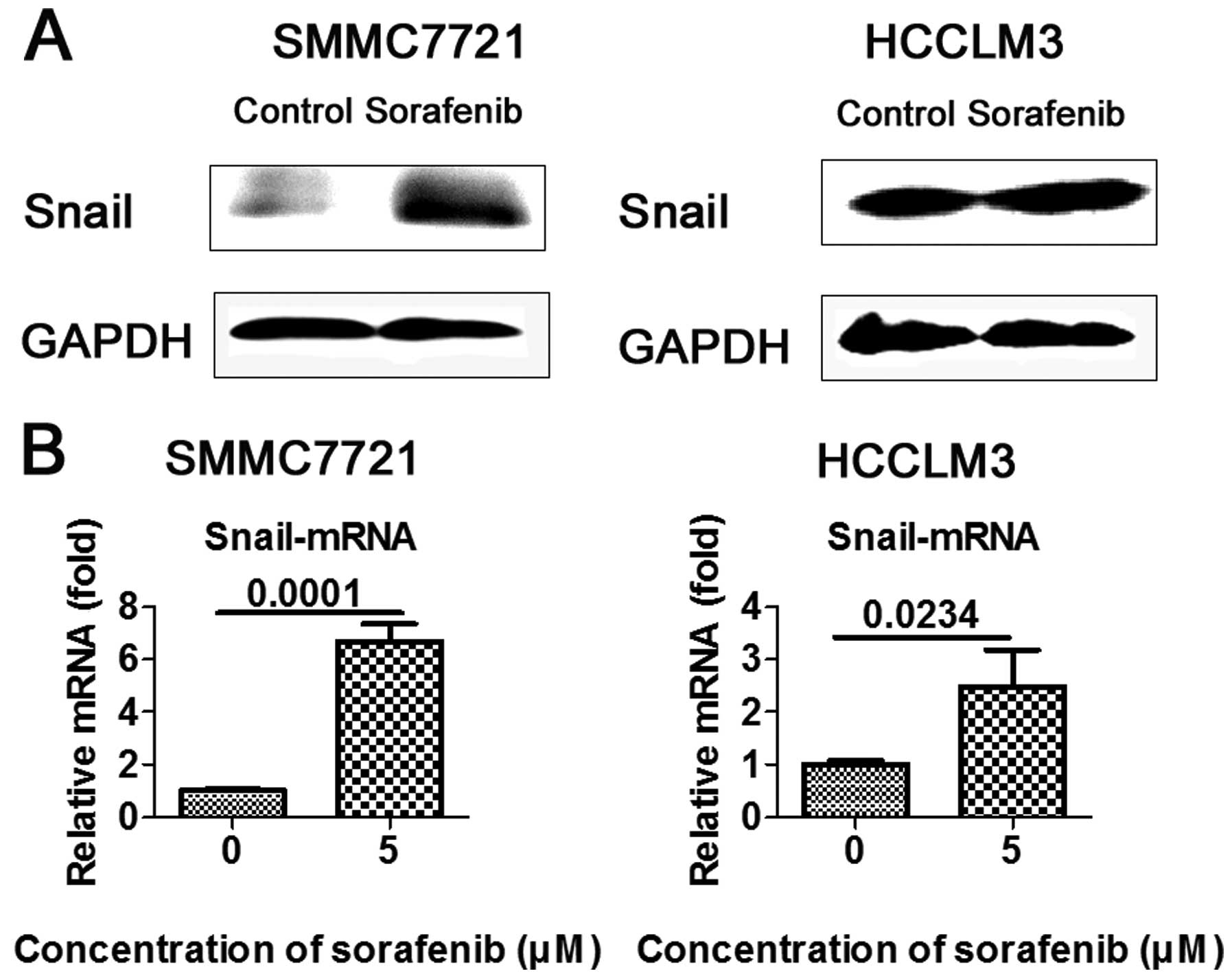
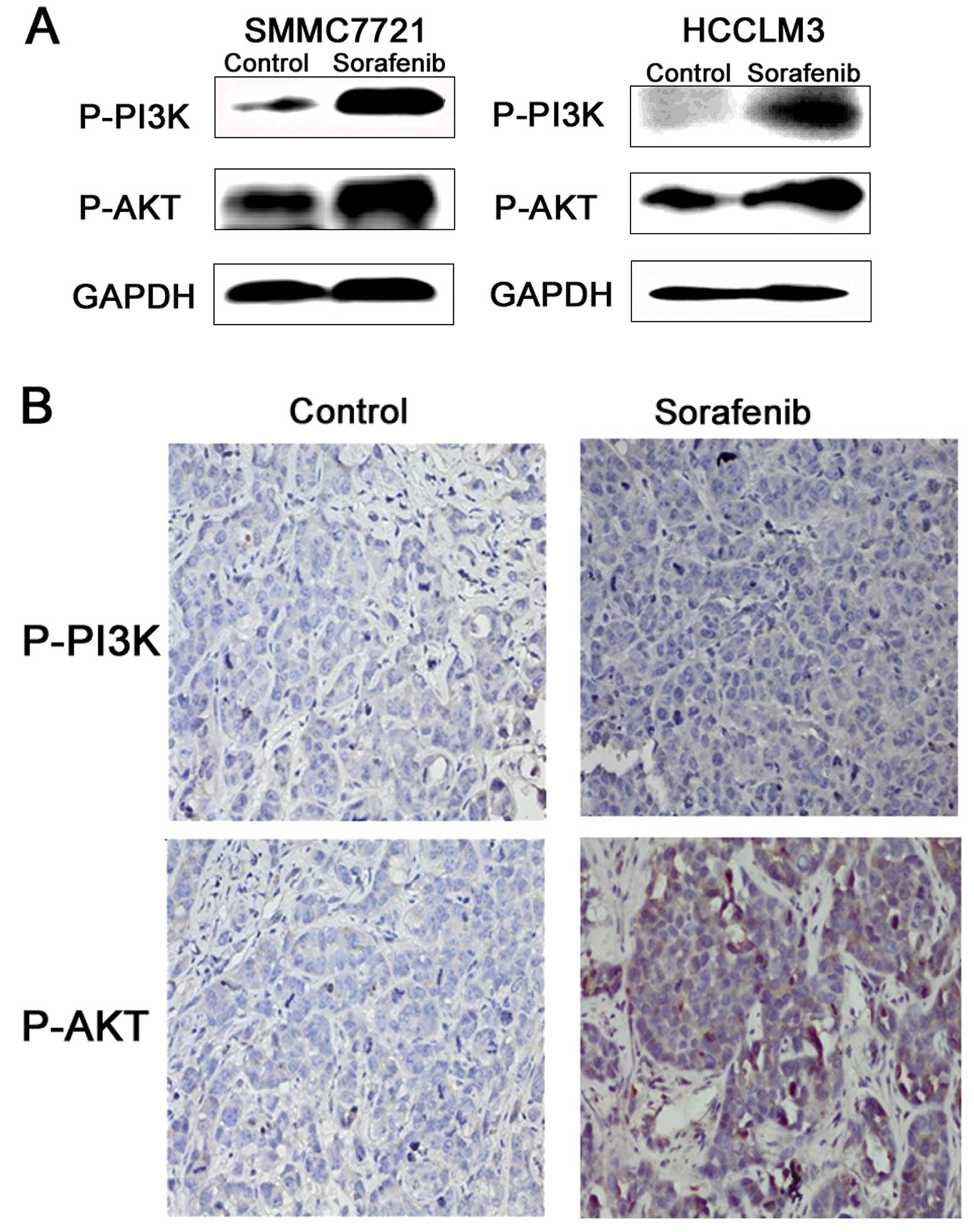
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gao JJ, Song PP, Tamura S, et al:
Standardization of perioperative management on
hepato-biliary-pancreatic surgery. Drug Discov Ther. 6:108–111.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Belghiti J and Fuks D: Liver resection and
transplantation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 1:71–82.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee Cheah Y and Chow KHP: Liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an appraisal of
current controversies. Liver Cancer. 1:183–189. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al: Efficacy
and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, et al:
Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
359:378–390. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Folkman J: Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic
implications. N Engl J Med. 285:1182–1186. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bergers G and Hanahan D: Modes of
resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:592–603.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason
GA, Christensen JG and Kerbel RS: Accelerated metastasis after
short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis.
Cancer Cell. 15:232–239. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pàez-Ribes M, Allen E, Hudock J, et al:
Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to
increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell.
15:220–231. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang W, Sun HC, Wang WQ, et al: Sorafenib
down-regulates expression of HTATIP2 to promote invasiveness and
metastasis of orthotopic hepatocellular carcinoma tumors in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:1641–1649. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lee JM, Dedhar S, Kalluri R and Thompson
EW: The epithelial-mesenchymal transition: new insights in
signaling, development, and disease. J Cell Biol. 172:973–981.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Barrallo-Gimeno A and Nieto MA: The Snail
genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: implications in
development and cancer. Development. 132:3151–3161. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martínez-Alvarez C, Blanco MJ, Pérez R, et
al: Snail family members and cell survival in physiological and
pathological cleft palates. Dev Biol. 265:207–218. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Emadi Baygi M, Soheili ZS, Schmitz I,
Sameie S and Schulz WA: Snail regulates cell survival and inhibits
cellular senescence in human metastatic prostate cancer cell lines.
Cell Biol Toxicol. 26:553–567. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cano A, Pérez-Moreno MA, Rodrigo I, et al:
The transcription factor snail controls epithelial-mesenchymal
transitions by repressing E-cadherin expression. Nat Cell Biol.
2:76–83. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang AL, Wang QS, Zhong YH, et al: Effect
of transcriptional factor snail on epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and tumor metastasis. Ai Zheng. 24:1301–1305. 2005.(In
Chinese).
|
|
19
|
Jordà M, Olmeda D, Vinyals A, et al:
Upregulation of MMP-9 in MDCK epithelial cell line in response to
expression of the Snail transcription factor. J Cell Sci.
118:3371–3385. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yokoyama K, Kamata N, Fujimoto R, et al:
Increased invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression by
Snail-induced mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinomas.
Int J Oncol. 22:891–898. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu P, Cheng H, Roberts TM and Zhao JJ:
Targeting the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway in cancer. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 8:627–644. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bakin AV, Tomlinson AK, Bhowmick NA, Moses
HL and Arteaga CL: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase function is
required for transforming growth factor β-mediated epithelial to
mesenchymal transition and cell migration. J Biol Chem.
275:36803–36810. 2000.
|
|
23
|
Grille SJ, Bellacosa A, Upson J, et al:
The protein kinase Akt induces epithelial mesenchymal transition
and promotes enhanced motility and invasiveness of squamous cell
carcinoma lines. Cancer Res. 63:2172–2178. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Altomare DA and Testa JR: Perturbations of
the AKT signaling pathway in human cancer. Oncogene. 24:7455–7464.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role
of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005.
|
|
26
|
Wang H, Quah SY, Dong JM, Manser E, Tang
JP and Zeng Q: PRL-3 down-regulates PTEN expression and signals
through PI3K to promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer
Res. 67:2922–2926. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song LB, Li J, Liao WT, et al: The
polycomb group protein Bmi-1 represses the tumor suppressor PTEN
and induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in human
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. J Clin Invest. 119:3626–3636.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yoo YA, Kang MH, Lee HJ, et al: Sonic
hedgehog pathway promotes metastasis via activation of AKT, EMT,
and MMP-9 in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 71:7061–7070. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zuo JH, Zhu W, Li MY, et al: Activation of
EGFR promotes squamous carcinoma SCC10A cell migration and invasion
via inducing EMT-like phenotype change and MMP-9-mediated
degradation of E-cadherin. J Cell Biochem. 112:2508–2517. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qiao M, Sheng S and Pardee AB: Metastasis
and AKT activation. Cell Cycle. 7:2991–2996. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Emadi Baygi M, Soheili ZS, Essmann F, et
al: Slug/SNAI2 regulates cell proliferation and invasiveness of
metastatic prostate cancer cell lines. Tumour Biol. 31:297–307.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bolós V, Peinado H, Pérez-Moreno MA, Fraga
MF, Esteller M and Cano A: The transcription factor Slug represses
E-cadherin expression and induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transitions: a comparison with Snail and E47 repressors. J Cell
Sci. 116:499–511. 2003.
|
|
33
|
Chen KF, Chen HL, Tai WT, et al:
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway
mediates acquired resistance to sorafenib in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 337:155–161. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gao Y, Li HX, Xu LT, et al: Bufalin
enhances the anti-proliferative effect of sorafenib on human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells through downregulation of ERK. Mol
Biol Rep. 39:1683–1689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang P, Chen Z, Meng ZQ, et al: Dual role
of Ski in pancreatic cancer cells: tumor-promoting versus
metastasis-suppressive function. Carcinogenesis. 30:1497–1506.
2009.
|
|
36
|
Li H, Wang P, Gao Y, et al:
Na+/K+-ATPase α3 mediates sensitivity of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells to bufalin. Oncol Rep. 25:825–830.
2011.
|
|
37
|
Yang MH, Chen CL, Chau GY, et al:
Comprehensive analysis of the independent effect of twist and snail
in promoting metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
50:1464–1474. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zucchini-Pascal N, Peyre L and Rahmani R:
Crosstalk between beta-catenin and snail in the induction of
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocarcinoma: role of
the ERK1/2 pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 14:20768–20792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, et al: Dual
regulation of Snail by GSK-3β-mediated phosphorylation in control
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol. 6:931–940.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wen W, Ding J, Sun W, et al: Cyclin
G1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition via phosphoinositide
3-kinase/Akt signaling facilitates liver cancer progression.
Hepatology. 55:1787–1798. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi GM, Ke AW, Zhou J, et al: CD151
modulates expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 and promotes
neoangiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 52:183–196. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Thiery JP and Sleeman JP: Complex networks
orchestrate epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 7:13–42. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Pérez-Tenorio G and Stål O; Southeast
Sweden Breast Cancer Group. Activation of AKT/PKB in breast cancer
predicts a worse outcome among endocrine treated patients. Br J
Cancer. 86:540–545. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Scheid MP and Woodgett JR: PKB/AKT:
functional insights from genetic models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:760–768. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xue G, Restuccia DF, Lan Q, et al:
Akt/PKB-mediated phosphorylation of Twist1 promotes tumor
metastasis via mediating cross-talk between PI3K/Akt and TGF-β
signaling axes. Cancer Discov. 2:248–259. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|