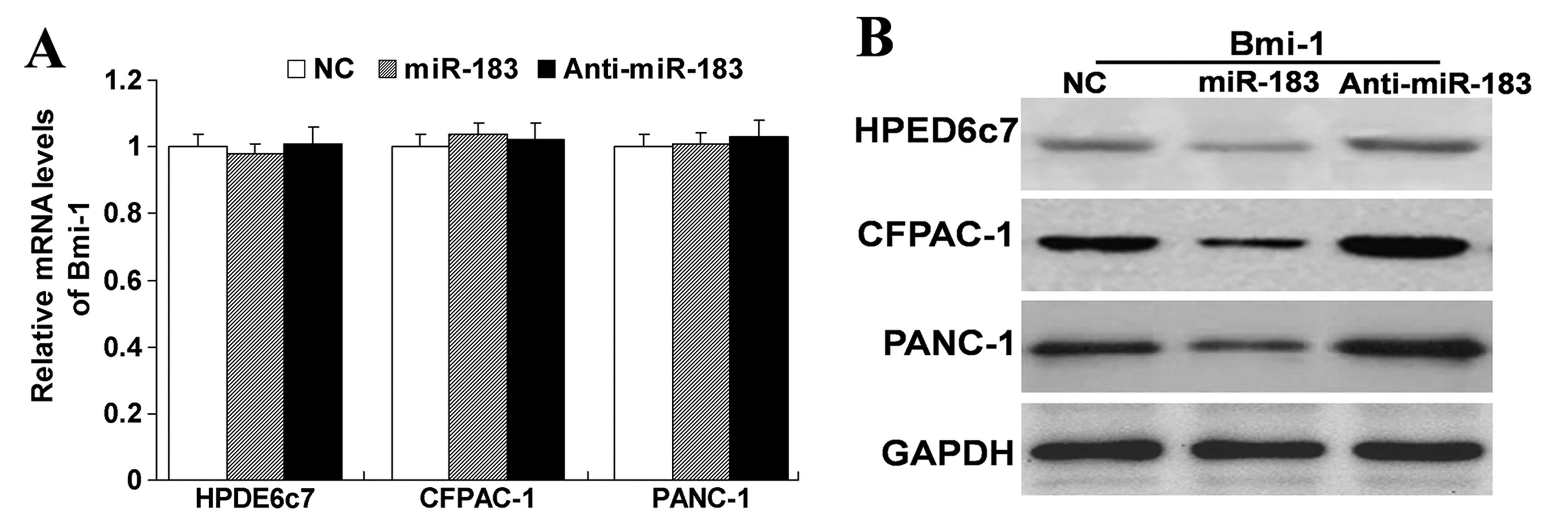
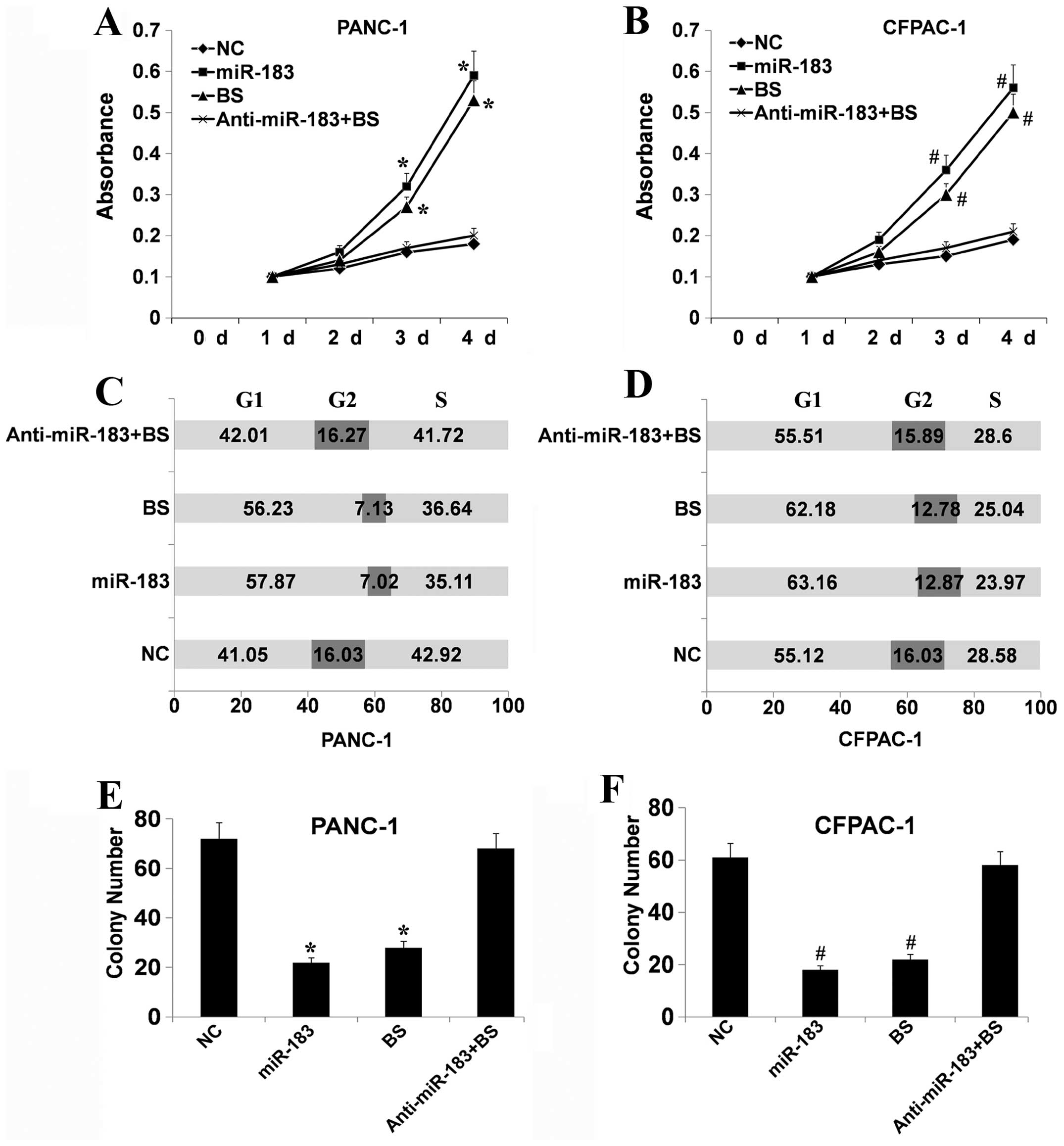
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN, Artus CG, et
al: Inhibition of translational initiation by Let-7 microRNA in
human cells. Science. 309:1573–1576. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zamore PD and Haley B: Ribo-gnome: the big
world of small RNAs. Science. 309:1519–1524. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bastian BC, LeBoit PE, Hamm H, Bröcker EB
and Pinkel D: Chromosomal gains and losses in primary cutaneous
melanomas detected by comparative genomic hybridization. Cancer
Res. 58:2170–2175. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Motoyama K, Inoue H, Takatsuno Y, et al:
Over- and under-expressed microRNAs in human colorectal cancer. Int
J Oncol. 34:1069–1075. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin WM, Baker AC, Beroukhim R, et al:
Modeling genomic diversity and tumor dependency in malignant
melanoma. Cancer Res. 68:664–673. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang G, Mao W and Zheng S: MicroRNA-183
regulates Ezrin expression in lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett.
582:3663–3668. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ambros V and Lee RC: Identification of
microRNAs and other tiny noncoding RNAs by cDNA cloning. Methods
Mol Biol. 265:131–158. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pillai RS, Bhattacharyya SN and Filipowicz
W: Repression of protein synthesis by miRNAs: how many mechanisms?
Trends Cell Biol. 17:118–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Caldas C and Brenton JD: Sizing up miRNAs
as cancer genes. Nat Med. 11:712–714. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kefas B, Godlewski J, Comeau L, et al:
microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the
Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res.
68:3566–3572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ladeiro Y, Couchy G, Balabaud C, et al:
MicroRNA profiling in hepatocellular tumors is associated with
clinical features and oncogene/tumor suppressor gene mutations.
Hepatology. 47:1955–1963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Agirre X, Jiménez-Velasco A, San
José-Enériz E, et al: Downregulation of hsa-miR-10a in
chronic myeloid leukemia CD34+ cells increases
USF2-mediated cell growth. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1830–1840. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Mattie MD, Benz CC, Bowers J, et al:
Optimized high-throughput microRNA expression profiling provides
novel biomarker assessment of clinical prostate and breast cancer
biopsies. Mol Cancer. 5:242006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Dwyer RM and Kerin
MJ: Dysregulated miR-183 inhibits migration in breast cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 10:5022010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, et al: The
EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing
stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 11:1487–1495. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jacobs JJ and van Lohuizen M: Polycomb
repression: from cellular memory to cellular proliferation and
cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1602:151–161. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kondo Y, Shen L, Cheng AS, et al: Gene
silencing in cancer by histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation
independent of promoter DNA methylation. Nat Genet. 40:741–750.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raaphorst FM: Deregulated expression of
Polycomb-group oncogenes in human malignant lymphomas and
epithelial tumors. Hum Mol Genet. 14(Spec1): R93–R100. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van Lohuizen M, Verbeek S, Scheijen B,
Wientjens E, van der Gulden H and Berns A: Identification of
cooperating oncogenes in Eμ-myc transgenic mice by provirus
tagging. Cell. 65:737–752. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID, et al: Hedgehog
signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant
human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:6063–6071. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Marino S, DePinho RA
and van Lohuizen M: The oncogene and Polycomb-group gene
bmi-1 regulates cell proliferation and senescence through
the ink4a locus. Nature. 397:164–168. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dimri GP, Martinez JL, Jacobs JJ, et al:
The Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and
immortalizes human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res.
62:4736–4745. 2002.
|
|
25
|
Mihic-Probst D, Kuster A, Kilgus S, et al:
Consistent expression of the stem cell renewal factor BMI-1 in
primary and metastatic melanoma. Int J Cancer. 121:1764–1770. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Effendi K, Mori T, Komuta M, Masugi Y, Du
W and Sakamoto M: Bmi-1 gene is upregulated in early-stage
hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with ATP-binding cassette
transporter B1 expression. Cancer Sci. 101:666–672. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sasaki M, Ikeda H, Itatsu K, et al: The
overexpression of polycomb group proteins Bmi-1 and EZH2 is
associated with the progression and aggressive biological behavior
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Lab Invest. 88:873–882. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Pan K, Zhang HK, et al: Increased
polycomb-group oncogene Bmi-1 expression correlates with poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
134:535–541. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song W, Tao K, Li H, et al: Bmi-1 is
related to proliferation, survival and poor prognosis in pancreatic
cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:1754–1760. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sparmann A and van Lohuizen M: Polycomb
silencers control cell fate, development and cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 6:846–856. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li DW, Tang HM, Fan JW, et al: Expression
level of Bmi-1 oncoprotein is associated with progression and
prognosis in colon cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:997–1006.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu JH, Song LB, Zhang X, et al: Bmi-1
expression predicts prognosis for patients with gastric carcinoma.
J Surg Oncol. 97:267–272. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Song LB, Zeng MS, Liao WT, et al: Bmi-1 is
a novel molecular marker of nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression
and immortalizes primary human nasopharyngeal epithelial cells.
Cancer Res. 66:6225–6232. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jiang Y, Su B, Meng X, et al: Effect of
siRNA-mediated silencing of Bmi-1 gene expression on HeLa cells.
Cancer Sci. 101:379–386. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|