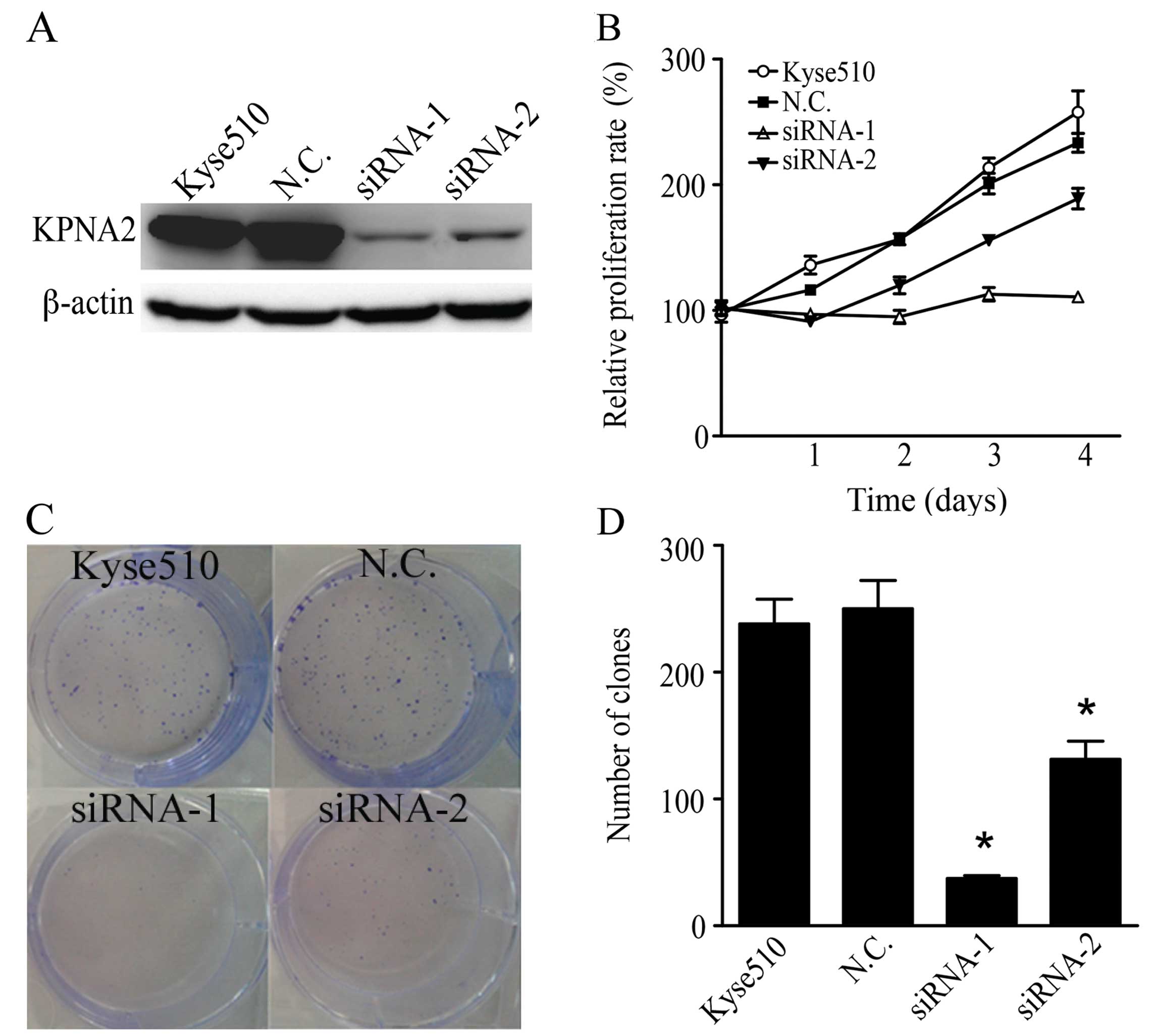
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang GQ, Abnet CC, Shen Q, Lewin KJ, Sun
XD, Roth MJ, Qiao YL, Mark SD, Dong ZW, Taylor PR and Dawsey SM:
Histological precursors of oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma:
results from a 13 year prospective follow up study in a high risk
population. Gut. 54:187–192. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kelley JB, Talley AM, Spencer A, Gioeli D
and Paschal BM: Karyopherin α7 (KPNA7), a divergent member of the
importin α family of nuclear import receptors. BMC Cell Biol.
11:632010.
|
|
4
|
Stewart M: Molecular mechanism of the
nuclear protein import cycle. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:195–208.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Goldfarb DS, Corbett AH, Mason DA,
Harreman MT and Adam SA: Importin α: a multipurpose
nuclear-transport receptor. Trends Cell Biol. 14:505–514. 2004.
|
|
6
|
Dahl E, Kristiansen G, Gottlob K, Klaman
I, Ebner E, Hinzmann B, Hermann K, Pilarsky C, Dürst M,
Klinkhammer-Schalke M, Blaszyk H, Knuechel R, Hartmann A, Rosenthal
A and Wild PJ: Molecular profiling of laser-microdissected matched
tumor and normal breast tissue identifies karyopherin α2 as a
potential novel prognostic marker in breast cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 12:3950–3960. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dankof A, Fritzsche FR, Dahl E, Pahl S,
Wild P, Dietel M, Hartmann A and Kristiansen G: KPNA2 protein
expression in invasive breast carcinoma and matched peritumoral
ductal carcinoma in situ. Virchows Arch. 451:877–881. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gluz O, Wild P, Meiler R, Diallo-Danebrock
R, Ting E, Mohrmann S, Schuett G, Dahl E, Fuchs T, Herr A, Gaumann
A, Frick M, Poremba C, Nitz UA and Hartmann A: Nuclear karyopherin
α2 expression predicts poor survival in patients with advanced
breast cancer irrespective of treatment intensity. Int J Cancer.
123:1433–1438. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Zheng M, Tang L, Huang L, Ding H, Liao WT,
Zeng MS and Wang HY: Overexpression of karyopherin-2 in epithelial
ovarian cancer and correlation with poor prognosis. Obstet Gynecol.
116:884–891. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Winnepenninckx V1, Lazar V, Michiels S,
Dessen P, Stas M, Alonso SR, Avril MF, Ortiz Romero PL, Robert T,
Balacescu O, Eggermont AM, Lenoir G, Sarasin A, Tursz T, van den
Oord JJ and Spatz A: Melanoma Group of the European Organization
for Research and Treatment of Cancer: Gene expression profiling of
primary cutaneous melanoma and clinical outcome. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 98:472–482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van der Watt PJ, Maske CP, Hendricks DT,
Parker MI, Denny L, Govender D, Birrer MJ and Leaner VD: The
Karyopherin proteins, Crm1 and Karyopherin β1, are overexpressed in
cervical cancer and are critical for cancer cell survival and
proliferation. Int J Cancer. 124:1829–1840. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Wang CI, Wang CL, Wang CW, Chen CD, Wu CC,
Liang Y, Tsai YH, Chang YS, Yu JS and Yu CJ: Importin subunit
alpha-2 is identified as a potential biomarker for non-small cell
lung cancer by integration of the cancer cell secretome and tissue
transcriptome. Int J Cancer. 128:2364–2372. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gousias K, Becker AJ, Simon M and
Niehusmann P: Nuclear karyopherin a2: a novel biomarker for
infiltrative astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 109:545–553. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mortezavi A, Hermanns T, Seifert HH,
Baumgartner MK, Provenzano M, Sulser T, Burger M, Montani M,
Ikenberg K, Hofstädter F, Hartmann A, Jaggi R, Moch H, Kristiansen
G and Wild PJ: KPNA2 expression is an independent adverse predictor
of biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Clin Cancer
Res. 17:1111–1121. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yoshitake K, Tanaka S, Mogushi K, Aihara
A, Murakata A, Matsumura S, Mitsunori Y, Yasen M, Ban D, Noguchi N,
Irie T, Kudo A, Nakamura N, Tanaka H and Arii S: Importin-α1 as a
novel prognostic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg
Oncol. 18:2093–2103. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Jensen JB1, Munksgaard PP, Sørensen CM,
Fristrup N, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K, Ulhøi BP, Jensen KM, Ørntoft TF
and Dyrskjøt L: High expression of karyopherin-α2 defines poor
prognosis in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and in patients
with invasive bladder cancer undergoing radical cystectomy. Eur
Urol. 59:841–848. 2011.
|
|
17
|
Sakai M, Sohda M, Miyazaki T, Suzuki S,
Sano A, Tanaka N, Inose T, Nakajima M, Kato H and Kuwano H:
Significance of karyopherin-α 2 (KPNA2) expression in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 30:851–856. 2010.
|
|
18
|
Sun Y, Mi W, Cai J, Ying W, Liu F, Lu H,
Qiao Y, Jia W, Bi X, Lu N, Liu S, Qian X and Zhao X: Quantitative
proteomic signature of liver cancer cells: tissue transglutaminase
2 could be a novel protein candidate of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Proteome Res. 7:3847–3859. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu Y, Zhou L, Huang J, Liu F, Yu J, Zhan
Q, Zhang L and Zhao X: Role of Smac in determining the
chemotherapeutic response of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 17:5412–5422. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
van der Watt PJ, Ngarande E and Leaner VD:
Overexpression of Kpnβ1 and Kpnα2 importin proteins in cancer
derives from deregulated E2F activity. PLoS One. 6:e277232011.
|
|
21
|
Wang CI, Chien KY, Wang CL, Liu HP, Cheng
CC, Chang YS, Yu JS and Yu CJ: Quantitative proteomics reveals
regulation of karyopherin subunit alpha-2 (KPNA2) and its potential
novel cargo proteins in nonsmall cell lung cancer. Mol Cell
Proteomics. 11:1105–1122. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ishida S, Huang E, Zuzan H, Spang R, Leone
G, West M and Nevins JR: Role for E2F in control of both DNA
replication and mitotic functions as revealed from DNA microarray
analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4684–4699. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu W, Giangrande PH and Nevins JR: E2Fs
link the control of G1/S and G2/M transcription. EMBO J.
23:4615–4626. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dong QM, Zhang JQ, Li Q, Bracher JC,
Hendricks DT and Zhao XH: Clinical significance of serum expression
of GROβ in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 17:2658–2662. 2011.
|
|
25
|
Quensel C, Friedrich B, Sommer T, Hartmann
E and Kohler M: In vivo analysis of importin α proteins reveals
cellular proliferation inhibition and substrate specificity. Mol
Cell Biol. 24:10246–10255. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Huang L, Wang HY, Li JD, Wang JH, Zhou Y,
Luo RZ, Yun JP, Zhang Y, Jia WH and Zheng M: KPNA2 promotes cell
proliferation and tumorigenicity in epithelial ovarian carcinoma
through upregulation of c-Myc and downregulation of FOXO3a. Cell
Death Dis. 4:e7452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ren B, Cam H, Takahashi Y, Volkert T,
Terragni J, Young RA and Dynlacht BD: E2F integrates cell cycle
progression with DNA repair, replication, and G2/M
checkpoints. Genes Dev. 16:245–256. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zannini L, Lecis D, Lisanti S, Benetti R,
Buscemi G, Schneider C and Delia D: Karyopherin-α2 protein
interacts with Chk2 and contributes to its nuclear import. J Biol
Chem. 278:42346–42351. 2003.
|
|
29
|
Narod SA and Foulkes WD: BRCA1 and
BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:665–676. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Tseng SF, Chang CY, Wu KJ and Teng SC:
Importin KPNA2 is required for proper nuclear localization and
multiple functions of NBS1. J Biol Chem. 280:39594–39600. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sandrock K, Bielek H, Schradi K, Schmidt G
and Klugbauer N: The nuclear import of the small GTPase Rac1 is
mediated by the direct interaction with karyopherin α2. Traffic.
11:198–209. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ebihara Y, Miyamoto M, Shichinohe T,
Kawarada Y, Cho Y, Fukunaga A, Murakami S, Uehara H, Kaneko H,
Hashimoto H, Murakami Y, Itoh T, Okushiba S, Kondo S and Katoh H:
Overexpression of E2F-1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
correlates with tumor progression. Dis Esophagus. 17:150–154. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|