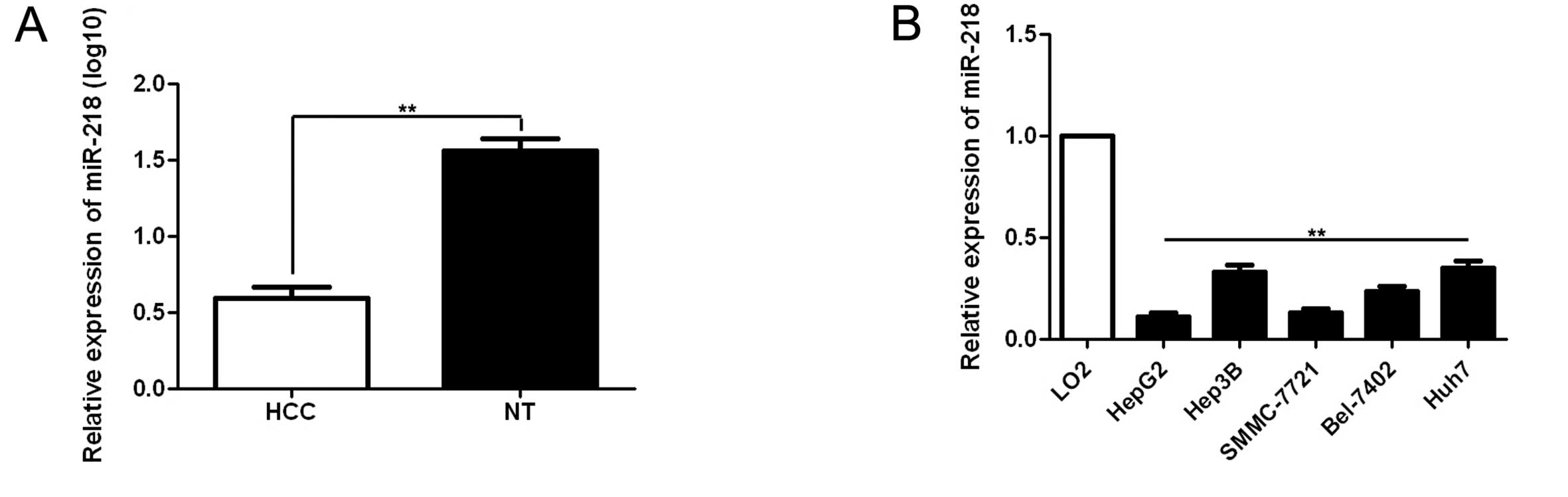
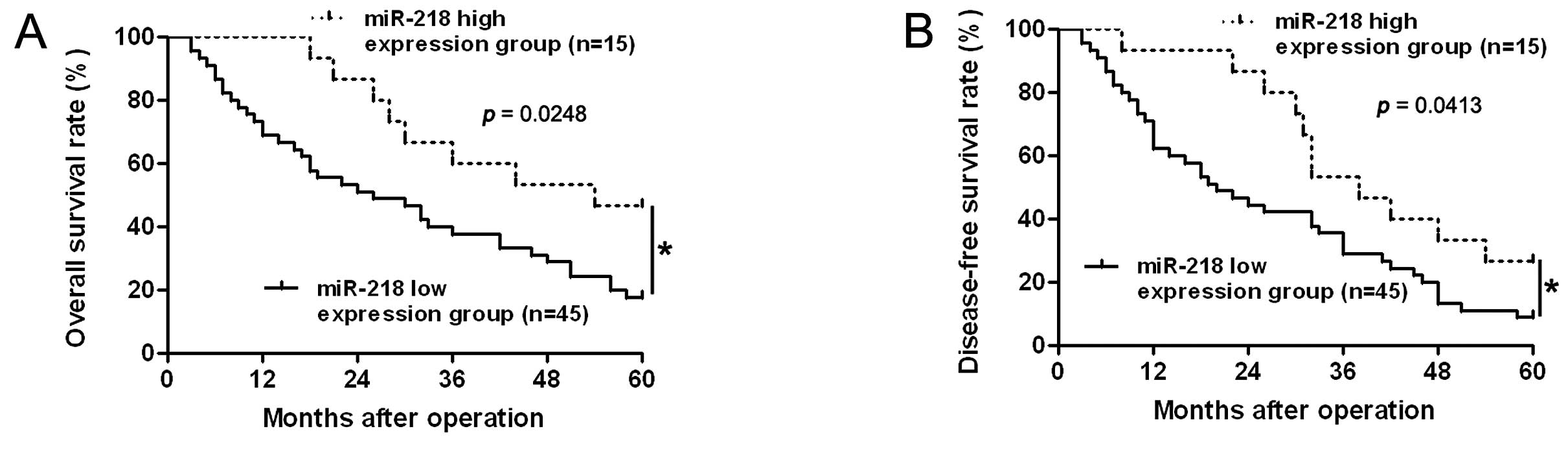
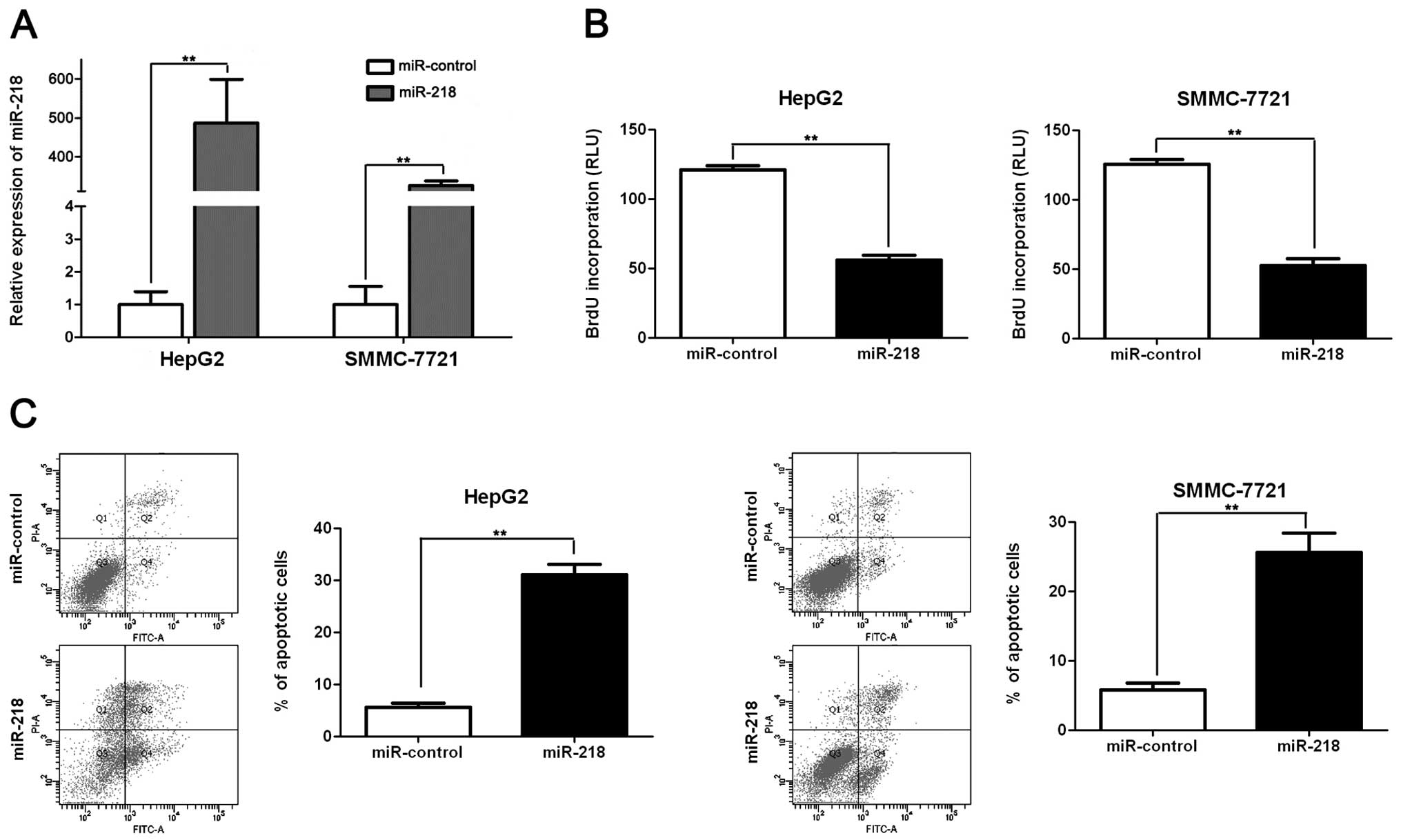
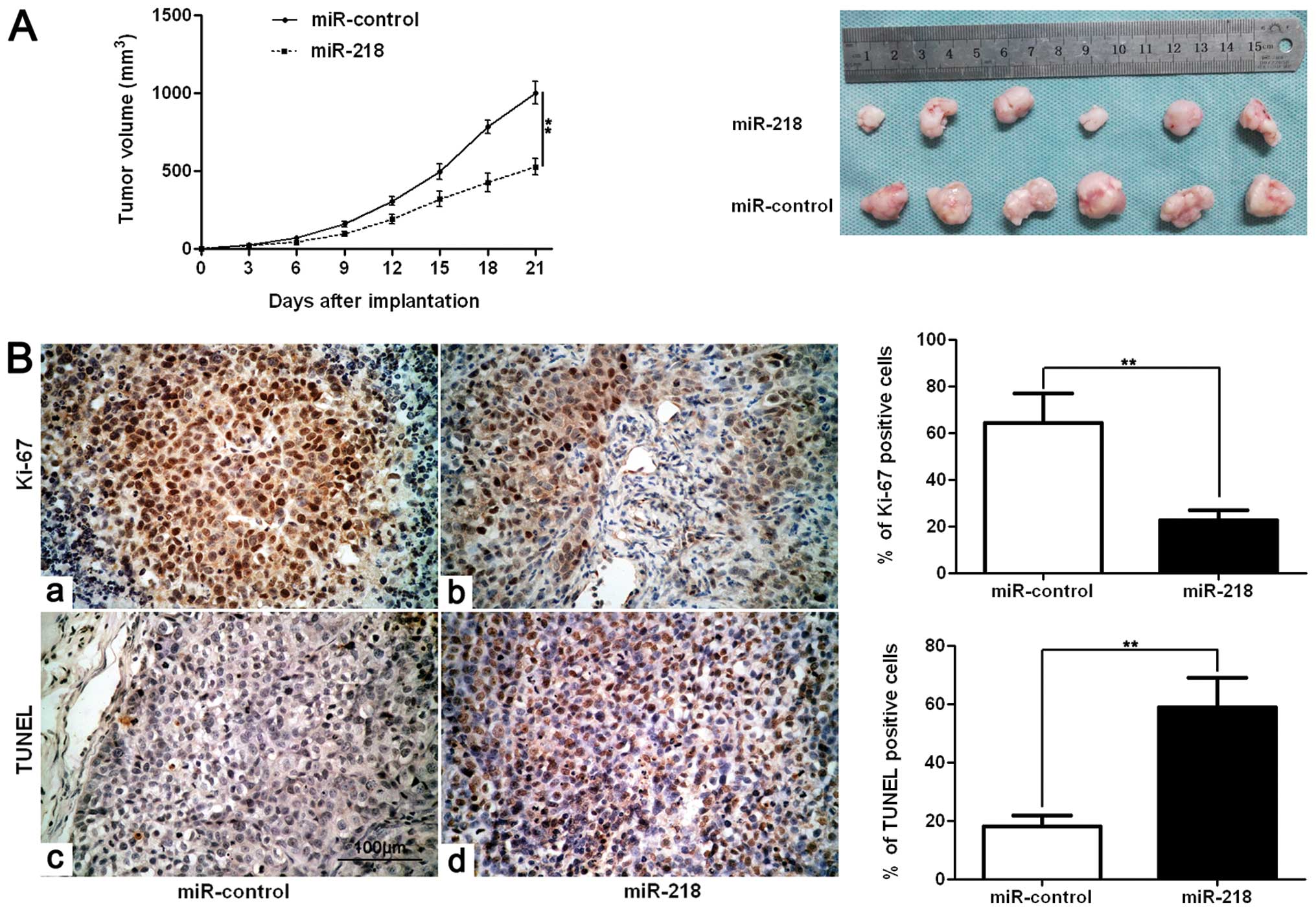
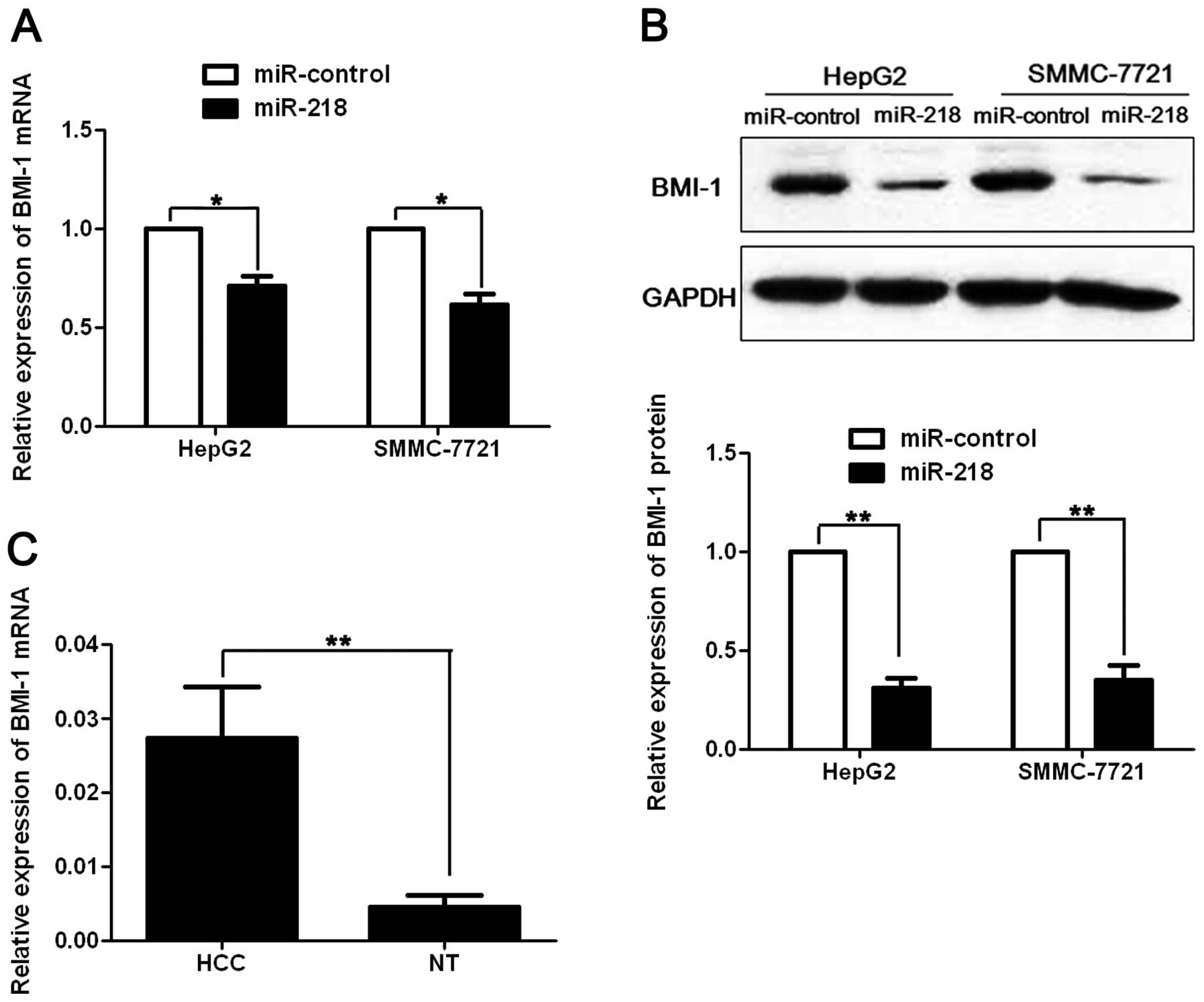
|
1
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Zan X, Han S, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with the
expression of c-Myc, cyclin E and p53 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 42:904–910. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Zhou Z, et al: Recombinant
human adenovirus-p53 injection induced apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cell lines mediated by p53-Fbxw7 pathway, which controls
c-Myc and cyclin E. PLoS One. 8:e685742013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jia Z, Wang K, Wang G, Zhang A and Pu P:
MiR-30a-5p antisense oligonucleotide suppresses glioma cell growth
by targeting SEPT7. PLoS One. 8:e550082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Baer C, Claus R and Plass C: Genome-wide
epigenetic regulation of miRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res. 73:473–477.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wong CM, Kai AK, Tsang FH and Ng IO:
Regulation of hepatocarcinogenesis by microRNAs. Front Biosci.
5:49–60. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gramantieri L, Fornari F, Callegari E, et
al: MicroRNA involvement in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Mol
Med. 12:2189–2204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Davidson MR, Larsen JE, Yang IA, et al:
MicroRNA-218 is deleted and down-regulated in lung squamous cell
carcinoma. PLoS One. 5:e125602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chiyomaru T, Enokida H, Kawakami K, et al:
Functional role of LASP1 in cell viability and its regulation by
microRNAs in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 30:434–443. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Song L, Huang Q, Chen K, et al: miR-218
inhibits the invasive ability of glioma cells by direct
downregulation of IKK-β. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 402:135–140.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tie J, Pan Y, Zhao L, et al: MiR-218
inhibits invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the
Robo1 receptor. PLoS Genet. 6:e10008792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li J, Ping Z and Ning H: MiR-218 impairs
tumor growth and increases chemo-sensitivity to cisplatin in
cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:16053–16064. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He X, Dong Y, Wu CW, et al: MicroRNA-218
inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes apoptosis in colon
cancer by downregulating BMI1 polycomb ring finger oncogene. Mol
Med. 18:1491–1498. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leite KR, Sousa-Canavez JM, Reis ST, et
al: Change in expression of miR-let7c, miR-100, and miR-218 from
high grade localized prostate cancer to metastasis. Urol Oncol.
29:265–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uesugi A, Kozaki K, Tsuruta T, et al: The
tumor suppressive microRNA miR-218 targets the mTOR
component Rictor and inhibits AKT phosphorylation in oral
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5765–5778. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li BS, Zhao YL, Guo G, et al: Plasma
microRNAs, miR-223, miR-21 and miR-218, as novel potential
biomarkers for gastric cancer detection. PLoS One. 7:e416292012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng X, Gai X, Ding F, Lu Z, Tu K, Yao Y
and Liu Q: Histone acetyltransferase PCAF up-regulated cell
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma via acetylating histone H4
and inactivating AKT signaling. Mol Cancer. 12:962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Yin G, Zan X, Yao Y and Liu
Q: Evaluation of Fbxw7 expression and its correlation with
expression of SREBP-1 in a mouse model of NAFLD. Mol Med Rep.
6:525–530. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang MK, Kim RH, Kim SJ, et al: Elevated
Bmi-1 expression is associated with dysplastic cell transformation
during oral carcinogenesis and is required for cancer cell
replication and survival. Br J Cancer. 96:126–133. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu Z, Xu Y, Du J, Tan J and Jiao H:
Expression of microRNA-218 in human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma and its correlation with tumor progression and
patient survival. J Surg Oncol. 109:89–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tu Y, Gao X, Li G, et al: MicroRNA-218
inhibits glioma invasion, migration, proliferation, and cancer
stem-like cell self-renewal by targeting the polycomb group gene
Bmi1. Cancer Res. 73:6046–6055. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tong YQ, Liu B, Zheng HY, He YJ, Gu J, Li
F and Li Y: Overexpression of BMI-1 is associated with poor
prognosis in cervical cancer. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 8:e55–e62.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yin T, Wei H, Leng Z, et al: Bmi-1
promotes the chemoresistance, invasion and tumorigenesis of
pancreatic cancer cells. Chemotherapy. 57:488–496. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schuringa JJ and Vellenga E: Role of the
polycomb group gene BMI1 in normal and leukemic hematopoietic stem
and progenitor cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 17:294–299. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Douglas D, Hsu JH, Hung L, et al: BMI-1
promotes ewing sarcoma tumorigenicity independent of CDKN2A
repression. Cancer Res. 68:6507–6515. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li X, Yang Z, Song W, et al:
Overexpression of Bmi-1 contributes to the invasion and metastasis
of hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing the expression of matrix
metalloproteinase (MMP)-2, MMP-9 and vascular endothelial growth
factor via the PTEN/ PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 43:793–802.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|