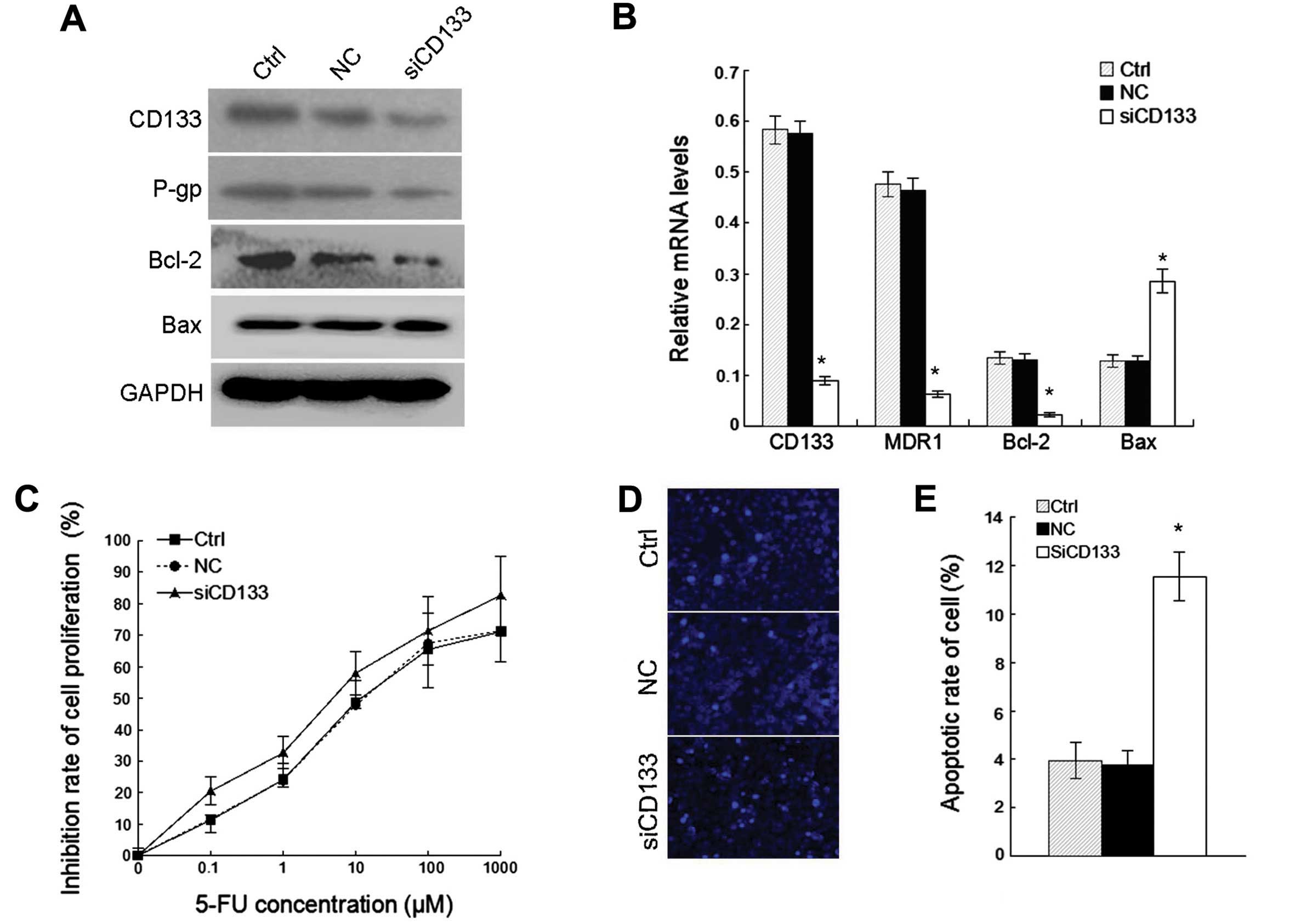
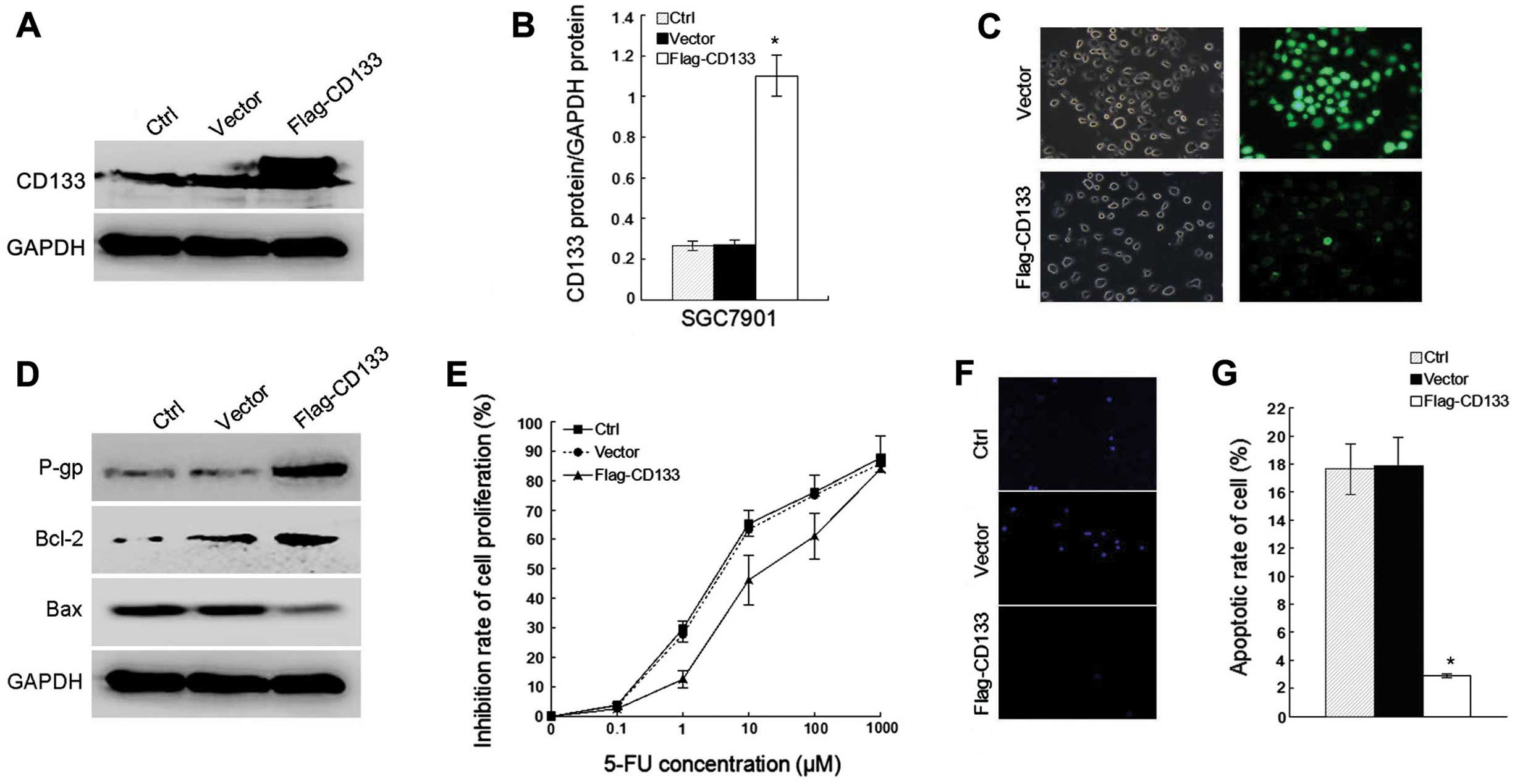
|
1
|
Bertuccio P, Chatenoud L, Levi F, Praud D,
Ferlay J, Negri E, Malvezzi M and La Vecchia C: Recent patterns in
gastric cancer: a global overview. Int J Cancer. 125:666–673. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ji JF: Several surgical problems in the
treatment of gastric cancer. J Pract Oncol. 18:341–346. 2003.
|
|
3
|
Peichev M, Naiyer AJ, Pereira D, Zhu Z,
Lane WJ, Williams M, Oz MC, Hicklin DJ, Witte L, Moore MA and Rafii
S: Expression of VEGFR-2 and AC133 by circulating human
CD34+ cells identifies a population of functional
endothelial precursors. Blood. 95:952–958. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
O’Brien CA, Pollett A, Gallinger S and
Dick JE: A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour
growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature. 445:106–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, Pilozzi E,
Biffoni M, Di Virgilio A, Conticello C, Ruco L, Peschle C and De
Maria R: Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung
cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 15:504–514. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Singh SK, Clarke ID, Terasaki M, Bonn VE,
Hawkins C, Squire J and Dirks PB: Identification of a cancer stem
cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 63:5821–5828.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hermann PC, Huber SL, Herrler T, Aicher A,
Ellwart JW, Guba M, Bruns CJ and Heeschen C: Distinct populations
of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity
in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell. 1:313–323. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee HH, Seo KJ, An CH, Kim JS and Jeon HM:
CD133 expression is correlated with chemoresistance and early
recurrence of gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 106:999–1004. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu G, Yuan X, Zeng Z, Tunici P, Ng H,
Abdulkadir IR, Lu L, Irvin D, Black KL and Yu JS: Analysis of gene
expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem
cells in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer. 5:672006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baba T, Convery PA, Matsumura N, Whitaker
RS, Kondoh E, Perry T, Huang Z, Bentley RC, Mori S, Fujii S, Marks
JR, Berchuck A and Murphy SK: Epigenetic regulation of CD133
and tumorigenicity of CD133+ ovarian cancer cells.
Oncogene. 28:209–218. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Zhu Y1, Jiang B, Cai C, Wang S, Wu J and
Yu J: Relationship between CD133 and chemoresistance in human
gastric cancer and its associated mechanism. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai
Ke Za Zhi. 17:168–174. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
12
|
Kim R, Emi M and Tanabe K: Role of
mitochondria as the gardens of cell death. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 57:545–553. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumor stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Haraguchi N, Utsunomiya T, Inoue H, Tanaka
F, Mimori K, Barnard GF and Mori M: Characterization of a side
population of cancer cells from human gastrointestinal system. Stem
Cells. 24:506–513. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma S, Lee TK, Zheng BJ, Chan KW and Guan
XY: CD133+ HCC cancer stem cells confer chemoresistance
by preferential expression of the Akt/PKB survival pathway.
Oncogene. 27:1749–1758. 2008.
|
|
16
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo
P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J and Greenberg ME: AKT
promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead
transcription factor. Cell. 96:857–868. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Curnock AP, Logan MK and Ward SG:
Chemokine signalling: pivoting around multiple phosphoinositide
3-kinases. Immunology. 105:125–136. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and
cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-κB. J Clin
Inves. 107:241–246. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Ozes ON, Mayo LD, Gustin JA, Pfeffer SR,
Pfeffer LM and Donner DB: NF-κB activation by tumour necrosis
factor requires the AKT serine-threonine kinase. Nature. 401:82–85.
1999.
|
|
21
|
Sartelet H, Imbriglio T, Nyalendo C,
Haddad E, Annabi B, Duval M, Fetni R, Victor K, Alexendrov L,
Sinnett D, Fabre M and Vassal G: CD133 expression is associated
with poor outcome in neuroblastoma via chemoresistance mediated by
the AKT pathway. Histopathology. 60:1144–1155. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang YK, Zhu YL, Qiu FM, Zhang T, Chen ZG,
Zheng S and Huang J: Activation of Akt and MAPK pathways enhances
the tumorigenicity of CD133+ primary colon cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 31:1376–1380. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lu RQ, Wu JG, Zhou GC, Jiang HG, Yu JW and
Jiang BJ: Sorting of CD133(+) subset cells in human gastric cancer
and the identification of their tumor initiating cell-like
properties. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 15:174–179. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, Wang SS,
Shibata W, Vigneshwaran R, Gordon SA, Shimada Y and Wang TC:
Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface
marker CD44. Stem Cells. 27:1006–1020. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin JY, Kim JO, Lee SK, Chae HS and Kang
JH: LY294002 may overcome 5-FU resistance via down-regulation of
activated p-AKT in Epstein-Barr virus-positive gastric cancer
cells. BMC Cancer. 10:4252010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wei Y, Jiang Y, Zou F, Liu Y, Wang S, Xu
N, Xu W, Cui C, Xing Y, Liu Y, Cao B, Liu C, Wu G, Ao H, Zhang X
and Jiang J: Activation of PI3K/Akt pathway by CD133-p85
interaction promotes tumorigenic capacity of glioma stem cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6829–6834. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Damdinsuren B, Nagano H, Kondo M, Natsag
J, Hanada H, Nakamura M, Wada H, Kato H, Marubashi S, Miyamoto A,
Takeda Y, Umeshita K, Dono K and Monden M: TGF-β1-induced cell
growth arrest and partial differentiation is related to the
suppression of Id1 in human hepatoma cells. Oncol Rep. 15:401–408.
2006.
|
|
28
|
Zhang Q, Shi S, Yen Y, Brown J, Ta JQ and
Le AD: A subpopulation of CD133+ cancer stem-like cells
characterized in human oral squamous cell carcinoma confer
resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 289:151–160. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Angelastro JM and Lamé MW: Overexpression
of CD133 promotes drug resistance in C6 glioma cells. Mol Cancer
Res. 8:1105–1115. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shimamura H, Terada Y, Okado T, Tanaka H,
Inoshita S and Sasaki S: The PI3-kinase-Akt pathway promotes
mesangial cell survival and inhibits apoptosis in vitro via NF-κB
and Bad. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:1427–1434. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bellacosa A, Kumar CC, Di Cristofano A and
Testa JR: Activation of AKT kinases in cancer: implications for
therapeutic targeting. Adv Cancer Res. 11:29–86. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|