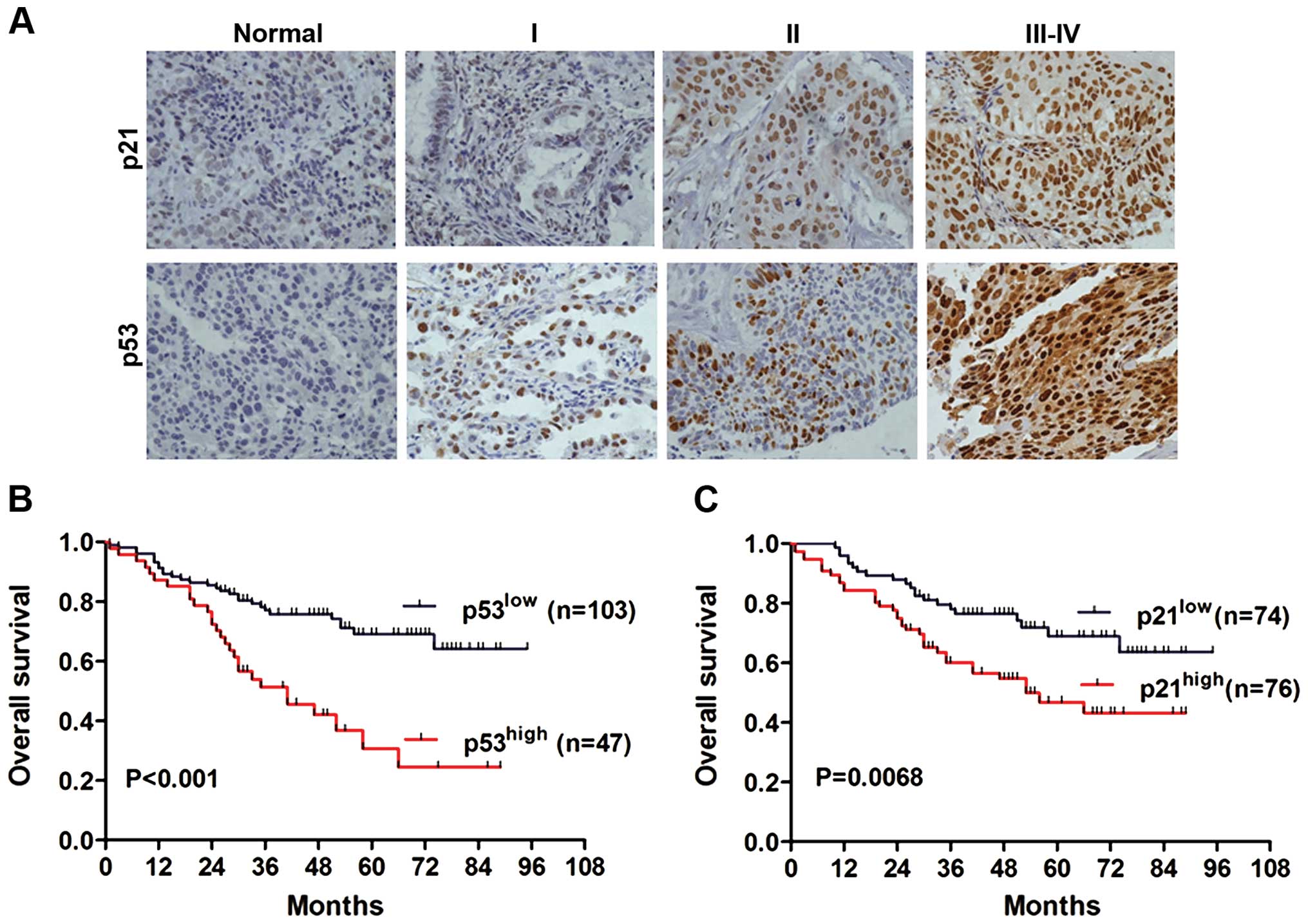
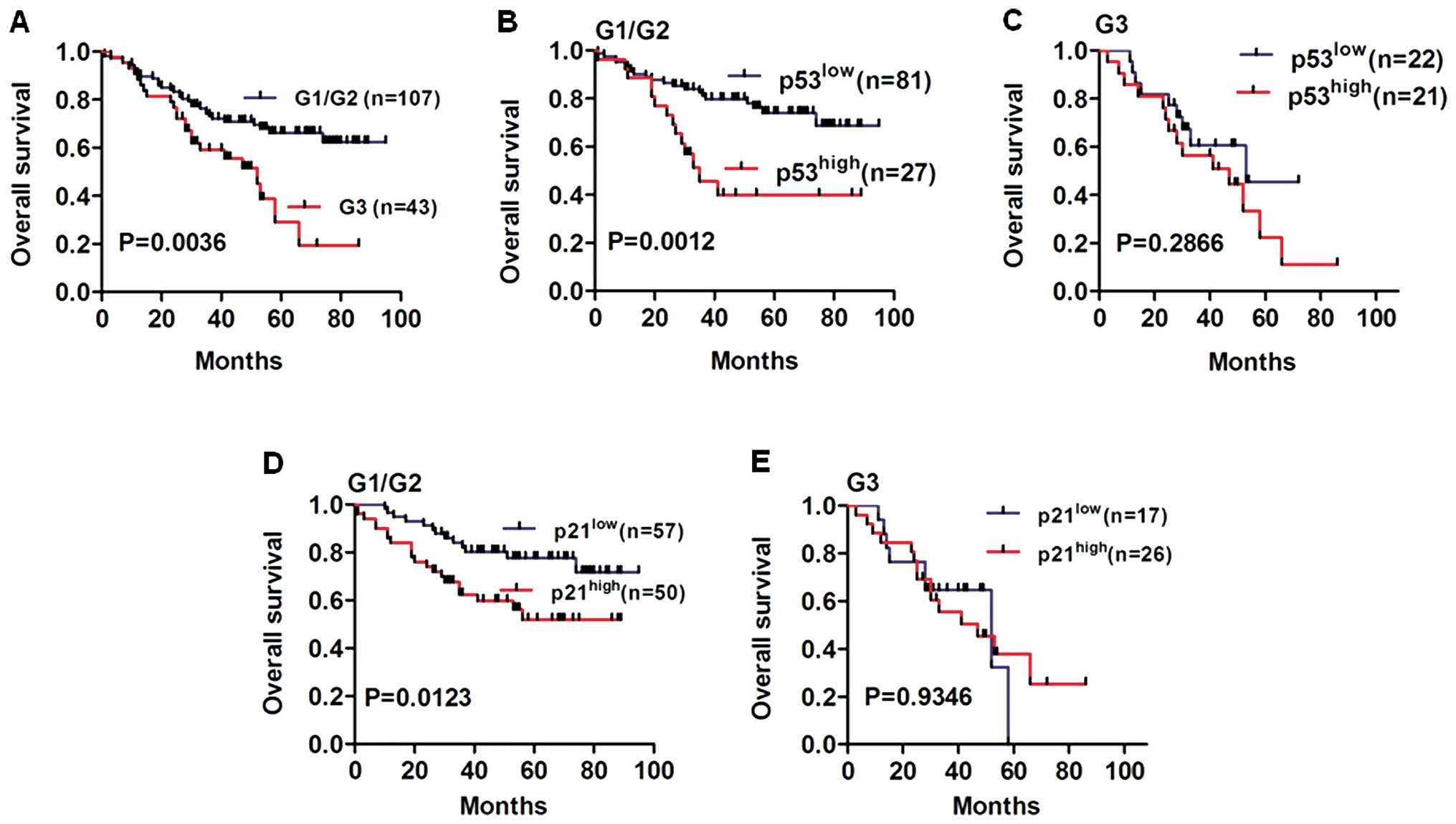
|
1
|
An Q, Liu Y, Gao Y, et al: Deletion of
tumor suppressor genes in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Lett. 184:189–195. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Liu X, Lin XJ, Wang CP, Yan KK, Zhao LY,
An WX and Liu XD: Association between smoking and p53 mutation in
lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 26:18–24.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsou JA, Hagen JA, Carpenter CL and
Laird-Offringa IA: DNA methylation analysis: a powerful new tool
for lung cancer diagnosis. Oncogene. 21:5450–5461. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Christiani DC, Wiencke JK, et al:
Mutations in the p53 gene in lung cancer are associated with
cigarette smoking and asbestos exposure. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 4:543–548. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hwang SJ, Cheng LS, Lozano G, Amos CI, Gu
X and Strong LC: Lung cancer risk in germline p53 mutation
carriers: association between an inherited cancer predisposition,
cigarette smoking, and cancer risk. Hum Genet. 113:238–243. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang H and Cai B: The impact of tobacco
on lung health in China. Respirology. 8:17–21. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Fujino M, Dosaka-Akita H, Harada M,
Hiroumi H, Kinoshita I, Akie K and Kawakami Y: Prognostic
significance of p53 and ras p21 expression in nonsmall cell lung
cancer. Cancer. 76:2457–2463. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Furrukh M: Tobacco smoking and lung
cancer: perception-changing facts. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J.
13:345–358. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pfeifer GP, Denissenko MF, Olivier M,
Tretyakova N, Hecht SS and Hainaut P: Tobacco smoke carcinogens,
DNA damage and p53 mutations in smoking-associated cancers.
Oncogene. 21:7435–7451. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Levine AJ, Momand J and Finlay CA: The p53
tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 351:453–456. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yi C, Wang Q, Wang L, et al: MiR-663, a
microRNA targeting p21(WAF1/CIP1), promotes the proliferation and
tumorigenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 31:4421–4433.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Giono LE and Manfredi JJ: The p53 tumor
suppressor participates in multiple cell cycle checkpoints. J Cell
Physiol. 209:13–20. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Abbas T and Dutta A: p21 in cancer:
intricate networks and multiple activities. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:400–414. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Waga S, Hannon GJ, Beach D and Stillman B:
The p21 inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases controls DNA
replication by interaction with PCNA. Nature. 369:574–578. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang MF, Zhang ZY, Fu J, Yang YF and Yun
JP: Correlation between expression of p53, p21/WAF1, and MDM2
proteins and their prognostic significance in primary
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Transl Med. 7:1102009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayashi H, Miyamoto H, Ito T, Kameda Y,
Nakamura N, Kubota Y and Kitamura H: Analysis of p21Waf1/Cip1
expression in normal, premalignant, and malignant cells during the
development of human lung adenocarcinoma. Am J Pathol. 151:461–470.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Remmele W and Stegner HE: Recommendation
for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for
immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast
cancer tissue. Pathologe. 8:138–140. 1987.(In German).
|
|
20
|
Cheng AN, Jiang SS, Fan CC, et al:
Increased Cdc7 expression is a marker of oral squamous cell
carcinoma and overexpression of Cdc7 contributes to the resistance
to DNA-damaging agents. Cancer Lett. 337:218–225. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hainaut P and Hollstein M: p53 and human
cancer: the first ten thousand mutations. Adv Cancer Res.
77:81–137. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hollstein M, Moeckel G, Hergenhahn M, et
al: On the origins of tumor mutations in cancer genes: insights
from the p53 gene. Mutat Res. 405:145–154. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lakin N and Jackson S: Regulation of p53
in response to DNA damage. Oncogene. 18:7644–7655. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Taghavi N, Biramijamal F, Sotoudeh M,
Moaven O, Khademi H, Abbaszadegan MR and Malekzadeh R: Association
of p53/p21 expression with cigarette smoking and prognosis in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. World J Gastroenterol.
16:4958–4967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cruz I, Snijders PJ, Van Houten V, Vosjan
M, Van der Waal I and Meijer CJ: Specific p53 immunostaining
patterns are associated with smoking habits in patients with oral
squamous cell carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 55:834–840. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mizobuchi S, Furihata M, Sonobe H, et al:
Association between p53 immunostaining and cigarette smoking in
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
30:423–428. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|