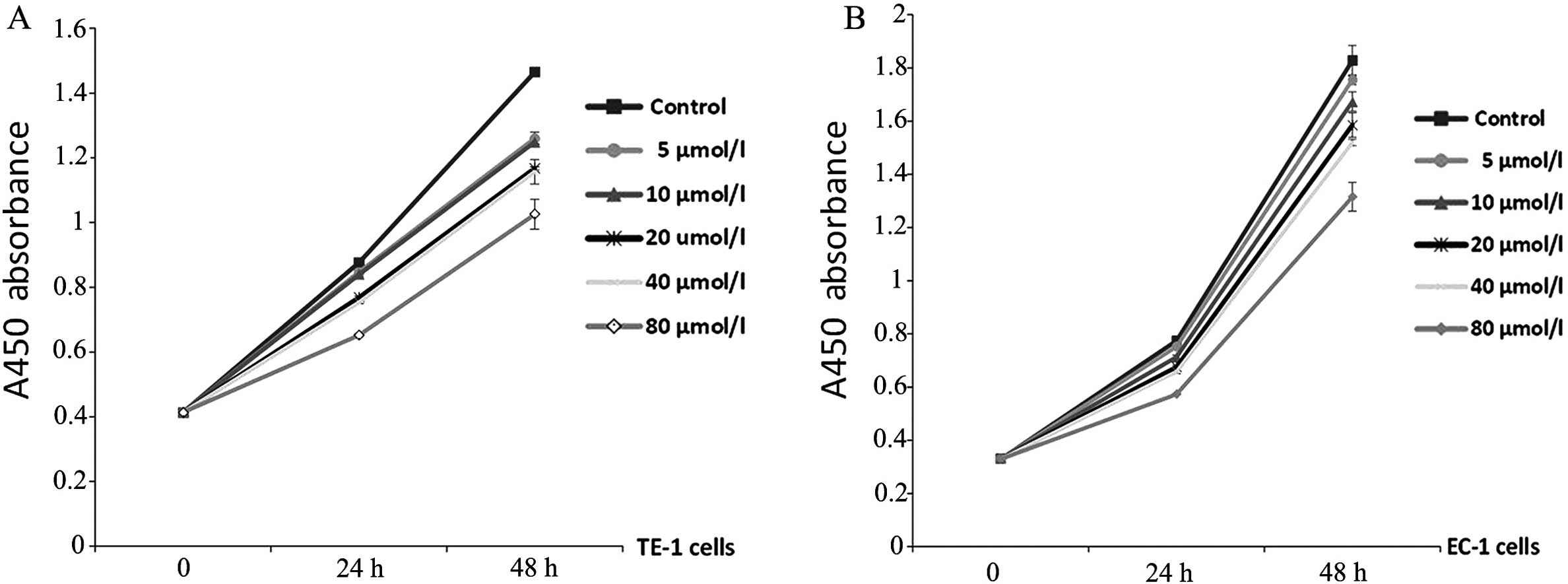
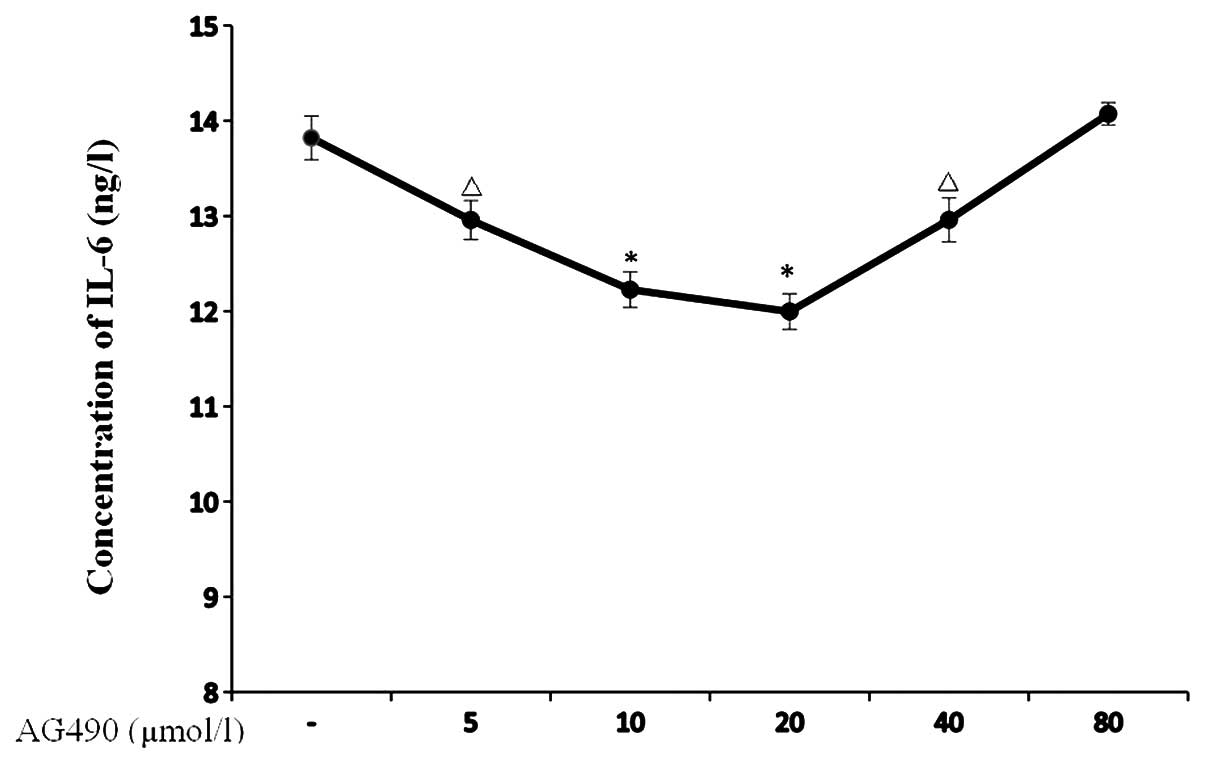
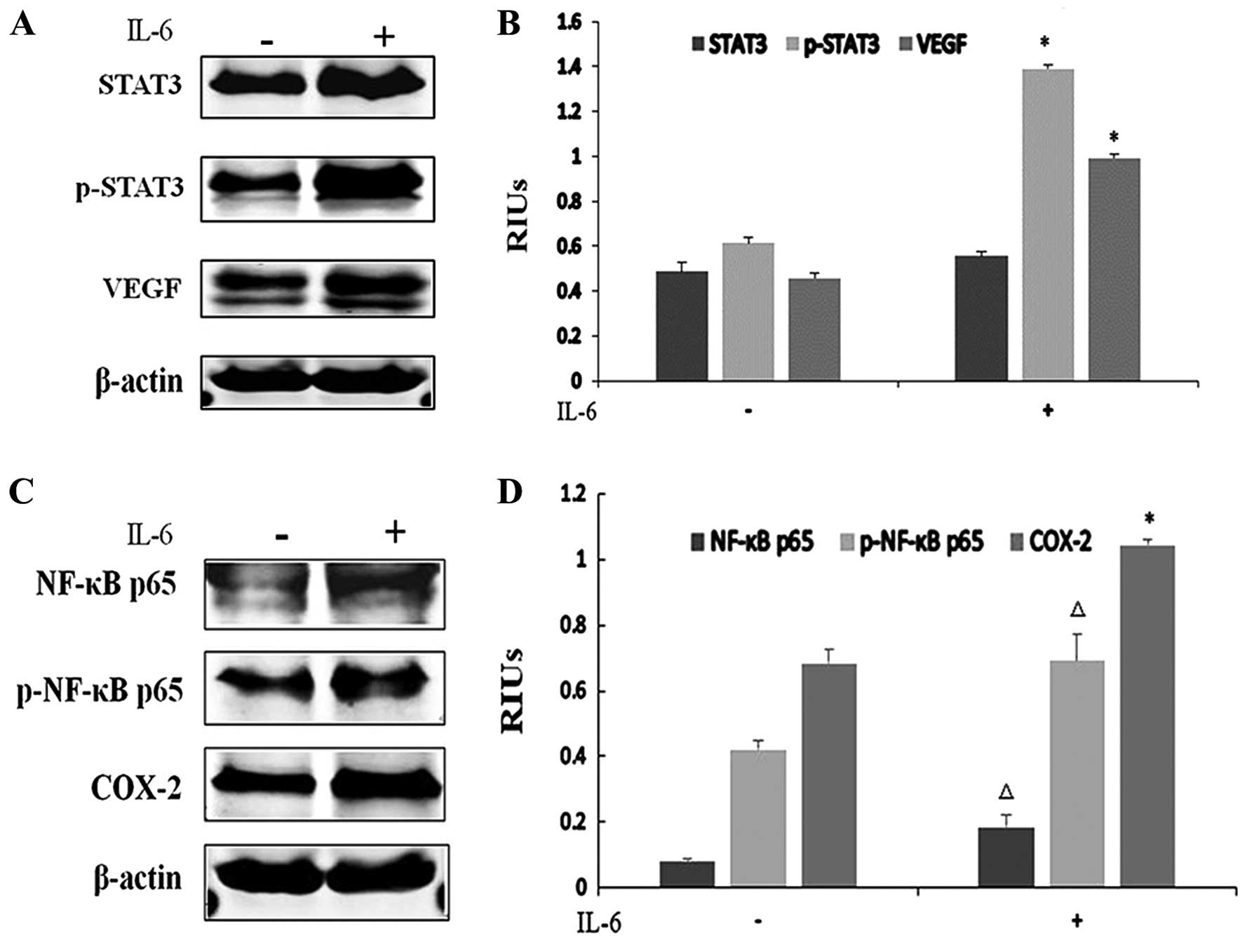
|
1
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wei WQ, Yang J, Zhang SW, Chen WQ and Qiao
YL: Analysis of the esophageal cancer mortality in 2004–2005 and
its trends during last 30 years in China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue
Za Zhi. 44:398–402. 2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Colotta F, Allavena P, Sica A, Garlanda C
and Mantovani A: Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark
of cancer: links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis.
30:1073–1081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuk L, Noffsinger AE, Hui YZ and
Fenoglio-Preiser CM: Detection of human papillomavirus in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 78:704–710. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Antunes LC, Prolla JC, de Barros Lopes A,
da Rocha MP and Fagundes RB: No evidence of HPV DNA in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma in a population of Southern Brazil. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:6598–6603. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang GZ, Li L, Ding HY and Zhou JS:
Cyclooxygenase-2 is over-expressed in Chinese esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma, and correlated with NF-κB: an immunohistochemical
study. Exp Mol Pathol. 79:214–218. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bollrath J and Greten FR: IKK/NF-κB and
STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated
tumour promotion and metastasis. EMBO Rep. 10:1314–1319. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chung SS, Giehl N, Wu Y and Vadgama JV:
STAT3 activation in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell traits. Int
J Oncol. 44:403–411. 2014.
|
|
11
|
Qu Y, Oyan AM, Liu R, et al: Generation of
prostate tumor-initiating cells is associated with elevation of
reactive oxygen species and IL-6/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res.
73:7090–7100. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Burke WM, Jin X, Lin HJ, et al: Inhibition
of constitutively active Stat3 suppresses growth of human ovarian
and breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 20:7925–7934. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang C, Cao J, Huang KJ, et al:
Inhibition of STAT3 activity with AG490 decreases the invasion of
human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Sci. 97:1417–1423.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, et al:
Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 10:287–297. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Turkson J and Jove R: STAT proteins: novel
molecular targets for cancer drug discovery. Oncogene.
19:6613–6626. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Schindler C and Darnell JE Jr:
Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT
pathway. Annu Rev Biochem. 64:621–652. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: a leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, et al: Dietary and
genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by
enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell. 140:197–208. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, et al:
IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of intestinal epithelial
cells and development of colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Cell.
15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-κB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Greten FR, Eckmann L, Greten TF, et al:
IKKβ links inflammation and tumorigenesis in a mouse model of
colitis-associated cancer. Cell. 118:285–296. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
He G and Karin M: NF-κB and STAT3 - key
players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 21:159–168.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lo HW, Hsu SC, Xia W, et al: Epidermal
growth factor receptor cooperates with signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 to induce epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cancer cells via up-regulation of TWIST gene
expression. Cancer Res. 67:9066–9076. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grivennikov SI and Karin M: Dangerous
liaisons: STAT3 and NF-κB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:11–19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Hao Q, Zhang C, Gao Y, et al: FOXP3
inhibits NF-κB activity and hence COX2 expression in gastric cancer
cells. Cell Signal. 26:564–569. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Pühringer F, et
al: Coexpression of cyclooxygenases (COX-1, COX-2) and vascular
endothelial growth factors (VEGF-A, VEGF-C) in esophageal
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:5038–5044. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhi H, Wang L, Zhang J, et al:
Significance of COX-2 expression in human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 27:1214–1221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|