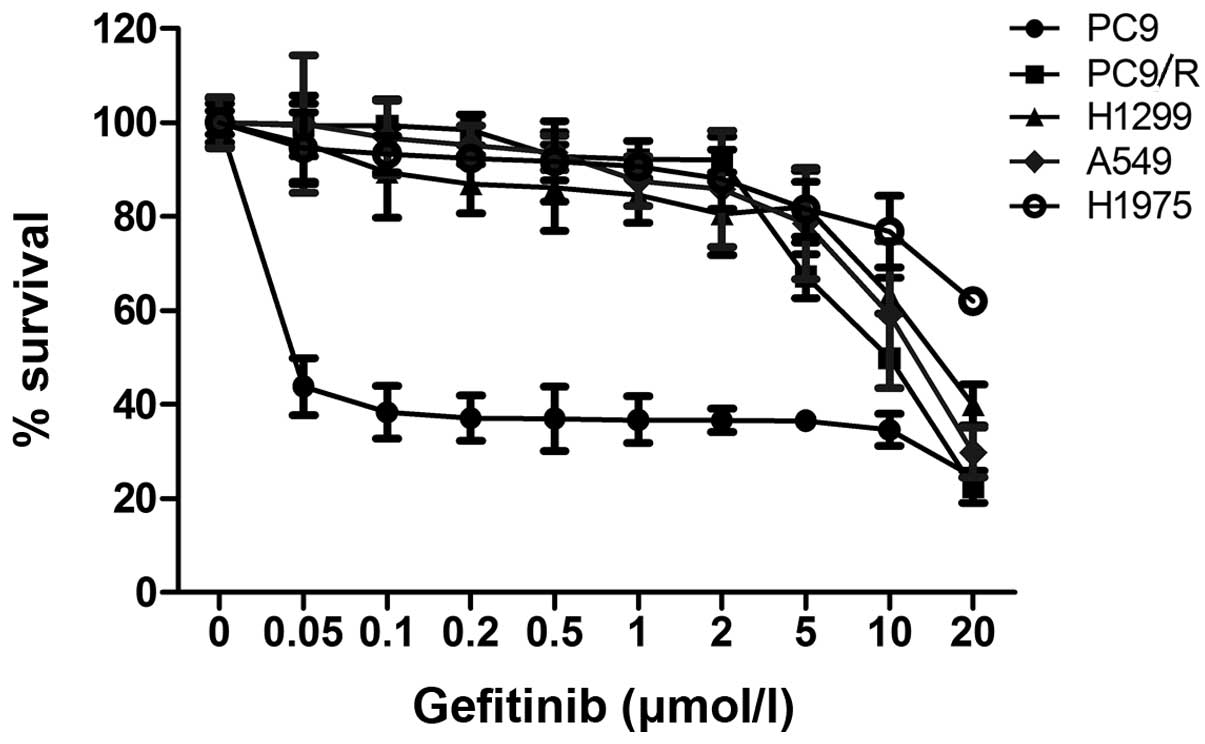
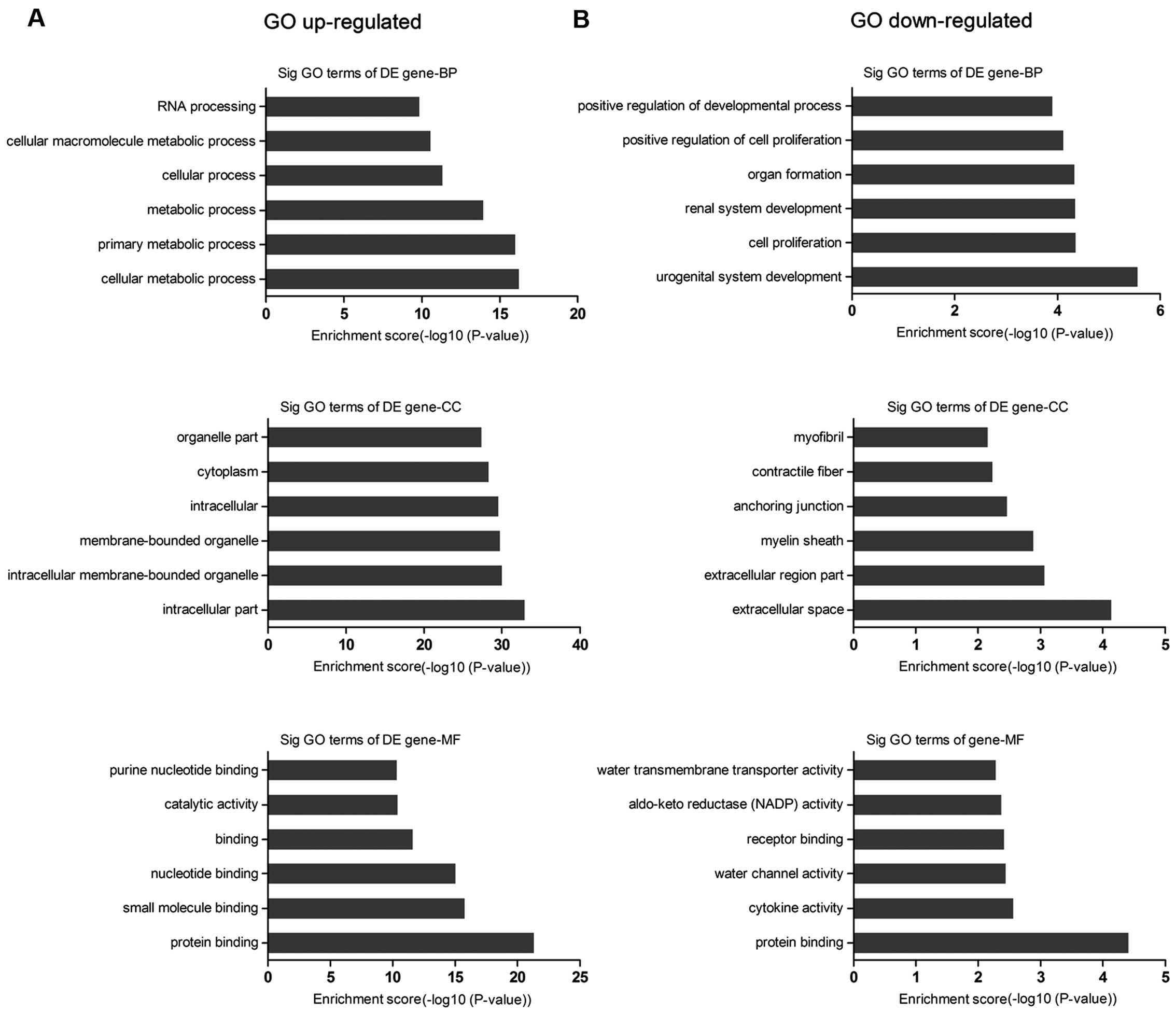
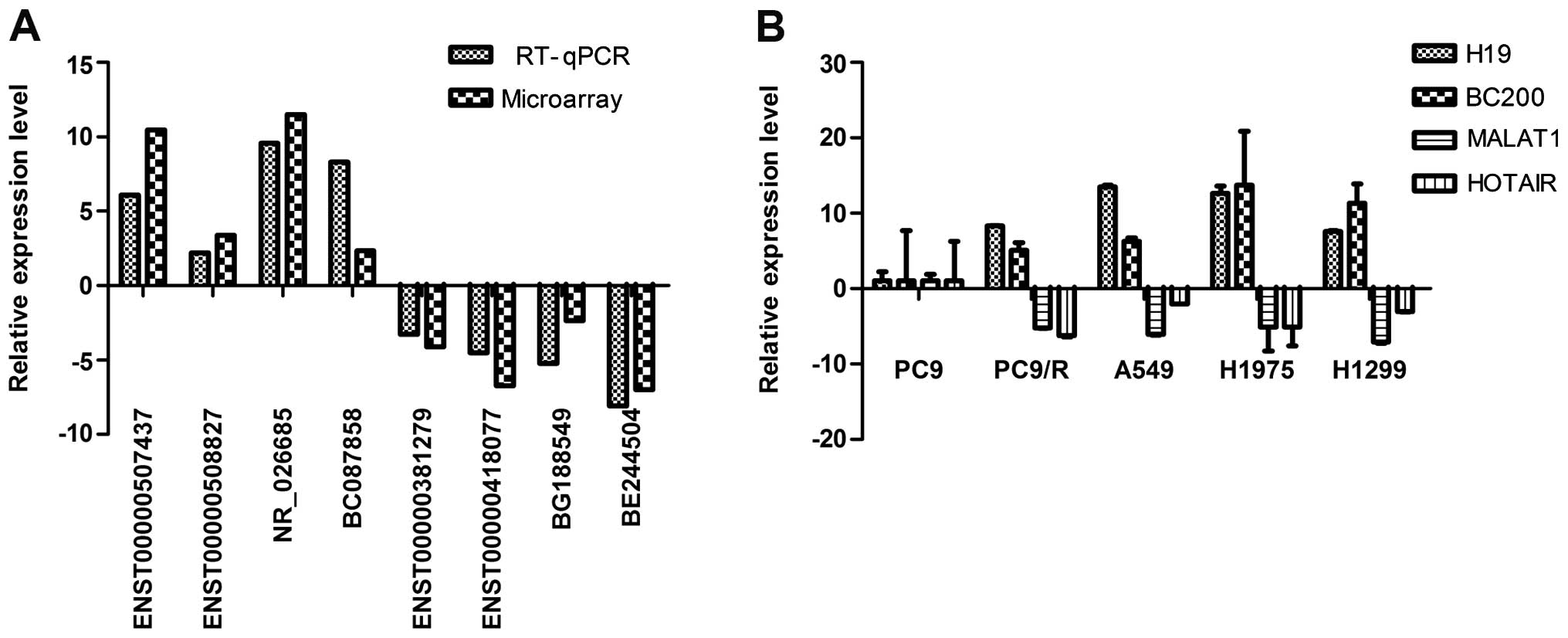
|
1
|
Zhang Z, Lee JC, Lin L, et al: Activation
of the AXL kinase causes resistance to EGFR-targeted therapy in
lung cancer. Nat Genet. 44:852–860. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhou C, Wu YL, Chen G, et al: Erlotinib
versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with
advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer
(OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): a multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase
3 study. Lancet Oncol. 12:735–742. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bar J and Onn A: Overcoming molecular
mechanisms of resistance to first-generation epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Clin Lung Cancer.
13:267–279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Turke AB, Zejnullahu K, Wu YL, et al:
Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR
mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell. 17:77–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bean J, Brennan C, Shih JY, et al: MET
amplification occurs with or without T790M mutations in EGFR mutant
lung tumors with acquired resistance to gefitinib or erlotinib.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:20932–20937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qiu M, Xu Y, Yang X, et al: CCAT2 is a
lung adenocarcinoma-specific long non-coding RNA and promotes
invasion of non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:5375–5380.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu Z, Sun M, Lu K, et al: The long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR contributes to cisplatin resistance of human
lung adenocarcinoma cells via downregualtion of
p21WAF1/CIP1 expression. PLoS One. 8:e772932013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gutschner T, Hämmerle M, Eissmann M, et
al: The noncoding RNA MALAT1 is a critical regulator of the
metastasis phenotype of lung cancer cells. Cancer Res.
73:1180–1189. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, et al: The long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and promotes
metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:4642013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takahashi K, Yan I, Haga H and Patel T:
Long noncoding RNA in liver diseases. Hepatology. 60:744–753. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhao J and Lawless MW: Long noncoding RNAs
and their role in the liver cancer axis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. Nov 19–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ren S, Wang F, Shen J, et al: Long
non-coding RNA metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma
transcript 1 derived miniRNA as a novel plasma-based biomarker for
diagnosing prostate cancer. Eur J Cancer. 49:2949–2959. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Iacoangeli A, Lin Y, Morley EJ, et al:
BC200 RNA in invasive and preinvasive breast cancer.
Carcinogenesis. 25:2125–2133. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Svoboda M, Slyskova J, Schneiderova M, et
al: HOTAIR long non-coding RNA is a negative prognostic factor not
only in primary tumors, but also in the blood of colorectal cancer
patients. Carcinogenesis. 35:1510–1515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yuan JH, Yang F, Wang F, et al: A long
noncoding RNA activated by TGF-β promotes the invasion-metastasis
cascade in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 25:666–681. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tsang WP and Kwok TT: Riboregulator H19
induction of MDR1-associated drug resistance in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 26:4877–4881. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsang WP, Wong TW, Cheung AH, et al:
Induction of drug resistance and transformation in human cancer
cells by the noncoding RNA CUDR. RNA. 13:890–898. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang M, Huang O, Xie Z, et al: A novel
long non-coding RNA-ARA: adriamycin resistance-associated. Biochem
Pharmacol. 87:254–283. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang Y, Li H, Hou S, et al: The noncoding
RNA expression profile and the effect of lncRNA AK126698 on
cisplatin resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cell. PLoS One.
8:e653092013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gainor JF and Shaw AT: Emerging paradigms
in the development of resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in
lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 31:3987–3996. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang EB, Yin DD, Sun M, et al:
P53-regulated long non-coding RNA TUG1 affects cell proliferation
in human non-small cell lung cancer, partly through epigenetically
regulating HOXB7 expression. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12432014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hauptman N and Glavač D: Long non-coding
RNA in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 14:4655–4669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li H, Schmid-Bindert G, Wang D, et al:
Blocking the PI3K/AKT and MEK/ERK signaling pathways can overcome
gefitinib-resistance in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. Adv
Med Sci. 56:275–284. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sordella R, Bell DW, Haber DA and
Settleman J: Gefitinibsensitizing EGFR mutations in lung cancer
activate anti-apoptotic pathways. Science. 305:1163–1167. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, et al: A
common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and
inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat
Med. 18:521–528. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z, Zhou S, Zhang L, et al: BIM
induction of apoptosis triggered by EGFR-sensitive and resistance
cell lines of non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Oncol. 28:572–577.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang F, Zhang L, Huo XS, et al: Long
noncoding RNA high expression in hepatocellular carcinoma
facilitates tumor growth through enhancer of zeste homolog 2 in
humans. Hepatology. 54:1679–1689. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia L, Huang W, Tian D, et al:
Overexpression of forkhead box C1 promotes tumor metastasis and
indicates poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
57:610–624. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang J, Ray PS, Sim MS, et al: FOXC1
regulates the functions of human basal-like breast cancer cells by
activating NF-κB signaling. Oncogene. 31:4798–4802. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Uramoto H, Iwata T, Onitsuka T, et al:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in EGFR-TKI acquired resistant
lung adenocarcinoma. Anticancer Res. 30:2513–2517. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bryant JL, Britson J, Balko JM, et al: A
microRNA gene expression signature predicts response to erlotinib
in epithelial cancer cell lines and targets EMT. Br J Cancer.
106:148–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
32
|
Cufi S, Bonavia R, Vazquez-Martin A, et
al: Silibinin suppresses EMT-driven erlotinib resistance by
reversing the high miR-21/low miR-200c signature in vivo. Sci Rep.
3:24592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu ZZ, Sun NK and Chao CC: Knockdown of
CITED2 using short-hairpin RNA sensitizes cancer cells to cisplatin
through stabilization of p53 and enhancement of p53-dependent
apoptosis. J Cell Physiol. 226:2415–2428. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Samatov TR, Tonevitsky AG and Schumacher
U: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: focus on metastatic cascade,
alternative splicing, non-coding RNAs and modulating compounds. Mol
Cancer. 12:1072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ying L, Chen Q, Wang Y, et al: Upregulated
MALAT-1 contributes to bladder cancer cell migration by inducing
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol Biosyst. 8:2289–2294.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung cancers
acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011.PubMed/NCBI
|