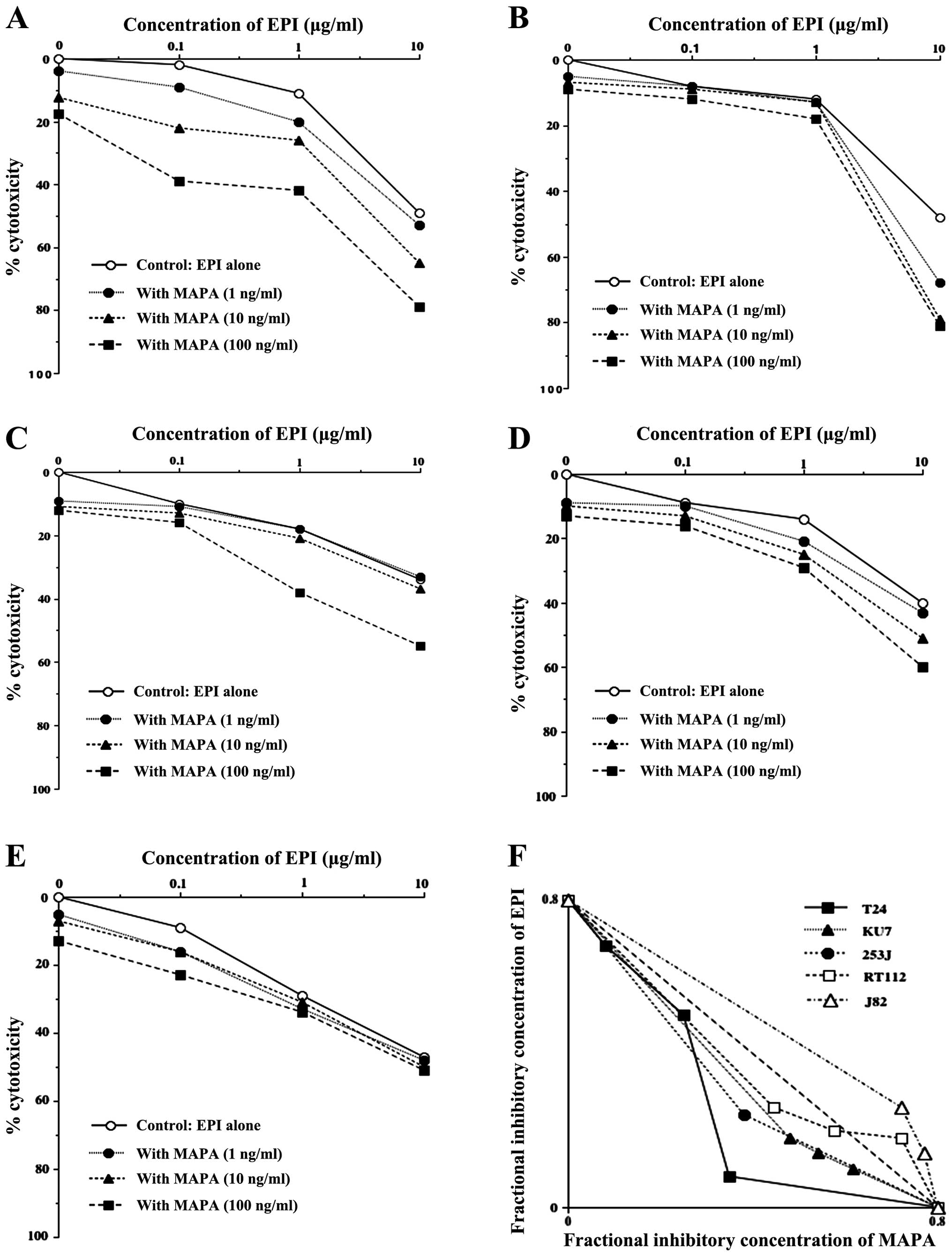
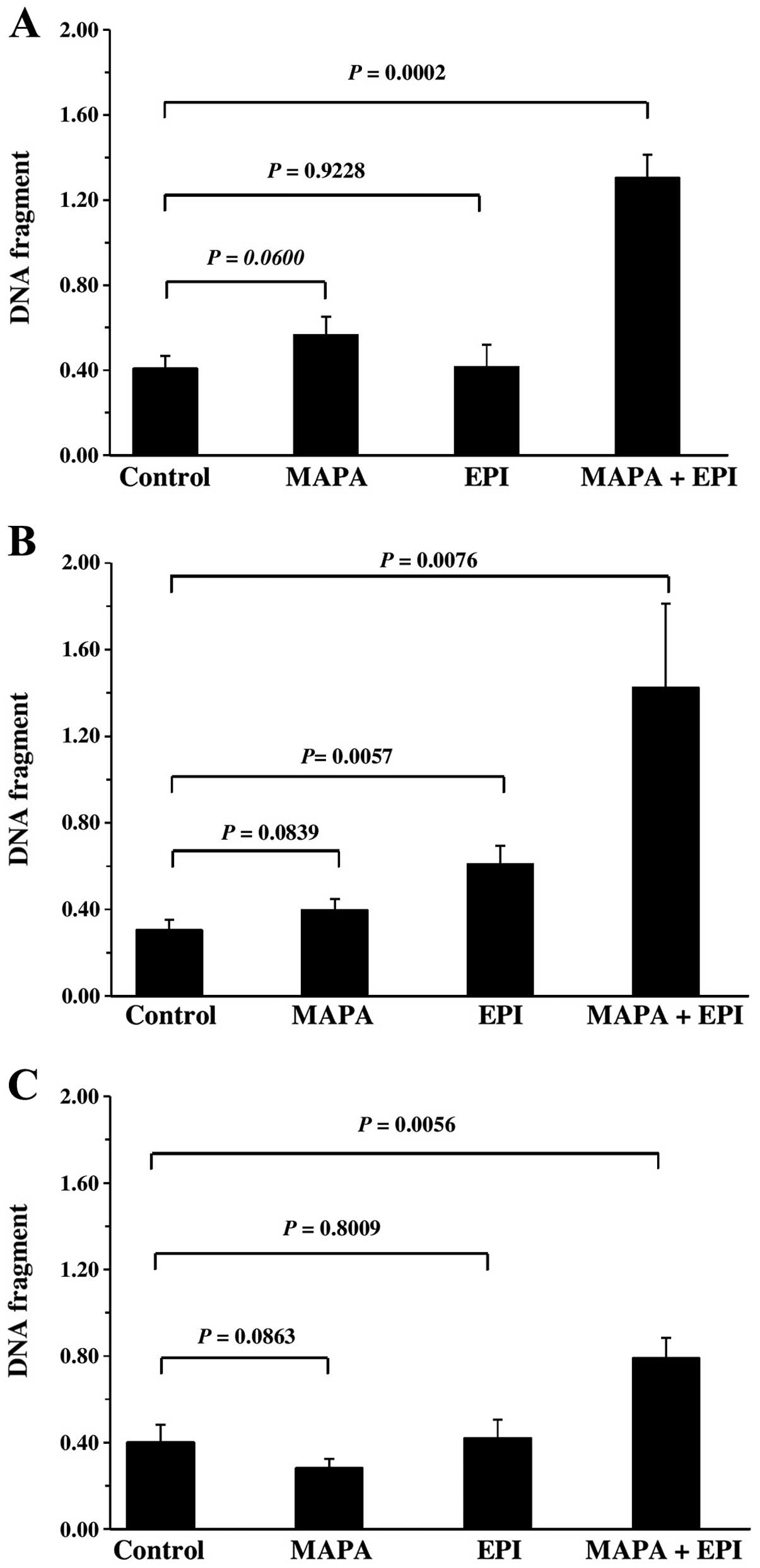
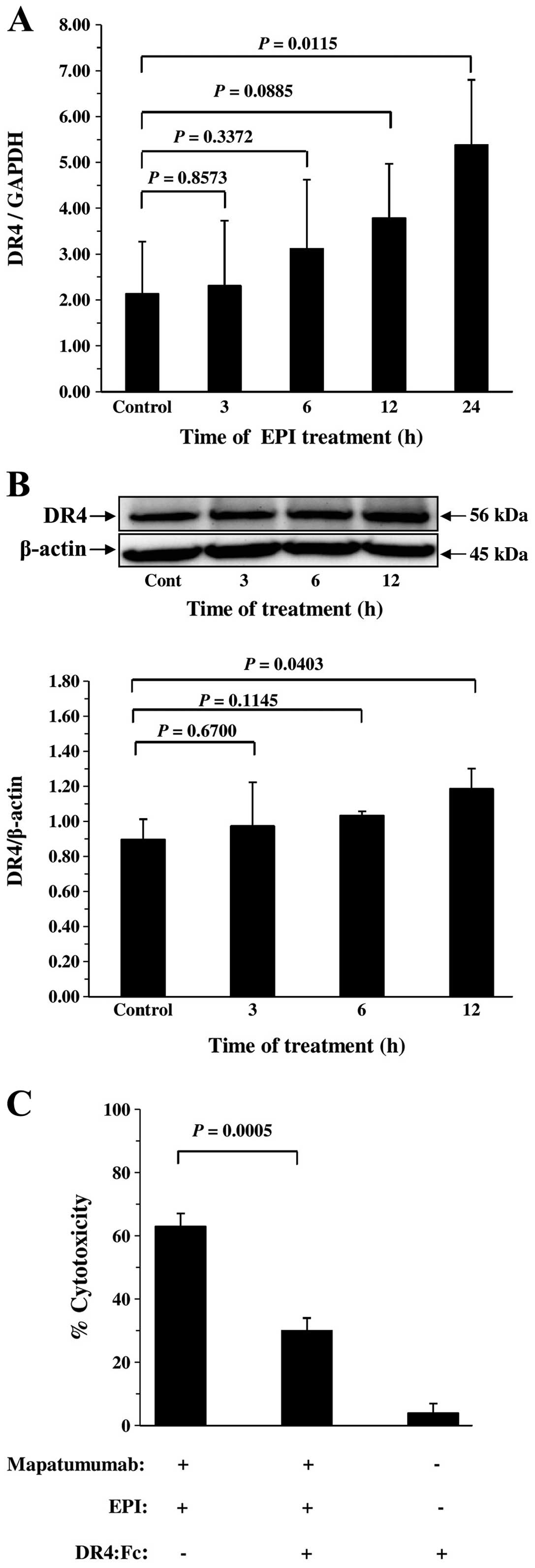
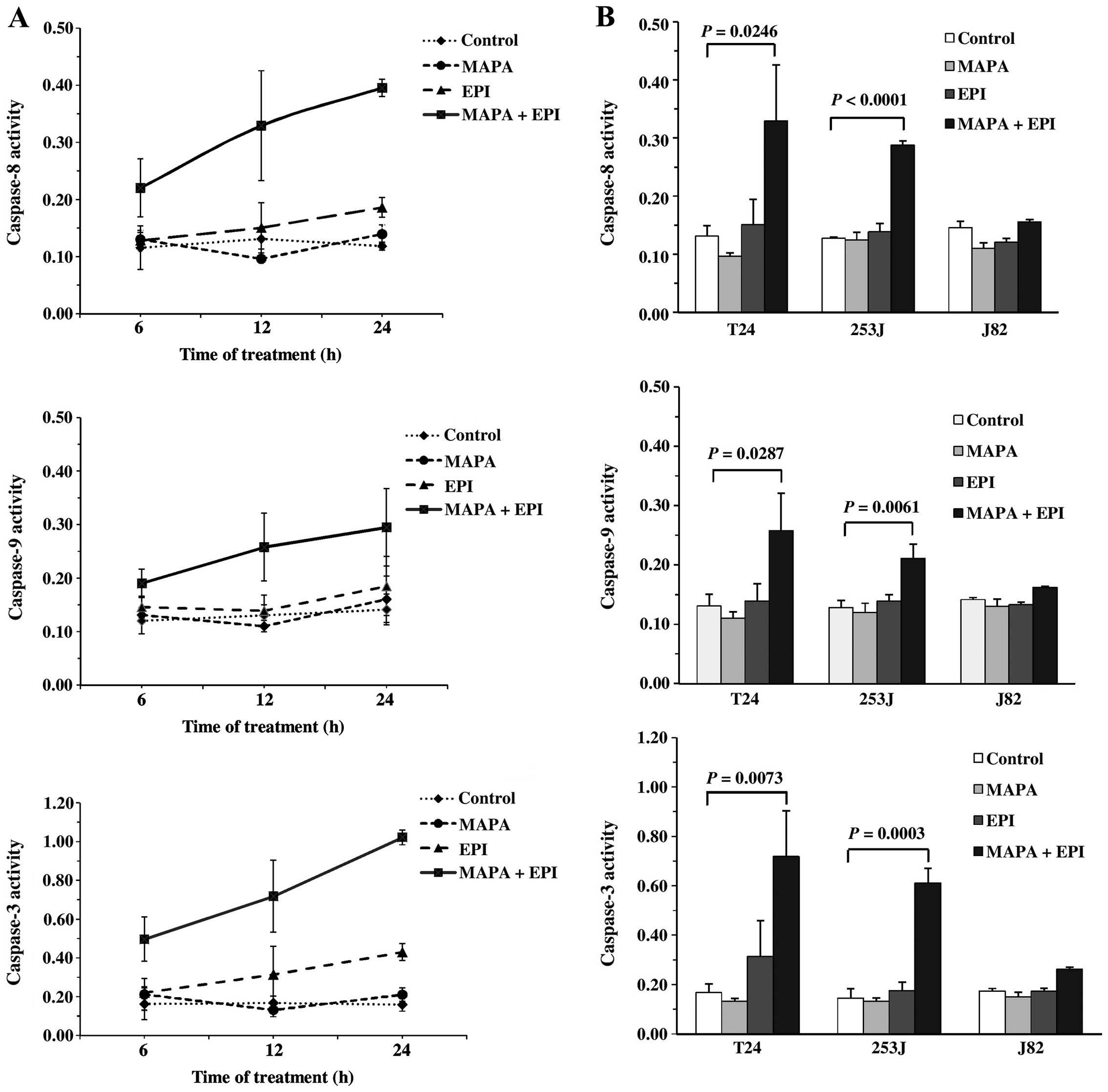
|
1
|
Griffiths TR; Action on Bladder Cancer.
Current perspectives in bladder cancer management. Int J Clin
Pract. 67:435–448. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li Y, Jin X, Li J, Yu J, Sun X, Chu Y, Xu
C, Li X, Wang X, Kakehi Y and Wu X: Expression of TRAIL, DR4, and
DR5 in bladder cancer: correlation with response to adjuvant
therapy and implications of prognosis. Urology. 79:968.e7–968.e15.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen SY, Du LD and Zhang YH: Pilot study
of intravesical instillation of two new generation anthracycline
antibiotics in prevention of superficial bladder cancer recurrence.
Chin Med J. 23:3422–3426. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Wu XX and Kakehi Y: Enhancement of
lexatumumab-induced apoptosis in human solid cancer cells by
cisplatin in caspase-dependent manner. Clin Cancer Res.
15:2039–2047. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, Gliniak B,
Griffith TS, Kubin M, Chin W, Jones J, Woodward A, Le T, Smith C,
Smolak P, Goodwin RG, Rauch CT, Schuh JC and Lynch DH: Tumoricidal
activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hao C, Song JH, Hsi B, Lewis J, Song DK,
Petruk KC, Tyrrell DL and Kneteman NM: TRAIL inhibits tumor growth
but is nontoxic to human hepatocytes in chimeric mice. Cancer Res.
64:8502–8506. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pan G, O’Rourke K, Chinnaiyan AM, Gentz R,
Ebner R, Ni J and Dixit VM: The receptor for the cytotoxic ligand
TRAIL. Science. 276:111–113. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pan G, Ni J, Wei YF, Yu G, Gentz R and
Dixit VM: An antagonist decoy receptor and a death
domain-containing receptor for TRAIL. Science. 277:815–818. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shimada O, Wu X, Jin X, Nouh MA, Fiscella
M, Albert V, Matsuda T and Kakehi Y: Human agonistic antibody to
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2
induces cytotoxicity and apoptosis in prostate cancer and bladder
cancer cells. Urology. 69:395–401. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chuntharapai A, Dodge K, Grimmer K,
Schroeder K, Marsters SA, Koeppen H, Ashkenazi A and Kim KJ:
Isotype-dependent inhibition of tumor growth in vivo by monoclonal
antibodies to death receptor 4. J Immunol. 166:4891–4898. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ichikawa K, Liu W, Zhao L, Wang Z, Liu D,
Ohtsuka T, Zhang H, Mountz JD, Koopman WJ, Kimberly RP and Zhou T:
Tumoricidal activity of a novel anti-human DR5 monoclonal antibody
without hepatocyte cytotoxicity. Nat Med. 7:954–960. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ohtsuka T, Buchsbaum D, Oliver P, Makhija
S, Kimberly R and Zhou T: Synergistic induction of tumor cell
apoptosis by death receptor antibody and chemotherapy agent through
JNK/p38 and mitochondrial death pathway. Oncogene. 22:2034–2044.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin X, Wu XX, Abdel-Muneem Nouh MA and
Kakehi Y: Enhancement of death receptor 4 mediated apoptosis and
cytotoxicity in renal cell carcinoma cells by subtoxic
concentrations of doxorubicin. J Urol. 177:1894–1899. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zeng Y, Wu XX, Fiscella M, Shimada O,
Humphreys R, Albert V and Kakehi Y: Monoclonal antibody to tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 2
(TRAIL-R2) induces apoptosis in primary renal cell carcinoma cells
in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Int J Oncol.
28:421–430. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szliszka E, Mazur B, Zydowicz G, Czuba ZP
and Krol W: TRAIL-induced apoptosis and expression of death
receptor TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in bladder cancer cells. Folia
Histochem Cytobiol. 47:579–585. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pukac L, Kanakaraj P, Humphreys R,
Alderson R, Bloom M, Sung C, Riccobene T, Johnson R, Fiscella M,
Mahoney A, Carrell J, Boyd E, Yao XT, Zhang L, Zhong L, von Kerczek
A, Shepard L, Vaughan T, Edwards B, Dobson C, Salcedo T and Albert
V: HGS-ETR1, a fully human TRAIL-receptor 1 monoclonal antibody,
induces cell death in multiple tumour types in vitro and in vivo.
Br J Cancer. 92:1430–1441. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tolcher AW, Mita M, Meropol NJ, von Mehren
M, Patnaik A, Padavic K, Hill M, Mays T, McCoy T, Fox NL, Halpern
W, Corey A and Cohen RB: Phase I pharmacokinetic and biologic
correlative study of mapatumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody
with agonist activity to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor-1. J Clin Oncol. 25:1390–1395.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Greco FA, Bonomi P, Crawford J, Kelly K,
Oh Y, Halpern W, Lo L, Gallant G and Klein J: Phase 2 study of
mapatumumab, a fully human agonistic monoclonal antibody which
targets and activates the TRAIL receptor-1, in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 61:82–90. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hotte SJ, Hirte HW, Chen EX, Siu LL, Le
LH, Corey A, Iacobucci A, MacLean M, Lo L, Fox NL and Oza AM: A
phase 1 study of mapatumumab (fully human monoclonal antibody to
TRAIL-R1) in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin Cancer
Res. 14:3450–3455. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Motzer RJ, Bander NH and Nanus DM:
Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 335:865–875. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berenbaum MC: Synergy, additivism and
antagonism in immunosuppression. A critical review. Clin Exp
Immunol. 28:1–18. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berenbaum MC: A method for testing for
synergy with any number of agents. J Infect Dis. 137:122–130. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gibson SB, Oyer R, Spalding AC, Anderson
SM and Johnson GL: Increased expression of death receptors 4 and 5
synergizes the apoptosis response to combined treatment with
etoposide and TRAIL. Mol Cell Biol. 20:205–212. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu XX, Jin XH, Zeng Y, El Hamed AM and
Kakehi Y: Low concentrations of doxorubicin sensitizes human solid
cancer cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL)-receptor (R) 2-mediated apoptosis by inducing
TRAIL-R2 expression. Cancer Sci. 98:1969–1976. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Green DR and Evan GI: A matter of life and
death. Cancer Cell. 1:19–30. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
von Pawel J, Harvey JH, Spigel DR, Dediu
M, Reck M, Cebotaru CL, Humphreys RC, Gribbin MJ, Fox NL and
Camidge DR: Phase II trial of mapatumumab, a fully human agonist
monoclonal antibody to tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor 1 (TRAIL-R1), in combination
with paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 15:188.e2–196.e2.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Amantana A, London CA, Iversen PL and Devi
GR: X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein inhibition induces
apoptosis and enhances chemotherapy sensitivity in human prostate
cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:699–707. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Q, Hilsenbeck S and Gazitt Y: Arsenic
trioxide-induced apoptosis in myeloma cells: p53-dependent
G1 or G2/M cell cycle arrest, activation of
caspase-8 or caspase-9, and synergy with APO2/TRAIL. Blood.
101:4078–4087. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, Wilson
TR, McLaughlin K and Johnston PG: Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated
colon cancer cell death: the roles of p53, TRAIL receptors, and
c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2026–2036. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lacour S, Hammann A, Wotawa A, Corcos L,
Solary E and Dimanche-Boitrel MT: Anticancer agents sensitize tumor
cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand-mediated caspase-8 activation and apoptosis. Cancer Res.
61:1645–1651. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu W, Bodle E, Chen JY, Gao M, Rosen GD
and Broaddus VC: Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand and chemotherapy cooperate to induce apoptosis in
mesothelioma cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 25:111–118.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tsai WS, Yeow WS, Chua A, Reddy RM and
Nguyen DM, Schrump DS and Nguyen DM: Enhancement of
Apo2L/TRAIL-mediated cytotoxicity in esophageal cancer cells by
cisplatin. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2977–2990. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Derosier LC, Vickers SM, Zinn KR, Huang Z,
Wang W, Grizzle WE, Sellers J, Stockard CR Jr, Zhou T, Oliver PG,
Arnoletti P, Lobuglio AF and Buchsbaum DJ: TRA-8 anti-DR5
monoclonal antibody and gemcitabine induce apoptosis and inhibit
radiologically validated orthotopic pancreatic tumor growth. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:3198–3207. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
O’Kane HF, Watson CJ, Johnston SR, Petak
I, Watson RW and Williamson KE: Targeting death receptors in
bladder, prostate and renal cancer. J Urol. 175:432–438. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|