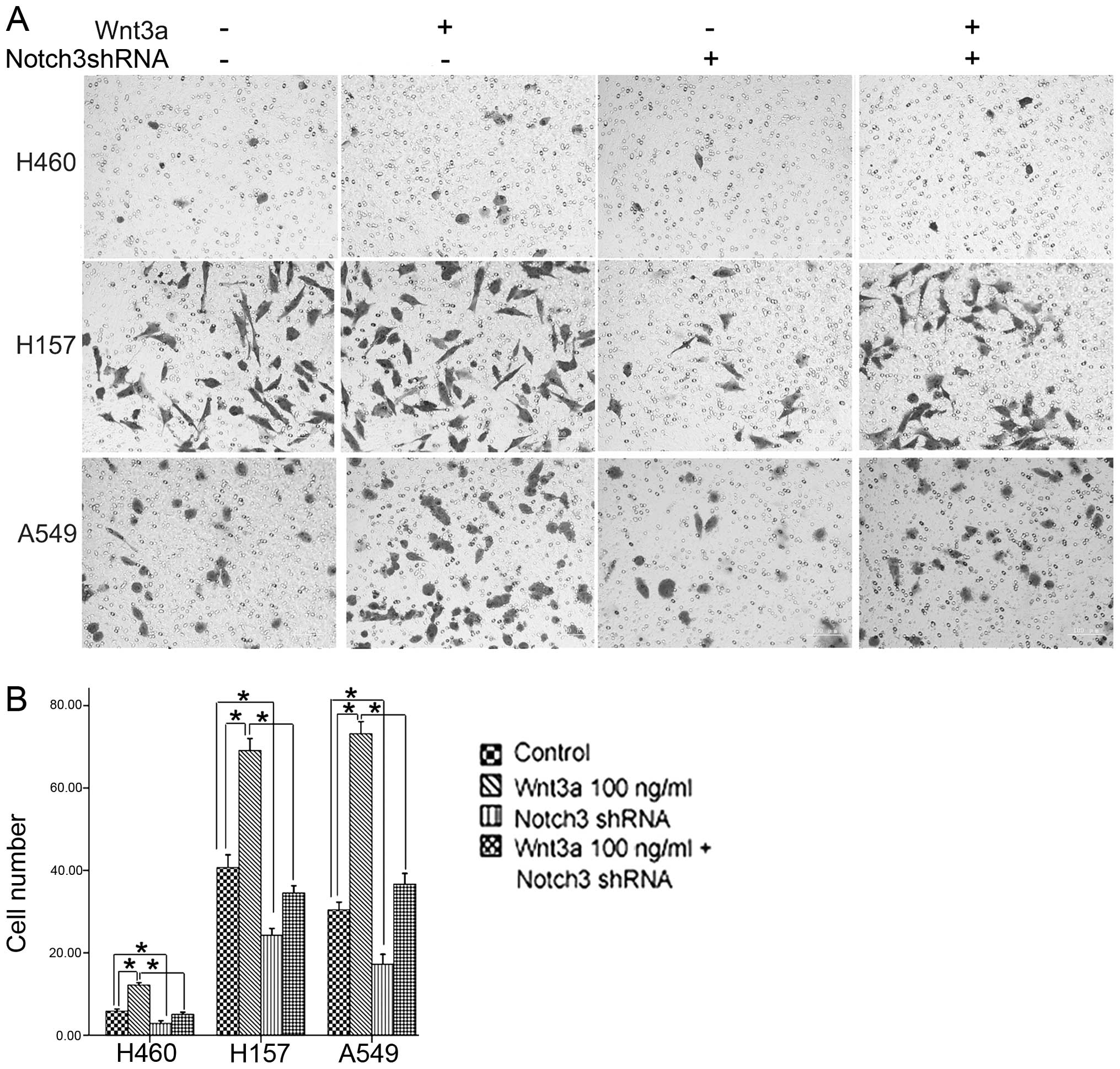
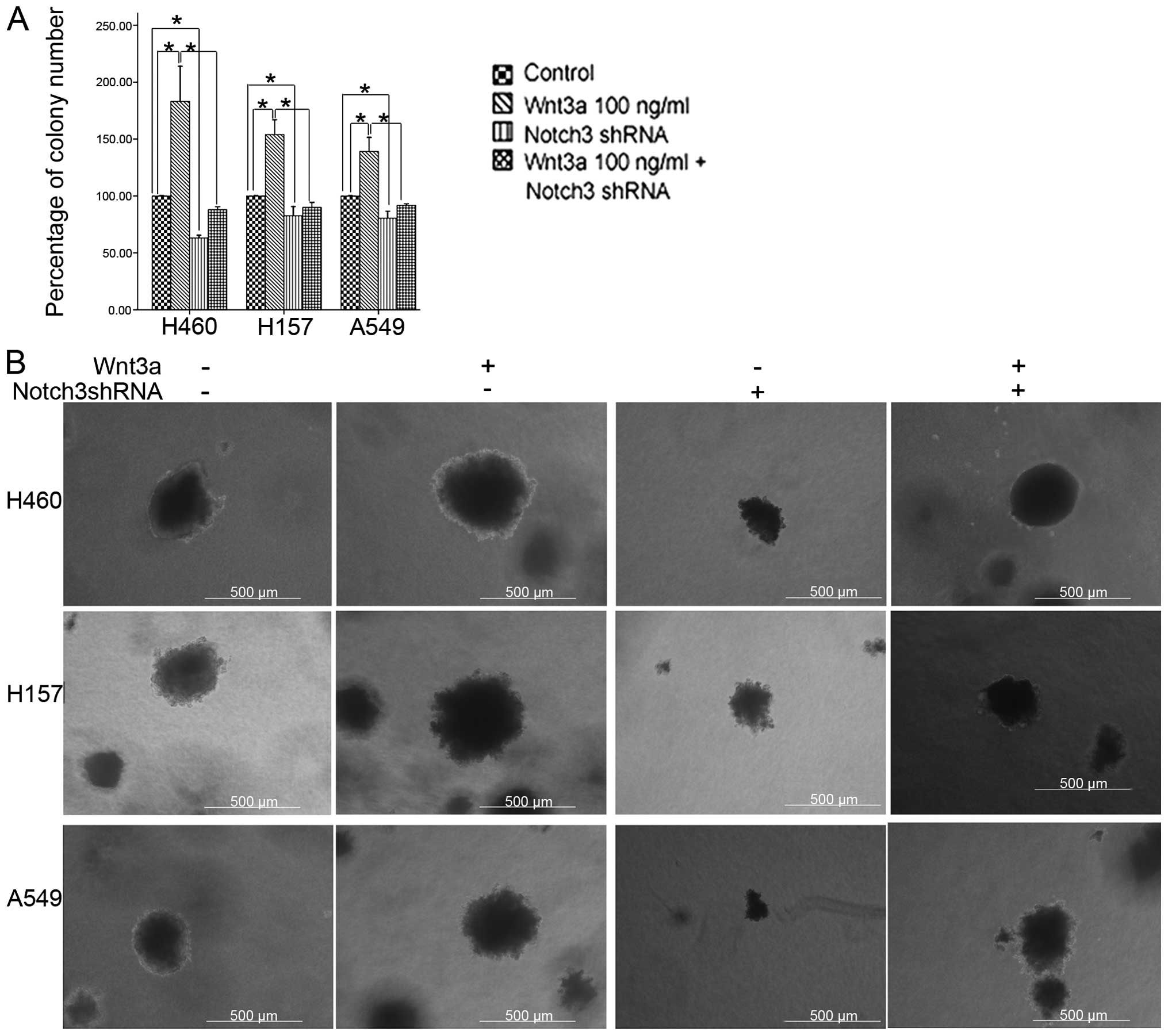
|
1
|
Perlikos F, Harrington KJ and Syrigos KN:
Key molecular mechanisms in lung cancer invasion and metastasis: A
comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 87:1–11. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie C, Jiang G, Fan C, et al: ARMC8α
promotes proliferation and invasion of non-small cell lung cancer
cells by activating the canonical Wnt signaling pathway. Tumour
Biol. 35:8903–8911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gao Y, Song C, Hui L, et al:
Overexpression of RNF146 in non-small cell lung cancer enhances
proliferation and invasion of tumors through the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 9:e853772014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Su K, Huang L, Li W, et al: TC-1 (c8orf4)
enhances aggressive biologic behavior in lung cancer through the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. J Surg Res. 185:255–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang S, Wang Y, Dai SD and Wang EH:
Down-regulation of NKD1 increases the invasive potential of
non-small-cell lung cancer and correlates with a poor prognosis.
BMC Cancer. 11:1862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren J, Wang R, Huang G, Song H, Chen Y and
Chen L: sFRP1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition in A549
human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
28:565–571. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Singh T and Katiyar SK: Honokiol inhibits
non-small cell lung cancer cell migration by targeting
PGE2-mediated activation of β-catenin signaling. PLoS
One. 8:e607492013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Westhoff B, Colaluca IN, D’Ario G, et al:
Alterations of the Notch pathway in lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 106:22293–22298. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu L, Chen X, Wang Y, et al: Notch3 is
important for TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
non-small cell lung cancer bone metastasis by regulating ZEB-1.
Cancer Gene Ther. 21:364–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li C, Zhang S, Lu Y, Zhang Y, Wang E and
Cui Z: The roles of Notch3 on the cell proliferation and apoptosis
induced by CHIR99021 in NSCLC cell lines: a functional link between
Wnt and Notch signaling pathways. PLoS One. 8:e846592013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao CF, Xie Q, Su YL, et al: Proliferation
and invasion: plasticity in tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:10528–10533. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Al-Mehdi AB, Tozawa K, Fisher AB, Shientag
L, Lee A and Muschel RJ: Intravascular origin of metastasis from
the proliferation of endothelium-attached tumor cells: a new model
for metastasis. Nat Med. 6:100–102. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kikuchi A, Yamamoto H and Kishida S:
Multiplicity of the interactions of Wnt proteins and their
receptors. Cell Signal. 19:659–671. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stapp AD, Gómez BI, Gifford CA, Hallford
DM and Hernandez Gifford JA: Canonical WNT signaling inhibits
follicle stimulating hormone mediated steroidogenesis in primary
cultures of rat granulosa cells. PLoS One. 9:e864322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yi F, Amarasinghe B and Dang TP: Manic
fringe inhibits tumor growth by suppressing Notch3 degradation in
lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 3:490–499. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zheng Y, de la Cruz CC, Sayles LC, et al:
A rare population of CD24(+)ITGB4(+)Notch(hi) cells drives tumor
propagation in NSCLC and requires Notch3 for self-renewal. Cancer
Cell. 24:59–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frisch SM and Francis H: Disruption of
epithelial cell-matrix interactions induces apoptosis. J Cell
Biol1. 24:619–626. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nomura Y, Tashiro H and Hisamatsu K: In
vitro clonogenic growth and metastatic potential of human operable
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 49:5288–5293. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nakanishi K, Sakamoto M, Yasuda J, et al:
Critical involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt
pathway in anchorage-independent growth and hematogeneous
intrahepatic metastasis of liver cancer. Cancer Res. 62:2971–2975.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tsai JH and Yang J: Epithelial-mesenchymal
plasticity in carcinoma metastasis. Genes Dev. 27:2192–2206. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Poste G and Fidler IJ: The pathogenesis of
cancer metastasis. Nature. 283:139–146. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bo H, Zhang S, Gao L, Chen Y, Zhang J,
Chang X and Zhu M: Upregulation of Wnt5a promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 13:4962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ford CE, Jary E, Ma SS, Nixdorf S,
Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA and Ward RL: The Wnt gatekeeper SFRP4
modulates EMT, cell migration and downstream Wnt signalling in
serous ovarian cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e543622013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kwon M, Lee SJ, Wang Y, et al: Filamin A
interacting protein 1-like inhibits WNT signaling and MMP
expression to suppress cancer cell invasion and metastasis. Int J
Cancer. 135:48–60. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jiang W, Crossman DK, Mitchell EH, Sohn P,
Crowley MR and Serra R: WNT5A inhibits metastasis and alters
splicing of Cd44 in breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e583292013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dey N, Barwick BG, Moreno CS, et al: Wnt
signaling in triple negative breast cancer is associated with
metastasis. BMC Cancer. 13:5372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Espinoza I and Miele L: Deadly crosstalk:
Notch signaling at the intersection of EMT and cancer stem cells.
Cancer Lett. 341:41–45. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Espinoza I, Pochampally R, Xing F, Watabe
K and Miele L: Notch signaling: targeting cancer stem cells and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther.
6:1249–1259. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Du R, Sun W, Xia L, et al: Hypoxia-induced
down-regulation of microRNA-34a promotes EMT by targeting the Notch
signaling pathway in tubular epithelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e307712012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Q, Bai X, Chen W, et al:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling enhances hypoxia-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma via
crosstalk with hif-1α signaling. Carcinogenesis. 34:962–973. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhai Y, Iura A, Yeasmin S, et al: MSX2 is
an oncogenic downstream target of activated WNT signaling in
ovarian endometrioid adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 30:4152–4162. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gupta N, Xu Z, El-Sehemy A, Steed H and Fu
Y: Notch3 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and attenuates
carboplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells. Gynecol
Oncol. 130:200–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Katoh M and Katoh M: NUMB is a break of
WNT-Notch signaling cycle. Int J Mol Med. 18:517–521.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bertrand FE, Angus CW, Partis WJ and
Sigounas G: Developmental pathways in colon cancer: crosstalk
between WNT, BMP, Hedgehog and Notch. Cell Cycle. 11:4344–4351.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|